Baltica (other) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Baltica is a
Baltica is a

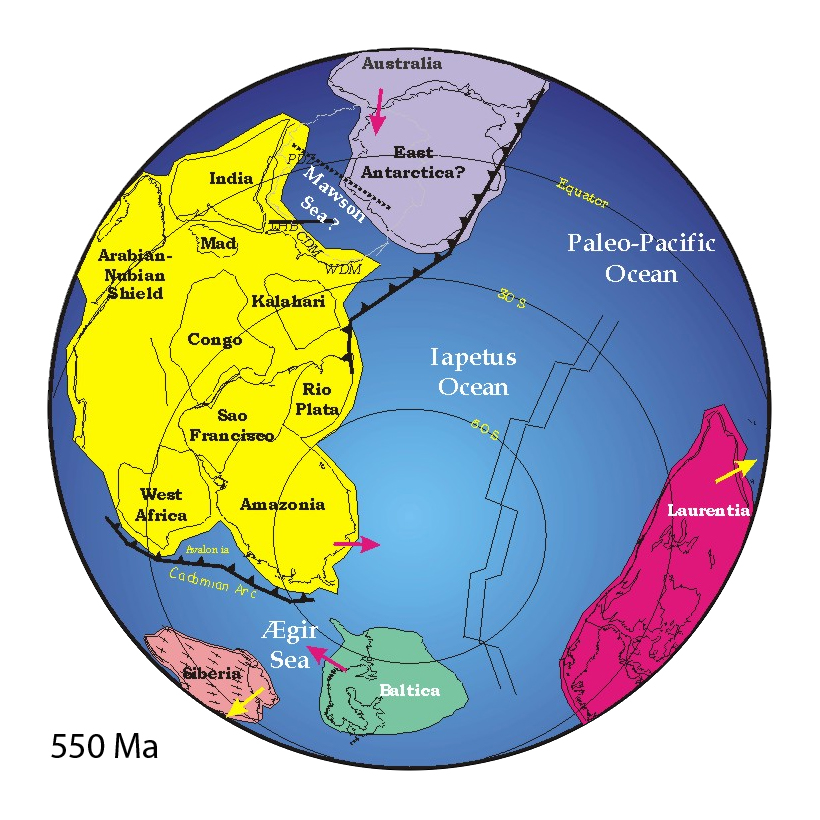 Baltica formed at 2.0–1.7 Ga by the collision of three Archaean- Proterozoic continental blocks: Fennoscandia (including the exposed Baltic Shield),
Baltica formed at 2.0–1.7 Ga by the collision of three Archaean- Proterozoic continental blocks: Fennoscandia (including the exposed Baltic Shield),
 Baltica is a
Baltica is a paleocontinent
A paleocontinent or palaeocontinent is a distinct area of continental crust that existed as a major landmass in the geological past. There have been many different landmasses throughout Earth's time. They range in sizes, some are just a collection ...
that formed in the Paleoproterozoic
The Paleoproterozoic Era (;, also spelled Palaeoproterozoic), spanning the time period from (2.5–1.6 Ga), is the first of the three sub-divisions ( eras) of the Proterozoic Eon. The Paleoproterozoic is also the longest era of the Earth's ...
and now constitutes northwestern Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago ...
, or Europe north of the Trans-European Suture Zone
The Trans-European Suture Zone (TESZ), also known as the Tornquist Zone, is the crustal boundary between the Precambrian East European Craton and the Phanerozoic orogens of South-Western Europe. The zone runs from the North Sea to the Black Sea. ...
and west of the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
.
The thick core of Baltica, the East European Craton
The East European Craton (EEC) is the core of the Baltica proto- plate and consists of three crustal regions/segments: Fennoscandia to the northwest, Volgo-Uralia to the east, and Sarmatia to the south. Fennoscandia includes the Baltic Shield ( ...
, is more than three billion years old and formed part of the Rodinia supercontinent at 1 .
Tectonic history

 Baltica formed at 2.0–1.7 Ga by the collision of three Archaean- Proterozoic continental blocks: Fennoscandia (including the exposed Baltic Shield),
Baltica formed at 2.0–1.7 Ga by the collision of three Archaean- Proterozoic continental blocks: Fennoscandia (including the exposed Baltic Shield), Sarmatia
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th c ...
(Ukrainian Shield
In geology the Ukrainian Shield (or Ukrainian Crystalline Massif) is the southwest shield of the East European craton. The Ukrainian Shield and the Voronezh Massif consist of 3.2-3.8 Ga Archaean crust in the southwest and east, and 2.3-2.1 Ga ...
and Voronezh Massif Voronezh Massif (also Voronezh Anteclise russian: Воронежская антеклиза, or Voronezh Uplift) is a tectonic anteclise in the south of the Central Russian Upland with a high occurrence of the Precambrian basement. It lies to th ...
), and Volgo-Uralia (covered by younger deposits). Sarmatia and Volgo-Uralia formed a proto-craton
A craton (, , or ; from grc-gre, κράτος "strength") is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, which consists of Earth's two topmost layers, the crust and the uppermost mantle. Having often survived cycles of merging an ...
(sometimes called "Proto-Baltica") at c. 2.0 Ga which collided with Fennoscandia c. 1.8–1.7 Ga. The sutures between these three blocks were reactivated during the Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic.
750–600 million years ago, Baltica and Laurentia
Laurentia or the North American Craton is a large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, althoug ...
rotated clockwise together and drifted away from the Equator towards the South Pole where they were affected by the Cryogenian Varanger glaciation
The Cryogenian (from grc, κρύος, krýos, meaning "cold" and , romanized: , meaning "birth") is a geologic period that lasted from . It forms the second geologic period of the Neoproterozoic Era, preceded by the Tonian Period and followed by ...
s. Initial rifting between the two continents is marked by the c. 650 Ma Egersund dike swarm in southern Norway and from 600 Ma they began to rotate up to 180° relative to each other, thus opening the Iapetus Ocean between the two landmasses. Laurentia quickly moved northward into low latitudes but Baltica remained an isolated continent in the temperate mid-latitudes of the Southern Hemisphere, closer to Gondwana, on which endemic trilobite
Trilobites (; meaning "three lobes") are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest-known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the ...
s evolved in the Early and Middle Ordovician.
During the Ordovician, Baltica moved northward, approaching Laurentia, which again allowed trilobites and brachiopods to cross the Iapetus Ocean. In the Silurian, c. 425 Ma, the final collision between Scotland-Greenland and Norway resulted in the closure of the Iapetus and the Scandian Orogeny.
Margins
Baltica is a very old continent and its core is a very well-preserved and thick craton. Its current margins, however, are the sutures that are the result of mergers with other, much younger continental blocks. These often deformed sutures do not represent the original, Precambrian–early Palaeozoic extent of Baltica; for example, the curved margin north of the Urals running parallel to Novaya Zemlya was probably deformed during the eruption of theSiberian Traps
The Siberian Traps (russian: Сибирские траппы, Sibirskiye trappy) is a large region of volcanic rock, known as a large igneous province, in Siberia, Russia. The massive eruptive event that formed the traps is one of the largest ...
in the Late Permian
Late may refer to:
* LATE, an acronym which could stand for:
** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia
** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law
** Local average treatment effect, ...
and Early Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a un ...
.
Baltica's western margin is the Caledonide orogen, which stretches northward from the Scandinavian Mountains across Barents Sea
The Barents Sea ( , also ; no, Barentshavet, ; russian: Баренцево море, Barentsevo More) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located off the northern coasts of Norway and Russia and divided between Norwegian and Russian territo ...
to Svalbard. Its eastern margin is the Timanide orogen
The Timanide Orogen (russian: Ороген Протоуралид-Тиманид, literally: "Protouralian–Timanide Orogen") is a Uralian orogeny, pre-Uralian orogen that formed in northeastern Baltica during the Neoproterozoic in the Timanide o ...
which stretches north to the Novaya Zemlya archipelago.
The extent of the Proterozoic continent are defined by the Iapetus Suture
The Iapetus Suture is one of several major Fault (geology), geological faults caused by the collision of several ancient land masses forming a suture (geology), suture. It represents in part the remains of what was once the Iapetus Ocean. Iapet ...
to the west; the Trollfjorden-Komagelva Fault Zone in the north; the Variscan-Hercynian suture to the south; the Tornquist Zone to the southwest; and the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
to the east.
Northern margin
At c. 555 Ma during the Timanian Orogeny the northern margin became an active margin and Baltica expanded northward with the accretion of a series of continental blocks: theTiman-Pechora Basin
The Timan-Pechora Basin is a sedimentary basin located between Timan Ridge and the Ural Mountains in northern Russia. The basin contains oil and gas fields.
Oil and gas extraction
A planned project to mine its oil and gas was conceived in the ...
, the northernmost Ural Mountains, and the Novaya Zemlya islands. This expansion coincided with the Marinoan or Varanger glaciation
The Cryogenian (from grc, κρύος, krýos, meaning "cold" and , romanized: , meaning "birth") is a geologic period that lasted from . It forms the second geologic period of the Neoproterozoic Era, preceded by the Tonian Period and followed by ...
s, also known as Snowball Earth.
Terrane
In geology, a terrane (; in full, a tectonostratigraphic terrane) is a crust (geology), crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate (or broken off from it) and Accretion (geology), accreted or "Suture (geology), sutured" to crust lying on another pla ...
s of the North American Cordillera, including Alaska-Chukotka, Alexander, Northern Sierra, and Eastern Klamath, share a rift history with Baltica and most likely were part of Baltica from the Caledonian orogeny until the formation of the Ural Mountains.
These terranes can be linked to either northeastern Laurentia, Baltica, or Siberia because of a similar sequence of fossils; detrital
Detritus (; adj. ''detrital'' ) is particles of rock derived from pre-existing rock through weathering and erosion.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Ed, Stephen Marshak, p G-7 A fragment of detritus is called a clast.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Ed, Stephe ...
zircon from 2–1 Ga-old sources and evidence of Grenvillian magmatism; and magmatism and island arc
Island arcs are long chains of active volcanoes with intense seismic activity found along convergent tectonic plate boundaries. Most island arcs originate on oceanic crust and have resulted from the descent of the lithosphere into the mantle alon ...
s from the Late Neoproterozoic and Ordovician-Silurian.
Southern margin
From at least 1.8 Ga to at least 0.8 Ga the southwestern margin of Baltica was connected toAmazonia
The Amazon rainforest, Amazon jungle or ; es, Selva amazónica, , or usually ; french: Forêt amazonienne; nl, Amazoneregenwoud. In English, the names are sometimes capitalized further, as Amazon Rainforest, Amazon Forest, or Amazon Jungle. ...
while the southeast margin was connected to the West African Craton
The West African Craton (WAC) is one of the five cratons of the Precambrian basement rock of Africa that make up the African Plate, the others being the Kalahari craton, Congo craton, Saharan Metacraton and Tanzania Craton.Jessell M.W., Liégeo ...
.
Baltica, Amazonia, and West Africa rotated 75° clockwise relative to Laurentia until Baltica and Amazonia collided with Laurentia in the 1.1–0.9 Ga Grenville- Sveconorwegian- Sunsás orogenies to form the supercontinent Rodinia. When the break-up of Rodinia was complete c. 0.6 Ga Baltica became an isolated continent — a 200 million year period when Baltica was truly a separate continent.
Laurentia and Baltica formed a single continent until 1.265 Ga which broke up some time before 0.99 Ga. After the subsequent closure of the Mirovoi Ocean Laurentia, Baltica and Amazonia remained merged until the opening of the Iapetus Ocean in the Neoproterozoic.
Western margin
TheWestern Gneiss Region
The Western Gneiss Region ( no, Gneisregionen) is a large geological unit in Norway chiefly made of gneiss rock that formed through metamorphism during the Caledonian orogeny. It makes up a tectono-stratigraphic terrane of the Scandinavian Caledon ...
in western Norway is composed of 1650–950 Ma-old gneiss
Gneiss ( ) is a common and widely distributed type of metamorphic rock. It is formed by high-temperature and high-pressure metamorphic processes acting on formations composed of igneous or sedimentary rocks. Gneiss forms at higher temperatures a ...
es overlain by continental
Continental may refer to:
Places
* Continent, the major landmasses of Earth
* Continental, Arizona, a small community in Pima County, Arizona, US
* Continental, Ohio, a small town in Putnam County, US
Arts and entertainment
* ''Continental'' ( ...
and oceanic
Oceanic may refer to:
*Of or relating to the ocean
*Of or relating to Oceania
**Oceanic climate
**Oceanic languages
**Oceanic person or people, also called "Pacific Islander(s)"
Places
* Oceanic, British Columbia, a settlement on Smith Island, ...
allochthon
upright=1.6, Schematic overview of a thrust system. The hanging wall block is (when it has reasonable proportions) called a nappe. If an erosional hole is created in the nappe that is called a window (geology)">window. A klippe is a solitary out ...
s that were transferred from Laurentia to Baltica during the Scandian orogeny. The allochthons were accreted to Baltica during the closure of the Iapetus Ocean c. 430–410 Ma; Baltica's basement and the allochthons were then subducted to UHP depth c. 425–400 Ma; and they were finally exhumed to their present location c. 400–385 Ma. The presence of micro-diamonds in two islands in western Norway, Otrøya
Otrøya (sometimes called ''Otterøya'' or ''Otrøy'') is the largest island in Molde Municipality in Møre og Romsdal county, Norway. The island sits at the entrance to Romsdalsfjord, west of the island of Midøya and east of the mainland R ...
and Flemsøya
Flemsøya or Skuløya is an island in Ålesund Municipality in Møre og Romsdal county, Norway. The island is located between the islands of Haramsøya and Fjørtofta. The island is connected to the neighboring island of Haramsøya by the Ullasu ...
, indicate that this margin of Baltica was buried c. for at least 25 million years around 429 Ma shortly after the Baltica-Laurentia collision.
The Baltica-Laurentia-Avalonia triple junction in the North Sea is the southwest corner of Baltica. The Baltica-Laurentia suture stretching northeast from the triple junction was deformed in the Late Cambrian in the Scandinavian Caledonides as well as in the Scandian Orogeny during the Silurian. Some Norwegian terranes have faunas distinct from those of either Baltica or Laurentia as a result of being island arcs that originated in the Iapetus Ocean and were later accreted to Baltica. The Baltica craton most likely underlies these terranes and the continent-ocean boundary The continent-ocean boundary (COB) or continent-ocean transition is the boundary between continental crust and oceanic crust on a passive margin. The identification of continent-ocean boundaries is important in the definition of plate boundaries at ...
passes several kilometres off Norway, but, since the North Atlantic opened c. 54 Ma where the Iapetus Ocean closed, it is unlikely the craton also reached into Laurentia. The margin stretches north to Novaya Zemlya where early Palaeozoic Baltica faunas have been found, but the sparsity of data makes it difficult to locate the margin in the Arctic. Ordovician faunas indicate that most of Svalbard, including Bjørnøya, was part of Laurentia, but Franz Josef Land
Franz Josef Land, Frantz Iosef Land, Franz Joseph Land or Francis Joseph's Land ( rus, Земля́ Фра́нца-Ио́сифа, r=Zemlya Frantsa-Iosifa, no, Fridtjof Nansen Land) is a Russian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. It is inhabited on ...
and Kvitøya
Kvitøya (English: "White Island") is an island in the Svalbard archipelago in the Arctic Ocean, with an area of . It is the easternmost part of the Kingdom of Norway. The closest Russian Arctic possession, Victoria Island, lies only to the e ...
(an eastern island of the Svalbard archipelago) most likely became part of Baltica in the Timanide Orogeny. The Taymyr Peninsula
The Taymyr Peninsula (russian: Таймырский полуостров, Taymyrsky poluostrov) is a peninsula in the Far North of Russia, in the Siberian Federal District, that forms the northernmost part of the mainland of Eurasia. Administrat ...
, in contrast, never was part of Baltica: southern Taymyr was part of Siberia whilst northern Taymyr and the Severnaya Zemlya
Severnaya Zemlya (russian: link=no, Сéверная Земля́ (Northern Land), ) is a archipelago in the Russian high Arctic. It lies off Siberia's Taymyr Peninsula, separated from the mainland by the Vilkitsky Strait. This archipelago ...
archipelago were part of the independent Kara Terrane in the early Palaeozoic.
Eastern margin
The eastern margin, the Uralide orogen, extends from the Arctic Novaya Zemlya archipelago to the Aral Sea. The orogen contains the record of at least two collisions between Baltica and intra-oceanic island arcs before the final collision between Baltica andKazakhstania
Kazakhstania ( kk, Qazaqstaniya), the Kazakh terranes, or the Kazakhstan Block, is a geological region in Central Asia which consists of the area roughly centered on Lake Balkhash, north and east of the Aral Sea, south of the Siberian craton and ...
-Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive region, geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a ...
during the formation of Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million y ...
. The Silurian-Devonian island arcs were accreted to Baltica along the Main Uralian Fault, east of which are metamorphosed fragments of volcanic arc mixed with small amounts of Precambrian and Paleozoic continental rocks. However, no rocks unambiguously originating from either Kazakhstania or Siberia have been found in the Urals.
The basement of the eastern margin is composed of an Archaean craton, metamorphosed rocks at least 1.6 Ga old, which is surrounded by the fold belt of the Timanide orogeny and overlain by Mesoproterozoic sediments. The margin became a passive margin
A passive margin is the transition between oceanic and continental lithosphere that is not an active plate margin. A passive margin forms by sedimentation above an ancient rift, now marked by transitional lithosphere. Continental rifting cre ...
facing the Ural Ocean in the Cambrian–Ordovician.
The eastern margin stretches south through the Ural Mountains from the northern end of the Novaya Zemlya archipelago. The margin follows the bent shape of Novaya Zemlya which was caused in the Late Permian by the Siberian Traps
The Siberian Traps (russian: Сибирские траппы, Sibirskiye trappy) is a large region of volcanic rock, known as a large igneous province, in Siberia, Russia. The massive eruptive event that formed the traps is one of the largest ...
. It is clear from Baltic endemic fossils in Novaya Zemlya that the islands have been part of Baltica since the Early Palaeozoic, whereas the Taymyr Peninsula farther east was part of the passive margin of Siberia in the Early Palaeozoic. Northern Taymyr, together with Severnaya Zemlya and parts of the crust of the Arctic Ocean, formed the Kara Terrane.
The Urals Mountains formed in the mid and late Palaeozoic when Laurussia
Laurasia () was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from around ( Mya), the other being Gondwana. It separated from Gondwana (beginning in the late Triassic period) during the breakup of Pan ...
collided with Kazakhstania
Kazakhstania ( kk, Qazaqstaniya), the Kazakh terranes, or the Kazakhstan Block, is a geological region in Central Asia which consists of the area roughly centered on Lake Balkhash, north and east of the Aral Sea, south of the Siberian craton and ...
, a series of terranes. The eastern margin, however, originally extended farther east to an active margin bordered by island arc
Island arcs are long chains of active volcanoes with intense seismic activity found along convergent tectonic plate boundaries. Most island arcs originate on oceanic crust and have resulted from the descent of the lithosphere into the mantle alon ...
s, but those parts have been compressed, fractured, and distorted especially in the eastern Urals. The early Palaeozoic eastern margin is better preserved south of the polar region (65 °N) where shallow-water sediments can be found in the western Urals whilst the eastern Urals are characterised by deep-water deposits. The oldest known mid-ocean hydrothermal vent in the south-central part of the Urals clearly delimits the eastern extent. The straightness of the mountain chain is the result of continuous strike-slip movements during the Late Carboniferous to Early Permian (300–290 Ma).
Baltic endemic faunas from the Early Ordovician have been found in Kazakhstan near the southern end of the eastern margin, or the triple junction between Baltica, the Mangyshlak Terrane, and the accretionary Altaids. Here the Early Palaeozoic rocks are buried under the Caspian Depression
The Caspian Depression ( kk, Каспий маңы ойпаты, ''Kaspıı mańy oıpaty''; rus, Прикаспи́йская ни́зменность, p=prʲɪkɐˈspʲijskəjə ˈnʲizmʲɪnnəsʲtʲ, Caspian Lowland) or Pricaspian/Peri-Casp ...
.
See also
*References
Notes
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{Authority control Historical continents Plate tectonics Proterozoic Paleozoic Natural history of Europe