|
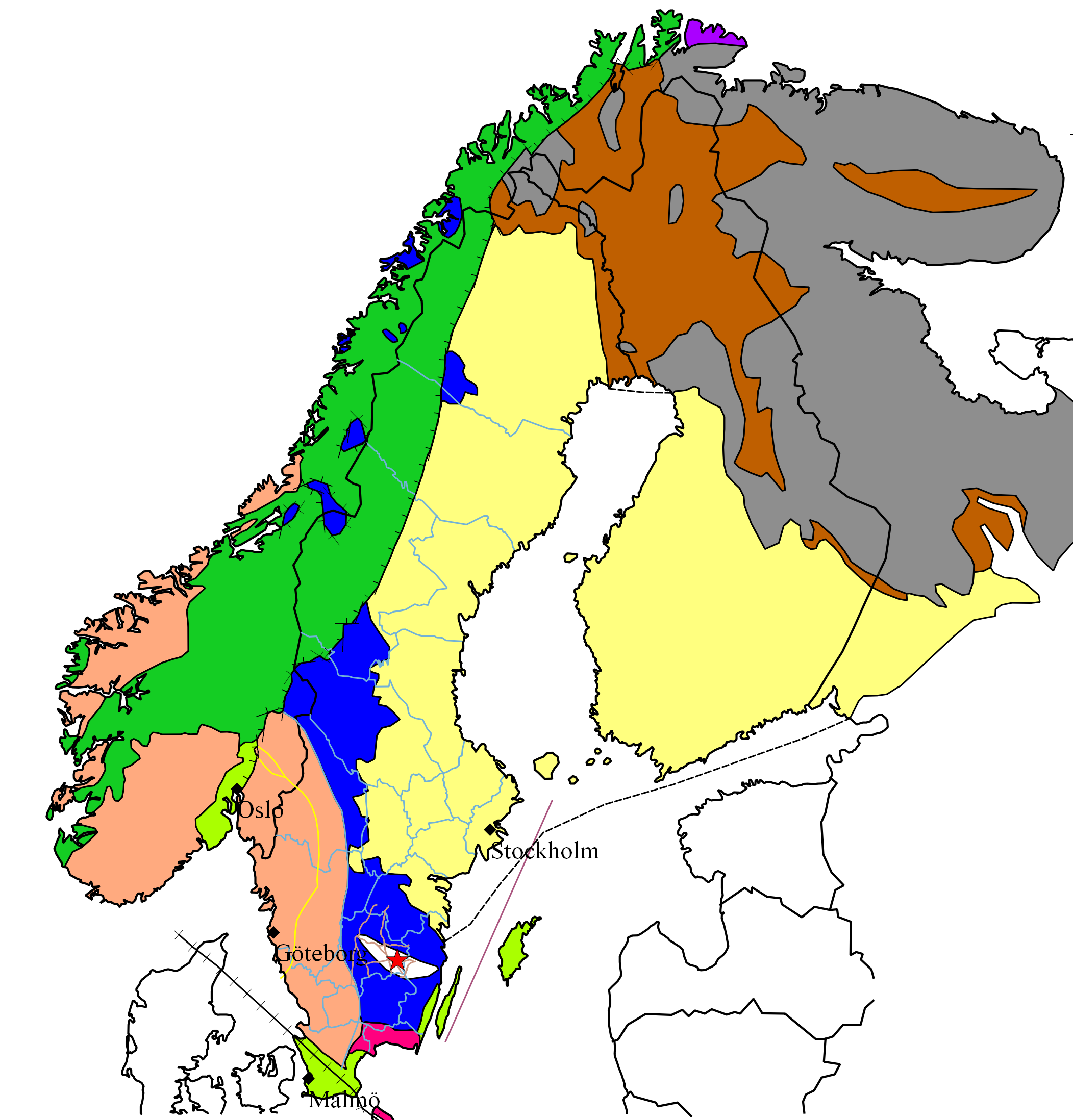
Western Gneiss Region
The Western Gneiss Region ( no, Gneisregionen) is a large geological unit in Norway chiefly made of gneiss rock that formed through metamorphism during the Caledonian orogeny. It makes up a tectono-stratigraphic terrane of the Scandinavian Caledonides and is also part of the Baltic shield. The region extends across western Norway from Bergen to Trondheim as a Caledonian window, outliers of the Western Gneiss Region crop out as far north as the Lofoten archipelago. The rocks of the Western Gneiss Region are made up of variously deformed Precambrian basement, and cover rocks of autochthonous and para-autochthonous origin with evidence of medium to high grade metamorphism including ultra-high-pressure metamorphism. Rocks of the Western Gneiss Region formed 1700 to 1600 million years ago in the Late Paleoproterozoic. What was to become the Western Gneiss Region was intruded by migmatites and granite Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock compos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Store Norske Leksikon
The ''Great Norwegian Encyclopedia'' ( no, Store Norske Leksikon, abbreviated ''SNL''), is a Norwegian-language online encyclopedia. The online encyclopedia is among the most-read Norwegian published sites, with more than two million unique visitors per month. Paper editions 1978–2007 The ''SNL'' was created in 1978, when the two publishing houses Aschehoug and Gyldendal merged their encyclopedias and created the company Kunnskapsforlaget. Up until 1978 the two publishing houses of Aschehoug and Gyldendal, Norway's two largest, had published ' and ', respectively. The respective first editions were published in 1907–1913 (Aschehoug) and 1933–1934 (Gyldendal). The slump in sales for paper-based encyclopedias around the turn of the 21st century hit Kunnskapsforlaget hard, but a fourth edition of the paper encyclopedia was secured by a grant of ten million Norwegian kroner from the foundation Fritt Ord in 2003. The fourth edition consisted of 16 volumes, a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precambrian
The Precambrian (or Pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pꞒ, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of the Phanerozoic Eon, which is named after Cambria, the Latinised name for Wales, where rocks from this age were first studied. The Precambrian accounts for 88% of the Earth's geologic time. The Precambrian is an informal unit of geologic time, subdivided into three eons ( Hadean, Archean, Proterozoic) of the geologic time scale. It spans from the formation of Earth about 4.6 billion years ago ( Ga) to the beginning of the Cambrian Period, about million years ago ( Ma), when hard-shelled creatures first appeared in abundance. Overview Relatively little is known about the Precambrian, despite it making up roughly seven-eighths of the Earth's history, and what is known has largely been discovered from the 1960s onwards. The Precambrian fos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sveconorwegian Orogeny
The Sveconorwegian orogeny was an orogenic system active 1140 to 960 million years ago and currently exposed as the Sveconorwegian orogenic belt in southwestern Sweden and southern Norway. In Norway the orogenic belt is exposed southeast of the front of the Caledonian nappe system and in nappe windows. The Sveconorwegian orogen is commonly grouped within the Grenvillian Mesoproterozoic orogens. Contrary to many other known orogenic belts the Sveconorwegian orogens eastern border does not have any known suture zone with ophiolites. Tectonic segments The Sveconorwegian orogen orogenic belt is composed of five segments largely made up of gneiss that were disrupted by both extension and compression in the timespan between 1140 and 980 million years ago. From west to east the segments are the terranes of Telemarkia, Bamble, Kongsberg and Idefjorden plus the Eastern Segment. The segments are separated from each other by large-scale shear zones. *Bamble Terrane: The Bamble Terrane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies underground. It is common in the continental crust of Earth, where it is found in igneous intrusions. These range in size from dikes only a few centimeters across to batholiths exposed over hundreds of square kilometers. Granite is typical of a larger family of ''granitic rocks'', or '' granitoids'', that are composed mostly of coarse-grained quartz and feldspars in varying proportions. These rocks are classified by the relative percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase (the QAPF classification), with true granite representing granitic rocks rich in quartz and alkali feldspar. Most granitic rocks also contain mica or amphibole minerals, though a few (known as leucogranites) contain almost no dark minerals. Granite is near ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Migmatites
Migmatite is a composite rock found in medium and high-grade metamorphic environments, commonly within Precambrian cratonic blocks. It consists of two or more constituents often layered repetitively: one layer is an older metamorphic rock that was reconstituted subsequently by partial melting ("paleosome"), while the alternate layer has a pegmatitic, aplitic, granitic or generally plutonic appearance ("neosome"). Commonly, migmatites occur below deformed metamorphic rocks that represent the base of eroded mountain chains. Migmatites form under extreme temperature and pressure conditions during prograde metamorphism, when partial melting occurs in metamorphic paleosome. Components exsolved by partial melting are called neosome (meaning ‘new body’), which may or may not be heterogeneous at the microscopic to macroscopic scale. Migmatites often appear as tightly, incoherently folded veins ( ptygmatic folds).Recommendations by the IUGS Subcommission on the Systematics o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleoproterozoic
The Paleoproterozoic Era (;, also spelled Palaeoproterozoic), spanning the time period from (2.5–1.6 Ga), is the first of the three sub-divisions ( eras) of the Proterozoic Eon. The Paleoproterozoic is also the longest era of the Earth's geological history. It was during this era that the continents first stabilized. Paleontological evidence suggests that the Earth's rotational rate ~1.8 billion years ago equated to 20-hour days, implying a total of ~450 days per year. Atmosphere Before the enormous increase in atmospheric oxygen, almost all existing lifeforms were anaerobic organisms whose metabolism was based on a form of cellular respiration that did not require oxygen. Free oxygen in large amounts is toxic to most anaerobic organisms. Consequently, most died when the atmospheric free oxygen levels soared in an extinction event called the Great Oxidation Event, which brought atmospheric oxygen levels to up to 10% of their current level. The only creatures that sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultra-high-pressure Metamorphism
Ultra-high-pressure metamorphism refers to metamorphic processes at pressures high enough to stabilize coesite, the high-pressure polymorph of SiO2. It is important because the processes that form and exhume ultra-high-pressure (UHP) metamorphic rocks may strongly affect plate tectonics, the composition and evolution of Earth's crust. The discovery of UHP metamorphic rocks in 1984 revolutionized our understanding of plate tectonics. Prior to 1984 there was little suspicion that continental rocks could reach such high pressures. The formation of many UHP terrains has been attributed to the subduction of microcontinents or continental margins and the exhumation of all UHP terrains has been ascribed principally to buoyancy caused by the low density of continental crust—even at UHP—relative to Earth's mantle. While the subduction proceeds at low thermal gradients of less than 10°C/km, the exhumation proceeds at elevated thermal gradients of 10-30°C/km. Definition Metamorphism of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphic Grade
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of chemically active fluids, but the rock remains mostly solid during the transformation. Metamorphism is distinct from weathering or diagenesis, which are changes that take place at or just beneath Earth's surface. Various forms of metamorphism exist, including regional, contact, hydrothermal, shock, and dynamic metamorphism. These differ in the characteristic temperatures, pressures, and rate at which they take place and in the extent to which reactive fluids are involved. Metamorphism occurring at increasing pressure and temperature conditions is known as ''prograde metamorphism'', while decreasing temperature and pressure characterize ''retrograde metamorphism''. Metamorphic petrology is the study of metamorphism. Metamorphic petrologists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autochthon (geology)
An autochthon in structural geology is a large block or mass of rock which is in the place of its original formation relative to its basement or foundation rock. It can be described as rooted to its basement rock as opposed to an allochthonous block or nappe which has been relocated from its site of formation. image:thrust system en.jpg, upright=1.6, Schematic overview of a thrust system. The hanging wall block is (when it has reasonable proportions) called a nappe In geology, a nappe or thrust sheet is a large sheetlike body of rock that has been moved more than or above a thrust fault from its original position. Nappes form in compressional tectonic settings like continental collision zones or on the ... which overlays the autochthonous (unrelocated) material. A hole in the nappe which exposes the underlying autochthonous material is called a window. A klippe is a solitary outcrop of the nappe in the middle of autochthonous material. While an autochthon may have experi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basement (geology)
In geology, basement and crystalline basement are crystalline rocks lying above the mantle and beneath all other rocks and sediments. They are sometimes exposed at the surface, but often they are buried under miles of rock and sediment. The basement rocks lie below a sedimentary platform or cover, or more generally any rock below sedimentary rocks or sedimentary basins that are metamorphic or igneous in origin. In the same way, the sediments or sedimentary rocks on top of the basement can be called a "cover" or "sedimentary cover". Crustal rocks are modified several times before they become basement, and these transitions alter their composition. Continental crust Basement rock is the thick foundation of ancient, and oldest, metamorphic and igneous rock that forms the crust of continents, often in the form of granite. Basement rock is contrasted to overlying sedimentary rocks which are laid down on top of the basement rocks after the continent was formed, such as sandstone and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lofoten
Lofoten () is an archipelago and a traditional district in the county of Nordland, Norway. Lofoten has distinctive scenery with dramatic mountains and peaks, open sea and sheltered bays, beaches and untouched lands. There are two towns, Svolvær and Leknes – the latter is approximately north of the Arctic Circle and approximately away from the North Pole. The archipelago experiences one of the world's largest elevated temperature anomalies relative to its high latitude. Etymology ''Lofoten'' ( non, Lófótr) was the original name of the island Vestvågøya. The first element is ''ló'' (i.e., " lynx") and the last element is derived from Norse ''fótr'' (i.e., "foot"), as the shape of the island must have been compared with that of a lynx's foot. (The old name of the neighbouring island Flakstadøya was ''Vargfót'', " wolf's foot", from ''vargr'' "wolf".) Alternatively it could derive from the word for light in reference to the presence of Aurora Borealis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Unit
A stratigraphic unit is a volume of rock of identifiable origin and relative age range that is defined by the distinctive and dominant, easily mapped and recognizable petrographic, lithologic or paleontologic features (facies) that characterize it. Units must be ''mappable'' and ''distinct'' from one another, but the contact need not be particularly distinct. For instance, a unit may be defined by terms such as "when the sandstone component exceeds 75%". Lithostratigraphic units Sequences of sedimentary and volcanic rocks are subdivided the basis of their shared or associated lithology. Formally identified lithostratigraphic units are structured in a hierarchy of lithostratigraphic rank, higher rank units generally comprising two or more units of lower rank. Going from smaller to larger in rank, the main lithostratigraphic ranks are Bed, Member, Formation, Group and Supergroup. Formal names of lithostratigraphic units are assigned by geological surveys. Units of formation or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |