Beveridge Park on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Kirkcaldy ( ; sco, Kirkcaldy; gd, Cair Chaladain) is a town and former
 The first document to recognise the town was issued in 1075, when the
The first document to recognise the town was issued in 1075, when the  A charter granted in 1363 by David II, King of Scots (reigned 1329–71), awarded the burgh the right to trade across the
A charter granted in 1363 by David II, King of Scots (reigned 1329–71), awarded the burgh the right to trade across the
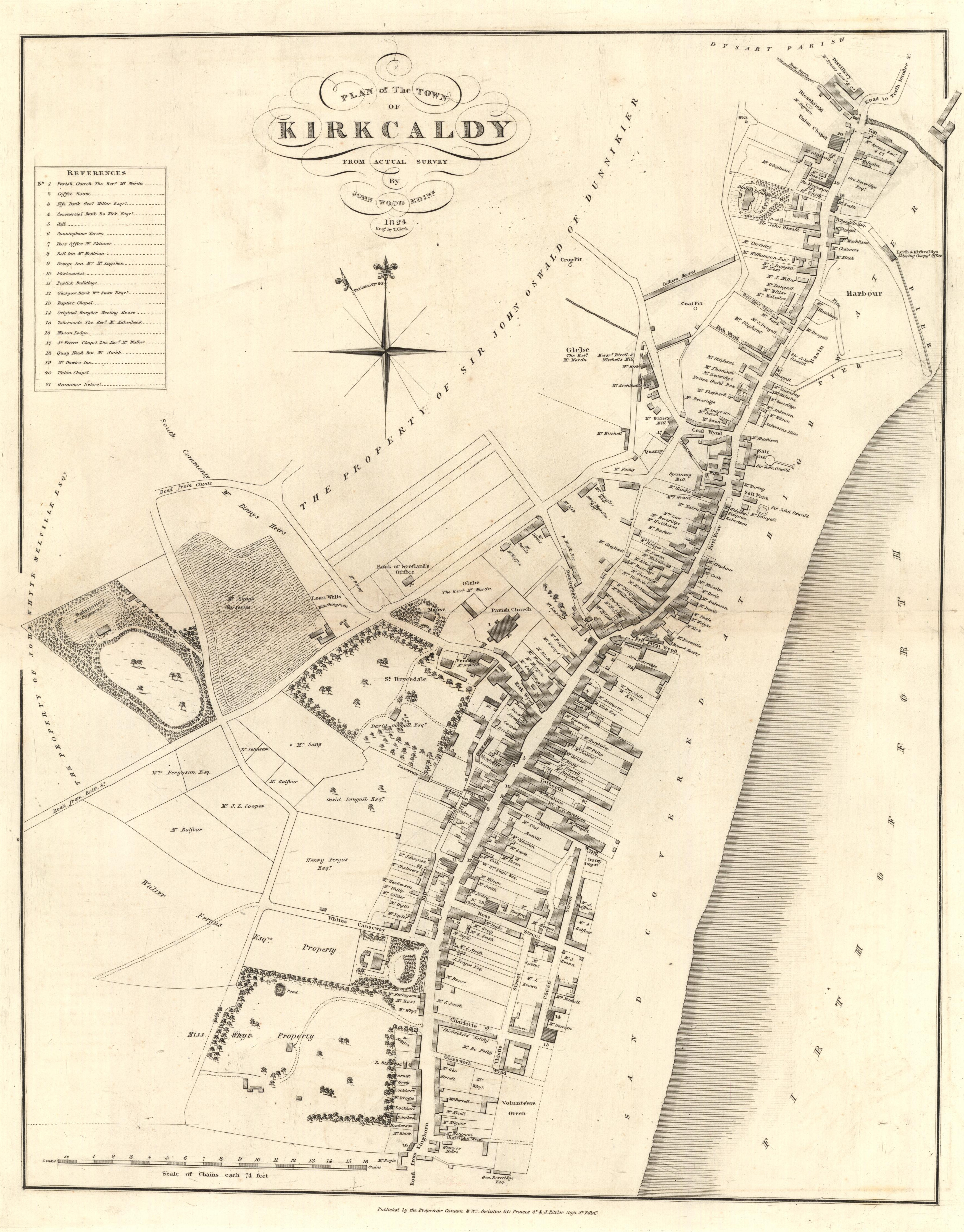
 Kirkcaldy is represented by several tiers of elected government. It is divided into six community council areas: Bennochy and Hayfield, Dysart, Kirkcaldy East, Kirkcaldy North, Kirkcaldy West, and Templehall. Of these, only Dysart, Kirkcaldy North and Kirkcaldy West have active
Kirkcaldy is represented by several tiers of elected government. It is divided into six community council areas: Bennochy and Hayfield, Dysart, Kirkcaldy East, Kirkcaldy North, Kirkcaldy West, and Templehall. Of these, only Dysart, Kirkcaldy North and Kirkcaldy West have active
 Kirkcaldy curves around a sandy cove between the Tiel (West) Burn to the south and the East Burn to the north, on a
Kirkcaldy curves around a sandy cove between the Tiel (West) Burn to the south and the East Burn to the north, on a
 The principal industrial and business estates include Mitchleston, Randolph, Hayfield, and John Smith Business Park. Local industrial activity has also increased with the reopening in 2011 of Kirkcaldy Harbour to cargo ships. This has been facilitated through a partnership between Forth Ports Ltd (the owners of the harbour), Hutchison's parent company of Carr's Flour Mills, and Transport Scotland, who provided a freight facilities grant of over £800,000. The work included new silos and conveyors to allow fast delivery from coastal ships.
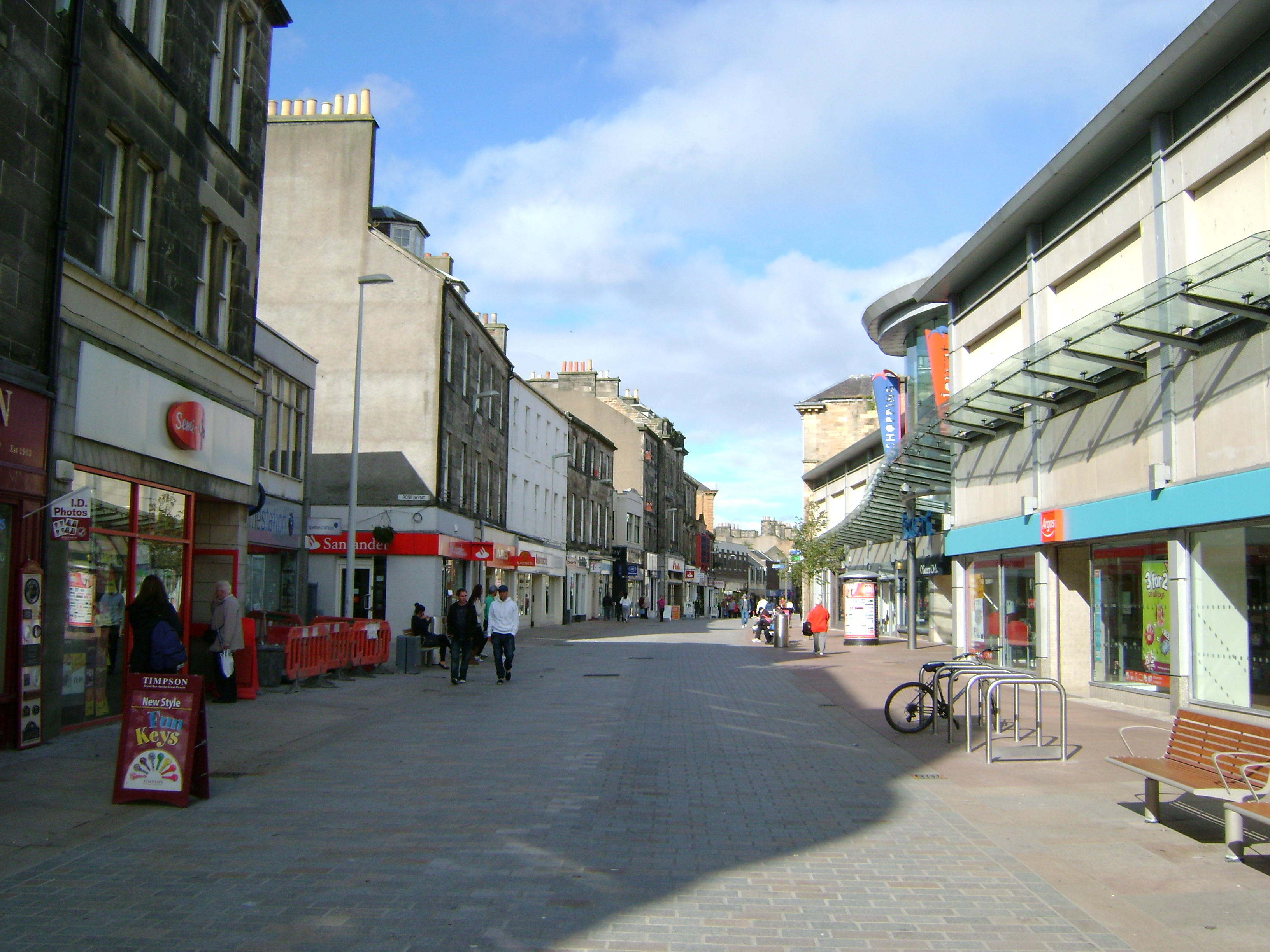
Kirkcaldy's town centre, which serves a large catchment area of around 130,000 residents within a 20-minute drive, is the largest in Fife in terms of retail floor space. Eligible businesses voted in favour of a BID (Business Improvement District) scheme for the town centre in 2010. The High Street, which runs parallel to the Esplanade, is home to the Mercat Shopping Centre. A regeneration programme to upgrade the appearance of the High Street was completed in late 2011. A separate project has also created a 'green corridor' to link the main railway station and bus station with the High Street. The budget for the entire project was £4 million, £2 million of which was provided through the Scottish Government's Town Centre Regeneration Fund.
An out-of-town
The principal industrial and business estates include Mitchleston, Randolph, Hayfield, and John Smith Business Park. Local industrial activity has also increased with the reopening in 2011 of Kirkcaldy Harbour to cargo ships. This has been facilitated through a partnership between Forth Ports Ltd (the owners of the harbour), Hutchison's parent company of Carr's Flour Mills, and Transport Scotland, who provided a freight facilities grant of over £800,000. The work included new silos and conveyors to allow fast delivery from coastal ships.
Kirkcaldy's town centre, which serves a large catchment area of around 130,000 residents within a 20-minute drive, is the largest in Fife in terms of retail floor space. Eligible businesses voted in favour of a BID (Business Improvement District) scheme for the town centre in 2010. The High Street, which runs parallel to the Esplanade, is home to the Mercat Shopping Centre. A regeneration programme to upgrade the appearance of the High Street was completed in late 2011. A separate project has also created a 'green corridor' to link the main railway station and bus station with the High Street. The budget for the entire project was £4 million, £2 million of which was provided through the Scottish Government's Town Centre Regeneration Fund.
An out-of-town
 Kirkcaldy Galleries is home to the town's museum and art gallery and central library. The building opened in 1925 under its former name of Kirkcaldy Museum and Art Gallery and was extended to provide a main library in 1928.Kirkcaldy Civic Society, 2005, p. 33.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2007, p. 72. In 2011, the building was closed to allow a £2.4 million renovation which was completed in June 2013. The work resulted in the integration of the facilities within the building through a single entrance and reception desk. The building also adopted its present name.
The Adam Smith Theatre, the town's main auditorium, plays host to theatrical and musical productions as well as showing a selection of
Kirkcaldy Galleries is home to the town's museum and art gallery and central library. The building opened in 1925 under its former name of Kirkcaldy Museum and Art Gallery and was extended to provide a main library in 1928.Kirkcaldy Civic Society, 2005, p. 33.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2007, p. 72. In 2011, the building was closed to allow a £2.4 million renovation which was completed in June 2013. The work resulted in the integration of the facilities within the building through a single entrance and reception desk. The building also adopted its present name.
The Adam Smith Theatre, the town's main auditorium, plays host to theatrical and musical productions as well as showing a selection of

Lothian Basketball League
A new £15 million leisure centre on the town's Esplanade opened its doors in September 2013. This has replaced the old Kirkcaldy Swimming Pool from the 1970s. The decision to build a new leisure centre on this site was controversial, as it resulted in the loss of a public car park. A petition organised by the campaign group Save The Car Park collected over 7,000 signatures in favour of keeping the car park open. The group said that the closure of the car park would discourage shoppers from coming to the High Street and raised issues over the loss of shopowners' right of access to the car park. This decision was severely criticised in an
 The oldest church in Kirkcaldy is the Old Kirk, the old parish church, on Kirk Wynd.Pearson 1993, p. 16. The earliest mention of the Old Kirk is the record of its consecration in 1244 to St Brisse and St Patrick by
The oldest church in Kirkcaldy is the Old Kirk, the old parish church, on Kirk Wynd.Pearson 1993, p. 16. The earliest mention of the Old Kirk is the record of its consecration in 1244 to St Brisse and St Patrick by  In the north-east are two homes of early wealthy merchants and shipowners connected with Kirkcaldy's harbour.Torrie and Coleman 1995, p. 61. The Merchant's House or Law's Close at 339–343 High Street;Pride 1998, pp. 55–58. once owned by the Law family, is one of the best surviving examples of a 16th-century town house in Scotland.Glen 2007, p. 22. Sailors' Walk, at 443–449 High Street; consists of two 17th century houses, resting on foundations dating back to around 1460.National Trust for Scotland 1976, p. 104. These two houses were once divided into four dwellings; three of which were owned by the Oliphant family and the fourth by James Ferguson of Raith.Glen 2007, p. 47.
North of the harbour area, on The Path, are two examples of distinctive architectural styles. Hutchison's House was designed by George Spears, the owner of the nearby East Bridge distillery, in 1793.Torrie and Coleman 1995, pp. 63–64. Path House, originally known as Dunnikier House, is a three-storey L-plan tower house designed by John Watson in 1692 for his bride, Euphan Orrock.Glen 2007, p. 67. In 1703 Watson sold the house to the Oswald family, who had important links with the town.
In the north-east are two homes of early wealthy merchants and shipowners connected with Kirkcaldy's harbour.Torrie and Coleman 1995, p. 61. The Merchant's House or Law's Close at 339–343 High Street;Pride 1998, pp. 55–58. once owned by the Law family, is one of the best surviving examples of a 16th-century town house in Scotland.Glen 2007, p. 22. Sailors' Walk, at 443–449 High Street; consists of two 17th century houses, resting on foundations dating back to around 1460.National Trust for Scotland 1976, p. 104. These two houses were once divided into four dwellings; three of which were owned by the Oliphant family and the fourth by James Ferguson of Raith.Glen 2007, p. 47.
North of the harbour area, on The Path, are two examples of distinctive architectural styles. Hutchison's House was designed by George Spears, the owner of the nearby East Bridge distillery, in 1793.Torrie and Coleman 1995, pp. 63–64. Path House, originally known as Dunnikier House, is a three-storey L-plan tower house designed by John Watson in 1692 for his bride, Euphan Orrock.Glen 2007, p. 67. In 1703 Watson sold the house to the Oswald family, who had important links with the town.  Two large stately homes also exist within the town. To the north of Kirkcaldy is Dunnikier House, built in the late 18th century as a seat for the Oswald family, replacing their previous residence at Path House.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2005, pp. 13–14. To the south-west of Kirkcaldy is Raith House, built in the late 17th century by Sir Alexander Raith, 4th Earl of Raith and Melville, for his wife, Barbara Dundas.Pride 1998, p. 103. The house remains a private residence of the Munro-Ferguson family.
To the east of the town are the ruins of
Two large stately homes also exist within the town. To the north of Kirkcaldy is Dunnikier House, built in the late 18th century as a seat for the Oswald family, replacing their previous residence at Path House.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2005, pp. 13–14. To the south-west of Kirkcaldy is Raith House, built in the late 17th century by Sir Alexander Raith, 4th Earl of Raith and Melville, for his wife, Barbara Dundas.Pride 1998, p. 103. The house remains a private residence of the Munro-Ferguson family.
To the east of the town are the ruins of
 The first school to be established in the town was Kirkcaldy Burgh School in 1582, a
The first school to be established in the town was Kirkcaldy Burgh School in 1582, a

 Kirkcaldy is the birthplace of social philosopher and
Kirkcaldy is the birthplace of social philosopher and
royal burgh
A royal burgh () was a type of Scottish burgh which had been founded by, or subsequently granted, a royal charter. Although abolished by law in 1975, the term is still used by many former royal burghs.
Most royal burghs were either created by ...
in Fife, on the east coast of Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a Anglo-Scottish border, border with England to the southeast ...
. It is about north of Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian on the southern shore of t ...
and south-southwest of Dundee. The town had a recorded population of 49,460 in 2011, making it Fife's second-largest settlement and the 12th most populous settlement in Scotland.
Kirkcaldy has long been nicknamed the Lang Toun (; Scots for "long town") in reference to the early town's main street, as indicated on maps from the 16th and 17th centuries. The street would finally reach a length of nearly , connecting the burgh to the neighbouring settlements of Linktown, Pathhead, Sinclairtown and Gallatown, which became part of the town in 1876. The formerly separate burgh of Dysart was also later absorbed into Kirkcaldy in 1930 under an act of Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
.
The area around Kirkcaldy has been inhabited since the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
. The first document to refer to the town is from 1075, when Malcolm III granted the settlement to the church of Dunfermline. David I David I may refer to:
* David I, Caucasian Albanian Catholicos c. 399
* David I of Armenia, Catholicos of Armenia (728–741)
* David I Kuropalates of Georgia (died 881)
* David I Anhoghin, king of Lori (ruled 989–1048)
* David I of Scotland ...
later gave the burgh to Dunfermline Abbey
Dunfermline Abbey is a Church of Scotland Parish Church in Dunfermline, Fife, Scotland. The church occupies the site of the ancient chancel and transepts of a large medieval Benedictine abbey, which was sacked in 1560 during the Scottish Reforma ...
, which had succeeded the church: a status which was officially recognised by Robert I in 1327. The town only gained its independence from Abbey rule when it was created a royal burgh by Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
in 1644.
From the early 16th century, the establishment of a harbour at the East Burn confirmed the town's early role as an important trading port. The town also began to develop around the salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quant ...
, coal mining and nail making
In woodworking and construction, a nail is a small object made of metal (or wood, called a tree nail or "trunnel") which is used as a fastener, as a peg to hang something, or sometimes as a decoration. Generally, nails have a sharp point on one e ...
industries. The production of linen which followed in 1672 was later instrumental in the introduction of floorcloth
A floorcloth, or floor-cloth, is a household furnishing used for warmth, decoration, or to protect expensive carpets. They were primarily produced and used from the early 18th to the early 20th century and were also referred to as oilcloth, wax cl ...
in 1847 by linen manufacturer, Michael Nairn. In 1877 this in turn contributed to linoleum
Linoleum, sometimes shortened to lino, is a floor covering made from materials such as solidified linseed oil (linoxyn), pine resin, ground cork dust, sawdust, and mineral fillers such as calcium carbonate, most commonly on a burlap or canva ...
, which became the town's most successful industry: Kirkcaldy was a world producer until well into the mid-1960s. The town expanded considerably in the 1950s and 1960s, though the decline of the linoleum industry and other manufacturing restricted its growth thereafter.
Today, the town is a major service centre for the central Fife area. Public facilities include a main leisure centre, theatre, museum and art gallery, three public parks and an ice rink. Kirkcaldy is also known as the birthplace of social philosopher and economist
An economist is a professional and practitioner in the social science discipline of economics.
The individual may also study, develop, and apply theories and concepts from economics and write about economic policy. Within this field there are ...
Adam Smith who wrote his magnum opus
A masterpiece, ''magnum opus'' (), or ''chef-d’œuvre'' (; ; ) in modern use is a creation that has been given much critical praise, especially one that is considered the greatest work of a person's career or a work of outstanding creativity, ...
''The Wealth of Nations
''An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations'', generally referred to by its shortened title ''The Wealth of Nations'', is the '' magnum opus'' of the Scottish economist and moral philosopher Adam Smith. First published in ...
'' in the town. In the early 21st century, employment is dominated by the service sector: the biggest employer in the town is PayWizard, formerly known as MGT plc (call centre). Other main employers include NHS Fife, Forbo (linoleum and vinyl floor coverings), Fife College
Fife College is a further and higher education college in Fife, Scotland.
Campuses
The college's main campuses are located in Dunfermline, Glenrothes and Kirkcaldy with smaller campuses in Leven, and Rosyth. The college also operates commun ...
, Whitworths (flour millers) and Smith Anderson (paper making).
History
Toponymy
The name Kirkcaldy means "place of the hard fort" or "place of Caled's fort". It is derived from thePictish
Pictish is the extinct Brittonic language spoken by the Picts, the people of eastern and northern Scotland from Late Antiquity to the Early Middle Ages. Virtually no direct attestations of Pictish remain, short of a limited number of geographica ...
* meaning "fort", *, which is Pictish "hard" or a personal name, and , a suffix meaning "place of". may describe the fort itself or be an epithet for a local "hard" ruler. An interpretation of the last element as ''din'' (again meaning "fort") rather than ''-in'' is incorrect. The Old Statistical Account gives a derivation from culdee
The Culdees ( ga, Céilí Dé, "Spouses of God") were members of ascetic Christian monastic and eremitical communities of Ireland, Scotland, Wales and England in the Middle Ages. Appearing first in Ireland and subsequently in Scotland, attac ...
, which has been repeated in later publications,Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2005, pp. 10–12.Torrie and Coleman 1995, pp. 12–13. but this is also incorrect.
Early
The discovery of 11Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
cist
A cist ( or ; also kist ;
from grc-gre, κίστη, Middle Welsh ''Kist'' or Germanic ''Kiste'') is a small stone-built coffin-like box or ossuary used to hold the bodies of the dead. Examples can be found across Europe and in the Middle Ea ...
burials which date from 2500 BC and 500 BC suggests that this is the most ancient funerary site in the area.Torrie and Coleman 1995, pp. 9–10. What probably made this location ideal was its natural terraces stretching away from the sand bay, and the close proximity of the East Burn to the north and the West (Tiel) Burn to the south. Four Bronze Age burials dating from around 4000 BC have also been found around the site of the unmarked Bogely or Dysart Standing Stone to the east of the present A92 road
The A92 is a major road that runs through Fife, Dundee, Angus, Aberdeenshire, and Aberdeen City in Scotland. From south to north, it runs from Dunfermline to Blackdog, just north of Aberdeen.
History
The A92's original route in southern ...
. Although there are few Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
sites in Fife, a Roman camp was known to exist at Carberry Farm on the town's outskirts.
The Battle of Raith
The Battle of Raith was the theory of E. W. B. Nicholson, librarian at the Bodleian Library, Oxford. He was aware of the poem Y Gododdin in the Book of Aneirin and was aware that no-one had identified the location "Catraeth". He parsed the nam ...
in AD 596 was once believed to have taken place to the west of the town's site but the theory no longer holds support. The battle was said to have been fought between the Angles
The Angles ( ang, Ængle, ; la, Angli) were one of the main Germanic peoples who settled in Great Britain in the post-Roman period. They founded several kingdoms of the Heptarchy in Anglo-Saxon England. Their name is the root of the name ...
and an alliance, led by King Áedán mac Gabráin
Áedán mac Gabráin (pronounced in Old Irish; ga, Aodhán mac Gabhráin, lang), also written as Aedan, was a king of Dál Riata from 574 until c. 609 AD. The kingdom of Dál Riata was situated in modern Argyll and Bute, Scotland, and par ...
of Dál Riata
Dál Riata or Dál Riada (also Dalriada) () was a Gaelic kingdom that encompassed the western seaboard of Scotland and north-eastern Ireland, on each side of the North Channel. At its height in the 6th and 7th centuries, it covered what is n ...
, of Scots, Picts
The Picts were a group of peoples who lived in what is now northern and eastern Scotland (north of the Firth of Forth) during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and what their culture was like can be inferred from e ...
and Britons
British people or Britons, also known colloquially as Brits, are the citizens of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, the British Overseas Territories, and the Crown dependencies.: British nationality law governs mod ...
.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2007, pp. 6–8.
Medieval
 The first document to recognise the town was issued in 1075, when the
The first document to recognise the town was issued in 1075, when the King of Scots
The monarch of Scotland was the head of state of the Kingdom of Scotland. According to tradition, the first King of Scots was Kenneth I MacAlpin (), who founded the state in 843. Historically, the Kingdom of Scotland is thought to have grown ...
, Malcolm III (reigned 1058–93) granted the shire of Kirkcaladunt, among other gifts, to the church at Dunfermline.MacBean 1908, pp. 33–34.Glen 2007, p. 13. The residents were expected to pay dues and taxes for the church's general upkeep. Two charters, later confirmed by Malcolm's son David I David I may refer to:
* David I, Caucasian Albanian Catholicos c. 399
* David I of Armenia, Catholicos of Armenia (728–741)
* David I Kuropalates of Georgia (died 881)
* David I Anhoghin, king of Lori (ruled 989–1048)
* David I of Scotland ...
in 1128 and 1130, refer to Kircalethin and Kirkcaladunit respectively, but do not indicate their locations.
In 1304, a weekly market and annual fair for Kirkcaldy was proposed by the Abbot of Dunfermline
The Prior, then Abbot and then Commendator of Dunfermline was the head of the Benedictine monastic community of Dunfermline Abbey, Fife, Scotland. The abbey itself was founded in 1128 by King David I of Scotland, but was of earlier origin. King ...
to King Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he ruled the duchies of Aquitaine and Gascony as a vassal ...
, during a period of English rule in Scotland from 1296 to 1306.Eunson 1998, pp. 3–4. During these discussions, the town may have been referred to as "one of the most ancient of burghs". This status as a burgh dependent on Dunfermline Abbey was later confirmed in 1327 by Robert I, King of Scots. A charter granted in 1363 by David II, King of Scots (reigned 1329–71), awarded the burgh the right to trade across the
A charter granted in 1363 by David II, King of Scots (reigned 1329–71), awarded the burgh the right to trade across the regality
A regality was a territorial jurisdiction in old Scots law which might be created by the King or Queen only, by granting lands to a subject ''in liberam regalitatem'', and the tract of land over which such a right extended.
A lord of regality h ...
of Dunfermline. This charter allowed the burgesses of Kirkcaldy to purchase and sell goods to the burgesses of the three other regality burghs – Queensferry, Dunfermline and Musselburgh – that belonged to the Abbey.Omand 2000, p. 138. By 1451, Kirkcaldy was awarded feu-ferme status. Under the status, responsibility would now lie with the bailies and council to deal with the routine administration of the town and its fiscal policies; conditional on an annual payment of two and a half marks
Marks may refer to:
Business
* Mark's, a Canadian retail chain
* Marks & Spencer, a British retail chain
* Collective trade marks, trademarks owned by an organisation for the benefit of its members
* Marks & Co, the inspiration for the novel ...
(33s 4d) to the Abbot of Dunfermline.
16th to 18th centuries
At the beginning of the 16th century, the town became an important trading port. The town took advantage of its east coast location, which facilitated trading contacts with theLow Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
, the Baltic region, England, and Northern France. The feu-ferme charter of 1451 between the Abbot of Dunfermline and the burgesses of Kirkcaldy mentioned a small but functioning harbour; it is not known when this harbour was established, or whether it was always located at the mouth of the East Burn.Torrie and Coleman 1995, p. 53. According to treasurers' accounts of the early 16th century, timber imported via the harbour—possibly from the Baltic countries—was used at Falkland Palace
Falkland Palace, in Falkland, Fife, Scotland, is a royal palace of the Scottish Kings. It was one of the favourite places of Mary, Queen of Scots, providing an escape from political and religious turmoil. Today it is under the stewardship of ...
and Edinburgh Castle, as well as in shipbuilding. Raw materials such as hides, wool, skins, herring, salmon, coal and salt were exported from the town until well into the 17th century.Glen 2007, p. 120.
A charter issued by Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
granting royal burgh
A royal burgh () was a type of Scottish burgh which had been founded by, or subsequently granted, a royal charter. Although abolished by law in 1975, the term is still used by many former royal burghs.
Most royal burghs were either created by ...
status in 1644 resulted in the end of the Abbey's jurisdiction over the town. As a gesture, the king bequeathed of common muir
"Muir" is the Scots word for "moorland", and Scots Gaelic for "sea", and is the etymological origin of the surname and Clan Muir/Mure/Moore in Scotland and other parts of the world.
Places United States
* Muir, Willits, California, a former unin ...
suitable for "bleaching of linen, drying of clothes, recreation and perpetuity".Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2005, pp. 17–18. In 1638, under the reign of Charles I, the town subscribed to the National Covenant, which opposed the introduction of episcopacy
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ca ...
and patronage in the Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their nam ...
church.Torrie and Coleman 1995, pp. 15–19. Support for the Covenanting cause cost the town over 250 men at the Battle of Kilsyth in 1645. The continuing civil wars
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government polici ...
killed at least another 480 men and led to the loss of many of the harbour's trading vessels. By 1660, this left the town with only twelve registered ships, down from 100 it is claimed were recorded between 1640 and 1644.
Towards the end of the 17th century, the economy recovered, with growth in manufacturing. During this period, Daniel Defoe described Kirkcaldy as a "larger, more populous, and better built town than ... any on this coast". A shipbuilding revival produced 38 vessels between 1778 and 1793.Glen, 2007, pp. 37–38. In the mid-19th century, whaling
Whaling is the process of hunting of whales for their usable products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that became increasingly important in the Industrial Revolution.
It was practiced as an organized industr ...
became important to the town for a short time. In 1813, the first Kirkcaldy whaling ship, ''The Earl Percy'', sailed north to the Davis Strait
Davis Strait is a northern arm of the Atlantic Ocean that lies north of the Labrador Sea. It lies between mid-western Greenland and Baffin Island in Nunavut, Canada. To the north is Baffin Bay. The strait was named for the English explorer Jo ...
; the town's last whaler, ''The Brilliant'', was sold in 1866 to Peterhead
Peterhead (; gd, Ceann Phàdraig, sco, Peterheid ) is a town in Aberdeenshire, Scotland. It is Aberdeenshire's biggest settlement (the city of Aberdeen itself not being a part of the district), with a population of 18,537 at the 2011 Census. ...
, bringing an end to the industry. Construction of a new turnpike
Turnpike often refers to:
* A type of gate, another word for a turnstile
* In the United States, a toll road
Turnpike may also refer to:
Roads United Kingdom
* A turnpike road, a principal road maintained by a turnpike trust, a body with powers ...
from Pettycur
Kinghorn (; gd, Ceann Gronna) is a town and parish in Fife, Scotland. A seaside resort with two beaches, Kinghorn Beach and Pettycur Bay, plus a fishing port, it stands on the north shore of the Firth of Forth, opposite Edinburgh. According ...
to Newport-on-Tay
Newport-on-Tay is a small town in the north-east of Fife in Scotland, acting as a Commuting, commuter suburb for Dundee. The Fife Coastal Path passes through Newport-on-Tay. The area itself is surrounded by views of the two bridges that cross the ...
via Cupar
Cupar ( ; gd, Cùbar) is a town, former royal burgh and parish in Fife, Scotland. It lies between Dundee and Glenrothes. According to a 2011 population estimate, Cupar had a population around 9,000, making it the ninth-largest settlement in Fif ...
in 1790, while improving only one section of Fife's isolated road system, brought a huge increase in traffic along Kirkcaldy's High Street
High Street is a common street name for the primary business street of a city, town, or village, especially in the United Kingdom and Commonwealth. It implies that it is the focal point for business, especially shopping. It is also a metonym fo ...
, and helped to strengthen the town's position.

Modern
For most of the 19th century, the main industries in the town wereflax
Flax, also known as common flax or linseed, is a flowering plant, ''Linum usitatissimum'', in the family Linaceae. It is cultivated as a food and fiber crop in regions of the world with temperate climates. Textiles made from flax are known in ...
spinning and linen weaving.Smith 1952, p. 480. To cope with increasing imports of flax, timber and hemp
Hemp, or industrial hemp, is a botanical class of ''Cannabis sativa'' cultivars grown specifically for industrial or medicinal use. It can be used to make a wide range of products. Along with bamboo, hemp is among the fastest growing plants o ...
, and exports of coal, salt and linen, between 1843 and 1846 a new wet dock and pier
image:Brighton Pier, Brighton, East Sussex, England-2Oct2011 (1).jpg, Seaside pleasure pier in Brighton, England. The first seaside piers were built in England in the early 19th century.
A pier is a raised structure that rises above a body of ...
was built at the harbour.Glen 2007, p. 87.Omand 2000, p. 195. In 1847 a canvas
Canvas is an extremely durable plain-woven fabric used for making sails, tents, marquees, backpacks, shelters, as a support for oil painting and for other items for which sturdiness is required, as well as in such fashion objects as handbags ...
manufacturer, Michael Nairn, took out a licence on Frederick Walton
Frederick Edward Walton (13 March 183416 May 1928), was an English manufacturer and inventor whose invention of Linoleum in Chiswick was patented in 1863. He also invented Lincrusta in 1877.
Early life
Walton was born in 1834, near Halifax. ...
's patent for the production of floorcloth
A floorcloth, or floor-cloth, is a household furnishing used for warmth, decoration, or to protect expensive carpets. They were primarily produced and used from the early 18th to the early 20th century and were also referred to as oilcloth, wax cl ...
, and opened a factory in nearby Pathhead.Smith 1952, pp. 287–288. When the patent expired in 1876, Nairn and other floorcloth manufacturers began the manufacture of linoleum. Production of both floorcloth and linoleum occupied seven factories in the town by 1883, employing 1,300. A further expansion of the harbour was completed between 1906 and 1908, for another increase in linoleum and coal.Eunson 1998, p. 6.Lamont-Brown, 2002, p. 145. The smell of the linoleum factories was notorious, giving rise to the famous lines in Mary Campbell Smith's 1913 poem The Boy in the Train: "For I ken mysel’ by the queer-like smell / That the next stop’s Kirkcaddy!".
The expansion of the town led in 1876 to the extension of the royal burgh's boundaries. The town absorbed its neighbouring settlements of Linktown, in the parish of Abbotshall; Invertiel in the parish of Kinghorn; and Pathhead, Sinclairtown and Gallatown in the parish of Dysart.Smith, 1952, pp. 470–471. These formerly separate settlements had once been forbidden by the old guild rights to sell their goods in Kirkcaldy.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2005, pp. 25–26. In 1922–1923 a seawall
A seawall (or sea wall) is a form of coastal defense constructed where the sea, and associated coastal processes, impact directly upon the landforms of the coast. The purpose of a seawall is to protect areas of human habitation, conservation ...
and esplanade
An esplanade or promenade is a long, open, level area, usually next to a river or large body of water, where people may walk. The historical definition of ''esplanade'' was a large, open, level area outside fortress or city walls to provide cle ...
were constructed, funded by the Unemployment Grants Commission and built by unemployed residents.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2005, p. 40.Glen 2007, p. 195. In 1930, the town would further expand to include the former royal burgh of Dysart under an act of Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
when its own town council became bankrupt.
During the 1950s and 1960s, new housing estate
A housing estate (or sometimes housing complex or housing development) is a group of homes and other buildings built together as a single development. The exact form may vary from country to country.
Popular throughout the United States a ...
s were built north-west of the town.Kirkcaldy Town Council, ''Development of Kirkcaldy'' This was followed by the redevelopment of the town centre in the 1960s and 1970s, which destroyed much of the old high street.Glen 2007, p. 286. There was speculation that the town's population could increase to around 55–60,000 by 1970. This did not happen: a decline in the linoleum industry in the mid-1960s led to a decrease in population, from a peak of 53,750 in 1961 to 47,962 in 1981.
In the 21st century, Kirkcaldy remains an important centre for the surrounding areas, with a Museum and Art Gallery, three public parks and shopping facilities. The town also hosts the annual Links Market, commonly known as ''Europe's longest street fair''. The production of linoleum continues, though on a greatly reduced scale, under Swiss ownership ( Forbo Holding AG). Kirkcaldy Harbour, which closed in 1992, re-opened in October 2011 to cargo ships.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2005, p. 82. A project between Carr's Flour Mills, the parent of Hutchison's, Forth Ports (owners of the harbour) and Transport Scotland
Transport Scotland ( gd, Còmhdhail Alba) is the national transport agency of Scotland. It was established by the Transport (Scotland) Act 2005, and began operating on 1 January 2006 as an Executive Agency of the Scottish Government.
Organisat ...
, will allow Carr's to bring in wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
via the harbour and remove a quarter of its lorries
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport cargo, carry specialized payloads, or perform other utilitarian work. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, but the vast majority feature body-on-frame construction ...
from the roads every year.
Governance
The grant of feu-ferme status in the middle of the 15th century meant that the town could deal with its own administrative issues and fiscal policies for the first time. The first mention of a town council was around 1582. The head courts of the burghs met either in the Common Muir (the surviving portion of the land now known as Volunteers' Green) or in the Tolbooth on Tolbooth Street, particularly in the summer months.Torrie and Coleman 1995, p. 30. When Kirkcaldy was awarded royal burgh status in 1644, the duties of the provost were initially performed by bailies, councillors, andmagistrate
The term magistrate is used in a variety of systems of governments and laws to refer to a civilian officer who administers the law. In ancient Rome, a '' magistratus'' was one of the highest ranking government officers, and possessed both judici ...
s. The first Lord Provost, Robert Whyt, was elected to the post around 1658. The burgh was one of four in Scotland to use two coats of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldic visual design on an escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the latter two being outer garments). The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full heraldic achievement, which in its wh ...
, introduced in 1673. One bears the motto ''Vigilando Munio'' ("I secure by watching"), and the other displays the figure of Saint Bryce, Kirkcaldy's patron saint.Fife Council 2000, p. 10.
Kirkcaldy enjoyed royal burgh status until this rank was abolished in 1975 under the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973
The Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973 (c. 65) is an Act of Parliament of the United Kingdom that altered local government in Scotland on 16 May 1975.
The Act followed and largely implemented the report of the Royal Commission on Local Gove ...
, in favour of a three-tier system of regions and districts. The royal burgh merged into Kirkcaldy District, which was one of three districts within the Fife region. The district council was abolished in 1996 under the Local Government etc (Scotland) Act 1994
The Local Government etc. (Scotland) Act 1994 (c. 39) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which created the current local government structure of 32 unitary authorities covering the whole of Scotland.
It abolished the two-tier st ...
when the region became a unitary council area
A unitary authority is a local authority responsible for all local government functions within its area or performing additional functions that elsewhere are usually performed by a higher level of sub-national government or the national governmen ...
. The new Fife Council
Fife Council is the local authority for the Fife area of Scotland and is the third largest Scottish council, with 75 elected council members.
Councillors are generally elected every five years. At the 2012 election there were 78 councillors ele ...
adopted the areas of the former districts as council management areas and created area committee
Many large local government councils in the United Kingdom have a system of area committees or area boards, which involve local people and organisations in decisions affecting council spending within their area. They cover a geographical area suc ...
s to represent each.
 Kirkcaldy is represented by several tiers of elected government. It is divided into six community council areas: Bennochy and Hayfield, Dysart, Kirkcaldy East, Kirkcaldy North, Kirkcaldy West, and Templehall. Of these, only Dysart, Kirkcaldy North and Kirkcaldy West have active
Kirkcaldy is represented by several tiers of elected government. It is divided into six community council areas: Bennochy and Hayfield, Dysart, Kirkcaldy East, Kirkcaldy North, Kirkcaldy West, and Templehall. Of these, only Dysart, Kirkcaldy North and Kirkcaldy West have active community councils
A community council is a public representative body in Great Britain.
In England they may be statutory Parish councils in England, parish councils by another name, under the Local Government and Public Involvement in Health Act 2007, or they may ...
, which form the lowest tier, and whose statutory role is to communicate local opinion to local and central government. Together with the nearby village of Thornton, the town forms the civil parish
In England, a civil parish is a type of administrative parish used for local government. It is a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government below districts and counties, or their combined form, the unitary authority ...
of Kirkcaldy and Dysart Kirkcaldy and Dysart is a civil parish on the south coast of Fife, Scotland, lying on the Firth of Forth, containing the towns of Kirkcaldy and Dysart and their hinterland. The civil parish was formed in December 1901 by an amalgamation of the par ...
, although civil parishes now have no administrative functions, and are used mainly for statistical purposes.
Fife Council, based in Glenrothes
Glenrothes (; , ; sco, Glenrothes; gd, Gleann Rathais) is a town situated in the heart of Fife, in east-central Scotland. It is about north of Edinburgh and south of Dundee. The town had a population of 39,277 in the 2011 census, making i ...
, the unitary local authority
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of public administration within a particular sovereign state. This particular usage of the word government refers specifically to a level of administration that is both geographically-loca ...
for Kirkcaldy, is the executive, deliberative Deliberative rhetoric (Greek: ''genos'' ''symbouleutikon;'' Latin: ''genus deliberativum,'' sometimes called legislative oratory) is one of the three kinds of rhetoric described by Aristotle. Deliberative rhetoric juxtaposes potential future outcome ...
, and legislative
A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country or city. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers of government.
Laws enacted by legislatures are usually known as p ...
body responsible for local governance. Kirkcaldy Town House is the main administrative headquarters for the Kirkcaldy area within the local authority. The Kirkcaldy area also sends 11 councillors, elected from three wards, to Fife Council. Beyond the tiers of local government, the Scottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament ( gd, Pàrlamaid na h-Alba ; sco, Scots Pairlament) is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Scotland. Located in the Holyrood area of the capital city, Edinburgh, it is frequently referred to by the metonym Holyro ...
is responsible for devolved matters from the Parliament of the United Kingdom
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster, London. It alone possesses legislative suprema ...
, such as education
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. Va ...
, health
Health, according to the World Health Organization, is "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity".World Health Organization. (2006)''Constitution of the World Health Organiza ...
, and justice
Justice, in its broadest sense, is the principle that people receive that which they deserve, with the interpretation of what then constitutes "deserving" being impacted upon by numerous fields, with many differing viewpoints and perspective ...
.
The first Member of Parliament to be elected to the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. ...
from Kirkcaldy was Colonel Abercrombie in 1710.MacBean 1908, p. 53. Prior to the Act of Union in 1707, Kirkcaldy sent a Member of Parliament to the old Scottish Parliament, which usually met in Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian on the southern shore of t ...
. Kirkcaldy was represented by the constituency of Dysart Burghs from 1707 to 1832, which was formed from the burgh itself and three other burghs, Dysart, Kinghorn
Kinghorn (; gd, Ceann Gronna) is a town and parish in Fife, Scotland. A seaside resort with two beaches, Kinghorn Beach and Pettycur Bay, plus a fishing port, it stands on the north shore of the Firth of Forth, opposite Edinburgh. According ...
, and Burntisland
Burntisland ( , sco, also Bruntisland) is a former royal burgh and parish in Fife, Scotland, on the northern shore of the Firth of Forth. According to the 2011 census, the town has a population of 6,269. It was previously known as Wester Kingho ...
.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2010, p. 1. Under the Reform Act of 1832
The Representation of the People Act 1832 (also known as the 1832 Reform Act, Great Reform Act or First Reform Act) was an Act of Parliament of the United Kingdom (indexed as 2 & 3 Will. IV c. 45) that introduced major changes to the electo ...
, the constituency of Kirkcaldy Burghs was created. Robert Ferguson of Raith was re-elected as Member of Parliament.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2010, p. 9. Kirkcaldy forms part of the county constituency
In the United Kingdom (UK), each of the electoral areas or divisions called constituencies elects one member to the House of Commons.
Within the United Kingdom there are five bodies with members elected by electoral districts called "constituenc ...
of Kirkcaldy and Cowdenbeath
Kirkcaldy and Cowdenbeath is a county constituency representing the areas around the towns of Kirkcaldy and Cowdenbeath, in Fife, Scotland, in the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It is currently represented by Alba Part ...
, electing one Member of Parliament to the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster, London. It alone possesses legislative suprema ...
by the first past the post
In a first-past-the-post electoral system (FPTP or FPP), formally called single-member plurality voting (SMP) when used in single-member districts or informally choose-one voting in contrast to ranked voting, or score voting, voters cast their ...
system. Since the 2017 UK General Election
The 2017 United Kingdom general election was held on Thursday 8 June 2017, two years after the previous general election in 2015; it was the first since 1992 to be held on a day that did not coincide with any local elections. The governing C ...
, Lesley Laird
Lesley Margaret Laird (' Langan; born 15 November 1958) is a Scottish politician who served as Deputy Leader of the Scottish Labour Party from 2017 to 2019. She was Member of Parliament (MP) for Kirkcaldy and Cowdenbeath from 2017 to 2019, and ...
of the Labour Party has been Member of Parliament for Kirkcaldy and Cowdenbeath.
Kirkcaldy forms part of the Kirkcaldy
Kirkcaldy ( ; sco, Kirkcaldy; gd, Cair Chaladain) is a town and former royal burgh in Fife, on the east coast of Scotland. It is about north of Edinburgh and south-southwest of Dundee. The town had a recorded population of 49,460 in 2011, ...
constituency of the Scottish Parliament (or ''Holyrood''), and is one of nine within the Mid Scotland and Fife electoral region. Each constituency elects one Member of the Scottish Parliament
Member of the Scottish Parliament (MSP; gd, Ball Pàrlamaid na h-Alba, BPA; sco, Memmer o the Scots Pairliament, MSP) is the title given to any one of the 129 individuals elected to serve in the Scottish Parliament.
Electoral system
The ad ...
by the first–past–the–post system of election, and the region elects seven additional members to produce a form of proportional representation
Proportional representation (PR) refers to a type of electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to geographical (e.g. states, regions) and political divis ...
. The Kirkcaldy seat was won at the 2011 Scottish Parliament election
The 2011 Scottish Parliament election was held on Thursday, 5 May 2011 to Members of the 4th Scottish Parliament, elect 129 members to the Scottish Parliament.
The election delivered the first majority government since the opening of Holyrood, ...
s by David Torrance for the Scottish National Party
The Scottish National Party (SNP; sco, Scots National Pairty, gd, Pàrtaidh Nàiseanta na h-Alba ) is a Scottish nationalist and social democratic political party in Scotland. The SNP supports and campaigns for Scottish independence from ...
(SNP). Following a review of Scottish Parliament constituency boundaries, the Kirkcaldy constituency was extended along the coast, taking in the Buckhaven, Methil
Methil (Scottish Gaelic: Meadhchill) is an eastern coastal town in Scotland. It was first recorded as "Methkil" in 1207, and belonged to the Bishop of St Andrews. Two Bronze Age cemeteries have been discovered which date the settlement as ov ...
, and East
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fa ...
and West Wemyss villages ward, ahead of the 2011 elections. Prior to Brexit
Brexit (; a portmanteau of "British exit") was the withdrawal of the United Kingdom (UK) from the European Union (EU) at 23:00 GMT on 31 January 2020 (00:00 1 February 2020 CET).The UK also left the European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC or ...
in 2020 it was part of the pan-Scotland European Parliament constituency
Members of the European Parliament (MEPs) are elected by the population of the member states of the European Union (EU). The European Electoral Act 2002 allows member states the choice to allocate electoral subdivisions or constituencies (, ...
, which elected seven Members of the European Parliament
A Member of the European Parliament (MEP) is a person who has been elected to serve as a popular representative in the European Parliament.
When the European Parliament (then known as the Common Assembly of the European Coal and Steel Commu ...
(MEPs).
Geography
bay
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a Gulf (geography), gulf, sea, sound (geography), sound, or bight (geogra ...
facing southeast onto the Firth of Forth
The Firth of Forth () is the estuary, or firth, of several Scottish rivers including the River Forth. It meets the North Sea with Fife on the north coast and Lothian on the south.
Name
''Firth'' is a cognate of ''fjord'', a Norse word meani ...
.Torrie and Coleman 1995, pp. 5–6. The town lies south-southeast of Glenrothes
Glenrothes (; , ; sco, Glenrothes; gd, Gleann Rathais) is a town situated in the heart of Fife, in east-central Scotland. It is about north of Edinburgh and south of Dundee. The town had a population of 39,277 in the 2011 census, making i ...
, east-northeast of Dunfermline
Dunfermline (; sco, Dunfaurlin, gd, Dùn Phàrlain) is a city, parish and former Royal Burgh, in Fife, Scotland, on high ground from the northern shore of the Firth of Forth. The city currently has an estimated population of 58,508. Accord ...
, west-southwest of Dundee and north-northeast of Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian on the southern shore of t ...
. The town adopted its nickname of the ''lang toun'' from the single street, recorded on early maps of the 16th and 17th centuries.Leighton 1860, p. 147. The street eventually reached a length of nearly , linking the burgh to its neighbouring suburbs of Linktown, Pathhead, Sinclairtown and Gallatown.Pride 1998, pp. 51–53.
Historians are not sure where the medieval centre of Kirkcaldy was located, but it may have been at the corner of Kirk Wynd and the High Street.Glen 2007, p. 10. This would have been the site of the town's Mercat cross and focal point of the burgh.Torrie and Coleman 1995, pp. 29–30. The linear market was important not only to the town itself but to the nearby hinterland. The main thoroughfare was either paved or cobbled
Cobblestone is a natural building material based on cobble-sized stones, and is used for pavement roads, streets, and buildings.
Setts, also called Belgian blocks, are often casually referred to as "cobbles", although a sett is distinct fr ...
, with flagstone
Flagstone (flag) is a generic flat stone, sometimes cut in regular rectangular or square shape and usually used for paving slabs or walkways, patios, flooring, fences and roofing. It may be used for memorials, headstones, facades and other con ...
s covering small burn
A burn is an injury to skin, or other tissues, caused by heat, cold, electricity, chemicals, friction, or ultraviolet radiation (like sunburn). Most burns are due to heat from hot liquids (called scalding), solids, or fire. Burns occur mainl ...
s running down the hill towards the sea across the High Street. Running back from the High Street were burgage
Burgage is a medieval land term used in Great Britain and Ireland, well established by the 13th century.
A burgage was a town ("borough" or "burgh") rental property (to use modern terms), owned by a king or lord. The property ("burgage tenement ...
plots or "rigs" of the burgesses; these narrow strips of land were at the front and to the rear of the houses. On the sea side of the High Street, plots may have served as beaching grounds for individual tenements
A tenement is a type of building shared by multiple dwellings, typically with flats or apartments on each floor and with shared entrance stairway access. They are common on the British Isles, particularly in Scotland. In the medieval Old Town, i ...
. The plots on the other side of the High Street rose steeply to the terracing of the Lomond foothills. A back lane running behind the plots from Kirk Wynd went to the west end of the High Street in a southerly direction. This lane would in time be developed as Hill Street. At the top of Kirk Wynd was the Parish Church of St Bryce, now known as the Old Kirk, overlooking the small settlement.
The small burns Burns may refer to:
* Burn, an injury (plural)
People:
* Burns (surname), includes list of people and characters
Business:
* Burns London, a British guitar maker
Places:
;In the United States
* Burns, Colorado, unincorporated community in Eagle ...
that are tributaries
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drainage b ...
to the East Burn contributed to the draining of the lands of Dunnikier Estate. The burn emerges from a deep-set culvert
A culvert is a structure that channels water past an obstacle or to a subterranean waterway. Typically embedded so as to be surrounded by soil, a culvert may be made from a pipe, reinforced concrete or other material. In the United Kingdom ...
to flow under the Victoria Viaduct
A viaduct is a specific type of bridge that consists of a series of arches, piers or columns supporting a long elevated railway or road. Typically a viaduct connects two points of roughly equal elevation, allowing direct overpass across a wide v ...
, down a deep gorge
A canyon (from ; archaic British English spelling: ''cañon''), or gorge, is a deep cleft between escarpments or cliffs resulting from weathering and the erosion, erosive activity of a river over geologic time scales. Rivers have a natural tenden ...
, through the site of Hutchison's Flour Mills before running parallel to the harbour wall and into the sea. From the mid-19th century, the Hutchison's buildings became a significant landmark adjacent to the burn. The flour millers chose this area for its railway connection which linked the main station to the harbour, rather than for the need to use the burn to power the mills. The West (or Tiel) Burn, was also important, providing power for textile mills. This burn flowed out of the Raith Estate lands where scenically and recreationally it was used to create Raith Lake (with its tributary, the Dronachy Burn). The mill owners in Linktown also made use of the burn.
Climate
Demography
Towards the end of the 16th century, a detailed assessment on the size of the townscape was carried out. The first estimate of the parish population in 1639 was between 3,000 and 3,200 and around 3,400 by 1691. At the beginning of the 18th century, the population declined. A census by Webster's ''Topographical Dictionary of Scotland'' in 1755, recorded an estimate of 2,296 in the parish. By the time of the first nationwide UK census in 1801, the population had risen to 3,248. The population of the burgh was recorded as 4,785 in the 1841 Census, and had risen to 34,079 by 1901. By the time of the 1951 Census, the figure stood at 49,050. According to the2001 UK Census
A nationwide census, known as Census 2001, was conducted in the United Kingdom on Sunday, 29 April 2001. This was the 20th UK census and recorded a resident population of 58,789,194.
The 2001 UK census was organised by the Office for National ...
, the census locality of Kirkcaldy has a total resident population of 46,912 representing 13.4% of Fife's total population. It hosts 21,365 households. 14.8% were married couples living together, 16.4% were one-person households, 18.8% were co-habiting couples and 7.9% were lone parents. A 2010 assessment estimated that the town had a population of 49,560. This had increased to 49,709 by the time of the 2011 UK Census
A census of the population of the United Kingdom is taken every ten years. The 2011 census was held in all countries of the UK on 27 March 2011. It was the first UK census which could be completed online via the Internet. The Office for National ...
. The total population in the wider Kirkcaldy area was estimated at 59,784 in 2016, with a projected increase of 18% by 2026. The number of households in the Kirkcaldy area in 2016 was recorded at 29,246; 67% of which were owner occupied, 27% social rented and 5% private rented. 36% of people live alone and 16.1% are on a low income. The median weekly income is calculated at £335 for the area.
The place of birth of the town's residents was 96.52% United Kingdom (including 87.15% from Scotland), 0.28% Republic of Ireland
Ireland ( ga, Éire ), also known as the Republic of Ireland (), is a country in north-western Europe consisting of 26 of the 32 counties of the island of Ireland. The capital and largest city is Dublin, on the eastern side of the island. A ...
, 1.18% from other European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
countries, and 1.86% from elsewhere in the world. The economic activity of residents aged 16–74 was 40.13% in full-time employment, 12.17% in part-time employment, 4.79% self-employed, 5.68% unemployed, 2.57% students with jobs, 3.06% students without jobs, 15.70% retired, 5.51% looking after home or family, 6.68% permanently sick or disabled, and 3.71% economically inactive for other reasons. Compared with the average demography of Scotland, Kirkcaldy has low proportions of immigrants, and has higher proportions for people over 75 years old.
In 2010, more than 7,000 people claimed benefits in the Kirkcaldy area; around 90 fewer than in 2009 but 500 more than the pre-recession
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction when there is a general decline in economic activity. Recessions generally occur when there is a widespread drop in spending (an adverse demand shock). This may be triggered by various ...
average for 2008. Recent Scottish Index of Multiple Deprivation
The Scottish index of multiple deprivation (SIMD) is a statistical tool used by local authorities, the Scottish government, the NHS and other government bodies in Scotland to support policy and decision making. It won the Royal Statistical Society ...
(SIMD) figures indicate that the most deprived datazone in Fife is Gallatown and Sinclairtown which has a rank of 82, meaning that it is amongst the 5% most deprived areas in Scotland. Linktown, Seafield, Hayfield, Smeaton and Templehall East areas in Kirkcaldy fall within the 5–10% banding of most deprived communities in Scotland.
In June 2017, there was a recorded 1,000 Jobseekers Allowance (JSA) claimants in the Kirkcaldy area representing a 2.8% rate, which was higher than the Fife and Scottish averages.
Economy
The first industries to develop in the town were coal mining and salt panning, which date back to the early 16th century. Early manufacturing both in Kirkcaldy and neighbouring Pathhead consisted of coarse cloth and nailmaking; the latter of which went to the Royal Master of Works for repairs atHolyrood Palace
The Palace of Holyroodhouse ( or ), commonly referred to as Holyrood Palace or Holyroodhouse, is the official residence of the British monarch in Scotland. Located at the bottom of the Royal Mile in Edinburgh, at the opposite end to Edinbu ...
until the 17th century. Linen weaving, which began in 1672, became important to the town, with yarn
Yarn is a long continuous length of interlocked fibres, used in sewing, crocheting, knitting, weaving, embroidery, ropemaking, and the production of textiles. Thread is a type of yarn intended for sewing by hand or machine. Modern manufact ...
imported from Hamburg
(male), (female) en, Hamburger(s),
Hamburgian(s)
, timezone1 = Central (CET)
, utc_offset1 = +1
, timezone1_DST = Central (CEST)
, utc_offset1_DST = +2
, postal ...
and Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (german: Stadtgemeinde Bremen, ), is the capital of the German state Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (''Freie Hansestadt Bremen''), a two-city-state consis ...
. The pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and por ...
industry, which was originally established in 1714 as an offshoot of the Linktown Brick and Tile Works, was centred around Linktown, Gallatown and Sinclairtown.Glen 2007, p. 158. The Fife Pottery, built by Andrew and Archibald Grey in 1817, produced Wemyss Ware, named after the family who owned Wemyss Castle
Wemyss Castle (pronounced eems is situated in Wemyss on the sea cliffs between the villages of East Wemyss and West Wemyss in Fife, Scotland. Wemyss Castle is considered to be a multi-period building, and today's castle includes many elements ...
.Glen 2007, p. 161.
The production of heavy canvas was started in 1828 by Michael Nairn at a small factory. Influenced by a visit to Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in ...
, Nairn started to make floorcloth at his new factory at Pathhead in 1847, where his company pioneered the use of ovens to season the floorcloth and reduce production times.Glen 2007, p. 140. When the patent belonging to Frederick Walton
Frederick Edward Walton (13 March 183416 May 1928), was an English manufacturer and inventor whose invention of Linoleum in Chiswick was patented in 1863. He also invented Lincrusta in 1877.
Early life
Walton was born in 1834, near Halifax. ...
expired, Nairn's were able to manufacture linoleum
Linoleum, sometimes shortened to lino, is a floor covering made from materials such as solidified linseed oil (linoxyn), pine resin, ground cork dust, sawdust, and mineral fillers such as calcium carbonate, most commonly on a burlap or canva ...
from 1877 onwards.Glen 2007, p. 142. Other factories producing floorcloth and later linoleum were established by former employees of Michael Nairn.
Approximately 22,200 people work in the Kirkcaldy area, the majority of which are in Kirkcaldy itself and to a lesser degree in Burntisland
Burntisland ( , sco, also Bruntisland) is a former royal burgh and parish in Fife, Scotland, on the northern shore of the Firth of Forth. According to the 2011 census, the town has a population of 6,269. It was previously known as Wester Kingho ...
. This represents approximately 13.6% of the 163,000 jobs in Fife. The local economy is dominated by service sector businesses. Other important economic sectors in the Kirkcaldy area are retailing and construction with moderate levels of jobs in financial and business services. The largest employer in the town is MGt plc. Other important local employers include NHS Fife, Forbo (vinyl floor coverings), Fife College (education), Whitworths Holdings (flour millers) and Smith Anderson (paper making).  The principal industrial and business estates include Mitchleston, Randolph, Hayfield, and John Smith Business Park. Local industrial activity has also increased with the reopening in 2011 of Kirkcaldy Harbour to cargo ships. This has been facilitated through a partnership between Forth Ports Ltd (the owners of the harbour), Hutchison's parent company of Carr's Flour Mills, and Transport Scotland, who provided a freight facilities grant of over £800,000. The work included new silos and conveyors to allow fast delivery from coastal ships.
Kirkcaldy's town centre, which serves a large catchment area of around 130,000 residents within a 20-minute drive, is the largest in Fife in terms of retail floor space. Eligible businesses voted in favour of a BID (Business Improvement District) scheme for the town centre in 2010. The High Street, which runs parallel to the Esplanade, is home to the Mercat Shopping Centre. A regeneration programme to upgrade the appearance of the High Street was completed in late 2011. A separate project has also created a 'green corridor' to link the main railway station and bus station with the High Street. The budget for the entire project was £4 million, £2 million of which was provided through the Scottish Government's Town Centre Regeneration Fund.
An out-of-town
The principal industrial and business estates include Mitchleston, Randolph, Hayfield, and John Smith Business Park. Local industrial activity has also increased with the reopening in 2011 of Kirkcaldy Harbour to cargo ships. This has been facilitated through a partnership between Forth Ports Ltd (the owners of the harbour), Hutchison's parent company of Carr's Flour Mills, and Transport Scotland, who provided a freight facilities grant of over £800,000. The work included new silos and conveyors to allow fast delivery from coastal ships.
Kirkcaldy's town centre, which serves a large catchment area of around 130,000 residents within a 20-minute drive, is the largest in Fife in terms of retail floor space. Eligible businesses voted in favour of a BID (Business Improvement District) scheme for the town centre in 2010. The High Street, which runs parallel to the Esplanade, is home to the Mercat Shopping Centre. A regeneration programme to upgrade the appearance of the High Street was completed in late 2011. A separate project has also created a 'green corridor' to link the main railway station and bus station with the High Street. The budget for the entire project was £4 million, £2 million of which was provided through the Scottish Government's Town Centre Regeneration Fund.
An out-of-town retail park
A retail park is a type of shopping centre found on the fringes of most large towns and cities in the United Kingdom and other European countries. They form a key aspect of European retail geographies, alongside indoor shopping centres, standalo ...
constructed in 1997 north-west of the town on Chapel Level, off the A92 is home to a number of warehouse retailers.Glen 2007, pp. 289–290. The retail park was purchased by Hammerson, a London-based property developer for £75 million in April 2005.
Culture
 Kirkcaldy Galleries is home to the town's museum and art gallery and central library. The building opened in 1925 under its former name of Kirkcaldy Museum and Art Gallery and was extended to provide a main library in 1928.Kirkcaldy Civic Society, 2005, p. 33.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2007, p. 72. In 2011, the building was closed to allow a £2.4 million renovation which was completed in June 2013. The work resulted in the integration of the facilities within the building through a single entrance and reception desk. The building also adopted its present name.
The Adam Smith Theatre, the town's main auditorium, plays host to theatrical and musical productions as well as showing a selection of
Kirkcaldy Galleries is home to the town's museum and art gallery and central library. The building opened in 1925 under its former name of Kirkcaldy Museum and Art Gallery and was extended to provide a main library in 1928.Kirkcaldy Civic Society, 2005, p. 33.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2007, p. 72. In 2011, the building was closed to allow a £2.4 million renovation which was completed in June 2013. The work resulted in the integration of the facilities within the building through a single entrance and reception desk. The building also adopted its present name.
The Adam Smith Theatre, the town's main auditorium, plays host to theatrical and musical productions as well as showing a selection of arthouse
An art film (or arthouse film) is typically an independent film, aimed at a niche market rather than a mass market audience. It is "intended to be a serious, artistic work, often experimental and not designed for mass appeal", "made primarily f ...
and commercial films.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2005, p. 54. Originally known as the Adam Smith Halls, the theatre adopted its present name in 1973 after a renovation of the building in time for the 250th anniversary of the birth of Adam Smith. The King's Theatre, originally opened in 1904 and derelict for some time is currently being redeveloped to become the biggest venue in Fife.
The Links Market originated as a farmers market
A farmers' market (or farmers market according to the AP stylebook, also farmer's market in the Cambridge Dictionary) is a physical retail marketplace intended to sell foods directly by farmers to consumers. Farmers' markets may be indoors or ...
on Links Street, before moving to its present site in 1903 on the Esplanade (then known as Sands Road).Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2007, p. 105. The market visits the town every April and celebrated its 700th anniversary in 2004. Kirkcaldy has had a twin-town link with Ingolstadt
Ingolstadt (, Austro-Bavarian: ) is an independent city on the Danube in Upper Bavaria with 139,553 inhabitants (as of June 30, 2022). Around half a million people live in the metropolitan area. Ingolstadt is the second largest city in Upper Bav ...
in Germany since
September 1962. There are plans for a joint celebration to recognise the 50th anniversary of the town's twinning with Ingolstadt in 2012.
There are three main public parks in Kirkcaldy.
:Beveridge Park, to the west of the town is a park created from the existing Robbie's Park, and land purchased from the Raith Estate.Kirkcaldy Civic Society, 2000, pp. 7–9. This was part of a £50,000 bequest from linen manufacturer and provost Michael Beveridge, who died in 1890. On 24 September 1892 a crowd of over 10,000 came to see the park's opening hosted by his widow, the provost, magistrates, and the town council of the royal burgh.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2000, p. 11. The park includes a boating lake, a formal garden with fountain, a skateboard park, rugby ground, football pitches and woodland walks. The park was awarded a green flag award
The Green Flag Award is an international accreditation given to publicly accessible parks and open spaces, managed under licence from the Department for Levelling Up, Housing and Communities, a UK Government department, by Keep Britain Tidy, ...
in both 2010 and 2011.
:Ravenscraig Park, to the east of the town was formed from the estate of Dysart House. The grounds were bequeathed to the town by the linoleum manufacturer Sir Michael Nairn in 1929.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2007, p. 56. It is adjacent to Ravenscraig Castle
Ravenscraig Castle is a ruined castle located in Kirkcaldy which dates from around 1460. The castle is an early example of artillery defence in Scotland.
History
The construction of Ravenscraig Castle by the mason Henry Merlion and the master ca ...
.
:Dunnikier Park, to the north of the town, purchased by the town council in 1945, consists of an area around Dunnikier House and is home to many woodland walkways.Omand 2000, p. 200. Dunnikier House was built around 1790 for James Townsend Oswald
James Townsend Oswald (23 February 1748 – 3 January 1814) was a Scottish politician who sat in the House of Commons between 1768 and 1779.
Oswald was the son of James Oswald, a politician of Kirkcaldy. The Oswald family became the dominant ...
, M.P.
Religion
There are several places of worship in Kirkcaldy including: Church of Scotland *Abbotshall *Bennochy *Linktown linked with Auchtertool *Pathhead *St Bryce Kirk *Templehall, Torbain and Viewforth linked with Thornton Roman Catholic *St Marie's *St Pius X Other Churches *Connect Church *Kirkcaldy Free Church *Newcraigs Evangelical Church *Pathhead Baptist Church *Redeemed Christian Church of God *St Peter's Episcopal Church * Kingdom Hall of Jehovah's Witnesses Islam *Kirkcaldy Central MosqueOn film and TV
*Unveiling of Kirkcaldy War Memorial (c1925) 10 mins – Kirkcaldy crowds and soldiers between the wars. *Road Races (1951–1952) 15 mins – Includes shots from Beveridge Park. *Kirkcaldy Youth Pageant (1952) 12 mins – Includes the Lang Toun Lass and Laddie with "Groucho Marx" *The Scottish footballer of the year (1957)Willie McNaught
William McNaught (9 May 1922 – 12 April 1989) was a Scottish footballer, who was born in Dumfries. McNaught holds the Raith Rovers club record for the number of appearances with the club of 657 between 1941 and 1962. McNaught was club captain ...
of Raith Rovers
Raith Rovers Football Club is a Scottish professional football club based in the town of Kirkcaldy, Fife. The club was founded in 1883 and currently competes in the Scottish Championship as a member of the Scottish Professional Football Leag ...
*The Queen Among Miners (1958) Includes shots of Queen Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until Death and state funeral of Elizabeth II, her death in 2022. She was queen ...
in a white boiler suit at Rothes Colliery.
*Fine Floors (c1963) 26 mins – A promotional film for the linoleum manufacturers, Michael Nairn and Company Ltd. See also this derivative.
*Kirkcaldy (1975) 22 mins – Guided by a cartoon disc jockey, the film looks at the Fife town of Kirkcaldy
*The 700th (2005) 56 mins – The 7th centenary of the Links Market
*The Town that Floored the World (first shown: BBC2 21 May 2018) 1 hour – Kirkcaldy and the linoleum industry.
Sport and leisure
Raith Rovers F.C.
Raith Rovers Football Club is a Scottish professional football club based in the town of Kirkcaldy, Fife. The club was founded in 1883 and currently competes in the Scottish Championship as a member of the Scottish Professional Football L ...
is the town's professional football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
team. They play in the Scottish Championship
The Scottish Championship, known as the cinch Championship for sponsorship reasons, is the second tier of the Scottish Professional Football League, the league competition for men's professional football clubs in Scotland
Scotland (, ...
, the second tier of Scottish football
Association football ( sco, fitbaa, gd, ball-coise) is one of the national sports of Scotland and the most popular sport in the country. There is a long tradition of "football" games in Orkney, Lewis and southern Scotland, especially the Scot ...
, at their Stark's Park
Stark's Park is a football stadium in Kirkcaldy, Scotland. It is the home ground of Raith Rovers, who have played there since 1891. The ground has an all-seated capacity of 9000
History
Raith started using the ground in 1891 and it seats ...
ground. Founded in 1883, the club were elected to the Scottish Football League
The Scottish Football League (SFL) was a league featuring professional and semi-professional football clubs mostly from Scotland.One club, Berwick Rangers, is based in the town of Berwick-upon-Tweed, which is located approximately 4 km south ...
in 1902.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2005, pp. 50–52.Potter and Jones 2008, p. 286. They reached their highest league position in the 1921–22 season, when they were placed third in the Scottish Football League
The Scottish Football League (SFL) was a league featuring professional and semi-professional football clubs mostly from Scotland.One club, Berwick Rangers, is based in the town of Berwick-upon-Tweed, which is located approximately 4 km south ...
. They achieved a British scoring record of 142 goals in 34 matches in the 1937–38 season. Under manager Jimmy Nicholl
James Michael Nicholl (born 28 December 1956) is a Northern Irish former professional Association football, footballer who played for several clubs, including Manchester United F.C., Manchester United and Rangers F.C., Rangers. He was mainly a ...
, the team were promoted to the Scottish Premier Division
The Scottish Football League Premier Division was, from 1975 until 1998, the top division of the Scottish Football League and the entire Scottish football league system. It lay above the Scottish Football League First, Second and (from 1994) Th ...
as Division One
The Football League First Division was a division of the Football League in England from 1888 until 2004. It was the top division in the English football league system from the season 1888–89 until 1991–92, a century in which the First ...
champions in the 1994–95 season. In 1994
File:1994 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The 1994 Winter Olympics are held in Lillehammer, Norway; The Kaiser Permanente building after the 1994 Northridge earthquake; A model of the MS Estonia, which Sinking of the MS Estonia, sank in ...
the club won their first national trophy, when they defeated Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
* Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Fo ...
6–5 on penalties
Penalty or The Penalty may refer to:
Sports
* Penalty (golf)
* Penalty (gridiron football)
* Penalty (ice hockey)
* Penalty (rugby)
* Penalty (rugby union)
* Penalty kick (association football)
* Penalty shoot-out (association football)
* Penalty ...
after finishing the game 2–2, to win the League Cup
In several sports, most prominently association football, a league cup or secondary cup generally signifies a cup competition for which entry is restricted only to teams in a particular league. The first national association football tournament t ...
.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2007, p. 52. This gained them qualification to the UEFA Cup
A cup is an open-top used to hold hot or cold liquids for pouring or drinking; while mainly used for drinking, it also can be used to store Solid, solids for pouring (e.g., sugar, flour, grains, salt). Cups may be made of glass, metal, porcela ...
in the following season
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and pol ...
, where they reached the second round
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds e ...
before losing to Bayern Munich
Fußball-Club Bayern München e. V. (FCB, ), also known as FC Bayern (), Bayern Munich, or simply Bayern, is a German professional sports club based in Munich, Bavaria. It is best known for its professional men's football team, which pla ...
.
The other senior football team, Kirkcaldy & Dysart, play at Denfield Park and compete in the , having moved from the Junior leagues in 2020. Kirkcaldy United were also a senior team based in the town, which dissolved in 1916.
Kirkcaldy RFC
Kirkcaldy Rugby Football Club is a rugby union club from Kirkcaldy, Fife, Scotland. The men's side currently plays in and the women's side currently plays in .
History
The team was established in 1873 Home games are played at Beveridge Park ...
are the senior rugby
Rugby may refer to:
Sport
* Rugby football in many forms:
** Rugby league: 13 players per side
*** Masters Rugby League
*** Mod league
*** Rugby league nines
*** Rugby league sevens
*** Touch (sport)
*** Wheelchair rugby league
** Rugby union: 1 ...
team and play at Beveridge Park in Scottish National League Division Two
The Scottish National League Division Two (known as Tennent's National League Division 2 for sponsorship reasons) is the third tier of the Scottish League Championship for amateur rugby union clubs in Scotland.
The division was established in it ...
, the third tier of Scottish club rugby. Fife Flyers
Fife Flyers is the oldest professional ice hockey club in the UK, established in 1938. The Flyers play their home games at Fife Ice Arena in Kirkcaldy which has a capacity of just over 3000 (seated and standing).
They joined the EIHL in 2011. ...
, established in 1938, are the oldest ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice hock ...
team in the United Kingdom. The team, who play at the Fife Ice Arena
Fife Ice Arena (originally known as Kirkcaldy Ice Rink) opened in 1938. Kirkcaldy Ice Rink was designed by architects Williamson & Hubbard. Fife Ice Arena is the home venue of the oldest ice hockey team in the UK – the Fife Flyers. It is als ...
, have been members of the Elite League since the 2011–12 season. Dunnikier Cricket Club play at Dunnikier Park and a flag football
Flag football is a variant of American football where, instead of tackling players to the ground, the defensive team must remove a flag or flag belt from the ball carrier ("deflagging") to end a Down (gridiron football), down. The sport has a ...
club play at Beveridge Park. The town has a range of leisure facilities such as a swimming pool, an ice rink, and two golf courses (Kirkcaldy and Dunnikier). In August 2019, Kirkcaldy held its first half marathon in nearly thirty years.
Fife Steel Basketball Club are Kirkcaldy's only BasketballScotland
basketballscotland is the governing body of the sport of basketball in Scotland. The organisation manages national competitions and runs the Scotland national basketball team. They also have a cup final for all age groups of the course of a w ...
affiliated basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular Basketball court, court, compete with the primary objective of #Shooting, shooting a basketball (ball), basketball (appr ...
club. Steel offer a number of age groups within the club and play in numerous National and Regional level competitions. Currently, the club are represented by 2 men's teams in theLothian Basketball League
A new £15 million leisure centre on the town's Esplanade opened its doors in September 2013. This has replaced the old Kirkcaldy Swimming Pool from the 1970s. The decision to build a new leisure centre on this site was controversial, as it resulted in the loss of a public car park. A petition organised by the campaign group Save The Car Park collected over 7,000 signatures in favour of keeping the car park open. The group said that the closure of the car park would discourage shoppers from coming to the High Street and raised issues over the loss of shopowners' right of access to the car park. This decision was severely criticised in an
internal audit
Internal auditing is an independent, objective assurance and consulting activity designed to add value and improve an organization's operations. It helps an organization accomplish its objectives by bringing a systematic, disciplined approach to ...
report.
Landmarks
 The oldest church in Kirkcaldy is the Old Kirk, the old parish church, on Kirk Wynd.Pearson 1993, p. 16. The earliest mention of the Old Kirk is the record of its consecration in 1244 to St Brisse and St Patrick by
The oldest church in Kirkcaldy is the Old Kirk, the old parish church, on Kirk Wynd.Pearson 1993, p. 16. The earliest mention of the Old Kirk is the record of its consecration in 1244 to St Brisse and St Patrick by David de Bernham
David de Bernham (died 1253) was Chamberlain of King Alexander II of Scotland and subsequently, Bishop of St Andrews. He was elected to the see in June 1239, and finally consecrated, after some difficulties, in January 1240. He died at Nenthorn ...
, Bishop of St Andrews
The Bishop of St. Andrews ( gd, Easbaig Chill Rìmhinn, sco, Beeshop o Saunt Andras) was the ecclesiastical head of the Diocese of St Andrews in the Catholic Church and then, from 14 August 1472, as Archbishop of St Andrews ( gd, Àrd-easbaig ...
. The building's deterioration in the late 18th century was addressed by major renovations to the main body of the church between 1807 and 1808.Torrie and Coleman 1995, p. 46.Glen 2007, p. 14. Only the square western tower, which dates from around 1500, was retained and is now the oldest building to have survived within the old burgh. In 2000 the Old Kirk was amalgamated with St Brycedale Church and was closed for public worship in 2008. It has since been re-opened by the Old Kirk Trust and is used for musical and dramatic performances. Other significant churches in the town include St Bryce Kirk built between 1877 and 1881 by James Matthews at the corner of St Brycedale Avenue and Kirk Wynd; Abbotshall Parish Church on Abbotshall Road, the current building completed in 1788 and Linktown Church built in 1830-1 by George Hay on Bethlefield Place.Glen 2007, p. 180.
Kirkcaldy Town House on Wemyssfield is the centrepiece of the town's main civic square.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2005, p. 114. The building was designed in the late 1930s by David Carr and William Howard of Edinburgh.Glen 2007, p. 261. With the advent of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, work was delayed on the building until 1950. Construction was split into two phases: the west wing, which was completed in 1953, and the east wing, completed in 1956.Fife Council 2000, p. 13.
Kirkcaldy War Memorial in War Memorial Gardens unveiled in 1925 was gifted to the town by John Nairn, linoleum manufacturer and grandson of Michael Nairn. This was dedicated to Ian Nairn, the son of John Nairn who died in the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
.Glen 2007, p. 244. A Second World War memorial, designed by Thomas Hubbard, was later added and unveiled in 1958. The memorial commemorates the lives of 1,012 people from the First World War and 452 from the Second World War.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2000, p. 9. Forming a centre piece to these gardens is Kirkcaldy Galleries, formerly known as Kirkcaldy Museum and Art Gallery, which was also donated by Nairn.
 In the north-east are two homes of early wealthy merchants and shipowners connected with Kirkcaldy's harbour.Torrie and Coleman 1995, p. 61. The Merchant's House or Law's Close at 339–343 High Street;Pride 1998, pp. 55–58. once owned by the Law family, is one of the best surviving examples of a 16th-century town house in Scotland.Glen 2007, p. 22. Sailors' Walk, at 443–449 High Street; consists of two 17th century houses, resting on foundations dating back to around 1460.National Trust for Scotland 1976, p. 104. These two houses were once divided into four dwellings; three of which were owned by the Oliphant family and the fourth by James Ferguson of Raith.Glen 2007, p. 47.
North of the harbour area, on The Path, are two examples of distinctive architectural styles. Hutchison's House was designed by George Spears, the owner of the nearby East Bridge distillery, in 1793.Torrie and Coleman 1995, pp. 63–64. Path House, originally known as Dunnikier House, is a three-storey L-plan tower house designed by John Watson in 1692 for his bride, Euphan Orrock.Glen 2007, p. 67. In 1703 Watson sold the house to the Oswald family, who had important links with the town.
In the north-east are two homes of early wealthy merchants and shipowners connected with Kirkcaldy's harbour.Torrie and Coleman 1995, p. 61. The Merchant's House or Law's Close at 339–343 High Street;Pride 1998, pp. 55–58. once owned by the Law family, is one of the best surviving examples of a 16th-century town house in Scotland.Glen 2007, p. 22. Sailors' Walk, at 443–449 High Street; consists of two 17th century houses, resting on foundations dating back to around 1460.National Trust for Scotland 1976, p. 104. These two houses were once divided into four dwellings; three of which were owned by the Oliphant family and the fourth by James Ferguson of Raith.Glen 2007, p. 47.
North of the harbour area, on The Path, are two examples of distinctive architectural styles. Hutchison's House was designed by George Spears, the owner of the nearby East Bridge distillery, in 1793.Torrie and Coleman 1995, pp. 63–64. Path House, originally known as Dunnikier House, is a three-storey L-plan tower house designed by John Watson in 1692 for his bride, Euphan Orrock.Glen 2007, p. 67. In 1703 Watson sold the house to the Oswald family, who had important links with the town.  Two large stately homes also exist within the town. To the north of Kirkcaldy is Dunnikier House, built in the late 18th century as a seat for the Oswald family, replacing their previous residence at Path House.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2005, pp. 13–14. To the south-west of Kirkcaldy is Raith House, built in the late 17th century by Sir Alexander Raith, 4th Earl of Raith and Melville, for his wife, Barbara Dundas.Pride 1998, p. 103. The house remains a private residence of the Munro-Ferguson family.
To the east of the town are the ruins of
Two large stately homes also exist within the town. To the north of Kirkcaldy is Dunnikier House, built in the late 18th century as a seat for the Oswald family, replacing their previous residence at Path House.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2005, pp. 13–14. To the south-west of Kirkcaldy is Raith House, built in the late 17th century by Sir Alexander Raith, 4th Earl of Raith and Melville, for his wife, Barbara Dundas.Pride 1998, p. 103. The house remains a private residence of the Munro-Ferguson family.
To the east of the town are the ruins of Ravenscraig Castle
Ravenscraig Castle is a ruined castle located in Kirkcaldy which dates from around 1460. The castle is an early example of artillery defence in Scotland.
History
The construction of Ravenscraig Castle by the mason Henry Merlion and the master ca ...
on a rocky spit of land extending into the Firth of Forth
The Firth of Forth () is the estuary, or firth, of several Scottish rivers including the River Forth. It meets the North Sea with Fife on the north coast and Lothian on the south.
Name
''Firth'' is a cognate of ''fjord'', a Norse word meani ...
.Omand 2000, p. 149. King James II began construction of the castle in 1460 for his queen, Mary of Guelders
Mary of Guelders (; c. 1434/1435 – 1 December 1463) was Queen of Scotland by marriage to King James II of Scotland. She ruled as regent of Scotland from 1460 to 1463.
Background
She was the daughter of Arnold, Duke of Guelders, and Cath ...
. It was also a means of defending the upper reaches of the Forth, including the port of Dysart. To a lesser extent it protected the harbour of Kirkcaldy against piracy and English rivalry. Ravenscraig is one of the earliest British castles designed to defend against and use artillery, an innovation demonstrated by the massive walls, the regularly placed shot holes, and the deep rock-cut ditch.Walker and Ritchie 1996, p. 117. Following the death of the King at the siege of Roxburgh Castle
Roxburgh Castle is a ruined royal castle that overlooks the junction of the rivers Tweed and Teviot, in the Borders region of Scotland. The town and castle developed into the royal burgh of Roxburgh, which the Scots destroyed along with the ca ...
(1460), work continued on Ravenscraig, and it became a home for Mary of Gueldres until her death in 1463.Glen 2007, p. 55. In 1470 King James III granted the castle and lands to William Sinclair, Earl of Orkney and Caithness, in exchange for the castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified r ...
in Kirkwall
Kirkwall ( sco, Kirkwaa, gd, Bàgh na h-Eaglaise, nrn, Kirkavå) is the largest town in Orkney, an archipelago to the north of mainland Scotland.
The name Kirkwall comes from the Norse name (''Church Bay''), which later changed to ''Kirkv ...
and the right to the Earldom of Orkney
The Earldom of Orkney is the official status of the Orkney, Orkney Islands. It was originally a Norsemen, Norse Feudalism, feudal dignity in Scotland which had its origins from the Viking period. In the ninth and tenth centuries it covered mor ...
.
Education
grammar school
A grammar school is one of several different types of school in the history of education in the United Kingdom and other English-speaking countries, originally a school teaching Latin, but more recently an academically oriented secondary school ...
, with the local minister, Dr David Spens, as principal. Until premises were found, pupils were taught in the minister's house.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2007, p. 41. Notable pupils include Robert Adam
Robert Adam (3 July 17283 March 1792) was a British neoclassical architect, interior designer and furniture designer. He was the son of William Adam (1689–1748), Scotland's foremost architect of the time, and trained under him. With his o ...
and Adam Smith.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2005, p. 21. The school was located at Hill Street before being rehoused in a new building on St Brycedale Avenue in 1843.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2007, p. 44. A Government list of 1872 described the school as being of 'higher class'. A new building for the school was given to the town in 1893 by Michael Barker Nairn, a linen manufacturer.Smith 1952, pp. 475–476. Other schools were established in the town, including girls schools, subscription schools, and apprentice
Apprenticeship is a system for training a new generation of practitioners of a trade or profession with on-the-job training and often some accompanying study (classroom work and reading). Apprenticeships can also enable practitioners to gain a ...
schools. The passing of the Education (Scotland) Act in 1872 replaced voluntary education in the town with a school-based education for all children aged 5 to 13.
Kirkcaldy has four secondary schools and eleven primary schools. Other educational facilities include a private school and a school for children with learning difficulties.Glen 2007, p. 116. Kirkcaldy High School
Kirkcaldy High School is a 6-year co-educational comprehensive state school in Kirkcaldy, Fife, Scotland.
History
The school was established in 1582 as Kirkcaldy Burgh School; the "High School" name dates from the middle part of the 19th&nb ...
, the oldest secondary school, serves pupils living in the north of the town and has occupied a site on Dunnikier Way since 1958.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2005, pp. 35–36. Balwearie High School
Balwearie High School is a non-denominational comprehensive secondary school at the west end of Kirkcaldy in Scotland. Balwearie serves around 1500 pupils aged from 11 to 18 and includes a Department of Additional Support (DAS for short) for ch ...
opened as a junior secondary school in 1964 and was upgraded to a high school in 1972. The school serves pupils living in the western end of the town and neighbouring Kinghorn
Kinghorn (; gd, Ceann Gronna) is a town and parish in Fife, Scotland. A seaside resort with two beaches, Kinghorn Beach and Pettycur Bay, plus a fishing port, it stands on the north shore of the Firth of Forth, opposite Edinburgh. According ...
and Burntisland
Burntisland ( , sco, also Bruntisland) is a former royal burgh and parish in Fife, Scotland, on the northern shore of the Firth of Forth. According to the 2011 census, the town has a population of 6,269. It was previously known as Wester Kingho ...
. Viewforth High School, which opened in 1908, was also initially a junior secondary school, but upgraded to a high school in 1980. Plans have been approved to build a new secondary school for Kirkcaldy East at the site of the Windmill Road Playing Fields. Work will be funded through the Building Fife's School Project for completion in August 2016. St Andrews RC High School, which opened in the late 1950s is one of two Roman Catholic secondary schools in Fife. This caters to pupils living in the eastern half of Fife, from St Andrews
St Andrews ( la, S. Andrea(s); sco, Saunt Aundraes; gd, Cill Rìmhinn) is a town on the east coast of Fife in Scotland, southeast of Dundee and northeast of Edinburgh. St Andrews had a recorded population of 16,800 , making it Fife's fou ...
to Burntisland and Lochgelly
Lochgelly ( ; gd, Loch Gheallaidh, IPA: �ɫ̪ɔxˈʝaɫ̪ai is a town in Fife, Scotland. It is located between Loch Ore, Lochs Ore and Gelly to the north-west and south-east respectively. It is separated from Cowdenbeath by the village of ...
.
Further education is provided by Fife College
Fife College is a further and higher education college in Fife, Scotland.
Campuses
The college's main campuses are located in Dunfermline, Glenrothes and Kirkcaldy with smaller campuses in Leven, and Rosyth. The college also operates commun ...
who have their main campus on St Brycedale Avenue.Fife College, "Think Fife College, Prospectus 2016–17", p. 46. The college was created in August 2013 from the merger of Adam Smith College, Fife and Carnegie College, Dunfermline. The University of Dundee
The University of Dundee; . Abbreviated as ''Dund.'' for post-nominals. is a public university, public research university based in Dundee, Scotland. It was founded as a University college#United Kingdom, university college in 1881 with a donation ...
also has a campus
A campus is traditionally the land on which a college or university and related institutional buildings are situated. Usually a college campus includes libraries, lecture halls, residence halls, student centers or dining halls, and park-like se ...
in the town which specialises as a School for Nursing
Nursing is a profession within the health care sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other health ...
and Midwifery
Midwifery is the health science and health profession that deals with pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period (including care of the newborn), in addition to the sexual and reproductive health of women throughout their lives. In many cou ...
. Originally built by the Fife Health Board for the use of the old Fife College of Further and Higher Education, this campus was taken over by the university in 1996.
Public services
Waste management is handled by thelocal authority
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of public administration within a particular sovereign state. This particular usage of the word government refers specifically to a level of administration that is both geographically-loca ...
, Fife Council. Kerbside recycling
Recycling is the process of converting waste materials into new materials and objects. The recovery of energy from waste materials is often included in this concept. The recyclability of a material depends on its ability to reacquire the p ...
operates in the town. A four-bin collection is in place for the majority of residents. Kirkcaldy has one recycling centre and several recycling points, all operated by Fife Council. Non-hazardous waste is sent to landfill at Lochhead near Dunfermline
Dunfermline (; sco, Dunfaurlin, gd, Dùn Phàrlain) is a city, parish and former Royal Burgh, in Fife, Scotland, on high ground from the northern shore of the Firth of Forth. The city currently has an estimated population of 58,508. Accord ...
, and Lower Melville Wood, near Ladybank
Ladybank () is a village and former burgh of Fife, Scotland. It is about north of Edinburgh, southwest of Cupar, close to the River Eden. Its 2006 population was estimated at 1,582.
History
Before the 18th century, this area was mostly marshl ...
.
Health care is supplied by NHS Fife, who have their main headquarters in the town at Hayfield House. The Victoria Hospital which is situated north of the town centre, is the town's acute
Acute may refer to:
Science and technology
* Acute angle
** Acute triangle
** Acute, a leaf shape in the glossary of leaf morphology
* Acute (medicine), a disease that it is of short duration and of recent onset.
** Acute toxicity, the adverse eff ...
general
A general officer is an Officer (armed forces), officer of highest military ranks, high rank in the army, armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers t ...
and maternity hospital
A maternity hospital specializes in caring for women during pregnancy and childbirth. It also provides care for newborn infants, and may act as a centre for clinical training in midwifery and obstetrics. Formerly known as lying-in hospitals, most o ...
. A new £152.5 million extension to the hospital was completed in February 2012. This new wing contains a maternity unit, children's department, 11 operating theatres and a new Accident and Emergency Department. Within the grounds of the hospital, a Maggie's Centre
Maggie's centres are a network of drop-in centres across the United Kingdom and Hong Kong, which aim to help anyone who has been affected by cancer. They are not intended as a replacement for conventional cancer therapy, but as a caring enviro ...
, under the name of Maggie's Fife, specialises in care for cancer patients. The centre, which was completed between 2004 and 2006, was the first building in the UK designed by Zaha Hadid
Dame Zaha Mohammad Hadid ( ar, زها حديد ''Zahā Ḥadīd''; 31 October 1950 – 31 March 2016) was an Iraqi-British architect, artist and designer, recognised as a major figure in architecture of the late 20th and early 21st centu ...
, the Iraqi-born architect.Glen 2007, p. 285. Whyteman's Brae Hospital
Whyteman's Brae Hospital is a health facility in Whyteman's Brae, Kirkcaldy, Scotland. It is managed by NHS Fife.
History
The facility, which provides psychiatry and services for elderly patients, was completed in 1983. A serious outbreak of ...
, which is also part of the complex, serves psychiatric and elderly patients.
Statutory emergency fire and rescue services are provided by the Scottish Fire and Rescue Service. The main fire station in the town is on Dunnikier Road. Policing in Kirkcaldy is operated by
Police Scotland
Police Scotland ( gd, Poileas Alba), officially the Police Service of Scotland (), is the national police force of Scotland. It was formed in 2013, through the merging of eight regional police forces in Scotland, as well as the specialist service ...
. The main police station in the town is on St Brycedale Avenue. Kirkcaldy is also served by the East Central Region of the Scottish Ambulance Service
The Scottish Ambulance Service ( gd, Seirbheis Ambaileans na h-Alba) is part of NHS Scotland, which serves all of Scotland's population. The Scottish Ambulance Service is governed by a special health board and is funded directly by the Health ...
, which covers Tayside
Tayside ( gd, Taobh Tatha) was one of the nine regions used for local government in Scotland from 15 May 1975 to 31 March 1996. The region was named for the River Tay.
It was created by the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973, following recom ...
, Forth Valley
The River Forth is a major river in central Scotland, long, which drains into the North Sea on the east coast of the country. Its drainage basin covers much of Stirlingshire in Scotland's Central Belt. The Gaelic name for the upper reach of t ...
, and Fife.
Media
There are two radio stations in the town,Victoria Radio Network
The Victoria Radio Network (VRN) is a hospital radio station based in Kirkcaldy, Scotland. It currently broadcasts 24 hours a day to the premises of the Victoria Hospital and surrounding facilities to patients' bedside radios and www.vrnkirk ...
a hospital radio station based in Victoria Hospital and K107, a community radio station.
Transport

Railway
Kirkcaldy railway station
Kirkcaldy railway station is a railway station in the town of Kirkcaldy, Fife, Scotland. The station is managed by ScotRail and is on the Fife Circle Line and principal East Coast Main Line, north east of . British Transport Police maintain a ...
is to the north-west of the town centre and is on the route for the Fife Circle Line
The Fife Circle Line is the local rail service north from Edinburgh. It links towns of south Fife and the coastal towns along the Firth of Forth before heading to Edinburgh. Operationally, the service is not strictly a circle route, but, rathe ...
and the East Coast Main Line
The East Coast Main Line (ECML) is a electrified railway between London and Edinburgh via Peterborough, Doncaster, York, Darlington, Durham and Newcastle. The line is a key transport artery on the eastern side of Great Britain running broa ...
.
Other services run to locations such as Aberdeen
Aberdeen (; sco, Aiberdeen ; gd, Obar Dheathain ; la, Aberdonia) is a city in North East Scotland, and is the third most populous city in the country. Aberdeen is one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas (as Aberdeen City), and ...
and Inverness
Inverness (; from the gd, Inbhir Nis , meaning "Mouth of the River Ness"; sco, Innerness) is a city in the Scottish Highlands. It is the administrative centre for The Highland Council and is regarded as the capital of the Highlands. Histori ...
to the north, and south as far as London King's Cross
King's Cross railway station, also known as London King's Cross, is a passenger railway terminus in the London Borough of Camden, on the edge of Central London. It is in the London station group, one of the busiest stations in the United King ...
and Penzance
Penzance ( ; kw, Pennsans) is a town, civil parish and port in the Penwith district of Cornwall, United Kingdom. It is the most westerly major town in Cornwall and is about west-southwest of Plymouth and west-southwest of London. Situated ...
.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2005, p. 110. Nearby stations such as Burntisland
Burntisland ( , sco, also Bruntisland) is a former royal burgh and parish in Fife, Scotland, on the northern shore of the Firth of Forth. According to the 2011 census, the town has a population of 6,269. It was previously known as Wester Kingho ...
and Kinghorn
Kinghorn (; gd, Ceann Gronna) is a town and parish in Fife, Scotland. A seaside resort with two beaches, Kinghorn Beach and Pettycur Bay, plus a fishing port, it stands on the north shore of the Firth of Forth, opposite Edinburgh. According ...
are to the south and west of the town.
Roads
The A92, which connects Dunfermline to the west withGlenrothes
Glenrothes (; , ; sco, Glenrothes; gd, Gleann Rathais) is a town situated in the heart of Fife, in east-central Scotland. It is about north of Edinburgh and south of Dundee. The town had a population of 39,277 in the 2011 census, making i ...
and Dundee to the north, passes immediately north of Kirkcaldy. The A910 road connects it to the western and central parts of the town. At Redhouse roundabout, the A921 connects the A92 to the eastern side of Kirkcaldy. It continues via St Clair Street and The Esplanade on to Kinghorn
Kinghorn (; gd, Ceann Gronna) is a town and parish in Fife, Scotland. A seaside resort with two beaches, Kinghorn Beach and Pettycur Bay, plus a fishing port, it stands on the north shore of the Firth of Forth, opposite Edinburgh. According ...
, Burntisland, and Aberdour
Aberdour (; Scots: , gd, Obar Dobhair) is a scenic and historic village on the south coast of Fife, Scotland. It is on the north shore of the Firth of Forth, looking south to the island of Inchcolm and its Abbey, and to Leith and Edinburgh beyo ...
to the south-west. The main route through the north of the town, the B981, runs roughly parallel to and one kilometre to the south of the A92. This road also connects to the A910 and the A921, from Chapel Junction via Chapel Level and Dunnikier Way to Gallatown.Nicolson Maps 2002, p. 7.Nicolson Maps 2002, p. 32. From here the A915, known locally as the ''Standing Stane Road'', connects the town to St Andrews and Leven Leven may refer to:
People
* Leven (name), list of people with the name
Nobility
* Earl of Leven a title in the Peerage of Scotland
Placenames
* Leven, Fife
Leven ( gd, Inbhir Lìobhann) is a seaside town in Fife, set in the east Central ...
to the north-east. The A955 runs along the coast from Dysart to East Wemyss
East Wemyss () is a village situated on the south coast of Fife, Scotland. According to the 2011 census, the village has a population of 1,928.
History
East Wemyss was traditionally one of several coal mining communities along the south coa ...
and Buckhaven to the north-east.Nicolson Maps 2002, pp. 35&52.Nicolson Maps 2002, pp. 37–39.
Buses
The main bus station, adjacent to the Postings Shopping Centre, is located between Hill Place and Hunter Street.Notable residents
economist
An economist is a professional and practitioner in the social science discipline of economics.
The individual may also study, develop, and apply theories and concepts from economics and write about economic policy. Within this field there are ...
Adam Smith,Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2005, p. 67. who wrote ''The Wealth of Nations
''An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations'', generally referred to by its shortened title ''The Wealth of Nations'', is the '' magnum opus'' of the Scottish economist and moral philosopher Adam Smith. First published in ...
'' at his mother's house at 220 High Street between 1765 and 1767.Torrie and Coleman 1995, p. 29. Architect and designer Robert Adam
Robert Adam (3 July 17283 March 1792) was a British neoclassical architect, interior designer and furniture designer. He was the son of William Adam (1689–1748), Scotland's foremost architect of the time, and trained under him. With his o ...
(and his father, William
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of Engl ...
) came from the town.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2005, p. 60. Sir Sandford Fleming, (1827–1915), engineer and inventor behind the development of worldwide standard time zones
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, to ...
and who worked on much of the Intercolonial Railway
The Intercolonial Railway of Canada , also referred to as the Intercolonial Railway (ICR), was a historic Canadian railway that operated from 1872 to 1918, when it became part of Canadian National Railways. As the railway was also completely ow ...
and the Canadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway (french: Chemin de fer Canadien Pacifique) , also known simply as CPR or Canadian Pacific and formerly as CP Rail (1968–1996), is a Canadian Class I railway incorporated in 1881. The railway is owned by Canadi ...
was born in the town before emigrating to Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2005, p. 62. Explorer John McDouall Stuart
John McDouall Stuart (7 September 18155 June 1866), often referred to as simply "McDouall Stuart", was a Scottish explorer and one of the most accomplished of all Australia's inland explorers.
Stuart led the first successful expedition to tra ...
, who led six expeditions into the centre and from the south to north of Australia, was born in nearby Dysart.Kirkcaldy Civic Society 2005, pp. 70–71.
Politicians who come from the town include Henry Balnaves
Henry Balnaves (1512? – February 1570) was a Scottish politician, Lord Justice Clerk, and religious reformer.
Biography
Born in Kirkcaldy, Fife, around 1512, he was educated at the University of St Andrews and on the continent, where he ado ...
(ca.1512–1570) a Scottish politician, Lord Justice Clerk
The Lord Justice Clerk is the second most senior judge in Scotland, after the Lord President of the Court of Session.
Originally ''clericus justiciarie'' or Clerk to the Court of Justiciary, the counterpart in the criminal courts of the Lord ...
and religious reformer; Ronald Munro Ferguson
Ronald Craufurd Munro Ferguson, 1st Viscount Novar, (6 March 1860 – 30 March 1934) was a British politician who served as the sixth Governor-General of Australia, in office from 1914 to 1920.
Munro Ferguson was born in Kirkcaldy, Fife, S ...
, the Governor-General of Australia
The governor-general of Australia is the representative of the monarch, currently King Charles III, in Australia.Glen 2007, p. 81.
David Steel
David Martin Scott Steel, Baron Steel of Aikwood, (born 31 March 1938) is a British politician. Elected as Member of Parliament for Roxburgh, Selkirk, and Peebles, followed by Tweeddale, Ettrick, and Lauderdale, he served as the final leade ...
, leader of the Liberal Party
The Liberal Party is any of many political parties around the world. The meaning of ''liberal'' varies around the world, ranging from liberal conservatism on the right to social liberalism on the left.
__TOC__ Active liberal parties
This is a li ...
from 1979 to 1988 and former Presiding Officer of the Scottish Parliament
sco, Preses o the Scots Pairlament
, body =
, member_of = Scottish Parliamentary Corporate BodyScottish Parliament
, insignia = Scottish_Parliament_logo_purple_vertical.png
, insigniasize = 150px
, insigniacaption = Logo used to represent ...
; and Bertha Wilson
Bertha Wernham Wilson (September 18, 1923April 28, 2007) was a Canadian jurist and the first female puisne justice of the Supreme Court of Canada. Before her ascension to Canada's highest court, she was the first female associate and partner at ...
, the first female judge of the Supreme Court of Canada
The Supreme Court of Canada (SCC; french: Cour suprême du Canada, CSC) is the Supreme court, highest court in the Court system of Canada, judicial system of Canada. It comprises List of Justices of the Supreme Court of Canada, nine justices, wh ...
and Court of Appeal for Ontario
The Court of Appeal for Ontario (frequently referred to as the Ontario Court of Appeal or ONCA) is the appellate court for the province of Ontario, Canada. The seat of the court is Osgoode Hall in downtown Toronto, also the seat of the Law Societ ...
. The former Chancellor of the Exchequer
The chancellor of the Exchequer, often abbreviated to chancellor, is a senior minister of the Crown within the Government of the United Kingdom, and head of His Majesty's Treasury. As one of the four Great Offices of State, the Chancellor is ...
, Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
and MP for the town's constituency until his retirement in 2015, Gordon Brown
James Gordon Brown (born 20 February 1951) is a British former politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom and Leader of the Labour Party (UK), Leader of the Labour Party from 2007 to 2010. He previously served as Chance ...
, was brought up in the town from the age of three.Allport, 2009, p. 18.
The mathematician Edward Sang
Edward Sang FRSE FRSSA LLD (30 January 1805 – 23 December 1890) was a Scottish mathematician and civil engineer, best known for having computed large tables of logarithms, with the help of two of his daughters. These tables went beyond the tab ...
was born in Kirkcaldy in 1805.
Patrick Don Swan FRSE
Fellowship of the Royal Society of Edinburgh (FRSE) is an award granted to individuals that the Royal Society of Edinburgh, Scotland's national academy of science and letters, judged to be "eminently distinguished in their subject". This soci ...
(1808–1889) founder of Swan Brothers shipbuilders. Son of William Swan, Provost of Kirkcaldy. Patrick served as Provost of Kirkcaldy for 37 years and was its most prominent person through most of the 19th century.
The Scottish crime writer
True crime is a nonfiction literary, podcast, and film genre in which the author examines an actual crime and details the actions of real people associated with and affected by criminal events.
The crimes most commonly include murder; about 40 per ...
Val McDermid
Valarie "Val" McDermid, (born 4 June 1955) is a Scottish crime writer, best known for a series of novels featuring clinical psychologist Dr. Tony Hill in a grim sub-genre that McDermid and others have identified as Tartan Noir.
Biography
M ...
was born in the town.
Guy Berryman
Guy Rupert Berryman (born 12 April 1978) is a Scottish musician, songwriter and producer, best known as the bassist of the rock band Coldplay and electronic supergroup Apparatjik. Raised in Kirkcaldy, he began to play bass from an early age, ...
, bassist of the alternative rock
Alternative rock, or alt-rock, is a category of rock music that emerged from the independent music underground of the 1970s and became widely popular in the 1990s. "Alternative" refers to the genre's distinction from Popular culture, mainstre ...
band Coldplay
Coldplay are a British rock band formed in London in 1997. They consist of vocalist and pianist Chris Martin, guitarist Jonny Buckland, bassist Guy Berryman, drummer Will Champion and creative director Phil Harvey. They met at University Col ...
, was born and brought up in the town until the age of thirteen.Roach 2010, p. 6.
Richard Park, the chief executive of Global Radio
Global Media & Entertainment Limited, trading as Global, is a British media company formed in 2007. It is the owner of the largest commercial radio company in Europe having expanded through a number of historical acquisitions, including Chrysa ...
and the headmaster on the BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board ex ...
talent show ''Fame Academy
''Fame Academy'' was a British television talent competition to search for and educate new musical talents. The winner received a chance to become a successful music artist and part of the international franchise ''Star Academy'' known under va ...
'' was born in the town, where he attended Kirkcaldy High School.
Sportsmen include the two-time world darts
Darts or dart-throwing is a competitive sport in which two or more players bare-handedly throw small projectile point, sharp-pointed projectile, missiles known as dart (missile), darts at a round shooting target, target known as a #Dartboard, dar ...
champion Jocky Wilson
John Thomas "Jocky" Wilson (22 March 1950 – 24 March 2012) was a Scottish professional darts player. After turning pro in 1979, he quickly rose to the top of the game, winning the World Professional Darts Championship in 1982, then again ...
, footballer
A football player or footballer is a sportsperson who plays one of the different types of football. The main types of football are association football, American football, Canadian football, Australian rules football, Gaelic football, rugby le ...
Colin Cameron, professional golfer
A professional golfer is somebody who receives payments or financial rewards in the sport of golf that are directly related to their skill or reputation. A person who earns money by teaching or playing golf is traditionally considered a "golf pr ...
Peter Whiteford
Peter William Whiteford (born 3 August 1980) is a Scottish professional golfer.
Whiteford was born in Kirkcaldy. He turned professional in 2002.
Whiteford won twice on PGA EuroPro Tour from 2002 to 2003 and has played on the Challenge and Euro ...
, professional ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice hock ...
player Adam Walker Adam Walker may refer to:
* Adam Walker (American football, born 1963), American football running back
* Adam Walker (American football, born 1968), American football running back
* Adam Walker (Australian politician) (1829–1902), Australian polit ...
and stock car driver Gordon Moodie. William Arnott (1827–1901), a biscuit manufacturer in Australia, also came from the town. David Potter, sports historian and author, was not born in Kirkcaldy but has lived there for over 40 years. David Danskin
David Danskin (9 January 1863 – 4 August 1948) was a Scottish mechanical engineer and footballer. He was a principal founding member of Dial Square F.C., later renamed Royal Arsenal, the team that are today known as Arsenal.
Born in Burntis ...
, who grew up in Kirkcaldy, was a principal founding member of Dial Square FC, later renamed Royal Arsenal, the team that are today known as Arsenal
An arsenal is a place where arms and ammunition are made, maintained and repaired, stored, or issued, in any combination, whether privately or publicly owned. Arsenal and armoury (British English) or armory (American English) are mostly ...
. Hibernian F.C.
Hibernian Football Club (), commonly known as Hibs, is a professional football club based in the Leith area of Edinburgh, Scotland. The club plays in the Scottish Premiership, the top tier of the Scottish Professional Football League (SPFL). ...
footballer Lewis Stevenson was born in Kirkcaldy. He is the only footballer in the club's history to have won both the Scottish League Cup
The Scottish League Cup (also known as the Viaplay Cup for sponsorship reasons) is a football competition open to all Scottish Professional Football League (SPFL) clubs. First held in 1946–47, it is the oldest national League Cup in existen ...
and Scottish Cup
The Scottish Football Association Challenge Cup,Frederick Coutts, the 8th
Kirkcaldy Civic Society
About Kirkcaldy
Kirkcaldy4all – Business Improvement District (BID)
Beveridge Park Website
{{authority control Large burghs Royal burghs Towns in Fife Mining communities in Fife Populated coastal places in Scotland
General
A general officer is an Officer (armed forces), officer of highest military ranks, high rank in the army, armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers t ...
, or international leader, of the Salvation Army
Salvation (from Latin: ''salvatio'', from ''salva'', 'safe, saved') is the state of being saved or protected from harm or a dire situation. In religion and theology, ''salvation'' generally refers to the deliverance of the soul from sin and its c ...
was born in Kirkcaldy.
The eminent zoologist, Prof David Raitt Robertson Burt
Prof David Raitt Robertson Burt BSc FRSE FLS FZS (1899-1983) was a Scottish zoologist with strong links to Ceylon. St Andrews University’s Burt Memorial Lecture is named after him. He is also credited with mounting the Bell Pettigrew Museum coll ...
FRSE
Fellowship of the Royal Society of Edinburgh (FRSE) is an award granted to individuals that the Royal Society of Edinburgh, Scotland's national academy of science and letters, judged to be "eminently distinguished in their subject". This soci ...
(1899–1983) was born and raised in Kirkcaldy, as was the botanist John Muirhead Macfarlane
John Muirhead Macfarlane FRSE LLD (28 September 1855, Kirkcaldy, Fife – 16 September 1943, Lancaster) was a Scottish botanist.
Life
He was born in Kirkcaldy in Fife on 28 September 1855. He was educated locally, then studied sciences at the ...
FRSE
Fellowship of the Royal Society of Edinburgh (FRSE) is an award granted to individuals that the Royal Society of Edinburgh, Scotland's national academy of science and letters, judged to be "eminently distinguished in their subject". This soci ...
(1855–1943).
The Very Rev John Drysdale, twice Moderator of the Church of Scotland
The Moderator of the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland is the minister or elder chosen to moderate (chair) the annual General Assembly of the Church of Scotland, which is held for a week in Edinburgh every year. After chairing the Asse ...
(1773 and 1784) was born and raised in Kirkcaldy.
Prof Carstairs Cumming Douglas FRSE
Fellowship of the Royal Society of Edinburgh (FRSE) is an award granted to individuals that the Royal Society of Edinburgh, Scotland's national academy of science and letters, judged to be "eminently distinguished in their subject". This soci ...
physician and hygienist was born in Kirkcaldy. He was largely the man responsible for introducing the obligatory use of Carbolic soap
Carbolic soap, sometimes referred to as red soap, is a mildly antiseptic soap containing carbolic acid (phenol) and/or cresylic acid (cresol), both of which are phenols derived from either coal tar or petroleum sources.
History
In 1834, German c ...
throughout Scottish schools in 1907.
Sir David Christie Martin FRS FRSE
Fellowship of the Royal Society of Edinburgh (FRSE) is an award granted to individuals that the Royal Society of Edinburgh, Scotland's national academy of science and letters, judged to be "eminently distinguished in their subject". This soci ...
FCS (1914–1976) born and raised in Kirkcaldy.
Dave Dryburgh
Dave Dryburgh (November 20, 1908July 11, 1948) was a Scotland-born Canadian sports journalist. A native of Kirkcaldy and an immigrant to Regina, he reported on the soccer games in which he played for ''The Leader-Post''. As the newspaper's spo ...
was born in Kirkcaldy in 1908. He later became a sports journalist and was inducted into the Canadian Football Hall of Fame
The Canadian Football Hall of Fame (CFHOF) is a not-for-profit corporation, located in Hamilton, Ontario, that celebrates great achievements in Canadian football. It is maintained by the Canadian Football League (CFL). It includes displays about t ...
.
Twin town
*Ingolstadt
Ingolstadt (, Austro-Bavarian: ) is an independent city on the Danube in Upper Bavaria with 139,553 inhabitants (as of June 30, 2022). Around half a million people live in the metropolitan area. Ingolstadt is the second largest city in Upper Bav ...
References
Notes
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Kirkcaldy Civic Society
About Kirkcaldy
Kirkcaldy4all – Business Improvement District (BID)
Beveridge Park Website
{{authority control Large burghs Royal burghs Towns in Fife Mining communities in Fife Populated coastal places in Scotland