|
Backup Battery
A backup battery provides power to a system when the primary source of power is unavailable. Backup batteries range from small single cells to retain clock time and date in computers, up to large battery room facilities that power uninterruptible power supply systems for large data centers. Small backup batteries may be primary cells; rechargeable backup batteries are kept charged by the prime power supply. Examples Aircraft emergency batteries Backup batteries in aircraft keep essential instruments and devices running in the event of an engine power failure. Each aircraft has enough power in the backup batteries to facilitate a safe landing. The batteries keeping navigation, ELUs (emergency lighting units), emergency pressure or oxygen systems running at altitude, and radio equipment operational. Larger aircraft have control surfaces that run on these backups as well. Aircraft batteries are either nickel-cadmium or valve-regulated lead acid type. The battery keeps all nece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battery Room
A battery room is a room that houses batteries for backup or uninterruptible power systems. The rooms are found in telecommunication central offices, and provide standby power for computing equipment in datacenters. Batteries provide direct current (DC) electricity, which may be used directly by some types of equipment, or which may be converted to alternating current (AC) by uninterruptible power supply (UPS) equipment. The batteries may provide power for minutes, hours or days, depending on each system's design, although they are most commonly activated during brief electric utility outages lasting only seconds. Battery rooms were used to segregate the fumes and corrosive chemicals of wet cell batteries (often lead–acid) from the operating equipment, and for better control of temperature and ventilation. In 1890, the Western Union central telegraph office in New York City had 20,000 wet cells, mostly of the primary zinc-copper type. Telecommunications Telephone system c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nickel Cadmium
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow to react with air under standard conditions because a passivation layer of nickel oxide forms on the surface that prevents further corrosion. Even so, pure native nickel is found in Earth's crust only in tiny amounts, usually in ultramafic rocks, and in the interiors of larger nickel–iron meteorites that were not exposed to oxygen when outside Earth's atmosphere. Meteoric nickel is found in combination with iron, a reflection of the origin of those elements as major end products of supernova nucleosynthesis. An iron–nickel mixture is thought to compose Earth's outer and inner cores. Use of nickel (as natural meteoric nickel–iron alloy) has been traced as far back as 3500 BCE. Nickel was first isolated and classified as an ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saved Game
A saved game (also called a game save, savegame, savefile, save point, or simply save) is a piece of digitally stored information about the progress of a player in a video game. From the earliest games in the 1970s onward, game platform hardware and memory improved, which led to bigger and more complex computer games, which, in turn, tended to take more and more time to play them from start to finish. This naturally led to the need to store in some way the progress, and how to handle the case where the player received a " game over". More modern games with a heavier emphasis on storytelling are designed to allow the player many choices that impact the story in a profound way later on, and some game designers do not want to allow more than one save game so that the experience will always be "fresh". Game designers allow players to prevent the loss of progress in the game (as might happen after a game over). Games designed this way encourage players to 'try things out', and on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random-access Memory
Random-access memory (RAM; ) is a form of computer memory that can be read and changed in any order, typically used to store working data and machine code. A random-access memory device allows data items to be read or written in almost the same amount of time irrespective of the physical location of data inside the memory, in contrast with other direct-access data storage media (such as hard disks, CD-RWs, DVD-RWs and the older magnetic tapes and drum memory), where the time required to read and write data items varies significantly depending on their physical locations on the recording medium, due to mechanical limitations such as media rotation speeds and arm movement. RAM contains multiplexing and demultiplexing circuitry, to connect the data lines to the addressed storage for reading or writing the entry. Usually more than one bit of storage is accessed by the same address, and RAM devices often have multiple data lines and are said to be "8-bit" or "16-bit", etc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Game
Video games, also known as computer games, are electronic games that involves interaction with a user interface or input device such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device to generate visual feedback. This feedback mostly commonly is shown on a video display device, such as a TV set, computer monitor, monitor, touchscreen, or virtual reality headset. Some computer games do not always depend on a graphics display, for example List of text-based computer games, text adventure games and computer chess can be played through teletype printers. Video games are often augmented with audio feedback delivered through loudspeaker, speakers or headphones, and sometimes with other types of feedback, including haptic technology. Video games are defined based on their computing platform, platform, which include arcade video games, console games, and PC game, personal computer (PC) games. More recently, the industry has expanded on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Electrotechnical Commission
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; in French: ''Commission électrotechnique internationale'') is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies – collectively known as " electrotechnology". IEC standards cover a vast range of technologies from power generation, transmission and distribution to home appliances and office equipment, semiconductors, fibre optics, batteries, solar energy, nanotechnology and marine energy as well as many others. The IEC also manages four global conformity assessment systems that certify whether equipment, system or components conform to its international standards. All electrotechnologies are covered by IEC Standards, including energy production and distribution, electronics, magnetics and electromagnetics, electroacoustics, multimedia, telecommunication and medical technology, as well as associated general disciplines such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ANSI
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private non-profit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organization also coordinates U.S. standards with international standards so that American products can be used worldwide. ANSI accredits standards that are developed by representatives of other standards organizations, government agencies, consumer groups, companies, and others. These standards ensure that the characteristics and performance of products are consistent, that people use the same definitions and terms, and that products are tested the same way. ANSI also accredits organizations that carry out product or personnel certification in accordance with requirements defined in international standards. The organization's headquarters are in Washington, D.C. ANSI's operations office is located in New York City. The ANSI annual operatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outside Plant
In telecommunication, the term outside plant has the following meanings: *In civilian telecommunications, outside plant refers to all of the physical cabling and supporting infrastructure (such as conduit, cabinets, tower or poles), and any associated hardware (such as repeaters) located between a demarcation point in a switching facility and a demarcation point in another switching center or customer premises. *In the United States, the DOD defines outside plant as the communications equipment located between a main distribution frame (MDF) and a user end instrument. The CATV industry divides its fixed assets between head end or inside plant, and outside plant. The electrical power industry also uses the term outside plant to refer to electric power distribution systems. Context Network connections between devices such as computers, printers, and phones require a physical infrastructure to carry and process signals. Typically, this infrastructure will consist of: * C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
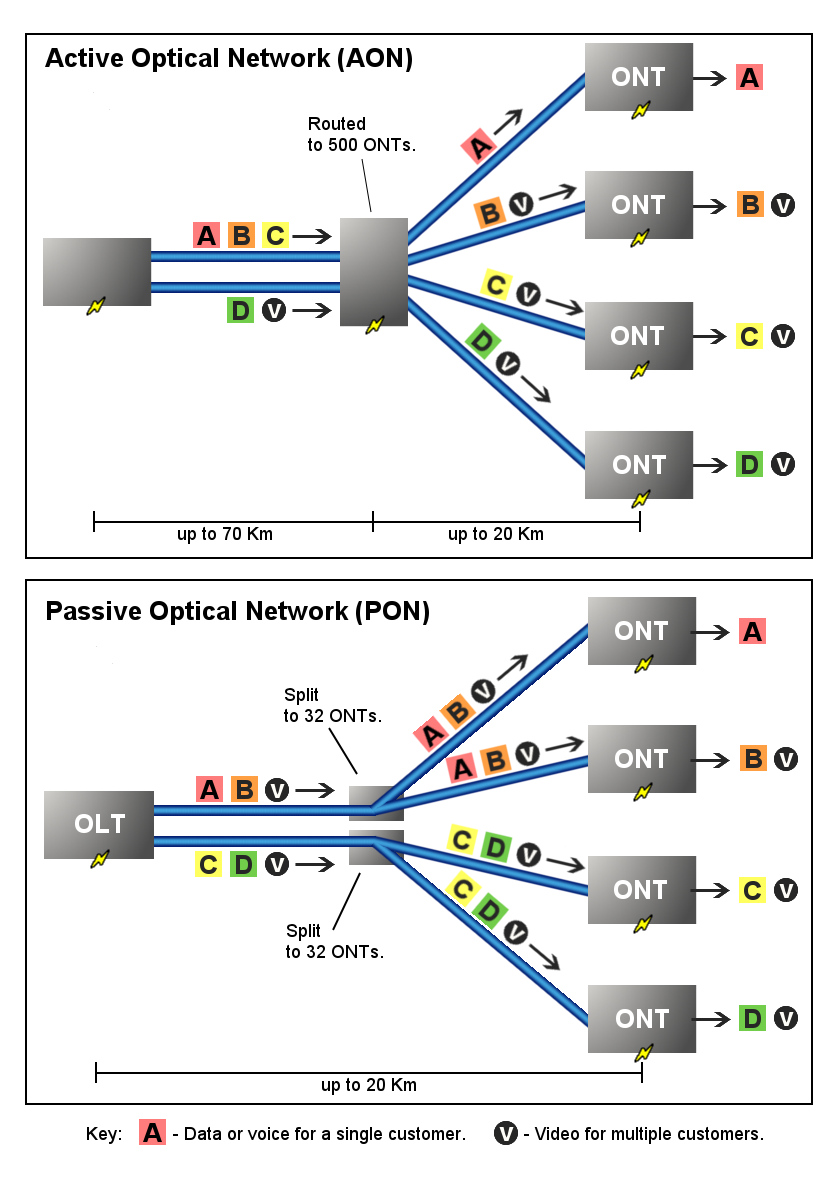
Passive Optical Network
A passive optical network (PON) is a fiber-optic telecommunications technology for delivering broadband network access to end-customers. Its architecture implements a point-to-multipoint topology in which a single optical fiber serves multiple endpoints by using unpowered (''passive'') fiber optic splitters to divide the fiber bandwidth among the endpoints. Passive optical networks are often referred to as the ''last mile'' between an Internet service provider (ISP) and its customers. Components and characteristics A passive optical network consists of an optical line terminal (OLT) at the service provider's central office (hub) and a number of optical network units (ONUs) or optical network terminals (ONTs), near end users. A PON reduces the amount of fiber and central office equipment required compared with point-to-point architectures. A passive optical network is a form of fiber-optic access network. In most cases, downstream signals are broadcast to all premises shari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magnetic material. The platters are paired with magnetic heads, usually arranged on a moving actuator arm, which read and write data to the platter surfaces. Data is accessed in a random-access manner, meaning that individual blocks of data can be stored and retrieved in any order. HDDs are a type of non-volatile storage, retaining stored data when powered off. Modern HDDs are typically in the form of a small rectangular box. Introduced by IBM in 1956, HDDs were the dominant secondary storage device for general-purpose computers beginning in the early 1960s. HDDs maintained this position into the modern era of servers and personal computers, though personal computing devices produced in large volume, like cell phones and tablets, rely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disk Buffer
In computer storage, disk buffer (often ambiguously called disk cache or cache buffer) is the embedded memory in a hard disk drive (HDD) or solid state drive (SSD) acting as a buffer between the rest of the computer and the physical hard disk platter or flash memory that is used for storage. Modern hard disk drives come with 8 to 256 MiB of such memory, and solid-state drives come with up to 4 GB of cache memory. Since the late 1980s, nearly all disks sold have embedded microcontrollers and either an ATA, Serial ATA, SCSI, or Fibre Channel interface. The drive circuitry usually has a small amount of memory, used to store the data going to and coming from the disk platters. The disk buffer is physically distinct from and is used differently from the page cache typically kept by the operating system in the computer's main memory. The disk buffer is controlled by the microcontroller in the hard disk drive, and the page cache is controlled by the computer to whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)