Beyoğlu SK on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Beyoğlu (; ) is a municipality and
 During the Byzantine period, the Genoese
During the Byzantine period, the Genoese
 During the 19th century it was again home to many European traders, and housed many
During the 19th century it was again home to many European traders, and housed many

 When the Ottoman Empire collapsed and the Turkish Republic was founded (during and after the
When the Ottoman Empire collapsed and the Turkish Republic was founded (during and after the
 The Istanbul metro M2 line runs through the district via Taksim and Şişhane stations. The T1 tram line runs in the district between the Kabataş and Karaköy stops and the T2 nostalgic tram line runs on the Istiklal Avenue. Funicular lines F1 and
The Istanbul metro M2 line runs through the district via Taksim and Şişhane stations. The T1 tram line runs in the district between the Kabataş and Karaköy stops and the T2 nostalgic tram line runs on the Istiklal Avenue. Funicular lines F1 and
 Foreigners, especially from Euro-Mediterranean and West European countries, have long resided in Beyoğlu. There is a
Foreigners, especially from Euro-Mediterranean and West European countries, have long resided in Beyoğlu. There is a
After the fire of 1870, the theatre was purchased by the local Greek banker Hristaki Zoğrafos Efendi, and architect Kleanthis Zannos designed the current building, which was called ''Cité de Péra'' or ''Hristaki Pasajı'' in its early years. ''Yorgo'nun Meyhanesi'' (Yorgo's Winehouse) was the first winehouse to be opened in the passage. In 1908 the Ottoman ''Pano'', established by Panayotis Papadopoulos in 1898, and the neighbouring ''Viktor Levi'', established in 1914, are among the oldest winehouses in the city and are located on Kalyoncu Kulluk Street near the British Consulate and Galatasaray Square. ''Cumhuriyet Meyhanesi'' (literally ''Republic Winehouse''), renamed in the early 1930s but originally established in the early 1890s, is another popular historic winehouse and is located in the nearby Sahne Street, along with the ''Hazzopulo Winehouse'', established in 1871, inside the ''Hazzopulo Pasajı'' which connects Sahne Street and Meşrutiyet Avenue. The famous ''Nevizade Street'', which has rows of historic pubs next to each other, is also in this area. Other historic pubs are found in the areas around ''Tünel Pasajı'' and the nearby ''Asmalımescit Street''. Some historic neighbourhoods around İstiklal Avenue have recently been recreated, such as ''Cezayir Street'' near
''Pano'', established by Panayotis Papadopoulos in 1898, and the neighbouring ''Viktor Levi'', established in 1914, are among the oldest winehouses in the city and are located on Kalyoncu Kulluk Street near the British Consulate and Galatasaray Square. ''Cumhuriyet Meyhanesi'' (literally ''Republic Winehouse''), renamed in the early 1930s but originally established in the early 1890s, is another popular historic winehouse and is located in the nearby Sahne Street, along with the ''Hazzopulo Winehouse'', established in 1871, inside the ''Hazzopulo Pasajı'' which connects Sahne Street and Meşrutiyet Avenue. The famous ''Nevizade Street'', which has rows of historic pubs next to each other, is also in this area. Other historic pubs are found in the areas around ''Tünel Pasajı'' and the nearby ''Asmalımescit Street''. Some historic neighbourhoods around İstiklal Avenue have recently been recreated, such as ''Cezayir Street'' near
 Primary and secondary schools in the district:
*
Primary and secondary schools in the district:
*
532
CITED: p
536
After a fire in 1848 it temporarily moved to the
532
CITED: p
537
Lycée Saint-Joseph, Istanbul was in Pera after its establishment; its official founding year is 1870.
district
A district is a type of administrative division that in some countries is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or county, counties, several municipality, municip ...
of Istanbul Province, Turkey. Its area is 9 km2, and its population is 225,920 (2022). It is on the European side of Istanbul
Istanbul is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, constituting the country's economic, cultural, and historical heart. With Demographics of Istanbul, a population over , it is home to 18% of the Demographics ...
, Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
, separated from the old city (historic peninsula of Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
) by the Golden Horn
The Golden Horn ( or ) is a major urban waterway and the primary inlet of the Bosphorus in Istanbul, Turkey. As a natural estuary that connects with the Bosphorus Strait at the point where the strait meets the Sea of Marmara, the waters of the ...
. It was known as the region of Pera (Πέρα, meaning "Beyond" in Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
) surrounding the ancient coastal town Galata
Galata is the former name of the Karaköy neighbourhood in Istanbul, which is located at the northern shore of the Golden Horn. The district is connected to the historic Fatih district by several bridges that cross the Golden Horn, most nota ...
which faced Constantinople across the Horn.
As the Ottoman capital of Constantinople grew during the 19th century, Pera/Beyoğlu became the modern
Modern may refer to:
History
*Modern history
** Early Modern period
** Late Modern period
*** 18th century
*** 19th century
*** 20th century
** Contemporary history
* Moderns, a faction of Freemasonry that existed in the 18th century
Philosophy ...
Western influenced quarter of the city, across from the old town, Fatih
Fatih () is a municipality and district of Istanbul Province, Turkey. Its area is 15 km2, and its population is 368,227 (2022). It is home to almost all of the provincial authorities (including the mayor's office, police headquarters, metro ...
. It was the center of the empire's politics, finance, diplomacy, culture, and commerce. Centered on the Grande Rue de Péra (today İstiklâl Avenue), it was a predominantly Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
(Armenians
Armenians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the Armenian highlands of West Asia.Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiq ...
, Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
, Levantine, and European expat) neighbourhood. Its population today mostly consists of Turks and Kurds who moved there after the Republic of Turkey was founded in 1923 and after the Istanbul pogrom
The Istanbul pogrom, also known as the Istanbul riots, were a series of state-sponsored anti-Greek mob attacks directed primarily at Istanbul's Greek minority on 6–7 September 1955. The pogrom was orchestrated by the governing Democrat ...
in 1955.
The district encompasses other neighborhoods located north of the Golden Horn, including Galata
Galata is the former name of the Karaköy neighbourhood in Istanbul, which is located at the northern shore of the Golden Horn. The district is connected to the historic Fatih district by several bridges that cross the Golden Horn, most nota ...
(the medieval Genoese citadel from which Beyoğlu itself originated, which is today known as Karaköy
Karaköy (), the modern name for the old Galata, is a commercial quarter in the Beyoğlu district of Istanbul, Turkey, located at the northern part of the Golden Horn mouth on the European side of Bosphorus.
Karaköy is one of the oldest and mo ...
), Tophane
Tophane () (lit. "Armoury") is a quarter in the Beyoğlu district of Istanbul, Turkey, running downhill from Galata to the shore of the Bosphorus where it joins up with Karaköy to the southwest and Fındıklı to the northeast.
In the Ottoman ...
, Cihangir
Cihangir is an affluent neighbourhood in the municipality and district of Beyoğlu, Istanbul Province, Turkey. Its population is 3,739 (2022). It is located between Taksim Square and Kabataş. It has many narrow streets, two parks, and many st ...
, Şişhane, Tepebaşı, Tarlabaşı, Dolapdere Dolapdere is a quarter of Beyoğlu district in central Istanbul, Turkey. It is surrounded by the quarters of Taksim, Kasımpaşa, Pangaltı and Kurtuluş.
Sites
* There is a museum dedicated to the memory of Adam Mickiewicz, the 19th century Pol ...
and Kasımpaşa, and is connected to the old city center across the Golden Horn through the Galata Bridge
The Galata Bridge (, ) is a bridge that spans the Golden Horn in Istanbul, Turkey. From the end of the 19th century in particular, the bridge has featured in Turkish literature, theater, poetry and novels. The current Galata Bridge is just the la ...
, Atatürk Bridge
Atatürk Bridge () is a road bridge across the Golden Horn in Istanbul, Turkey. It is named after Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, the founder and first President of the Republic of Turkey but is sometimes called the Unkapanı Bridge after the district on ...
and Golden Horn Metro Bridge. Beyoğlu is the most active art, entertainment and nightlife centre of Istanbul.
Name
Beyoğlu continued to be named Pera during theMiddle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
and, in western languages, into the early 20th century.
According to the prevailing theory, the Turkish name of Pera, ''Beyoğlu'', meaning "Bey
Bey, also spelled as Baig, Bayg, Beigh, Beig, Bek, Baeg, Begh, or Beg, is a Turkic title for a chieftain, and a royal, aristocratic title traditionally applied to people with special lineages to the leaders or rulers of variously sized areas in ...
's Son" in Turkish, is a modification by folk etymology
Folk etymology – also known as (generative) popular etymology, analogical reformation, (morphological) reanalysis and etymological reinterpretation – is a change in a word or phrase resulting from the replacement of an unfamiliar form by a mo ...
of the Venetian title of ''Bailo
''Bailo'' or ''baylo'' (plural ''baili'' or ''bayli'') is a Venetian title that derives from the Latin term '' baiulus'', meaning "porter, bearer". In English, it may be translated bailiff, or otherwise rendered as bailey, baili, bailie, bailli o ...
''. The 15th century ambassador of Venice in Istanbul, Andrea Gritti
Andrea Gritti (17 April 1455 – 28 December 1538) was the Doge of the Venetian Republic from 1523 to 1538, following a distinguished diplomatic and military career. He started out as a successful merchant in Constantinople and transitioned into ...
(who later became the Doge of Venice
The Doge of Venice ( ) – in Italian, was the doge or highest role of authority within the Republic of Venice (697–1797). The word derives from the Latin , meaning 'leader', and Venetian Italian dialect for 'duke', highest official of the ...
in 1523) had a mansion in this area. His son Alvise Gritti, who had close relations with the Sublime Porte
The Sublime Porte, also known as the Ottoman Porte or High Porte ( or ''Babıali''; ), was a synecdoche or metaphor used to refer collectively to the central government of the Ottoman Empire in Istanbul. It is particularly referred to the buildi ...
, also stayed there and was probably the person who was specifically referred to as ''Bey Oğlu'' after his father became the Doge of Venice. Located further south in Beyoğlu and originally built in the early 16th century, the "Venetian Palace" was the seat of the Bailo. The original palace building was replaced by the existing one in 1781, which later became the Italian Embassy following Italian unification
The unification of Italy ( ), also known as the Risorgimento (; ), was the 19th century political and social movement that in 1861 ended in the annexation of various states of the Italian peninsula and its outlying isles to the Kingdom of ...
in 1861, and the Italian Consulate in 1923, when Ankara
Ankara is the capital city of Turkey and List of national capitals by area, the largest capital by area in the world. Located in the Central Anatolia Region, central part of Anatolia, the city has a population of 5,290,822 in its urban center ( ...
became the capital of the Republic of Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
.
History
The area now known as Beyoğlu has been inhabited sinceByzas
Byzas (Ancient Greek: Βύζας, ''Býzas'') was the legendary founder of Byzantium (Ancient Greek: Βυζάντιον, ''Byzántion''), the city later known as Constantinople and then Istanbul.
Background
The legendary history of the founding ...
founded the City of Byzantium in the 7th century BC, and predates the founding of Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
. During the Byzantine era
The Byzantine calendar, also called the Roman calendar, the Creation Era of Constantinople or the Era of the World (, also or ; 'Roman year since the creation of the universe', abbreviated as ε.Κ.), was the calendar used by the Eastern Orth ...
, Greek speaking inhabitants named the hillside covered with orchards Sykai (The Fig Orchard), or Peran en Sykais (The Fig Field on the Other Side), referring to the "other side" of the Golden Horn. As the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
grew, so did Constantinople and its environs. The northern side of the Golden Horn became built up as a suburb of Byzantium as early as the 5th century. In this period the area began to be called Galata
Galata is the former name of the Karaköy neighbourhood in Istanbul, which is located at the northern shore of the Golden Horn. The district is connected to the historic Fatih district by several bridges that cross the Golden Horn, most nota ...
, and Emperor Theodosius II
Theodosius II ( ; 10 April 401 – 28 July 450), called "the Calligraphy, Calligrapher", was Roman emperor from 402 to 450. He was proclaimed ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' as an infant and ruled as the Eastern Empire's sole emperor after the ...
(reigned 402–450) built a fortress. The Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
believe that the name comes either from ''galatas'' (meaning "milkman
Milk delivery is a Delivery (commerce), delivery service dedicated to supplying milk, typically in milk bottle, bottles or cartons, to customers' homes. This service is performed by a milkman, milkwoman, or milk deliverer. (In contrast, a Cowman ...
"), as the area was used by shepherds in the early medieval period, or from the word ''Galatai'' (meaning "Gauls
The Gauls (; , ''Galátai'') were a group of Celts, Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age Europe, Iron Age and the Roman Gaul, Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). Th ...
"), as the Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foot ...
tribe of Gauls were thought to have camped here during the Hellenistic
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
period before settling into Galatia
Galatia (; , ''Galatía'') was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace (cf. Tylis), who settled here ...
in central Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, becoming known as the Galatians. The inhabitants of Galatia are famous for the Epistle to the Galatians
The Epistle to the Galatians is the ninth book of the New Testament. It is a letter from Paul the Apostle to a number of Early Christian communities in Galatia. Scholars have suggested that this is either the Galatia (Roman province), Roman pro ...
and the Dying Galatian statue. The name may have also derived from the Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
word ''Calata'', meaning "downward slope", as Galata, formerly a colony of the Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( ; ; ) was a medieval and early modern Maritime republics, maritime republic from the years 1099 to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italy, Italian coast. During the Late Middle Ages, it was a major commercial power in ...
between 1273 and 1453, stands on a hilltop that goes downwards to the sea.
Genoese and Venetian periods
The area came to be the base ofEurope
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
an merchants, particularly from Genoa and Venice, in what was then known as Pera. Following the Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
in 1204, and during the Latin Empire
The Latin Empire, also referred to as the Latin Empire of Constantinople, was a feudal Crusader state founded by the leaders of the Fourth Crusade on lands captured from the Byzantine Empire. The Latin Empire was intended to replace the Byzantin ...
of Constantinople (1204–1261), the Venetians became more prominent in Pera. The Dominican Church of St. Paul (1233), today known as the ''Arap Camii'', is from this period.Müller-Wiener (1977), p. 79
In 1273 the Byzantine Emperor
The foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, which Fall of Constantinople, fell to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as legitimate rulers and exercised s ...
Michael VIII Palaiologos
Michael VIII Palaiologos or Palaeologus (; 1224 – 11 December 1282) reigned as Byzantine emperor from 1261 until his death in 1282, and previously as the co-emperor of the Empire of Nicaea from 1259 to 1261. Michael VIII was the founder of th ...
granted Pera to the Republic of Genoa in recognition of Genoa's support of the Empire after the Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
and the sacking of Constantinople in 1204. Pera became a flourishing trade colony, ruled by a .
The ''Genoese Palace'' (Palazzo del Comune) was built in 1316 by Montano de Marinis, the Podestà
(), also potestate or podesta in English, was the name given to the holder of the highest civil office in the government of the cities of central and northern Italy during the Late Middle Ages. Sometimes, it meant the chief magistrate of a c ...
of Galata (Pera), and still remains today in ruins, near the Bankalar Caddesi (Banks Street) in Karaköy
Karaköy (), the modern name for the old Galata, is a commercial quarter in the Beyoğlu district of Istanbul, Turkey, located at the northern part of the Golden Horn mouth on the European side of Bosphorus.
Karaköy is one of the oldest and mo ...
, along with its adjacent buildings and numerous Genoese houses from the early 14th century.
In 1348 the Genoese built the famous Galata Tower
The Galata Tower (), officially the Galata Tower Museum (), is a medieval Genoese tower in the Galata part of the Beyoğlu district of Istanbul, Turkey. Built as a watchtower at the highest point of the mostly demolished Walls of Galata, the t ...
, one of the most prominent landmarks of Istanbul. Pera (Galata) remained under Genoese control until May 29, 1453, when it was conquered by the Ottomans
Ottoman may refer to:
* Osman I, historically known in English as "Ottoman I", founder of the Ottoman Empire
* Osman II, historically known in English as "Ottoman II"
* Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empir ...
along with the rest of the city, after the Siege of Constantinople.
 During the Byzantine period, the Genoese
During the Byzantine period, the Genoese Podestà
(), also potestate or podesta in English, was the name given to the holder of the highest civil office in the government of the cities of central and northern Italy during the Late Middle Ages. Sometimes, it meant the chief magistrate of a c ...
ruled over the Italian community of Galata (Pera), which was mostly made up of the Genoese, Venetians, Tuscans and Ragusans.
Venice, Genoa's archrival, regained control in the strategic citadel of Galata (Pera), which they were forced to leave in 1261 when the Byzantines retook Constantinople and brought an end to the Latin Empire
The Latin Empire, also referred to as the Latin Empire of Constantinople, was a feudal Crusader state founded by the leaders of the Fourth Crusade on lands captured from the Byzantine Empire. The Latin Empire was intended to replace the Byzantin ...
(1204–1261) that was established by Enrico Dandolo
Enrico Dandolo (Anglicised as Henry Dandolo, and Latinised as Henricus Dandulus; – May/June 1205) was the doge of Venice from 1192 until his death in 1205. He is remembered for his avowed piety, longevity, and shrewdness, and his role in the ...
, the Doge of Venice
The Doge of Venice ( ) – in Italian, was the doge or highest role of authority within the Republic of Venice (697–1797). The word derives from the Latin , meaning 'leader', and Venetian Italian dialect for 'duke', highest official of the ...
.
In 1432, Bertrandon de la Broquière described Pera as "a large town, inhabited by Greeks, Jews and Genoese: the last are masters of it, under the duke of Milan, who styles himself Lord of Pera ... The port is the handsomest of all I have seen, and I believe I may add, of any in the possession of the Christians, for the largest genoese vessels may lie alongside the quay."
Following the Ottoman siege of Constantinople in 1453, during which the Genoese sided with the Byzantines and defended the city together with them, the Ottoman Sultan Mehmed II
Mehmed II (; , ; 30 March 14323 May 1481), commonly known as Mehmed the Conqueror (; ), was twice the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from August 1444 to September 1446 and then later from February 1451 to May 1481.
In Mehmed II's first reign, ...
allowed the Genoese (who had fled to their colonies in the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some . In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea, which in turn con ...
such as Lesbos
Lesbos or Lesvos ( ) is a Greek island located in the northeastern Aegean Sea. It has an area of , with approximately of coastline, making it the third largest island in Greece and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, eighth largest ...
and Chios
Chios (; , traditionally known as Scio in English) is the fifth largest Greece, Greek list of islands of Greece, island, situated in the northern Aegean Sea, and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, tenth largest island in the Medi ...
) to return to the city, but Galata was no longer run by a Genoese Podestà.
Venice immediately established political and commercial ties with the Ottoman Empire, and a Venetian Bailo was sent to Pera as an ambassador, during the Byzantine period. It was the Venetians who suggested Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 1452 - 2 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially rested o ...
to Bayezid II
Bayezid II (; ; 3 December 1447 – 26 May 1512) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1481 to 1512. During his reign, Bayezid consolidated the Ottoman Empire, thwarted a pro-Safavid dynasty, Safavid rebellion and finally abdicated his throne ...
when the Sultan mentioned his intention to construct a bridge over the Golden Horn, and Leonardo designed his Galata Bridge
The Galata Bridge (, ) is a bridge that spans the Golden Horn in Istanbul, Turkey. From the end of the 19th century in particular, the bridge has featured in Turkish literature, theater, poetry and novels. The current Galata Bridge is just the la ...
in 1502.
The Bailo's seat was the "Venetian Palace", originally built in Beyoğlu in the early 16th century and replaced by the existing palace building in 1781; which later became the "Italian Embassy" after the unification of Italy in 1861, and the "Italian Consulate" in 1923, when Ankara became the new Turkish capital.
The Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
had an interesting relationship with the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 ...
. Even though the two states often went to war over the control of East Mediterranean territories and islands, they were keen on restoring their trade pacts once the wars were over, such as the renewed trade pacts of 1479, 1503, 1522, 1540, and 1575, following major sea wars between the two sides. The Venetians were also the first Europeans to taste Ottoman delicacies such as coffee
Coffee is a beverage brewed from roasted, ground coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content, but decaffeinated coffee is also commercially a ...
, centuries before other Europeans saw coffee beans for the first time in their lives during the Battle of Vienna
The Battle of Vienna took place at Kahlenberg Mountain near Vienna on 1683 after the city had been besieged by the Ottoman Empire for two months. The battle was fought by the Holy Roman Empire (led by the Habsburg monarchy) and the Polish–Li ...
in 1683. These encounters can be described as the beginning of today's rich "coffee culture
Coffee culture is the set of traditions and social behaviors that surround the consumption of coffee, particularly as a social lubricant. The term also refers to the cultural diffusion and adoption of coffee as a widely consumed stimulant. In the ...
" in both Venice (and later the rest of Italy) and Vienna.
Following the conquest of Constantinople and Pera in 1453, the coast and the low-lying areas were quickly settled by the Turks, but the European presence in the area did not end. Several Roman Catholic churches, as St. Anthony of Padua, SS. Peter and Paul in Galata
Galata is the former name of the Karaköy neighbourhood in Istanbul, which is located at the northern shore of the Golden Horn. The district is connected to the historic Fatih district by several bridges that cross the Golden Horn, most nota ...
and St. Mary Draperis were established for the needs of the Levantine population.
Nineteenth-century
 During the 19th century it was again home to many European traders, and housed many
During the 19th century it was again home to many European traders, and housed many embassies
A diplomatic mission or foreign mission is a group of people from a state or organization present in another state to represent the sending state or organization officially in the receiving or host state. In practice, the phrase usually denotes a ...
, especially along the Grande Rue de Péra (today İstiklâl Avenue). Reyhan Zetler stated "Pera was considered to be a small copy of the 19th century Europe (especially Paris and London)." The presence of such a prominent European population - commonly referred to as Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
ines - made it the most Westernized part of Constantinople, especially when compared to the Old City at the other side of the Golden Horn
The Golden Horn ( or ) is a major urban waterway and the primary inlet of the Bosphorus in Istanbul, Turkey. As a natural estuary that connects with the Bosphorus Strait at the point where the strait meets the Sea of Marmara, the waters of the ...
, and allowed for influxes of modern technology, fashion, and arts. Thus, Pera was one of the first parts of Constantinople to have telephone line
A telephone line or telephone circuit (or just line or circuit industrywide) is a single-user circuit on a telephone communication system. It is designed to reproduce speech of a quality that is understandable. It is the physical wire or oth ...
s, electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
, tram
A tram (also known as a streetcar or trolley in Canada and the United States) is an urban rail transit in which Rolling stock, vehicles, whether individual railcars or multiple-unit trains, run on tramway tracks on urban public streets; some ...
s, municipal government
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
and even an underground railway, the Tünel
The Tünel (, designated as the F2 line on the Istanbul transport map) is a historic, underground, rubber-tyred funicular line in Istanbul, Turkey. It has two stations, connecting Karaköy and Beyoğlu. The tunnel runs uphill from near the con ...
, inaugurated in 1875 as the world's second subway line (after London's Underground) to carry the people of Pera up and down from the port of Galata and the nearby business and banking district of Karaköy
Karaköy (), the modern name for the old Galata, is a commercial quarter in the Beyoğlu district of Istanbul, Turkey, located at the northern part of the Golden Horn mouth on the European side of Bosphorus.
Karaköy is one of the oldest and mo ...
, where the '' Bankalar Caddesi'' (''Avenue of the Banks''), the financial center of the Ottoman Empire, is located. The theatre, cinema, patisserie and café culture that still remains strong in Beyoğlu dates from this late Ottoman period. Shops like İnci, famous for its chocolate mousse and profiterole
A profiterole (), ''chou à la crème'' (), also known alternatively as a cream puff (US), is a Filling (cooking), filled French choux pastry ball with a typically sweet and moist filling of whipped cream, custard, pastry cream, or ice cream. Th ...
s, predate the founding of the republic and survived until recently.
Pera and Galata in the late 19th and early 20th centuries were a part of the ''Municipality of the Sixth Circle'' (), established under the laws of 11 Jumada al-Thani
Jumada al-Thani (), also known as Jumada al-Akhirah (), Jumada al-Akhir (), or Jumada II, is the sixth month of the Islamic calendar. The word ''Jumda'' (), from which the name of the month is derived, is used to denote dry, parched land, a lan ...
(Djem. II) and 24 Shawwal
Shawwal () is the tenth month of the Islamic calendar. It comes after Ramadan and before Dhu al-Qa'da.
''Shawwāl'' stems from the Arabic verb ''shāla'' (), which means to 'lift or carry', generally to take or move things from one place to an ...
(Chev.) 1274, in 1858; the organisation of the central city in the city walls, "Stamboul" (), was not affected by these laws. All of Constantinople was in the ''Prefecture of the City of Constantinople'' ().
The foreign communities also built their own schools, many of which went on to educate the elite of future generations of Turks, and still survive today as some of the best schools in Istanbul (see list of schools in Istanbul
The list of high schools in Istanbul lists high schools within the city limits of Istanbul.
Adalar
* Heybeliada Anadolu Lisesi
* Heybeliada Deniz Lisesi
* Heybeliada Hüseyin Rahmi Gürpınar Çok Programlı Lisesi
* Özel Heybeliada Rum Er ...
).
The rapid modernization
Modernization theory or modernisation theory holds that as societies become more economically modernized, wealthier and more educated, their political institutions become increasingly liberal democratic and rationalist. The "classical" theories ...
which took place in Europe and left Ottoman Turkey behind was symbolized by the differences between Beyoğlu, and the historic Turkish quarters such as Eminönü
Eminönü, historically known as Pérama, is a predominantly commercial waterfront area of Istanbul within the Fatih district near the confluence of the Golden Horn with the southern entrance of the Bosphorus strait and the Sea of Marmara. It is l ...
and Fatih
Fatih () is a municipality and district of Istanbul Province, Turkey. Its area is 15 km2, and its population is 368,227 (2022). It is home to almost all of the provincial authorities (including the mayor's office, police headquarters, metro ...
across the Golden Horn, in the Old City. When the Ottoman sultans finally initiated a modernization program with the Edict of Tanzimat
The (, , lit. 'Reorganization') was a period of liberal reforms in the Ottoman Empire that began with the Edict of Gülhane of 1839 and ended with the First Constitutional Era in 1876. Driven by reformist statesmen such as Mustafa Reşid Pash ...
(Reorganization) in 1839, they started constructing numerous buildings in Pera that mixed traditional Ottoman styles with newer European ones.
In addition, Sultan Abdülmecid stopped living in the Topkapı Palace
The Topkapı Palace (; ), or the Seraglio, is a large museum and library in the east of the Fatih List of districts of Istanbul, district of Istanbul in Turkey. From the 1460s to the completion of Dolmabahçe Palace in 1856, it served as the ad ...
and built a new palace near Pera, called the Dolmabahçe Palace
Dolmabahçe Palace ( ) is a 19th-century imperial palace located in Istanbul, Turkey, along the European shore of the Bosporus, which served as the main administrative center of the Ottoman Empire from 1856 to 1887 and from 1909 to 1922.
Histor ...
, which blended the Neo-Classical, Baroque
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western Style (visual arts), style of Baroque architecture, architecture, Baroque music, music, Baroque dance, dance, Baroque painting, painting, Baroque sculpture, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from ...
and Rococo
Rococo, less commonly Roccoco ( , ; or ), also known as Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and dramatic style of architecture, art and decoration which combines asymmetry, scrolling curves, gilding, white and pastel colours, sculpte ...
styles.
During the İstanbul bombings of 18 October 1918, the area suffered.
20th-21st centuries
 When the Ottoman Empire collapsed and the Turkish Republic was founded (during and after the
When the Ottoman Empire collapsed and the Turkish Republic was founded (during and after the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
) Pera, which became known as Beyoğlu in English in the modern era, went into gradual decline. The decline accelerated with the departure of the large Greek population of Beyoğlu and adjacent Galata
Galata is the former name of the Karaköy neighbourhood in Istanbul, which is located at the northern shore of the Golden Horn. The district is connected to the historic Fatih district by several bridges that cross the Golden Horn, most nota ...
as a result of Turkish pressure over the Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
conflict, during the 1950s and 1960s. The widespread political violence between leftist and rightist groups which troubled Turkey in the late 1970s also severely affected the lifestyle of the district, and accelerated its decline with the flight of the middle-class citizens to newer suburban areas such as Levent
Levent is a neighbourhood in the municipality and district of Beşiktaş, Istanbul Province, Turkey. Its population is 2,911 (2022). It is one of the main business districts of Istanbul located on the European side of the city. It is situated ...
and Yeşilköy
(; meaning "Green Village"; prior to 1926, San Stefano or Santo Stefano , ) is an affluent neighbourhood () in the municipality and district of Bakırköy, Istanbul Province, Turkey. Its population is 25,039 (2022). on the Marmara Sea about ...
.
By the late 1980s, many of the grandiose Neoclassical and Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau ( ; ; ), Jugendstil and Sezessionstil in German, is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. It was often inspired by natural forms such as the sinuous curves of plants and ...
apartment-blocks, formerly the residences of the late Ottoman élite, became home to immigrants from the countryside. While Beyoğlu continued to enjoy a reputation for its cosmopolitan and sophisticated atmosphere until the 1940s and 1950s, by the 1980s the area had become economically and socially troubled.
The first decades of the 21st century have witnessed the rapid gentrification of these neighborhoods. Istiklal Avenue has once again become a destination for tourists, and formerly bohemian neighborhoods like Cihangir have once again become fashionable and quite expensive. Some 19th and early 20th century buildings have been tastefully restored, while others have been converted into mammoth luxury malls of dubious aesthetic value. As newer, more international and affluent residents have begun to creep down the hills into Tophane and Tarlabasi, disagreements with more conservative elements in the neighborhoods have become common.
The low-lying areas such as Tophane
Tophane () (lit. "Armoury") is a quarter in the Beyoğlu district of Istanbul, Turkey, running downhill from Galata to the shore of the Bosphorus where it joins up with Karaköy to the southwest and Fındıklı to the northeast.
In the Ottoman ...
, Kasımpaşa and Karaköy, and the side-streets of the area consist of older buildings.
Infrastructure
Roads
Parallel to İstiklal Avenue runs the wide bi-directional boulevard named Tarlabaşı Caddesi, which carries most of the traffic through the area and was constructed in the 1980s. The streets on either side of this road contain historic buildings and churches. The once cosmopolitan areas surrounding them have deteriorated. However, recent gentrification projects have seen some of the buildings restored. Istanbul's first beltway, the Kasımpaşa-Hasköy Tunnel, Piyalepaşa Avenue, Meclis-i Mebusan Avenue and Kulturuş Deresi Avenue are other major thoroughfares. Many Istanbul bus lines and the Istanbul Metrobus (only the Halıcıoğlu stop) provide transportation to the district.Rail transport
 The Istanbul metro M2 line runs through the district via Taksim and Şişhane stations. The T1 tram line runs in the district between the Kabataş and Karaköy stops and the T2 nostalgic tram line runs on the Istiklal Avenue. Funicular lines F1 and
The Istanbul metro M2 line runs through the district via Taksim and Şişhane stations. The T1 tram line runs in the district between the Kabataş and Karaköy stops and the T2 nostalgic tram line runs on the Istiklal Avenue. Funicular lines F1 and Tünel
The Tünel (, designated as the F2 line on the Istanbul transport map) is a historic, underground, rubber-tyred funicular line in Istanbul, Turkey. It has two stations, connecting Karaköy and Beyoğlu. The tunnel runs uphill from near the con ...
also provide transport for the district.
Culture
 Foreigners, especially from Euro-Mediterranean and West European countries, have long resided in Beyoğlu. There is a
Foreigners, especially from Euro-Mediterranean and West European countries, have long resided in Beyoğlu. There is a cosmopolitan
Cosmopolitan may refer to:
Internationalism
* World citizen, one who eschews traditional geopolitical divisions derived from national citizenship
* Cosmopolitanism, the idea that all of humanity belongs to a single moral community
* Cosmopolitan ...
atmosphere in the heart of the district, where people from various cultures live in Cihangir and Gümüşsuyu. Beyoğlu also has a number of historical Tekkes and Türbe
''Türbe'' refers to a Muslim mausoleum, tomb or grave often in the Turkish-speaking areas and for the mausolea of Ottoman sultans, nobles and notables. A typical türbe is located in the grounds of a mosque or complex, often endowed by the ...
s. Several Sufi
Sufism ( or ) is a mysticism, mystic body of religious practice found within Islam which is characterized by a focus on Islamic Tazkiyah, purification, spirituality, ritualism, and Asceticism#Islam, asceticism.
Practitioners of Sufism are r ...
orders, such as the ''Cihangirî'' (pronounced ''Jihangiri'') order, were founded here.
Most of the consulate
A consulate is the office of a consul. A type of mission, it is usually subordinate to the state's main representation in the capital of that foreign country (host state), usually an embassy (or, only between two Commonwealth countries, a ...
s (former embassies
A diplomatic mission or foreign mission is a group of people from a state or organization present in another state to represent the sending state or organization officially in the receiving or host state. In practice, the phrase usually denotes a ...
until 1923, when Ankara
Ankara is the capital city of Turkey and List of national capitals by area, the largest capital by area in the world. Located in the Central Anatolia Region, central part of Anatolia, the city has a population of 5,290,822 in its urban center ( ...
became the new Turkish capital) are still in this area; the Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
, British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
, Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
, Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
n, Dutch
Dutch or Nederlands commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
** Dutch people as an ethnic group ()
** Dutch nationality law, history and regulations of Dutch citizenship ()
** Dutch language ()
* In specific terms, i ...
, and Swedish consulates are significant in terms of their history and architecture.
Beyoğlu is also home to many high schools like Galatasaray Lisesi, Deutsche Schule Istanbul
Deutsche Schule Istanbul (, shortened as DSI), with formal Turkish language, Turkish name Özel Alman Lisesi () or İstanbul Alman Lisesi () or simply Alman Lisesi () is a Private school, private international high school in the Beyoğlu district o ...
, St. George's Austrian High School, Lycée Sainte Pulchérie, Liceo Italiano, Beyoğlu Anatolian High School, Beyoğlu Kız Lisesi, Zografeion Lyceum, Zappeion Lyceum, and numerous others.
The unique international art project United Buddy Bears
''Buddy Bears'' are painted, life-size fiberglass bear sculptures developed by German businesspeople Klaus and Eva Herlitz, in cooperation with sculptor Roman Strobl. They have become a landmark of Berlin and are considered unofficial ambassa ...
was presented in Beyoğlu during the winter of 2004–2005.
Tourism
The main thoroughfare is İstiklâl Caddesi, running into the neighbourhood from Taksim Square, a pedestrianised long street of shops, cafés, patisseries, restaurants, pubs, winehouses and clubs, as well as bookshops, theatres, cinemas and art galleries. Some of İstiklâl Avenue has a 19th-century metropolitan character, and the avenue is lined with Neoclassical andArt Nouveau
Art Nouveau ( ; ; ), Jugendstil and Sezessionstil in German, is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. It was often inspired by natural forms such as the sinuous curves of plants and ...
buildings. The nostalgic tram which runs on İstiklal Avenue, between Taksim Square and Tünel
The Tünel (, designated as the F2 line on the Istanbul transport map) is a historic, underground, rubber-tyred funicular line in Istanbul, Turkey. It has two stations, connecting Karaköy and Beyoğlu. The tunnel runs uphill from near the con ...
, was also re-installed in the early 1990s with the aim of reviving the historic atmosphere of the district.
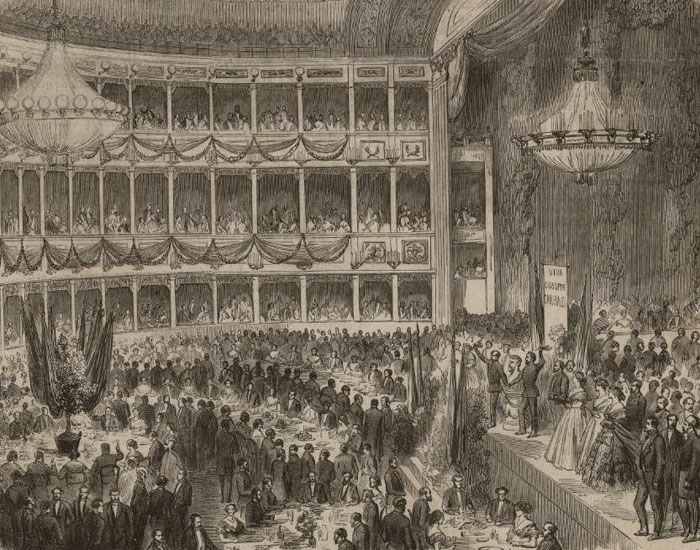
Some of the city's historic pubs and winehouses are located in the areas around İstiklal Avenue (İstiklal Caddesi) in Beyoğlu. The 19th century Çiçek Pasajı
Çiçek Pasajı ( Turkish: ''Flower Passage''), originally called the Cité de Péra, is a famous historic passage ( galleria or arcade) on İstiklal Avenue in the Beyoğlu district of Istanbul, Turkey. A covered arcade with rows of historic c ...
(literally ''Flower Passage'' in Turkish, or ''Cité de Péra'' in French, opened in 1876) on İstiklal Avenue can be described as a miniature version of the famous Galleria in Milan, Italy, and has rows of historic pubs, winehouses and restaurants. The site of Çiçek Pasajı was originally occupied by the Naum Theatre, which was burned during the great fire of Pera in 1870. The theatre was frequently visited by Sultans Abdülaziz
Abdulaziz (; ; 8 February 18304 June 1876) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 25 June 1861 to 30 May 1876, when he was 1876 Ottoman coup d'état, overthrown in a government coup. He was a son of Sultan Mahmud II and succeeded his brother ...
and Abdülhamid II
Abdulhamid II or Abdul Hamid II (; ; 21 September 184210 February 1918) was the 34th sultan of the Ottoman Empire, from 1876 to 1909, and the last sultan to exert effective control over the fracturing state. He oversaw a period of decline wit ...
, and hosted Giuseppe Verdi
Giuseppe Fortunino Francesco Verdi ( ; ; 9 or 10 October 1813 – 27 January 1901) was an Italian composer best known for List of compositions by Giuseppe Verdi, his operas. He was born near Busseto, a small town in the province of Parma ...
's play ''Il Trovatore'' before the opera houses of Paris.Tarihi Çiçek PasajıAfter the fire of 1870, the theatre was purchased by the local Greek banker Hristaki Zoğrafos Efendi, and architect Kleanthis Zannos designed the current building, which was called ''Cité de Péra'' or ''Hristaki Pasajı'' in its early years. ''Yorgo'nun Meyhanesi'' (Yorgo's Winehouse) was the first winehouse to be opened in the passage. In 1908 the Ottoman
Grand Vizier
Grand vizier (; ; ) was the title of the effective head of government of many sovereign states in the Islamic world. It was first held by officials in the later Abbasid Caliphate. It was then held in the Ottoman Empire, the Mughal Empire, the Soko ...
Sait Paşa purchased the building, and it became known as the Sait Paşa Passage. Following the Russian Revolution of 1917
The Russian Revolution was a period of Political revolution (Trotskyism), political and social revolution, social change in Russian Empire, Russia, starting in 1917. This period saw Russia Dissolution of the Russian Empire, abolish its mona ...
, many impoverished noble Russian women, including a Baroness, sold flowers here. By the 1940s the building was mostly occupied by flower shops, hence the present Turkish name ''Çiçek Pasajı'' (Flower Passage). Following the restoration of the building in 1988, it was reopened as a galleria of pubs and restaurants.
 ''Pano'', established by Panayotis Papadopoulos in 1898, and the neighbouring ''Viktor Levi'', established in 1914, are among the oldest winehouses in the city and are located on Kalyoncu Kulluk Street near the British Consulate and Galatasaray Square. ''Cumhuriyet Meyhanesi'' (literally ''Republic Winehouse''), renamed in the early 1930s but originally established in the early 1890s, is another popular historic winehouse and is located in the nearby Sahne Street, along with the ''Hazzopulo Winehouse'', established in 1871, inside the ''Hazzopulo Pasajı'' which connects Sahne Street and Meşrutiyet Avenue. The famous ''Nevizade Street'', which has rows of historic pubs next to each other, is also in this area. Other historic pubs are found in the areas around ''Tünel Pasajı'' and the nearby ''Asmalımescit Street''. Some historic neighbourhoods around İstiklal Avenue have recently been recreated, such as ''Cezayir Street'' near
''Pano'', established by Panayotis Papadopoulos in 1898, and the neighbouring ''Viktor Levi'', established in 1914, are among the oldest winehouses in the city and are located on Kalyoncu Kulluk Street near the British Consulate and Galatasaray Square. ''Cumhuriyet Meyhanesi'' (literally ''Republic Winehouse''), renamed in the early 1930s but originally established in the early 1890s, is another popular historic winehouse and is located in the nearby Sahne Street, along with the ''Hazzopulo Winehouse'', established in 1871, inside the ''Hazzopulo Pasajı'' which connects Sahne Street and Meşrutiyet Avenue. The famous ''Nevizade Street'', which has rows of historic pubs next to each other, is also in this area. Other historic pubs are found in the areas around ''Tünel Pasajı'' and the nearby ''Asmalımescit Street''. Some historic neighbourhoods around İstiklal Avenue have recently been recreated, such as ''Cezayir Street'' near Galatasaray High School
Galatasaray High School (, ), established in Istanbul in 1481, is the oldest and Selective school, highly selective high school in Turkey. It is also the second-oldest Turkish educational institution after Istanbul University, which was establi ...
, which became known as ''La Rue Française'' and has rows of francophone
The Francophonie or Francophone world is the whole body of people and organisations around the world who use the French language regularly for private or public purposes. The term was coined by Onésime Reclus in 1880 and became important a ...
pubs, cafés and restaurants playing live French music. ''Artiste Terasse'' (Artist Teras) on Cezayir Street is a popular restaurant-bar which offers panoramic views of the Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia (; ; ; ; ), officially the Hagia Sophia Grand Mosque (; ), is a mosque and former Church (building), church serving as a major cultural and historical site in Istanbul, Turkey. The last of three church buildings to be successively ...
, Topkapı Palace
The Topkapı Palace (; ), or the Seraglio, is a large museum and library in the east of the Fatih List of districts of Istanbul, district of Istanbul in Turkey. From the 1460s to the completion of Dolmabahçe Palace in 1856, it served as the ad ...
, Sultan Ahmed Mosque
The Blue Mosque, officially the Sultan Ahmed Mosque (), is an Ottoman-era historical imperial mosque located in Istanbul, Turkey. It was constructed between 1609 and 1617 during the rule of Ahmed I and remains a functioning mosque today. It al ...
and Galata Tower.
Throughout Beyoğlu, there are many night clubs for all kinds of tastes. There are restaurants on the top of historic buildings with a view of the city. ''Asmalımescit Street'' has rows of traditional Turkish restaurants and ''Ocakbaşı'' (grill) houses, while the streets around the historic ''Balıkpazarı'' (Fish Market) is full of eateries offering seafood like fried mussels
Mussel () is the common name used for members of several families of bivalve molluscs, from saltwater and freshwater habitats. These groups have in common a shell whose outline is elongated and asymmetrical compared with other edible clams, whic ...
and calamari along with beer
Beer is an alcoholic beverage produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches from cereal grain—most commonly malted barley, although wheat, maize (corn), rice, and oats are also used. The grain is mashed to convert starch in the ...
or rakı
Rakı, Türk Rakısı or Turkish Raki (, Turkish pronunciation: ) is an alcoholic beverage made of twice-distilled grape pomace and flavored with aniseed. It is a national drink of Turkey, although fewer than 17% of Turks drink alcohol. Among ...
, or the traditional '' kokoreç''. Beyoğlu also has many elegant ''pasaj'' (passages) from the 19th century, most of which have historic and classy chocolateries and patisseries along with many shops lining their alleys. There is also a wide range of fast-food restaurants in the district.
Apart from the hundreds of shops lining the streets and avenues of the district, there is also a business community. ''Odakule'', a 1970s high rise building (the first "structural expressionism" style building in Turkey) is the headquarters of ''İstanbul Sanayi Odası (ISO)'' (Istanbul Chamber of Industry) and is located between İstiklal Avenue and Tepebaşı, next to the Pera Museum
Pera Museum () is an art museum in the Tepebaşı quarter of the Beyoğlu (formerly called ''Pera'') district in Istanbul, Turkey, at Meşrutiyet Avenue No. 65, adjacent to İstiklal Avenue and in close proximity to Taksim Square. It has a parti ...
. Most of the upper floors of the buildings in Beyoğlu are office space, and small workshops are found on the side streets.
Landmarks
Istanbul Modern
Istanbul Museum of Modern Art, colloquially referred to as Istanbul Modern (), is a contemporary art gallery located inside the Galataport complex in the Beyoğlu district of Istanbul, Turkey. Inaugurated on December 11, 2004, Istanbul Modern was ...
, located near Karaköy Port on the Bosphorus, frequently hosts the exhibitions of renowned Turkish and foreign artists.
Pera Museum
Pera Museum () is an art museum in the Tepebaşı quarter of the Beyoğlu (formerly called ''Pera'') district in Istanbul, Turkey, at Meşrutiyet Avenue No. 65, adjacent to İstiklal Avenue and in close proximity to Taksim Square. It has a parti ...
exhibits some of the works of art from the late Ottoman period, such as the ''Kaplumbağa Terbiyecisi'' (Turtle Trainer) by Osman Hamdi Bey
Osman Hamdi Bey (30 December 1842 – 24 February 1910) was an Ottoman Turkish administrator, intellectual, art expert and also a prominent and pioneering painter. He was the Ottoman Empire's first modern archaeologist, and is regarded as the ...
. Apart from its permanent collection, the museum also hosts visiting exhibitions, which included the works of renowned artists such as Rembrandt
Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn (; ; 15 July 1606 – 4 October 1669), mononymously known as Rembrandt was a Dutch Golden Age painter, printmaker, and Drawing, draughtsman. He is generally considered one of the greatest visual artists in ...
.
Doğançay Museum, Turkey's first contemporary art museum dedicated to the works of a single artist, officially opened its doors to the public in 2004. While the museum almost exclusively displays the works of its founder Burhan Doğançay
Burhan C. Doğançay (11 September 1929 – 16 January 2013) was a Turkish-American artist. Doğançay is best known for tracking walls in various cities across the world for half a century, integrating them in his artistic work.
Biograph ...
, a contemporary artists, one floor has been set aside for the works of the artist's father, Adil Doğançay.
Hotel Pera Palace was built in the district in 1892 for hosting the passengers of the Orient Express
The ''Orient Express'' was a long-distance passenger luxury train service created in 1883 by the Belgian company ''Compagnie Internationale des Wagons-Lits'' (CIWL) that operated until 2009. The train traveled the length of continental Europe, w ...
. Agatha Christie
Dame Agatha Mary Clarissa Christie, Lady Mallowan, (; 15 September 1890 – 12 January 1976) was an English people, English author known for her 66 detective novels and 14 short story collections, particularly those revolving ...
wrote the novel ''Murder on the Orient Express
''Murder on the Orient Express'' is a work of detective fiction by English writer Agatha Christie featuring the Belgian detective Hercule Poirot. It was first published in the United Kingdom by the Collins Crime Club on 1 January 1934. In the U ...
'' in this hotel. Her room is conserved as a museum.
S. Antonio di Padova, the largest Catholic church in Turkey, and the Neve Shalom Synagogue
The Neve Shalom Synagogue (; ) is a Jewish congregation and synagogue, located at Büyük Hendek Caddesi 61, in the Karaköy quarter of the Beyoğlu district of Istanbul, in the Istanbul Province of Turkey.
History
The synagogue was built i ...
, the largest synagogue in Turkey, are also in Beyoğlu. There are other important Catholic and Orthodox churches in the area, such as the Saint Mary Draperis church or centrally located Hagia Triada Church at the conjunction point between Istiklal Avenue and Taksim Square. It is the seat of the Chaldean Catholic
The Chaldean Catholic Church is an Eastern Catholic particular church ('' sui iuris'') in full communion with the Holy See and the rest of the Catholic Church, and is headed by the Chaldean Patriarchate. Employing in its liturgy the East Syri ...
Archeparchy of Diyarbakir.
The only Jewish Museum of Turkey, which has been converted from a synagogue, is located in the Karaköy
Karaköy (), the modern name for the old Galata, is a commercial quarter in the Beyoğlu district of Istanbul, Turkey, located at the northern part of the Golden Horn mouth on the European side of Bosphorus.
Karaköy is one of the oldest and mo ...
quarter, which was known as Galata
Galata is the former name of the Karaköy neighbourhood in Istanbul, which is located at the northern shore of the Golden Horn. The district is connected to the historic Fatih district by several bridges that cross the Golden Horn, most nota ...
in the medieval period.
İstiklal Avenue
İstiklal Avenue () is a 1.4 kilometre (0.87 mi) pedestrian street in the historic Beyoğlu (Pera) district in Istanbul, Turkey. It is one of the most famous avenues in the city. It acquired its modern name after the declaration of the Repub ...
is also located in the historic Beyoğlu (Pera) district. The famous street with shops, cafes, cinemas and other venues stretches for 1.4 kilometres (0.87 mi) and hosts up to 3 million people each day.
The 1948-opened Atlas Cinema is situated in a 1877-built historic building at Istiklal Avenue.
Education
 Primary and secondary schools in the district:
*
Primary and secondary schools in the district:
*Deutsche Schule Istanbul
Deutsche Schule Istanbul (, shortened as DSI), with formal Turkish language, Turkish name Özel Alman Lisesi () or İstanbul Alman Lisesi () or simply Alman Lisesi () is a Private school, private international high school in the Beyoğlu district o ...
* Galatasaray High School
Galatasaray High School (, ), established in Istanbul in 1481, is the oldest and Selective school, highly selective high school in Turkey. It is also the second-oldest Turkish educational institution after Istanbul University, which was establi ...
* Liceo Italiano di Istanbul
* Lycée Français Pierre Loti d'Istanbul Beyoglu Campus
* St. George's Austrian High School
;Universities:
* Beykent University Taksim Campus
* Mimar Sinan Fine Arts University
Mimar Sinan Fine Arts University (, or MSGSÜ) is a public art university in Istanbul, Turkey. The university's campus is located in the Fındıklı, Beyoğlu. The university was established in 1882 under the leadership of Osman Hamdi Bey. Hi ...
The original campus of the Ottoman Imperial School of Medicine, established in 1827, was in Galatasaray
Galatasaray Spor Kulübü (, ''Galatasaray Sports Club''), more commonly referred to as simply Galatasaray and familiarly as Cimbom, is a Turkish sports club based on the European side of the city of Istanbul including basketball, wheelchair ...
, Pera.Sarell, R. "Turkey." In: Dobell, Horace Benge (editor). ''Reports on the Progress of Practical & Scientific Medicine in Different Parts of the World'', Volume 2. Longmans, Green, Reader & Dyer, 1871. Start: p532
CITED: p
536
After a fire in 1848 it temporarily moved to the
Golden Horn
The Golden Horn ( or ) is a major urban waterway and the primary inlet of the Bosphorus in Istanbul, Turkey. As a natural estuary that connects with the Bosphorus Strait at the point where the strait meets the Sea of Marmara, the waters of the ...
.Sarell, R. "Turkey." In: Dobell, Horace Benge (editor). ''Reports on the Progress of Practical & Scientific Medicine in Different Parts of the World'', Volume 2. Longmans, Green, Reader & Dyer, 1871. Start: p532
CITED: p
537
Lycée Saint-Joseph, Istanbul was in Pera after its establishment; its official founding year is 1870.
Quarters and neighborhoods
Quarters within Beyoğlu * Ayaspaşa * Azapkapı * Çıksalın * Çukurcuma *Dolapdere Dolapdere is a quarter of Beyoğlu district in central Istanbul, Turkey. It is surrounded by the quarters of Taksim, Kasımpaşa, Pangaltı and Kurtuluş.
Sites
* There is a museum dedicated to the memory of Adam Mickiewicz, the 19th century Pol ...
* Fındıklı
* Galata
Galata is the former name of the Karaköy neighbourhood in Istanbul, which is located at the northern shore of the Golden Horn. The district is connected to the historic Fatih district by several bridges that cross the Golden Horn, most nota ...
* Galatasaray
Galatasaray Spor Kulübü (, ''Galatasaray Sports Club''), more commonly referred to as simply Galatasaray and familiarly as Cimbom, is a Turkish sports club based on the European side of the city of Istanbul including basketball, wheelchair ...
* Hacıhüsrev
* Hasköy
* Kabataş
* Karaköy
Karaköy (), the modern name for the old Galata, is a commercial quarter in the Beyoğlu district of Istanbul, Turkey, located at the northern part of the Golden Horn mouth on the European side of Bosphorus.
Karaköy is one of the oldest and mo ...
* Kasımpaşa
* Kuledibi
* Şişhane
* Taksim
* Talimhane
* Tarlabaşı
* Tepebaşı
* Tophane
Tophane () (lit. "Armoury") is a quarter in the Beyoğlu district of Istanbul, Turkey, running downhill from Galata to the shore of the Bosphorus where it joins up with Karaköy to the southwest and Fındıklı to the northeast.
In the Ottoman ...
* Tünel
The Tünel (, designated as the F2 line on the Istanbul transport map) is a historic, underground, rubber-tyred funicular line in Istanbul, Turkey. It has two stations, connecting Karaköy and Beyoğlu. The tunnel runs uphill from near the con ...
There are 45 neighbourhoods
A neighbourhood (Commonwealth English) or neighborhood (American English) is a geographically localized community within a larger town, city, suburb or rural area, sometimes consisting of a single street and the buildings lining it. Neighbourh ...
in Beyoğlu District:
* Asmalı Mescit
* Azapkapı
* Bedrettin
* Bereketzade
* Bostan
* Bülbül
* Camiikebir
* Çatma Mescit
* Cihangir
Cihangir is an affluent neighbourhood in the municipality and district of Beyoğlu, Istanbul Province, Turkey. Its population is 3,739 (2022). It is located between Taksim Square and Kabataş. It has many narrow streets, two parks, and many st ...
* Çukur
* Emekyemez
* Evliya Çelebi
* Fetihtepe
* Firüzağa
* Gümüşsuyu
* Hacıahmet
* Hacımimi
* Halıcıoğlu
* Hüseyinağa
* İstiklal
* Kadımehmet Efendi
* Kalyoncukulluk
* Kamerhatun
* Kaptanpaşa
* Katipmustafa Çelebi
* Keçeçipiri
* Kemankeş Karamustafapaşa
* Kılıçali Paşa
* Kocatepe
* Küçük Piyale
* Kulaksız
* Kuloğlu
* Müeyyetzade
* Ömer Avni
* Örnektepe
* Piri Mehmet Paşa
* Piyalepaşa
* Pürtelaş Hasan Efendi
* Şahkulu
* Şehit Muhtar
* Sururi
* Sütlüce
* Tomtom
* Yahya Kahya
* Yenişehir
International relations
In the Ottoman period the embassy of the United States to the Ottoman Empire was located in Pera. - caption is in FrenchTwin towns — sister cities
Beyoğlu is twinned with: *Benalmádena
Benalmádena () is a town in Andalusia in southern Spain, 12 km west of Málaga, on the Costa del Sol between Torremolinos and Fuengirola.
Benalmádena is rich in attractive beaches and interesting places like the Colomares Castle, the 33-me ...
, Spain
* Bunkyō (Tokyo), Japan
* Centar (Skopje), North Macedonia
* Chengdu
Chengdu; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ; Chinese postal romanization, previously Romanization of Chinese, romanized as Chengtu. is the capital city of the Chinese province of Sichuan. With a ...
, China
* Chornomorsk, Ukraine
* Dubrovnik
Dubrovnik, historically known as Ragusa, is a city in southern Dalmatia, Croatia, by the Adriatic Sea. It is one of the most prominent tourist destinations in the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean, a Port, seaport and the centre of the Dubrovni ...
, Croatia
* Genoa
Genoa ( ; ; ) is a city in and the capital of the Italian region of Liguria, and the sixth-largest city in Italy. As of 2025, 563,947 people live within the city's administrative limits. While its metropolitan city has 818,651 inhabitan ...
, Italy
* Hebron
Hebron (; , or ; , ) is a Palestinian city in the southern West Bank, south of Jerusalem. Hebron is capital of the Hebron Governorate, the largest Governorates of Palestine, governorate in the West Bank. With a population of 201,063 in ...
, Palestine
* Mitte (Berlin), Germany
* Novi Grad (Sarajevo), Bosnia and Herzegovina
* Schaerbeek
(French language, French, ; former History of Dutch orthography, Dutch spelling) or (modern Dutch language, Dutch, ) is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Reg ...
, Belgium
* Sector 1 (Bucharest)
Sector 1 is an sectors of Bucharest, administrative unit of Bucharest located in the northern part of the city. It contains also the northwestern districts of Băneasa and Pipera. Sector 1 is thought to be the wealthiest sector in Bucharest. Like ...
, Romania
* Seongbuk (Seoul), South Korea
* Sidi Bernoussi (Casablanca), Morocco
* Tozeur, Tunisia
* Vitacura
Vitacura is a communes of Chile, commune of Chile located in Santiago Province, Chile, Santiago Province, Santiago Metropolitan Region. It is one of the most expensive and fashionable areas of Santiago, Chile, Santiago. Inhabitants are primarily h ...
, Chile
Friendly cities
*Catania
Catania (, , , Sicilian and ) is the second-largest municipality on Sicily, after Palermo, both by area and by population. Despite being the second city of the island, Catania is the center of the most densely populated Sicilian conurbation, wh ...
, Italy
* Pécs
Pécs ( , ; ; Slovak language, Slovak: ''Päťkostolie''; also known by #Name, alternative names) is List of cities and towns of Hungary#Largest cities in Hungary, the fifth largest city in Hungary, on the slopes of the Mecsek mountains in the c ...
, Hungary
* Dortmund
Dortmund (; ; ) is the third-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia, after Cologne and Düsseldorf, and the List of cities in Germany by population, ninth-largest city in Germany. With a population of 614,495 inhabitants, it is the largest city ...
, Germany
* Mannheim
Mannheim (; Palatine German language, Palatine German: or ), officially the University City of Mannheim (), is the List of cities in Baden-Württemberg by population, second-largest city in Baden-Württemberg after Stuttgart, the States of Ger ...
, Germany
See also
*List of restaurant districts and streets
This is a list of restaurant districts and streets. Restaurant districts and streets are sometimes referred to as "restaurant row".Beyoğlu Municipality official websiteGalata TowerPera MuseumÇiçek Pasajı - Cité de PéraTiyatro Pera - Pera TheaterGalatasaray High School
{{DEFAULTSORT:Beyoglu Districts of Istanbul Province Entertainment districts in Turkey Metropolitan district municipalities in Turkey Populated places in Istanbul Province Restaurant districts and streets in Turkey
{{DEFAULTSORT:Beyoglu Districts of Istanbul Province Entertainment districts in Turkey Metropolitan district municipalities in Turkey Populated places in Istanbul Province Restaurant districts and streets in Turkey