Bahamas Ministry Of Transport on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the
. CIA World Factbook.
 Columbus's first landfall in what was to Europeans a "New World" was on an island he named San Salvador (known to the Lucayans as '' Guanahani''). Whilst there is a general consensus that this island lay within the Bahamas, precisely which island Columbus landed on is a matter of scholarly debate. Some researchers believe the site to be present-day San Salvador Island (formerly known as Watling's Island), situated in the southeastern Bahamas, whilst an alternative theory holds that Columbus landed to the southeast on Samana Cay, according to calculations made in 1986 by ''
Columbus's first landfall in what was to Europeans a "New World" was on an island he named San Salvador (known to the Lucayans as '' Guanahani''). Whilst there is a general consensus that this island lay within the Bahamas, precisely which island Columbus landed on is a matter of scholarly debate. Some researchers believe the site to be present-day San Salvador Island (formerly known as Watling's Island), situated in the southeastern Bahamas, whilst an alternative theory holds that Columbus landed to the southeast on Samana Cay, according to calculations made in 1986 by ''

 During proprietary rule, the Bahamas became a haven for
During proprietary rule, the Bahamas became a haven for
''Network to Freedom'', National Park Service, 2010, accessed 10 April 2013 Some of their descendants in Red Bays continue African Seminole traditions in basket making and grave marking. In 1818, the Home Office in London had ruled that "any slave brought to the Bahamas from outside the British West Indies would be manumitted." This led to a total of nearly 300 enslaved people owned by US nationals being freed from 1830 to 1835. Horne, p. 103 The American slave ships ''Comet'' and ''Encomium'' used in the United States domestic
1837, The section, "Brigs Encomium and Enterprise", has a collection of lengthy correspondence between US (including M. Van Buren), Vail, the US chargé d'affaires in London, and British agents, including Lord Palmerston, sent to the Senate on 13 February 1837, by President Andrew Jackson, as part of the continuing process of seeking compensation. Slavery was abolished in the British Empire on 1 August 1834. After that British colonial officials freed 78 North American slaves from the '' Enterprise'', which went into Bermuda in 1835; and 38 from the ''Hermosa'', which wrecked off Abaco Island in 1840. The most notable case was that of the '' Creole'' in 1841: as a result of a slave revolt on board, the leaders ordered the US brig to Nassau. It was carrying 135 slaves from Virginia destined for sale in New Orleans. The Bahamian officials freed the 128 slaves who chose to stay in the islands. The ''Creole'' case has been described as the "most successful slave revolt in U.S. history".
These incidents, in which a total of 447 enslaved people belonging to US nationals were freed from 1830 to 1842, increased tension between the United States and the United Kingdom. They had been co-operating in patrols to suppress the international slave trade. However, worried about the stability of its large domestic slave trade and its value, the United States argued that the United Kingdom should not treat its domestic ships that came to its colonial ports under duress as part of the international trade. The United States worried that the success of the ''Creole'' slaves in gaining freedom would encourage more slave revolts on merchant ships.
During the American Civil War of the 1860s, the islands briefly prospered as a focus for
Slavery was abolished in the British Empire on 1 August 1834. After that British colonial officials freed 78 North American slaves from the '' Enterprise'', which went into Bermuda in 1835; and 38 from the ''Hermosa'', which wrecked off Abaco Island in 1840. The most notable case was that of the '' Creole'' in 1841: as a result of a slave revolt on board, the leaders ordered the US brig to Nassau. It was carrying 135 slaves from Virginia destined for sale in New Orleans. The Bahamian officials freed the 128 slaves who chose to stay in the islands. The ''Creole'' case has been described as the "most successful slave revolt in U.S. history".
These incidents, in which a total of 447 enslaved people belonging to US nationals were freed from 1830 to 1842, increased tension between the United States and the United Kingdom. They had been co-operating in patrols to suppress the international slave trade. However, worried about the stability of its large domestic slave trade and its value, the United States argued that the United Kingdom should not treat its domestic ships that came to its colonial ports under duress as part of the international trade. The United States worried that the success of the ''Creole'' slaves in gaining freedom would encourage more slave revolts on merchant ships.
During the American Civil War of the 1860s, the islands briefly prospered as a focus for
 In August 1940, the Duke of Windsor (erstwhile King Edward VIII) was appointed Governor of the Bahamas. He arrived in the colony with his wife. Although disheartened at the condition of Government House, they "tried to make the best of a bad situation". Higham, pp. 300–302 He did not enjoy the position, and referred to the islands as "a third-class British colony". He opened the small local parliament on 29 October 1940. The couple visited the "Out Islands" that November, on Axel Wenner-Gren's yacht, which caused controversy; Higham, pp. 307–309 the British Foreign Office strenuously objected because they had been advised by United States intelligence that Wenner-Gren was a close friend of the Luftwaffe commander Hermann Göring of Nazi Germany.
The Duke was praised at the time for his efforts to combat poverty on the islands. A 1991 biography by Philip Ziegler, however, described him as contemptuous of the Bahamians and other non-European peoples of the Empire. He was praised for his resolution of civil unrest over low wages in
In August 1940, the Duke of Windsor (erstwhile King Edward VIII) was appointed Governor of the Bahamas. He arrived in the colony with his wife. Although disheartened at the condition of Government House, they "tried to make the best of a bad situation". Higham, pp. 300–302 He did not enjoy the position, and referred to the islands as "a third-class British colony". He opened the small local parliament on 29 October 1940. The couple visited the "Out Islands" that November, on Axel Wenner-Gren's yacht, which caused controversy; Higham, pp. 307–309 the British Foreign Office strenuously objected because they had been advised by United States intelligence that Wenner-Gren was a close friend of the Luftwaffe commander Hermann Göring of Nazi Germany.
The Duke was praised at the time for his efforts to combat poverty on the islands. A 1991 biography by Philip Ziegler, however, described him as contemptuous of the Bahamians and other non-European peoples of the Empire. He was praised for his resolution of civil unrest over low wages in
"Edward VIII, later Prince Edward, Duke of Windsor (1894–1972)"
, ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, , retrieved 1 May 2010 (Subscription required) Higham, p. 359 places the date of his resignation as 15 March, and that he left on 5 April.
 Modern political development began after the Second World War. The first political parties were formed in the 1950s, split broadly along ethnic lines, with the United Bahamian Party (UBP) representing the English-descended Bahamians (known informally as the "Bay Street Boys") and the Progressive Liberal Party (PLP) representing the Black-Bahamian majority.
A new constitution granting the Bahamas internal autonomy went into effect on 7 January 1964, with Chief Minister
Modern political development began after the Second World War. The first political parties were formed in the 1950s, split broadly along ethnic lines, with the United Bahamian Party (UBP) representing the English-descended Bahamians (known informally as the "Bay Street Boys") and the Progressive Liberal Party (PLP) representing the Black-Bahamian majority.
A new constitution granting the Bahamas internal autonomy went into effect on 7 January 1964, with Chief Minister
 In 1992, Pindling was unseated by Hubert Ingraham of the FNM. Ingraham went on to win the
In 1992, Pindling was unseated by Hubert Ingraham of the FNM. Ingraham went on to win the
 The landmass that makes up what is the modern-day Bahamas, lies at the northern part of the Greater Antilles region and was believed to have been formed 200 million years ago when they began to separate from the supercontinent Pangaea. The Pleistocene Ice Age around 3 million years ago, had a profound impact on the archipelago's formation.
The Bahamas consists of a chain of islands spread out over some in the Atlantic Ocean, located to the east of Florida in the United States, north of Cuba and
The landmass that makes up what is the modern-day Bahamas, lies at the northern part of the Greater Antilles region and was believed to have been formed 200 million years ago when they began to separate from the supercontinent Pangaea. The Pleistocene Ice Age around 3 million years ago, had a profound impact on the archipelago's formation.
The Bahamas consists of a chain of islands spread out over some in the Atlantic Ocean, located to the east of Florida in the United States, north of Cuba and
 According to the Köppen climate classification, the climate of The Bahamas is mostly tropical savannah climate or ''Aw'', with a hot and wet season and a warm and dry season. The low latitude, warm tropical
According to the Köppen climate classification, the climate of The Bahamas is mostly tropical savannah climate or ''Aw'', with a hot and wet season and a warm and dry season. The low latitude, warm tropical

 It was generally believed that the Bahamas were formed in approximately 200 million years ago, when Pangaea started to break apart. In current times, it endures as an archipelago containing over 700 islands and cays, fringed around different coral reefs. The limestone that comprises the Banks has been accumulating since at least the Cretaceous period, and perhaps as early as the Jurassic; today the total thickness under the Great Bahama Bank is over 4.5 kilometres (2.8 miles). As the limestone was deposited in shallow water, the only way to explain this massive column is to estimate that the entire platform has subsided under its own weight at a rate of roughly 3.6 centimetres (2 inches) per 1,000 years.
The Bahamas is part of the Lucayan Archipelago, which continues into the Turks and Caicos Islands, the
It was generally believed that the Bahamas were formed in approximately 200 million years ago, when Pangaea started to break apart. In current times, it endures as an archipelago containing over 700 islands and cays, fringed around different coral reefs. The limestone that comprises the Banks has been accumulating since at least the Cretaceous period, and perhaps as early as the Jurassic; today the total thickness under the Great Bahama Bank is over 4.5 kilometres (2.8 miles). As the limestone was deposited in shallow water, the only way to explain this massive column is to estimate that the entire platform has subsided under its own weight at a rate of roughly 3.6 centimetres (2 inches) per 1,000 years.
The Bahamas is part of the Lucayan Archipelago, which continues into the Turks and Caicos Islands, the
 The Bahamas is a parliamentary constitutional monarchy, with King of the Bahamas Charles III as head of state represented locally by a
The Bahamas is a parliamentary constitutional monarchy, with King of the Bahamas Charles III as head of state represented locally by a
 The Bahamas has a two-party system dominated by the centre-left Progressive Liberal Party and the centre-right Free National Movement. A handful of other political parties have been unable to win election to parliament; these have included the
The Bahamas has a two-party system dominated by the centre-left Progressive Liberal Party and the centre-right Free National Movement. A handful of other political parties have been unable to win election to parliament; these have included the
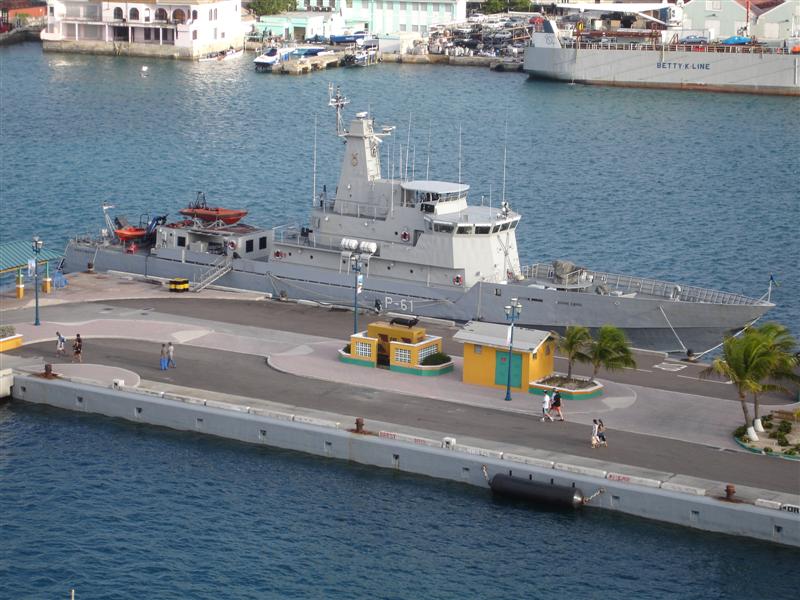 The Bahamian military is the Royal Bahamas Defence Force (RBDF), the navy of The Bahamas which includes a land unit called Commando Squadron (Regiment) and an Air Wing (Air Force). Under the Defence Act, the RBDF has been mandated, in the name of the King, to defend The Bahamas, protect its territorial integrity, patrol its waters, provide assistance and relief in times of disaster, maintain order in conjunction with the law enforcement agencies of The Bahamas, and carry out any such duties as determined by the National Security Council. The Defence Force is also a member of the Caribbean Community ( CARICOM)'s Regional Security Task Force.
The RBDF came into existence on 31 March 1980. Its duties include defending The Bahamas, stopping drug smuggling, illegal immigration and poaching, and providing assistance to mariners. The Defence Force has a fleet of 26 coastal and inshore patrol craft along with 3 aircraft and over 1,100 personnel including 65 officers and 74 women.
The Bahamian military is the Royal Bahamas Defence Force (RBDF), the navy of The Bahamas which includes a land unit called Commando Squadron (Regiment) and an Air Wing (Air Force). Under the Defence Act, the RBDF has been mandated, in the name of the King, to defend The Bahamas, protect its territorial integrity, patrol its waters, provide assistance and relief in times of disaster, maintain order in conjunction with the law enforcement agencies of The Bahamas, and carry out any such duties as determined by the National Security Council. The Defence Force is also a member of the Caribbean Community ( CARICOM)'s Regional Security Task Force.
The RBDF came into existence on 31 March 1980. Its duties include defending The Bahamas, stopping drug smuggling, illegal immigration and poaching, and providing assistance to mariners. The Defence Force has a fleet of 26 coastal and inshore patrol craft along with 3 aircraft and over 1,100 personnel including 65 officers and 74 women.
 In terms of
In terms of
 The Bahamas contains about of paved roads. Inter-island transport is conducted primarily via ship and air. The country has 61 airports, the chief of which are
The Bahamas contains about of paved roads. Inter-island transport is conducted primarily via ship and air. The country has 61 airports, the chief of which are
 The Bahamas had a population of at the 2018 Census, of which 25.9% were 14 or under, 67.2% 15 to 64 and 6.9% over 65. It has a population growth rate of 0.925% (2010), with a birth rate of 17.81/1,000 population, death rate of 9.35/1,000, and net migration rate of −2.13 migrant(s)/1,000 population. The
The Bahamas had a population of at the 2018 Census, of which 25.9% were 14 or under, 67.2% 15 to 64 and 6.9% over 65. It has a population growth rate of 0.925% (2010), with a birth rate of 17.81/1,000 population, death rate of 9.35/1,000, and net migration rate of −2.13 migrant(s)/1,000 population. The
 Since the colonial era of plantations,
Since the colonial era of plantations,
 The culture of the islands is a mixture of African (Afro-Bahamians being the largest ethnicity), British and
The culture of the islands is a mixture of African (Afro-Bahamians being the largest ethnicity), British and
 The Bahamian flag was adopted in 1973. Its colours symbolise the strength of the Bahamian people; its design reflects aspects of the natural environment (sun and sea) and economic and social development. The flag is a black equilateral triangle against the mast, superimposed on a horizontal background made up of three equal stripes of aquamarine, gold and aquamarine.
The Bahamian flag was adopted in 1973. Its colours symbolise the strength of the Bahamian people; its design reflects aspects of the natural environment (sun and sea) and economic and social development. The flag is a black equilateral triangle against the mast, superimposed on a horizontal background made up of three equal stripes of aquamarine, gold and aquamarine.
 The coat of arms of The Bahamas contains a shield with the national symbols as its focal point. The shield is supported by a marlin and a flamingo, which are the national animals of The Bahamas. The flamingo is located on the land, and the marlin on the sea, indicating the geography of the islands.
On top of the shield is a conch shell, which represents the varied marine life of the island chain. The conch shell rests on a helmet. Below this is the actual shield, the main symbol of which is a ship representing the '' Santa María'' of Christopher Columbus, shown sailing beneath the sun. Along the bottom, below the shield appears a banner upon which is the national motto:
The coat of arms of The Bahamas contains a shield with the national symbols as its focal point. The shield is supported by a marlin and a flamingo, which are the national animals of The Bahamas. The flamingo is located on the land, and the marlin on the sea, indicating the geography of the islands.
On top of the shield is a conch shell, which represents the varied marine life of the island chain. The conch shell rests on a helmet. Below this is the actual shield, the main symbol of which is a ship representing the '' Santa María'' of Christopher Columbus, shown sailing beneath the sun. Along the bottom, below the shield appears a banner upon which is the national motto:
 Sport is a significant part of Bahamian culture. The national sport is
Sport is a significant part of Bahamian culture. The national sport is
The Bahamas
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' *
The Bahamas
from the BBC News
Key Development Forecasts for The Bahamas
from
Maps of the Bahamas from the American Geographical Society Library''The Nassau Guardian''
newspaper, 1849–1922, as
North Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe and ...
. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the archipelago's population. The archipelagic state
An archipelagic state is an island country that consists of an archipelago. The designation is legally defined by the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS). In various conferences, The Bahamas, Fiji, Indonesia, Papua New Guine ...
consists of more than 3,000 islands, cays, and islets in the Atlantic Ocean, and is located north of Cuba and northwest of the island of Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ; es, La Española; Latin and french: Hispaniola; ht, Ispayola; tnq, Ayiti or Quisqueya) is an island in the Caribbean that is part of the Greater Antilles. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and th ...
(split between the Dominican Republic and Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
) and the Turks and Caicos Islands, southeast of the U.S. state of Florida, and east of the Florida Keys
The Florida Keys are a coral cay archipelago located off the southern coast of Florida, forming the southernmost part of the continental United States. They begin at the southeastern coast of the Florida peninsula, about south of Miami, and e ...
. The capital is Nassau
Nassau may refer to:
Places Bahamas
*Nassau, Bahamas, capital city of the Bahamas, on the island of New Providence
Canada
*Nassau District, renamed Home District, regional division in Upper Canada from 1788 to 1792
*Nassau Street (Winnipeg), ...
on the island of New Providence
New Providence is the most populous island in the Bahamas, containing more than 70% of the total population. It is the location of the national capital city of Nassau, whose boundaries are coincident with the island; it had a population of 246 ...
. The Royal Bahamas Defence Force describes The Bahamas' territory as encompassing of ocean space.
The Bahama Islands were inhabited by the Lucayans, a branch of the Arawakan
Arawakan (''Arahuacan, Maipuran Arawakan, "mainstream" Arawakan, Arawakan proper''), also known as Maipurean (also ''Maipuran, Maipureano, Maipúre''), is a language family that developed among ancient indigenous peoples in South America. Branch ...
-speaking
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words (that is, all English words sound different from all French words, even if they are th ...
Taíno, for many centuries. Christopher Columbus was the first European to see the islands, making his first landfall in the " New World" in 1492 when he landed on the island of San Salvador. Later, the Spanish shipped the native Lucayans to and enslaved them on Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ; es, La Española; Latin and french: Hispaniola; ht, Ispayola; tnq, Ayiti or Quisqueya) is an island in the Caribbean that is part of the Greater Antilles. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and th ...
, after which the Bahama islands were mostly deserted from 1513 until 1648 due to nearly all native Bahamians being forcefully removed through enslavement or dying due to diseases brought to the islands by the Europeans. In 1649, English colonists from Bermuda, known as the Eleutheran Adventurers, settled on the island of Eleuthera.
The Bahamas became a British crown colony
A Crown colony or royal colony was a colony administered by The Crown within the British Empire. There was usually a Governor, appointed by the British monarch on the advice of the UK Government, with or without the assistance of a local Counci ...
in 1718, when the British clamped down on piracy. After the American Revolutionary War, the Crown resettled thousands of American Loyalists to the Bahamas; they took enslaved people with them and established plantations on land grants. Enslaved Africans and their descendants constituted the majority of the population from this period on. The slave trade was abolished by the British in 1807; slavery in the Bahamas
Slavery in the Bahamas dates back several centuries.
19th century Golden Grove uprising
In December 1831, a slave riot occurred on the estate of Joseph Hunter, who had the largest slave holdings on Golden Grove. Although the Consolidated Slave Ac ...
was abolished in 1834. Subsequently, The Bahamas became a haven for freed African slaves. Africans liberated from illegal slave ships were resettled on the islands by the Royal Navy, while some North American slaves and Seminoles escaped to The Bahamas from Florida. Bahamians were even known to recognise the freedom of enslaved people carried by the ships of other nations which reached The Bahamas. Today Black-Bahamians make up 90% of the population of 400,516.
The country gained governmental independence in 1973, led by Sir Lynden O. Pindling. Charles III is currently its monarch. In terms of gross domestic product per capita, The Bahamas is one of the richest independent countries in the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
(following the United States and Canada), with an economy based on tourism and offshore finance.Country Comparison :: GDP – per capita (PPP). CIA World Factbook.
Naming and etymology
The name ''Bahamas'' is derived from the Lucayan name ' ('large upper middle island'), used by the indigenous Taíno people for the island ofGrand Bahama
Grand Bahama is the northernmost of the islands of the Bahamas, with the town of West End located east of Palm Beach, Florida. It is the third largest island in the Bahamas island chain of approximately 700 islands and 2,400 cays. The island is ...
. Tourist guides often state that the name comes from the Spanish ' ('shallow sea'). Wolfgang Ahrens of York University argues that this is a folk etymology
Folk etymology (also known as popular etymology, analogical reformation, reanalysis, morphological reanalysis or etymological reinterpretation) is a change in a word or phrase resulting from the replacement of an unfamiliar form by a more famili ...
. Alternatively, it may originate from ', a local name of unclear meaning.
First attested on the 1523 Turin Map
Turin ( , Piedmontese language, Piedmontese: ; it, Torino ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in Northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital ...
, ''Bahama'' originally referred to Grand Bahama alone but was used inclusively in English by 1670. Toponymist Isaac Taylor
Isaac Taylor (17 August 1787 – 28 June 1865) was an English philosophical and historical writer, artist, and inventor.
Life
He was the eldest surviving son of Isaac Taylor of Ongar. He was born at Lavenham, Suffolk, on 17 August 1787, and m ...
argues that the name was derived from ''Bimani'' ( Bimini), which Spaniards in Haiti identified with Palombe
Kollam (), also known by its former name Quilon , is an ancient seaport and city on the Malabar Coast of India bordering the Laccadive Sea, which is a part of the Arabian Sea. It is north of the state capital Thiruvananthapuram. The city i ...
, a legendary place where John Mandeville's ''Travels'' said there was a fountain of youth.
History
Pre-colonial era
The first inhabitants of the Bahamas were the Taino people, who moved into the uninhabited southern islands fromHispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ; es, La Española; Latin and french: Hispaniola; ht, Ispayola; tnq, Ayiti or Quisqueya) is an island in the Caribbean that is part of the Greater Antilles. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and th ...
and Cuba around the 800s–1000s AD, having migrated there from South America; they came to be known as the Lucayan people. An estimated 30,000 Lucayans inhabited the Bahamas at the time of Christopher Columbus's arrival in 1492.
Arrival of the Spanish
 Columbus's first landfall in what was to Europeans a "New World" was on an island he named San Salvador (known to the Lucayans as '' Guanahani''). Whilst there is a general consensus that this island lay within the Bahamas, precisely which island Columbus landed on is a matter of scholarly debate. Some researchers believe the site to be present-day San Salvador Island (formerly known as Watling's Island), situated in the southeastern Bahamas, whilst an alternative theory holds that Columbus landed to the southeast on Samana Cay, according to calculations made in 1986 by ''
Columbus's first landfall in what was to Europeans a "New World" was on an island he named San Salvador (known to the Lucayans as '' Guanahani''). Whilst there is a general consensus that this island lay within the Bahamas, precisely which island Columbus landed on is a matter of scholarly debate. Some researchers believe the site to be present-day San Salvador Island (formerly known as Watling's Island), situated in the southeastern Bahamas, whilst an alternative theory holds that Columbus landed to the southeast on Samana Cay, according to calculations made in 1986 by ''National Geographic
''National Geographic'' (formerly the ''National Geographic Magazine'', sometimes branded as NAT GEO) is a popular American monthly magazine published by National Geographic Partners. Known for its photojournalism, it is one of the most widely ...
'' writer and editor Joseph Judge, based on Columbus's log. On the landfall island, Columbus made first contact with the Lucayans and exchanged goods with them, claiming the islands for the Crown of Castile
The Crown of Castile was a medieval polity in the Iberian Peninsula that formed in 1230 as a result of the third and definitive union of the crowns and, some decades later, the parliaments of the kingdoms of Castile and León upon the accessi ...
, before proceeding to explore the larger isles of the Greater Antilles.
The 1494 Treaty of Tordesillas
The Treaty of Tordesillas, ; pt, Tratado de Tordesilhas . signed in Tordesillas, Spain on 7 June 1494, and authenticated in Setúbal, Portugal, divided the newly discovered lands outside Europe between the Portuguese Empire and the Spanish Emp ...
theoretically divided the new territories between the Kingdom of Castile and the Kingdom of Portugal
The Kingdom of Portugal ( la, Regnum Portugalliae, pt, Reino de Portugal) was a monarchy in the western Iberian Peninsula and the predecessor of the modern Portuguese Republic. Existing to various extents between 1139 and 1910, it was also kno ...
, placing the Bahamas in the Spanish sphere; however they did little to press their claim on the ground. The Spanish did however exploit the native Lucayan peoples, many of whom were enslaved and sent to Hispaniola for use as forced labour. The slaves suffered harsh conditions and most died from contracting diseases
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that ar ...
to which they had no immunity
Immunity may refer to:
Medicine
* Immunity (medical), resistance of an organism to infection or disease
* ''Immunity'' (journal), a scientific journal published by Cell Press
Biology
* Immune system
Engineering
* Radiofrequence immunity desc ...
; half of the Taino died from smallpox alone. As a result of these depredations the population of the Bahamas was severely diminished.
Arrival of the English
The English had expressed an interest in the Bahamas as early as 1629. However, it was not until 1648 that the first English settlers arrived on the islands. Known as the Eleutherian Adventurers and led by William Sayle, they migrated from Bermuda seeking greater religious freedom. These English Puritans established the first permanent European settlement on an island which they named Eleuthera, Greek for ''free''. They later settledNew Providence
New Providence is the most populous island in the Bahamas, containing more than 70% of the total population. It is the location of the national capital city of Nassau, whose boundaries are coincident with the island; it had a population of 246 ...
, naming it Sayle's Island. Life proved harder than envisaged however, and many – including Sayle – chose to return to Bermuda. To survive, the remaining settlers salvaged goods from wrecks.
In 1670, King Charles II granted the islands to the Lords Proprietors of the Carolinas
The Carolinas are the U.S. states of North Carolina and South Carolina, considered collectively. They are bordered by Virginia to the north, Tennessee to the west, and Georgia to the southwest. The Atlantic Ocean is to the east.
Combining Nort ...
in North America. They rented the islands from the king with rights of trading, tax, appointing governors, and administering the country from their base on New Providence. Piracy and attacks from hostile foreign powers were a constant threat. In 1684, Spanish corsair
A corsair is a privateer or pirate, especially:
* Barbary corsair, Ottoman and Berber pirates and privateers operating from North Africa
* French corsairs, privateers operating on behalf of the French crown
Corsair may also refer to:
Arts and ...
Juan de Alcon raided the capital Charles Town (later renamed Nassau
Nassau may refer to:
Places Bahamas
*Nassau, Bahamas, capital city of the Bahamas, on the island of New Providence
Canada
*Nassau District, renamed Home District, regional division in Upper Canada from 1788 to 1792
*Nassau Street (Winnipeg), ...
),Mancke/Shammas
Shammas is a surname and given name. Notable people with the name include:
Surname
*Anton Shammas (born 1950), Palestinian writer and poet
*Carole Shammas (born 1943), American historian, academic, and author
*Hazem Shammas
Hazem Shammas is a ...
p. 255 and in 1703, a joint Franco-Spanish expedition briefly occupied Nassau during the War of the Spanish Succession.Marley (2005), p. 7.Marley (1998), p. 226.
18th century

 During proprietary rule, the Bahamas became a haven for
During proprietary rule, the Bahamas became a haven for pirates
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, v ...
, including Blackbeard (''circa'' 1680–1718). To put an end to the " Pirates' republic" and restore orderly government, Britain made the Bahamas a crown colony
A Crown colony or royal colony was a colony administered by The Crown within the British Empire. There was usually a Governor, appointed by the British monarch on the advice of the UK Government, with or without the assistance of a local Counci ...
in 1718, which they dubbed "the Bahama islands" under the governorship of Woodes Rogers. After a difficult struggle, he succeeded in suppressing piracy. In 1720, the Spanish attacked Nassau during the War of the Quadruple Alliance. In 1729, a local assembly was established giving a degree of self-governance for British settlers.Dwight C. Hart (2004) ''The Bahamian parliament, 1729–2004: Commemorating the 275th anniversary'' Jones Publications, p4 The reforms had been planned by the previous Governor George Phenney and authorised in July 1728.
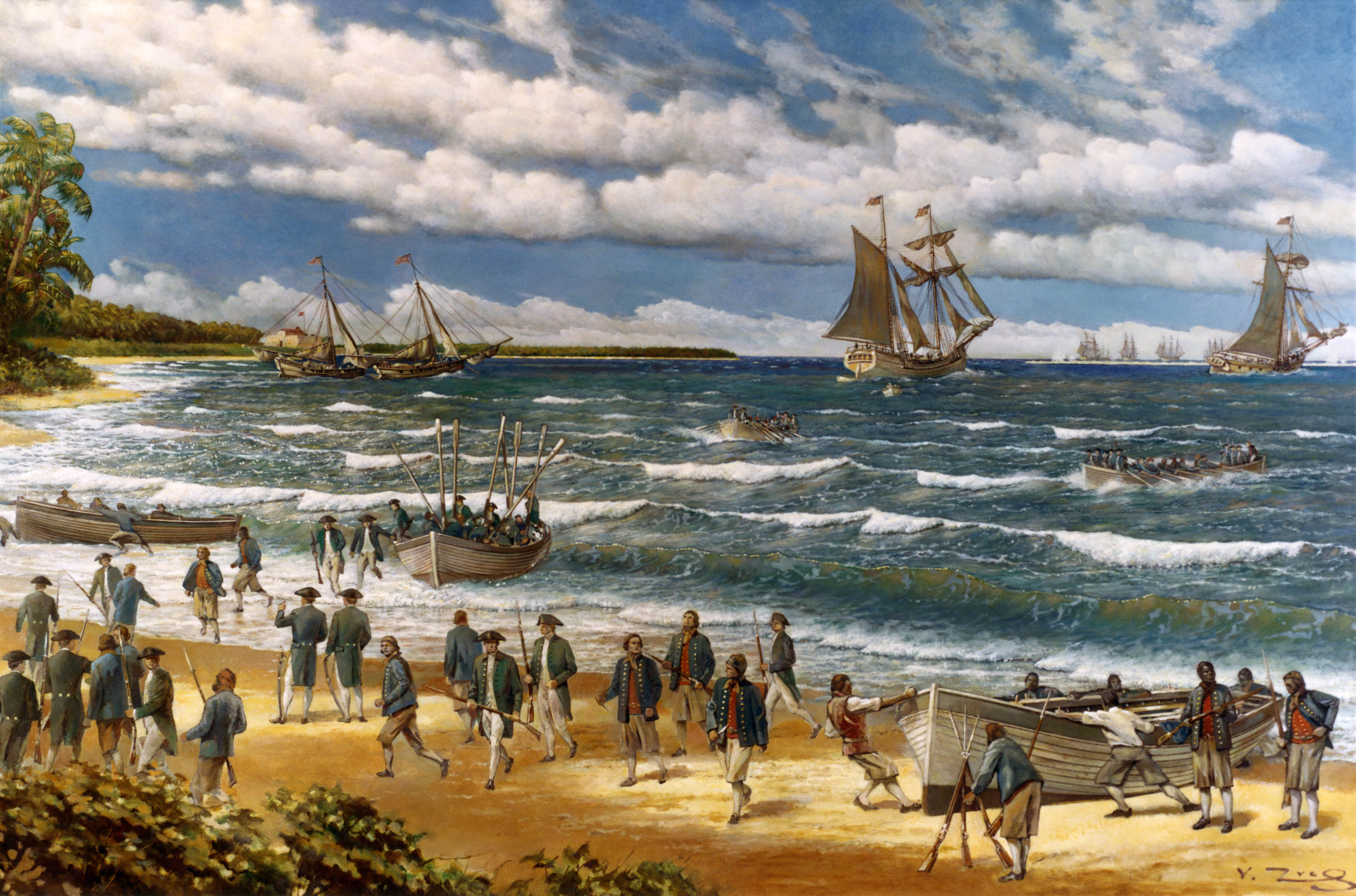
During the American War of Independence
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
in the late 18th century, the islands became a target for US naval forces. Under the command of Commodore Esek Hopkins
Esek Hopkins (April 26, 1718February 26, 1802) was an American naval officer, merchant captain, and privateer. Achieving the rank of Commodore, Hopkins was the only Commander in Chief of the Continental Navy during the American Revolutionary War ...
, US Marines, the US Navy occupied Nassau in 1776, before being evacuated a few days later. In 1782 a Spanish fleet appeared off the coast of Nassau, and the city surrendered without a fight. Later, in April 1783, on a visit made by Prince William of the United Kingdom (later to become King William IV) to Luis de Unzaga at his residence in the Captaincy General of Havana, they made prisoner exchange agreements and also dealt with the preliminaries of the Treaty of Paris (1783), in which the recently conquered Bahamas would be exchanged for East Florida, which would still have to conquer the city of St. Augustine, Florida
St. Augustine ( ; es, San Agustín ) is a city in the Southeastern United States and the county seat of St. Johns County on the Atlantic coast of northeastern Florida. Founded in 1565 by Spanish explorers, it is the oldest continuously inhabit ...
in 1784 by order of Luis de Unzaga; after that, also in 1784, the Bahamas would be declared a British colony.
After US independence, the British resettled some 7,300 Loyalists with their African slaves in the Bahamas, including 2,000 from New York and at least 1,033 European, 2,214 African ancestrals and a few Native American Creeks from East Florida. Most of the refugees resettled from New York had fled from other colonies, including West Florida, which the Spanish captured during the war. The government granted land to the planters to help compensate for losses on the continent. These Loyalists, who included Deveaux and also Lord Dunmore, established plantations on several islands and became a political force in the capital. European Americans were outnumbered by the African-American slaves they brought with them, and ethnic Europeans remained a minority in the territory.
19th century
The Slave Trade Act 1807 abolished slave trading to British possessions, including the Bahamas. The United Kingdom pressured other slave-trading countries to also abolish slave-trading, and gave the Royal Navy the right to intercept ships carrying slaves on the high seas. Thousands of Africans liberated from slave ships by the Royal Navy were resettled in the Bahamas. In the 1820s during the period of the Seminole Wars in Florida, hundreds of North American slaves and African Seminoles escaped fromCape Florida
Bill Baggs Cape Florida State Recreation Area occupies approximately the southern third of the island of Key Biscayne, at coordinates . This park includes the Cape Florida Light, the oldest standing structure in Greater Miami. In 2005, it was ra ...
to the Bahamas. They settled mostly on northwest Andros Island, where they developed the village of Red Bays. From eyewitness accounts, 300 escaped in a mass flight in 1823, aided by Bahamians in 27 sloop
A sloop is a sailboat with a single mast typically having only one headsail in front of the mast and one mainsail aft of (behind) the mast. Such an arrangement is called a fore-and-aft rig, and can be rigged as a Bermuda rig with triangular sa ...
s, with others using canoes for the journey. This was commemorated in 2004 by a large sign at Bill Baggs Cape Florida State Park."Bill Baggs Cape Florida State Park"''Network to Freedom'', National Park Service, 2010, accessed 10 April 2013 Some of their descendants in Red Bays continue African Seminole traditions in basket making and grave marking. In 1818, the Home Office in London had ruled that "any slave brought to the Bahamas from outside the British West Indies would be manumitted." This led to a total of nearly 300 enslaved people owned by US nationals being freed from 1830 to 1835. Horne, p. 103 The American slave ships ''Comet'' and ''Encomium'' used in the United States domestic
coastwise slave trade
The coastwise slave trade existed along the eastern coastal areas of the United States in the antebellum years prior to 1861. Shiploads and boatloads of slaves in the domestic trade were transported from place to place on the waterways. Hundreds of ...
, were wrecked off Abaco Island in December 1830 and February 1834, respectively. When wreckers took the masters, passengers and slaves into Nassau, customs officers seized the slaves and British colonial officials freed them, over the protests of the Americans. There were 165 slaves on the ''Comet'' and 48 on the ''Encomium''. The United Kingdom finally paid an indemnity to the United States in those two cases in 1855, under the Treaty of Claims of 1853, which settled several compensation cases between the two countries. Register of Debates in Congress, Gales & Seaton1837, The section, "Brigs Encomium and Enterprise", has a collection of lengthy correspondence between US (including M. Van Buren), Vail, the US chargé d'affaires in London, and British agents, including Lord Palmerston, sent to the Senate on 13 February 1837, by President Andrew Jackson, as part of the continuing process of seeking compensation.
 Slavery was abolished in the British Empire on 1 August 1834. After that British colonial officials freed 78 North American slaves from the '' Enterprise'', which went into Bermuda in 1835; and 38 from the ''Hermosa'', which wrecked off Abaco Island in 1840. The most notable case was that of the '' Creole'' in 1841: as a result of a slave revolt on board, the leaders ordered the US brig to Nassau. It was carrying 135 slaves from Virginia destined for sale in New Orleans. The Bahamian officials freed the 128 slaves who chose to stay in the islands. The ''Creole'' case has been described as the "most successful slave revolt in U.S. history".
These incidents, in which a total of 447 enslaved people belonging to US nationals were freed from 1830 to 1842, increased tension between the United States and the United Kingdom. They had been co-operating in patrols to suppress the international slave trade. However, worried about the stability of its large domestic slave trade and its value, the United States argued that the United Kingdom should not treat its domestic ships that came to its colonial ports under duress as part of the international trade. The United States worried that the success of the ''Creole'' slaves in gaining freedom would encourage more slave revolts on merchant ships.
During the American Civil War of the 1860s, the islands briefly prospered as a focus for
Slavery was abolished in the British Empire on 1 August 1834. After that British colonial officials freed 78 North American slaves from the '' Enterprise'', which went into Bermuda in 1835; and 38 from the ''Hermosa'', which wrecked off Abaco Island in 1840. The most notable case was that of the '' Creole'' in 1841: as a result of a slave revolt on board, the leaders ordered the US brig to Nassau. It was carrying 135 slaves from Virginia destined for sale in New Orleans. The Bahamian officials freed the 128 slaves who chose to stay in the islands. The ''Creole'' case has been described as the "most successful slave revolt in U.S. history".
These incidents, in which a total of 447 enslaved people belonging to US nationals were freed from 1830 to 1842, increased tension between the United States and the United Kingdom. They had been co-operating in patrols to suppress the international slave trade. However, worried about the stability of its large domestic slave trade and its value, the United States argued that the United Kingdom should not treat its domestic ships that came to its colonial ports under duress as part of the international trade. The United States worried that the success of the ''Creole'' slaves in gaining freedom would encourage more slave revolts on merchant ships.
During the American Civil War of the 1860s, the islands briefly prospered as a focus for blockade runners
A blockade runner is a merchant vessel used for evading a naval blockade of a port or strait. It is usually light and fast, using stealth and speed rather than confronting the blockaders in order to break the blockade. Blockade runners usuall ...
aiding the Confederate States.
Early 20th century
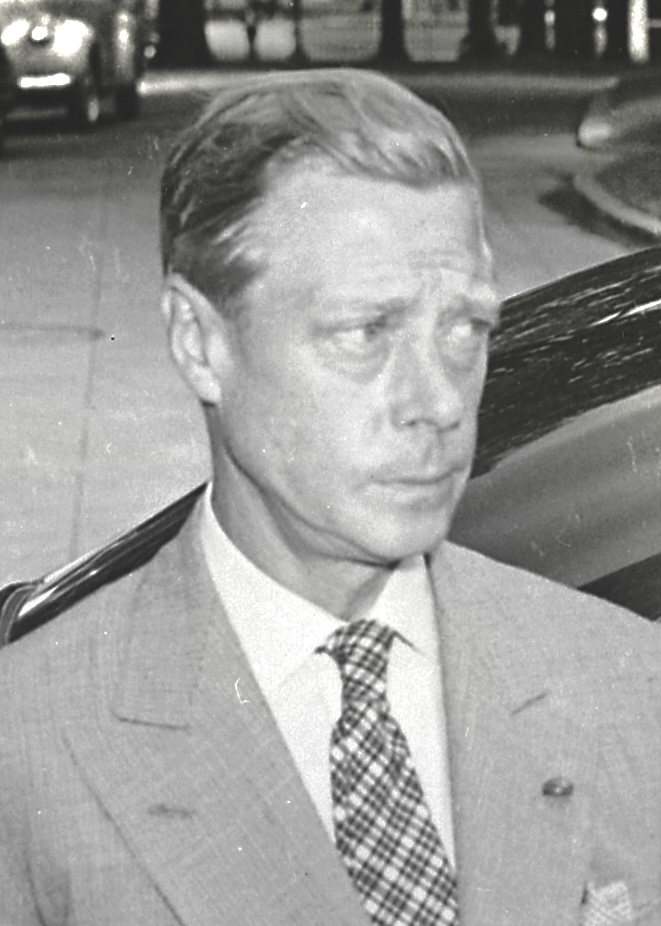
The early decades of the 20th century were ones of hardship for many Bahamians, characterised by a stagnant economy and widespread poverty. Many eked out a living via subsistence agriculture or fishing. In August 1940, the Duke of Windsor (erstwhile King Edward VIII) was appointed Governor of the Bahamas. He arrived in the colony with his wife. Although disheartened at the condition of Government House, they "tried to make the best of a bad situation". Higham, pp. 300–302 He did not enjoy the position, and referred to the islands as "a third-class British colony". He opened the small local parliament on 29 October 1940. The couple visited the "Out Islands" that November, on Axel Wenner-Gren's yacht, which caused controversy; Higham, pp. 307–309 the British Foreign Office strenuously objected because they had been advised by United States intelligence that Wenner-Gren was a close friend of the Luftwaffe commander Hermann Göring of Nazi Germany.
The Duke was praised at the time for his efforts to combat poverty on the islands. A 1991 biography by Philip Ziegler, however, described him as contemptuous of the Bahamians and other non-European peoples of the Empire. He was praised for his resolution of civil unrest over low wages in
In August 1940, the Duke of Windsor (erstwhile King Edward VIII) was appointed Governor of the Bahamas. He arrived in the colony with his wife. Although disheartened at the condition of Government House, they "tried to make the best of a bad situation". Higham, pp. 300–302 He did not enjoy the position, and referred to the islands as "a third-class British colony". He opened the small local parliament on 29 October 1940. The couple visited the "Out Islands" that November, on Axel Wenner-Gren's yacht, which caused controversy; Higham, pp. 307–309 the British Foreign Office strenuously objected because they had been advised by United States intelligence that Wenner-Gren was a close friend of the Luftwaffe commander Hermann Göring of Nazi Germany.
The Duke was praised at the time for his efforts to combat poverty on the islands. A 1991 biography by Philip Ziegler, however, described him as contemptuous of the Bahamians and other non-European peoples of the Empire. He was praised for his resolution of civil unrest over low wages in Nassau
Nassau may refer to:
Places Bahamas
*Nassau, Bahamas, capital city of the Bahamas, on the island of New Providence
Canada
*Nassau District, renamed Home District, regional division in Upper Canada from 1788 to 1792
*Nassau Street (Winnipeg), ...
in June 1942, when there was a "full-scale riot". Higham, pp. 331–332 Ziegler said that the Duke blamed the trouble on "mischief makers – communists" and "men of Central European Jewish descent, who had secured jobs as a pretext for obtaining a deferment of draft".Ziegler, Philip
Philip Sandeman Ziegler (born 24 December 1929) is a British biographer and historian.
Background
Born in Ringwood, Hampshire, Ziegler was educated at St Cyprian's School, Eastbourne, and went with the school when it merged with Summer Field ...
(1991). ''King Edward VIII: The Official Biography''. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. . pp. 471–472 The Duke resigned from the post on 16 March 1945. Matthew, H. C. G. (September 2004; online edition January 2008"Edward VIII, later Prince Edward, Duke of Windsor (1894–1972)"
, ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, , retrieved 1 May 2010 (Subscription required) Higham, p. 359 places the date of his resignation as 15 March, and that he left on 5 April.
Post-Second World War
Sir Roland Symonette
Sir Roland Theodore Symonette, NH (16 December 1898 – 13 March 1980) was a Bahamian politician and the first Premier of the Bahamas after self-government was achieved in 1964. He was leader of the United Bahamian Party (UBP), which some felt ...
of the UBP becoming the first Premier.Nohlen, D. (2005), ''Elections in the Americas: A data handbook, Volume I'' In 1967, Lynden Pindling of the PLP became the first black Premier of the Bahamian colony; in 1968, the title of the position was changed to Prime Minister. In 1968, Pindling announced that the Bahamas would seek full independence. A new constitution giving the Bahamas increased control over its own affairs was adopted in 1968. In 1971, the UBP merged with a disaffected faction of the PLP to form a new party, the Free National Movement (FNM), a centre-right party which aimed to counter the growing power of Pindling's PLP.
The United Kingdom Government gave the Bahamas its independence by an Order in Council dated 20 June 1973. The Order came into force on 10 July 1973, on which date Prince Charles
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms. He was the longest-serving heir apparent and Prince of Wales and, at age 73, became the oldest person to ...
delivered the official documents to Prime Minister Lynden Pindling. This date is now celebrated as the country's Independence Day
An independence day is an annual event commemorating the anniversary of a nation's independence or statehood, usually after ceasing to be a group or part of another nation or state, or more rarely after the end of a military occupation. Man ...
. It joined the Commonwealth of Nations on the same day. Sir Milo Butler
Sir Milo Boughton Butler (11 August 190622 January 1979) was a Bahamian politician who served as the second governor-general of the Bahamas from 1973 to 1979. He died in office aged 72.
Early life and family
Butler was born in Nassau, The Bah ...
was appointed the first governor-general of The Bahamas (the official representative of Queen Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until Death and state funeral of Elizabeth II, her death in 2022. She was queen ...
) shortly after independence.
Post-independence
Shortly after independence, The Bahamas joined the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank on 22 August 1973, and later the United Nations on 18 September 1973. Politically, the first two decades were dominated by Pindling's PLP, who went on to win a string of electoral victories. Allegations of corruption, links with drug cartels and financial malfeasance within the Bahamian government failed to dent Pindling's popularity. Meanwhile, the economy underwent a dramatic growth period fuelled by the twin pillars of tourism andoffshore finance
An offshore financial centre (OFC) is defined as a "country or jurisdiction that provides financial services to nonresidents on a scale that is incommensurate with the size and the financing of its domestic economy."
"Offshore" does not refer ...
, significantly raising the standard of living
Standard of living is the level of income, comforts and services available, generally applied to a society or location, rather than to an individual. Standard of living is relevant because it is considered to contribute to an individual's quality ...
on the islands. The Bahamas' booming economy led to it becoming a beacon for immigrants, most notably from Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
.
 In 1992, Pindling was unseated by Hubert Ingraham of the FNM. Ingraham went on to win the
In 1992, Pindling was unseated by Hubert Ingraham of the FNM. Ingraham went on to win the 1997 Bahamian general election
General elections were held in the Bahamas on 14 March 1997.Dieter Nohlen (2005) ''Elections in the Americas: A data handbook, Volume I'', p78 The result was a victory for the Free National Movement, which won 34 of the 40 seats. Hubert Ingraham ...
, before being defeated in 2002
IN, In or in may refer to:
Places
* India (country code IN)
* Indiana, United States (postal code IN)
* Ingolstadt, Germany (license plate code IN)
* In, Russia, a town in the Jewish Autonomous Oblast
Businesses and organizations
* Independ ...
, when the PLP returned to power under Perry Christie. Ingraham returned to power from 2007 to 2012, followed by Christie again from 2012 to 2017. With economic growth faltering, Bahamians re-elected the FNM in 2017, with Hubert Minnis becoming the fourth prime minister.
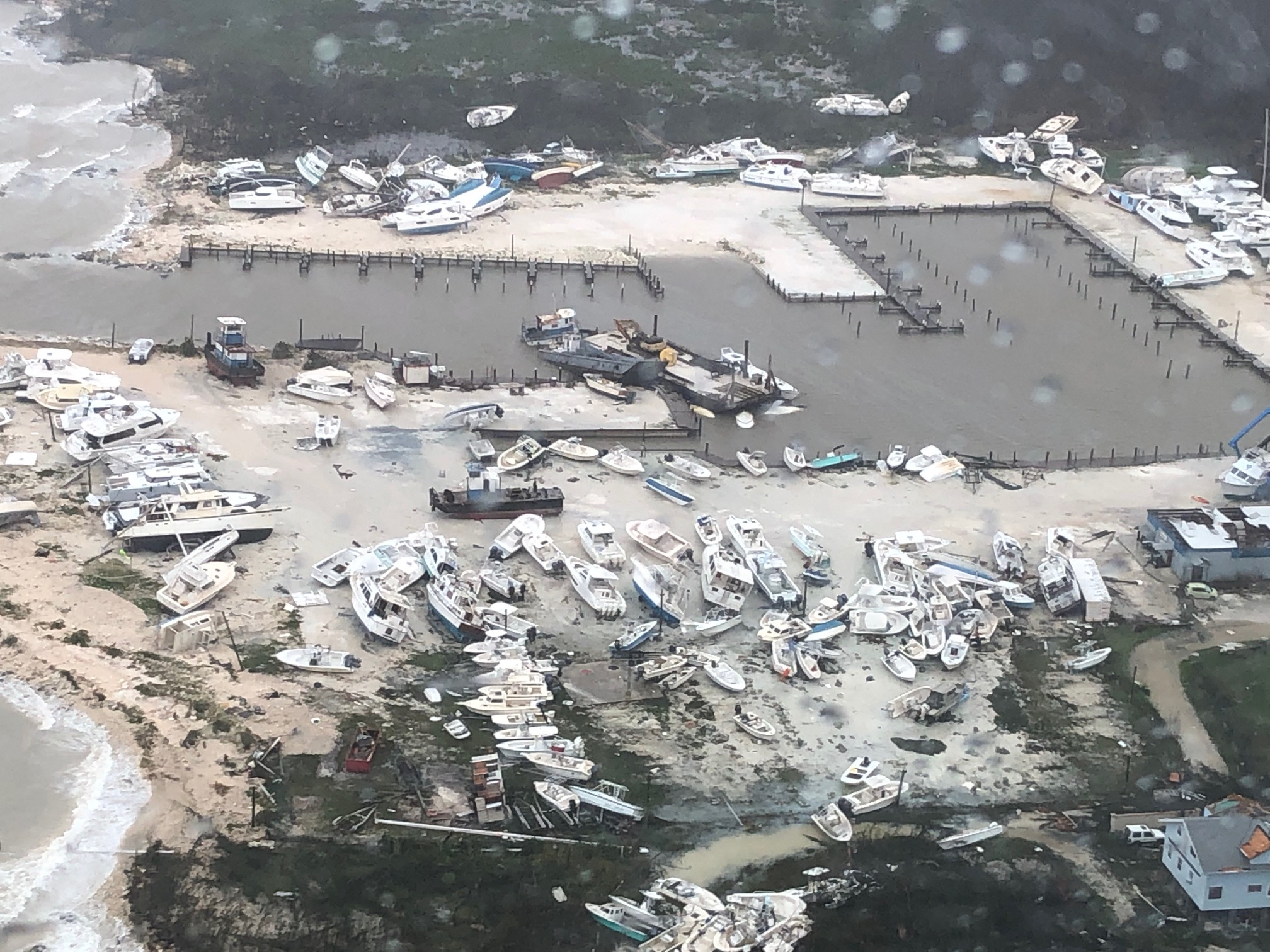
In September 2019, Hurricane Dorian struck the Abaco Islands
Abaco is a variant Italian form of the Biblical name "Habakkuk" (but normally Abacùc or Abacucco).
Abaco may refer to:
People
*Evaristo Felice Dall'Abaco (1675–1742), Italian composer and violinist
*Joseph Abaco (1710–1805), Belgian compose ...
and Grand Bahama
Grand Bahama is the northernmost of the islands of the Bahamas, with the town of West End located east of Palm Beach, Florida. It is the third largest island in the Bahamas island chain of approximately 700 islands and 2,400 cays. The island is ...
at Category 5 intensity, devastating the northwestern Bahamas. The storm inflicted at least US$
The United States dollar (symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the official ...
7 billion in damages and killed more than 50 people, with 1,300 people still missing.
In September 2021, the ruling Free National Movement lost to the opposition Progressive Liberal Party in a snap election, as the economy struggled to recover from its deepest crash since at least 1971. Progressive Liberal Party (PLP) won 32 of the 39 seats in the House of Assembly. Free National Movement (FNM), led by Minnis, took the remaining seats. On 17 September 2021, the chairman of the Progressive Liberal Party (PLP) Phillip "Brave" Davis was sworn in as the new Prime Minister of Bahamas to succeed Hubert Minnis.
Geography
 The landmass that makes up what is the modern-day Bahamas, lies at the northern part of the Greater Antilles region and was believed to have been formed 200 million years ago when they began to separate from the supercontinent Pangaea. The Pleistocene Ice Age around 3 million years ago, had a profound impact on the archipelago's formation.
The Bahamas consists of a chain of islands spread out over some in the Atlantic Ocean, located to the east of Florida in the United States, north of Cuba and
The landmass that makes up what is the modern-day Bahamas, lies at the northern part of the Greater Antilles region and was believed to have been formed 200 million years ago when they began to separate from the supercontinent Pangaea. The Pleistocene Ice Age around 3 million years ago, had a profound impact on the archipelago's formation.
The Bahamas consists of a chain of islands spread out over some in the Atlantic Ocean, located to the east of Florida in the United States, north of Cuba and Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ; es, La Española; Latin and french: Hispaniola; ht, Ispayola; tnq, Ayiti or Quisqueya) is an island in the Caribbean that is part of the Greater Antilles. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and th ...
and west of the British Overseas Territory of the Turks and Caicos Islands (with which it forms the Lucayan archipelago). It lies between latitudes 20° and 28°N, and longitudes 72° and 80°W and straddles the Tropic of Cancer. There are some 700 islands and 2,400 cays in total (of which 30 are inhabited) with a total land area of .
Nassau
Nassau may refer to:
Places Bahamas
*Nassau, Bahamas, capital city of the Bahamas, on the island of New Providence
Canada
*Nassau District, renamed Home District, regional division in Upper Canada from 1788 to 1792
*Nassau Street (Winnipeg), ...
, capital city of The Bahamas, lies on the island of New Providence
New Providence is the most populous island in the Bahamas, containing more than 70% of the total population. It is the location of the national capital city of Nassau, whose boundaries are coincident with the island; it had a population of 246 ...
; the other main inhabited islands are Grand Bahama
Grand Bahama is the northernmost of the islands of the Bahamas, with the town of West End located east of Palm Beach, Florida. It is the third largest island in the Bahamas island chain of approximately 700 islands and 2,400 cays. The island is ...
, Eleuthera, Cat Island, Rum Cay, Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated island in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of New York (state), New York, part of the New York metropolitan area. With over 8 million people, Long Island is the most populous island in the United Sta ...
, San Salvador Island, Ragged Island, Acklins
Acklins is an island and district of the Bahamas.
It is one of a group of islands arranged along a large, shallow lagoon called the Bight of Acklins, of which the largest are Crooked Island () in the north and Acklins () in the southeast, and ...
, Crooked Island, Exuma
Exuma is a district of The Bahamas, consisting of over 365 islands, also called cays.
The largest of the cays is Great Exuma, which is 37 mi (60 km) in length and joined to another island, Little Exuma, by a small bridge. The capital ...
, Berry Islands, Mayaguana
Mayaguana (from Taíno language ''Mayaguana'', meaning "Lesser Midwestern Land") is the easternmost island and district of The Bahamas. Its population was 277 in the 2010 census. It has an area of about .
About north of Great Inagua and southea ...
, the Bimini islands, Great Abaco and Great Inagua. The largest island is Andros.
All the islands are low and flat, with ridges that usually rise no more than . The highest point in the country is Mount Alvernia
Mount Alvernia (formerly Como Hill) is located on Cat Island in the Bahamas and is the highest point in the country at above sea level. The mountain shares its name with a school in Montego Bay, Jamaica.
Originally named "Como Hill", it was re ...
(formerly Como Hill) on Cat Island at .
The country contains three terrestrial ecoregions: Bahamian dry forests
The Bahamian dry forests are a tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forest ecoregion in the Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands, covering an area of . They are found on much of the northern Bahamas, including Andros, Abaco, and Grand Bah ...
, Bahamian pine mosaic
The Bahamian pineyards are a tropical and subtropical coniferous forest ecoregion in the Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands.
Geography
The Bahamian pineyards cover an area of . Pineyards are found on four of the northern islands in the Ba ...
, and Bahamian mangroves
The Greater Antilles mangroves is a mangrove ecoregion that includes the coastal mangrove forests of the Greater Antilles – Cuba, Hispaniola, Jamaica, and Puerto Rico.
Geography
Mangroves are estimated to cover 5,569 km in Cuba (or 4.8% of the ...
. It had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 7.35/10, ranking it 44th globally out of 172 countries.
Climate
Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Current, North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida a ...
, and low elevation give The Bahamas a warm and winterless climate.
As with most tropical climates, seasonal rainfall follows the sun, and summer is the wettest season. There is only a difference between the warmest month and coolest month in most of the Bahama islands. Every few decades low temperatures can fall below for a few hours when a severe cold outbreak comes down from the North American mainland, however there has never been a frost or freeze recorded in the Bahamian Islands. Only once in recorded history has snow been seen in the air anywhere in The Bahamas, this occurred in Freeport on 19 January 1977, when snow mixed with rain was seen in the air for a short time. The Bahamas are often sunny and dry for long periods of time, and average more than 3,000 hours or 340 days of sunlight annually. Much of the natural vegetation is tropical scrub and cactus and succulents are common in landscapes.
Tropical storms and hurricanes occasionally impact The Bahamas. In 1992, Hurricane Andrew
Hurricane Andrew was a very powerful and destructive Category 5 Atlantic hurricane that struck the Bahamas, Florida, and Louisiana in August 1992. It is the most destructive hurricane to ever hit Florida in terms of structures damaged ...
passed over the northern portions of the islands, and Hurricane Floyd passed near the eastern portions of the islands in 1999. Hurricane Dorian of 2019 passed over the archipelago at destructive Category 5 strength with sustained winds of and wind gusts up to , becoming the strongest tropical cyclone on record to impact the northwestern islands of Grand Bahama and Great Abaco.
Geology
Mouchoir Bank
Mouchoir Bank, in Spanish also called ''Banco de Pañuelo Blanco'', is a submerged bank that is part of the Turks and Caicos Islands and falls within its exclusive economic zone.
The bank, located southeast of the Turks islands, is the geograp ...
, the Silver Bank
Silver Bank ( es, Banco de la Plata) is a submerged bank in the Atlantic Ocean north of the Dominican Republic and southeast of the territory of Turks and Caicos Islands. It covers an area of . It is separated from Mouchoir Bank in the west by ...
, and the Navidad Bank
Navidad Bank ( es, Banco de la Navidad) is a submerged bank in the Atlantic Ocean north of the Dominican Republic and southeast of the Territory of Turks & Caicos. It is separated from Silver Bank by the wide Navidad Bank Passage.
Geography
Navid ...
. The Bahamas Platform, which includes The Bahamas, Southern Florida, Northern Cuba, the Turks and Caicos, and the Blake Plateau, formed about 150 Ma, not long after the formation of the North Atlantic. The thick limestones, which predominate in The Bahamas, date back to the Cretaceous. These limestones would have been deposited in shallow seas, assumed to be a stretched and thinned portion of the North American continental crust. Sediments were forming at about the same rate as the crust below was sinking due to the added weight. Thus, the entire area consisted of a large marine plain with some islands. Then, at about 80 Ma, the area became flooded by the Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Current, North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida a ...
. This resulted in the drowning of the Blake Plateau, the separation of The Bahamas from Cuba and Florida, the separation of the southeastern Bahamas into separate banks, the creation of the Cay Sal Bank, plus the Little and Great Bahama Banks. Sedimentation from the "carbonate factory" of each bank, or atoll, continues today at the rate of about per kyr
The abbreviation kyr means "thousand years".
kyr was formerly common in some English language works, especially in geology and astronomy, for the unit of 1,000 years or millennium. The "k" is the unit prefix for kilo- or thousand with the suffix ...
. Coral reefs form the "retaining walls" of these atolls, within which oolite
Oolite or oölite (''egg stone'') is a sedimentary rock formed from ooids, spherical grains composed of concentric layers. The name derives from the Ancient Greek word for egg (ᾠόν). Strictly, oolites consist of ooids of diameter 0.25–2 ...
s and pellets form.
Coral growth was greater through the Tertiary, until the start of the ice ages, and hence those deposits are more abundant below a depth of . In fact, an ancient extinct reef exists half a kilometre seaward of the present one, below sea level. Oolites form when oceanic water penetrate the shallow banks, increasing the temperature about and the salinity by 0.5 per cent. Cemented ooids are referred to as grapestone. Additionally, giant stromatolites are found off the Exuma Cays
Exuma is a district of The Bahamas, consisting of over 365 islands, also called cays.
The largest of the cays is Great Exuma, which is 37 mi (60 km) in length and joined to another island, Little Exuma, by a small bridge. The capital ...
.
Sea level changes resulted in a drop in sea level, causing wind blown oolite to form sand dune
A dune is a landform composed of wind- or water-driven sand. It typically takes the form of a mound, ridge, or hill. An area with dunes is called a dune system or a dune complex. A large dune complex is called a dune field, while broad, fl ...
s with distinct cross-bedding. Overlapping dunes form oolitic ridges, which become rapidly lithified through the action of rainwater, called eolianite. Most islands have ridges ranging from , though Cat Island has a ridge in height. The land between ridges is conducive to the formation of lakes and swamps.
Solution weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals as well as wood and artificial materials through contact with water, atmospheric gases, and biological organisms. Weathering occurs ''in situ'' (on site, with little or no movement), ...
of the limestone results in a "Bahamian Karst
Karst is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum. It is characterized by underground drainage systems with sinkholes and caves. It has also been documented for more weathering-resistant ro ...
" topography. This includes potholes, blue holes such as Dean's Blue Hole
__NOTOC__
Dean's Blue Hole is a blue hole located in The Bahamas in a bay west of Clarence Town on Long Island and is the world's second deepest, after the Dragon Hole in the South China Sea, with a depth of .
Formation
A blue hole is a water ...
, sinkholes, beachrock such as the Bimini Road
The Bimini Road, sometimes called the Bimini Wall, is an underwater rock formation near North Bimini island in the Bahamas. The Road consists of a -long northeast-southwest linear feature composed of roughly rectangular limestone blocks. Various c ...
("pavements of Atlantis"), limestone crust, caves due to the lack of rivers, and sea caves. Several blue holes are aligned along the South Andros Fault line. Tidal flats and tidal creeks are common, but the more impressive drainage patterns are formed by troughs and canyons such as Great Bahama Canyon
The Great Bahama Canyon is a V-shaped submarine canyon system in the Bahamas that cuts between the Abaco Islands to the north and Eleuthera island to the south. It separates the Bahama Banks and forms one of the deepest underwater canyon systems k ...
with the evidence of turbidity currents and turbidite deposition.
The stratigraphy
Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock (geology), rock layers (Stratum, strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary rock, sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks.
Stratigrap ...
of the islands consists of the Middle Pleistocene Owl's Hole Formation
Formation may refer to:
Linguistics
* Back-formation, the process of creating a new lexeme by removing or affixes
* Word formation, the creation of a new word by adding affixes
Mathematics and science
* Cave formation or speleothem, a secondar ...
, overlain by the Late Pleistocene
The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as Upper Pleistocene from a Stratigraphy, stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth division of ...
Grotto Beach Formation, and then the Holocene Rice Bay Formation. However, these units are not necessarily stacked on top of each other but can be located laterally. The oldest formation, Owl's Hole, is capped by a terra rosa paleosoil
In the geosciences, paleosol (''palaeosol'' in Great Britain and Australia) is an ancient soil that formed in the past. The precise definition of the term in geology and paleontology is slightly different from its use in soil science.
In geolo ...
, as is the Grotto Beach, unless eroded. The Grotto Beach Formation is the most widespread.
Government and politics
 The Bahamas is a parliamentary constitutional monarchy, with King of the Bahamas Charles III as head of state represented locally by a
The Bahamas is a parliamentary constitutional monarchy, with King of the Bahamas Charles III as head of state represented locally by a governor-general
Governor-general (plural ''governors-general''), or governor general (plural ''governors general''), is the title of an office-holder. In the context of governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general are appointed as viceroy t ...
. Political and legal traditions closely follow those of England and the Westminster system. The Bahamas is a member of the Commonwealth of Nations and shares
In financial markets, a share is a unit of equity ownership in the capital stock of a corporation, and can refer to units of mutual funds, limited partnerships, and real estate investment trusts. Share capital refers to all of the shares of an ...
its head of state with some other Commonwealth realms.
The prime minister is the head of government and is the leader of the party with the most seats in the House of Assembly. Executive power is exercised by the Cabinet, selected by the prime minister and drawn from his supporters in the House of Assembly. The current governor-general is The Honourable Cornelius A. Smith, and the current prime minister is The Hon.
''The Honourable'' (British English) or ''The Honorable'' (American English; see spelling differences) (abbreviation: ''Hon.'', ''Hon'ble'', or variations) is an honorific style that is used as a prefix before the names or titles of certain ...
Philip Davis MP.
Legislative power is vested in a bicameral
Bicameralism is a type of legislature, one divided into two separate assemblies, chambers, or houses, known as a bicameral legislature. Bicameralism is distinguished from unicameralism, in which all members deliberate and vote as a single grou ...
parliament, which consists of a 38-member House of Assembly (the lower house
A lower house is one of two Debate chamber, chambers of a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the upper house. Despite its official position "below" the upper house, in many legislatures worldwide, the lower house has co ...
), with members elected from single-member districts, and a 16-member Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
, with members appointed by the governor-general, including nine on the advice of the Prime Minister, four on the advice of the leader of His Majesty's Loyal Opposition, and three on the advice of the prime minister after consultation with the Leader of the Opposition. As under the Westminster system, the prime minister may dissolve Parliament and call a general election at any time within a five-year term.
Constitutional safeguards include freedom of speech
Freedom of speech is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or a community to articulate their opinions and ideas without fear of retaliation, censorship, or legal sanction. The right to freedom of expression has been recogni ...
, press
Press may refer to:
Media
* Print media or news media, commonly called "the press"
* Printing press, commonly called "the press"
* Press (newspaper), a list of newspapers
* Press TV, an Iranian television network
People
* Press (surname), a famil ...
, worship
Worship is an act of religious devotion usually directed towards a deity. It may involve one or more of activities such as veneration, adoration, praise, and praying. For many, worship is not about an emotion, it is more about a recognition ...
, movement
Movement may refer to:
Common uses
* Movement (clockwork), the internal mechanism of a timepiece
* Motion, commonly referred to as movement
Arts, entertainment, and media
Literature
* "Movement" (short story), a short story by Nancy Fu ...
and association. The Judiciary of the Bahamas
The basis of the Bahamian Law and legal system lies within the English Common Law tradition. Justices of the Supreme Court, Registrars and Magistrates are all appointed by The Governor-General acting on the advice of the Judicial and Legal Servi ...
is independent of the executive and the legislature. Jurisprudence is based on English law
English law is the common law legal system of England and Wales, comprising mainly criminal law and civil law, each branch having its own courts and procedures.
Principal elements of English law
Although the common law has, historically, be ...
.
Political culture
 The Bahamas has a two-party system dominated by the centre-left Progressive Liberal Party and the centre-right Free National Movement. A handful of other political parties have been unable to win election to parliament; these have included the
The Bahamas has a two-party system dominated by the centre-left Progressive Liberal Party and the centre-right Free National Movement. A handful of other political parties have been unable to win election to parliament; these have included the Bahamas Democratic Movement
The Bahamas Democratic Movement (BDM) is a liberal-populist political party in the Bahamas representing the interests of young people.
Party formation of Bahamas Democratic Movement
The party was formed in late 1998 in Nassau, Bahamas and w ...
, the Coalition for Democratic Reform, Bahamian Nationalist Party and the Democratic National Alliance.
Foreign relations
The Bahamas has strong bilateral relationships with the United States and the United Kingdom, represented by an ambassador in Washington and High Commissioner in London. The Bahamas also associates closely with other nations of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM). The embassy of the United States in Nassau donated $3.6 million to the Minister for Disaster Preparedness, Management, and Reconstruction for modular shelters, medical evacuation boats, and construction materials. The donation was made 2 weeks after the one year anniversary of Hurricane Dorian.Armed forces
 The Bahamian military is the Royal Bahamas Defence Force (RBDF), the navy of The Bahamas which includes a land unit called Commando Squadron (Regiment) and an Air Wing (Air Force). Under the Defence Act, the RBDF has been mandated, in the name of the King, to defend The Bahamas, protect its territorial integrity, patrol its waters, provide assistance and relief in times of disaster, maintain order in conjunction with the law enforcement agencies of The Bahamas, and carry out any such duties as determined by the National Security Council. The Defence Force is also a member of the Caribbean Community ( CARICOM)'s Regional Security Task Force.
The RBDF came into existence on 31 March 1980. Its duties include defending The Bahamas, stopping drug smuggling, illegal immigration and poaching, and providing assistance to mariners. The Defence Force has a fleet of 26 coastal and inshore patrol craft along with 3 aircraft and over 1,100 personnel including 65 officers and 74 women.
The Bahamian military is the Royal Bahamas Defence Force (RBDF), the navy of The Bahamas which includes a land unit called Commando Squadron (Regiment) and an Air Wing (Air Force). Under the Defence Act, the RBDF has been mandated, in the name of the King, to defend The Bahamas, protect its territorial integrity, patrol its waters, provide assistance and relief in times of disaster, maintain order in conjunction with the law enforcement agencies of The Bahamas, and carry out any such duties as determined by the National Security Council. The Defence Force is also a member of the Caribbean Community ( CARICOM)'s Regional Security Task Force.
The RBDF came into existence on 31 March 1980. Its duties include defending The Bahamas, stopping drug smuggling, illegal immigration and poaching, and providing assistance to mariners. The Defence Force has a fleet of 26 coastal and inshore patrol craft along with 3 aircraft and over 1,100 personnel including 65 officers and 74 women.
Administrative divisions
The districts of The Bahamas provide a system of local government everywhere exceptNew Providence
New Providence is the most populous island in the Bahamas, containing more than 70% of the total population. It is the location of the national capital city of Nassau, whose boundaries are coincident with the island; it had a population of 246 ...
(which holds 70 percent of the national population), whose affairs are handled directly by the central government. In 1996, the Bahamian Parliament passed the "Local Government Act" to facilitate the establishment of family island administrators, local government districts, local district councillors and local town committees for the various island communities. The overall goal of this act is to allow the various elected leaders to govern and oversee the affairs of their respective districts without the interference of the central government. In total, there are 32 districts, with elections being held every five years. There are 110 councillors and 281 town committee members elected to represent the various districts.
Each councillor or town committee member is responsible for the proper use of public funds for the maintenance and development of their constituency.
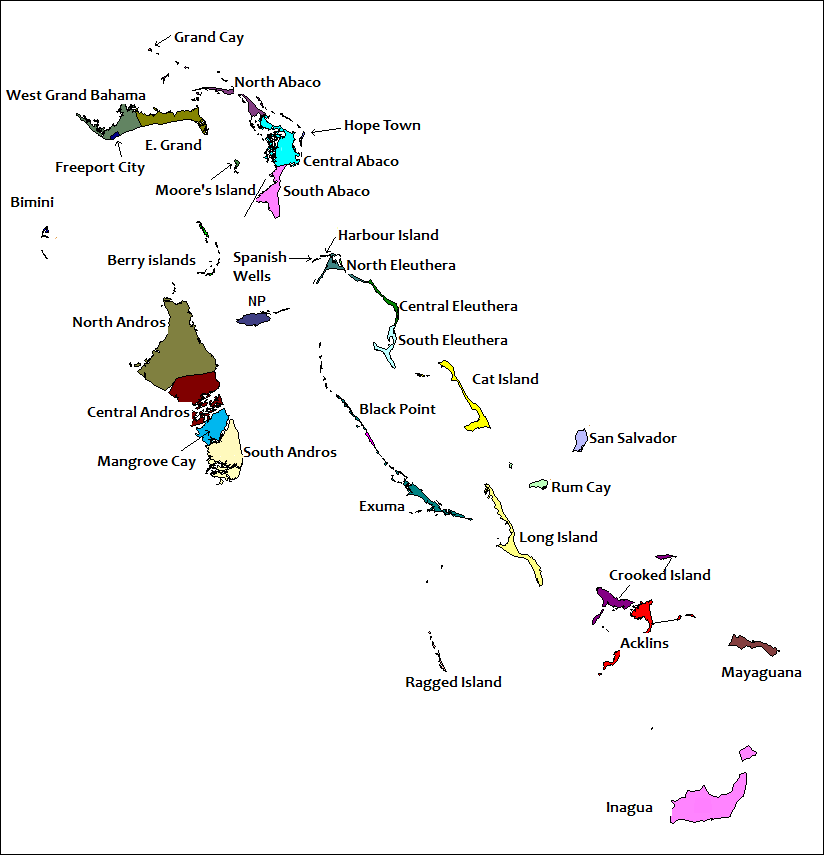
The districts other than New Providence are:

Economy
GDP per capita
Lists of countries by GDP per capita list the countries in the world by their gross domestic product (GDP) per capita. The lists may be based on nominal or purchasing power parity GDP. Gross national income (GNI) per capita accounts for inflows ...
, The Bahamas is one of the richest countries in the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
. Its currency (the Bahamian dollar) is kept at a 1-to-1 peg with the US dollar.
The Bahamas relies heavily on tourism to generate most of its economic activity. Tourism as an industry not only accounts for about 70% of the Bahamian GDP, but also provides jobs for about half of the country's workforce. The Bahamas attracted 5.8 million visitors in 2012, more than 70% of whom were cruise visitors.
After tourism, the next most important economic sector is banking and offshore international financial services, accounting for some 15% of GDP. It was revealed in the Panama Papers
The Panama Papers ( es, Papeles de Panamá) are 11.5 million leaked documents (or 2.6 terabytes of data) that were published beginning on April 3, 2016. The papers detail financial and attorney–client information for more than 214,488 ...
that The Bahamas is the jurisdiction with the most offshore entities or companies in the world.
The economy has a very competitive tax regime (classified by some as a tax haven). The government derives its revenue from import tariffs, VAT
A value-added tax (VAT), known in some countries as a goods and services tax (GST), is a type of tax that is assessed incrementally. It is levied on the price of a product or service at each stage of production, distribution, or sale to the en ...
, licence fees, property and stamp taxes, but there is no income tax, corporate tax, capital gains tax, or wealth tax. Payroll taxes fund social insurance benefits and amount to 3.9% paid by the employee and 5.9% paid by the employer. In 2010, overall tax revenue as a percentage of GDP was 17.2%.
Agriculture and manufacturing form the third largest sector of the Bahamian economy, representing 5–7% of total GDP. An estimated 80% of the Bahamian food supply is imported. Major crops include onions, okra, tomatoes, oranges, grapefruit
The grapefruit (''Citrus'' × ''paradisi'') is a subtropical citrus tree known for its relatively large, sour to semi-sweet, somewhat bitter fruit. The interior flesh is segmented and varies in color from pale yellow to dark pink.
Grapefruit is ...
, cucumber
Cucumber (''Cucumis sativus'') is a widely-cultivated Vine#Horticultural climbing plants, creeping vine plant in the Cucurbitaceae family that bears usually cylindrical Fruit, fruits, which are used as culinary vegetables.
s, sugar cane, lemons, limes, and sweet potato
The sweet potato or sweetpotato (''Ipomoea batatas'') is a dicotyledonous plant that belongs to the Convolvulus, bindweed or morning glory family (biology), family, Convolvulaceae. Its large, starchy, sweet-tasting tuberous roots are used as a r ...
es.
Access to biocapacity in the Bahamas is much higher than world average. In 2016, the Bahamas had 9.2 global hectares of biocapacity per person within its territory, much more than the world average of 1.6 global hectares per person. In 2016 the Bahamas used 3.7 global hectares of biocapacity per person - their ecological footprint
The ecological footprint is a method promoted by the Global Footprint Network to measure human demand on natural capital, i.e. the quantity of nature it takes to support people or an economy. It tracks this demand through an ecological accounti ...
of consumption. This means they use less biocapacity than the Bahamas contains. As a result, the Bahamas is running a biocapacity reserve.
Transport
 The Bahamas contains about of paved roads. Inter-island transport is conducted primarily via ship and air. The country has 61 airports, the chief of which are
The Bahamas contains about of paved roads. Inter-island transport is conducted primarily via ship and air. The country has 61 airports, the chief of which are Lynden Pindling International Airport
Lynden Pindling International Airport , formerly known as Nassau International Airport, is the largest airport in the Bahamas and the largest international gateway into the country. It is a major hub for Bahamasair, Western Air, and Pineapple ...
on New Providence, Grand Bahama International Airport
Grand Bahama International Airport (GBIA) is an international airport in Freeport, Bahamas. It was privately owned until the government of the Bahamas purchased it in April 2021.
The airport was a joint venture between Hutchison Port Holding ...
on Grand Bahama Island and Leonard M. Thompson International Airport (formerly Marsh Harbour Airport) on Abaco Island.
Demographics
infant mortality rate
Infant mortality is the death of young children under the age of 1. This death toll is measured by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the probability of deaths of children under one year of age per 1000 live births. The under-five morta ...
is 23.21 deaths/1,000 live births. Residents have a life expectancy at birth of 69.87 years: 73.49 years for females, 66.32 years for males. The total fertility rate is 2.0 children born/woman (2010). The latest official estimate (as at 2022) is 400,516.
The most populous islands are New Providence
New Providence is the most populous island in the Bahamas, containing more than 70% of the total population. It is the location of the national capital city of Nassau, whose boundaries are coincident with the island; it had a population of 246 ...
, where Nassau
Nassau may refer to:
Places Bahamas
*Nassau, Bahamas, capital city of the Bahamas, on the island of New Providence
Canada
*Nassau District, renamed Home District, regional division in Upper Canada from 1788 to 1792
*Nassau Street (Winnipeg), ...
, the capital and largest city, is located; and Grand Bahama
Grand Bahama is the northernmost of the islands of the Bahamas, with the town of West End located east of Palm Beach, Florida. It is the third largest island in the Bahamas island chain of approximately 700 islands and 2,400 cays. The island is ...
, home to the second largest city of Freeport Freeport, a variant of free port, may refer to:
Places United States
*Freeport, California
*Freeport, Florida
*Freeport, Illinois
*Freeport, Indiana
*Freeport, Iowa
*Freeport, Kansas
*Freeport, Maine, a New England town
**Freeport (CDP), Maine, the ...
.
Racial and ethnic groups
According to the 99% response rate obtained from the race question on the 2010 Census questionnaire, 90.6% of the population identified themselves as being Black, 4.7% White and 2.1% of a Mixed (African and European). Three centuries prior, in 1722 when the first official census of The Bahamas was taken, 74% of the population was native European and 26% native African.Africans
African or Africans may refer to:
* Anything from or pertaining to the continent of Africa:
** People who are native to Africa, descendants of natives of Africa, or individuals who trace their ancestry to indigenous inhabitants of Africa
*** Ethn ...
or Afro-Bahamians have been the largest ethnic group in The Bahamas, whose primary ancestry was based in West Africa. The first Africans to arrive to The Bahamas were freed slaves from Bermuda; they arrived with the Eleutheran Adventurers looking for new lives.
The Haitian community in The Bahamas is also largely of African descent and numbers about 80,000. Due to an extremely high immigration of Haitians to The Bahamas, the Bahamian government started deporting illegal Haitian immigrants to their homeland in late 2014.
The white Bahamian population are mainly the descendants of the English Puritans
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to purify the Church of England of Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should become more Protestant. ...
and American Loyalists escaping the American Revolution who arrived in 1649 and 1783, respectively. Many Southern Loyalists went to the Abaco Islands
Abaco is a variant Italian form of the Biblical name "Habakkuk" (but normally Abacùc or Abacucco).
Abaco may refer to:
People
*Evaristo Felice Dall'Abaco (1675–1742), Italian composer and violinist
*Joseph Abaco (1710–1805), Belgian compose ...
, half of whose population was of European descent as of 1985. The term ''white'' is usually used to identify Bahamians with Anglo ancestry, as well as some light-skinned Afro-Bahamians. Sometimes Bahamians use the term '' Conchy Joe'' to describe people of Anglo descent. Generally, however, Bahamians self-identify as white or black along the lines similar to the distinction made in the US.
A small portion of the Euro-Bahamian population are Greek Bahamians, descended from Greek labourers who came to help develop the sponging industry in the 1900s. They make up less than 2% of the nation's population, but have still preserved their distinct Greek Bahamian culture.
Religion
The islands' population is predominantlyChristian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
. Protestant denominations collectively account for more than 70% of the population, with Baptists
Baptists form a major branch of Protestantism distinguished by baptizing professing Christian believers only ( believer's baptism), and doing so by complete immersion. Baptist churches also generally subscribe to the doctrines of soul compe ...
representing 35% of the population, Anglicans 15%, Pentecostals 8%, Church of God 5%, Seventh-day Adventists 5% and Methodists 4%. There is also a significant Roman Catholic community accounting for about 14%.
Jews in the Bahamas have a history dating back to the Columbus
Columbus is a Latinized version of the Italian surname "''Colombo''". It most commonly refers to:
* Christopher Columbus (1451-1506), the Italian explorer
* Columbus, Ohio, capital of the U.S. state of Ohio
Columbus may also refer to:
Places ...
expeditions, where Luis De Torres
Luis de Torres (died 1493) was Christopher Columbus's interpreter on his first voyage to America.
De Torres was a converso, apparently born Yosef ben HaLevi HaIvri chosen by Columbus for his knowledge of Hebrew, Chaldaic, and Arabic. After arriv ...
, an interpreter and member of Columbus' party, is believed to have been secretly Jewish. Today, there is a small community with about 200 members, according to census data, although higher estimates place this figure at 300.
Muslims also have a minority presence. While some slaves and free Africans in the colonial era were Muslim, the religion was eradicated until around the 1970s, when it experienced a revival. Today, there are about 300 Muslims.
There are also smaller communities of Baháʼís, Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
s, Rastafari
Rastafari, sometimes called Rastafarianism, is a religion that developed in Jamaica during the 1930s. It is classified as both a new religious movement and a social movement by scholars of religion. There is no central authority in control of ...
ans and practitioners of traditional African religions such as Obeah.
Languages
The official language of The Bahamas is English. Many people speak an English-based creole language called ''Bahamian dialect'' (known simply as "dialect") or "Bahamianese". Laurente Gibbs, a Bahamian writer and actor, was the first to coin the latter name in a poem and has since promoted its usage. Both are used as autoglossonyms.Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole (; ht, kreyòl ayisyen, links=no, ; french: créole haïtien, links=no, ), commonly referred to as simply ''Creole'', or ''Kreyòl'' in the Creole language, is a French-based creole language spoken by 10–12million people wor ...
, a French-based creole language
A French creole, or French-based creole language, is a creole for which French is the lexifier. Most often this lexifier is not modern French but rather a 17th- or 18th-century koiné of French from Paris, the French Atlantic harbors, and the ...
is spoken by Haitians and their descendants, who make up of about 25% of the total population. It is known simply as ''Creole'' to differentiate it from Bahamian English.
Education
According to 2011 estimates, 95% of the Bahamian adult population are literate. The University of the Bahamas (UB) is the national higher education/tertiary system. Offering baccalaureate, masters and associate degrees, UB has three campuses, and teaching and research centres throughout The Bahamas. The University of the Bahamas was chartered on 10 November 2016.Culture
 The culture of the islands is a mixture of African (Afro-Bahamians being the largest ethnicity), British and
The culture of the islands is a mixture of African (Afro-Bahamians being the largest ethnicity), British and American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
due to historical family ties, migration of freed slaves from the United States to The Bahamas, and as the dominant country in the region and source of most tourists).
A form of African-based folk magic is practiced by some Bahamians, mainly in the Family Islands (out-islands) of The Bahamas. The practice of obeah is illegal in The Bahamas and punishable in law.
In the outer islands also called Family Islands, handicrafts include basketry made from palm fronds. This material, commonly called "straw", is plaited into hats and bags that are popular tourist items.
Junkanoo is a traditional Afro-Bahamian street parade of 'rushing', music, dance and art held in Nassau (and a few other settlements) every Boxing Day
Boxing Day is a holiday celebrated after Christmas Day, occurring on the second day of Christmastide (26 December). Though it originated as a holiday to give gifts to the poor, today Boxing Day is primarily known as a shopping holiday. It ...
and New Year's Day
New Year's Day is a festival observed in most of the world on 1 January, the first day of the year in the modern Gregorian calendar. 1 January is also New Year's Day on the Julian calendar, but this is not the same day as the Gregorian one. Wh ...
. Junkanoo is also used to celebrate other holidays and events such as Emancipation Day.
Regatta
Boat racing is a sport in which boats, or other types of watercraft, race on water. Boat racing powered by oars is recorded as having occurred in ancient Egypt, and it is likely that people have engaged in races involving boats and other wate ...
s are important social events in many family island settlements. They usually feature one or more days of sailing by old-fashioned work boats
A boat is a watercraft of a large range of types and sizes, but generally smaller than a ship, which is distinguished by its larger size, shape, cargo or passenger capacity, or its ability to carry boats.
Small boats are typically found on inl ...
, as well as an onshore festival.
Many dishes are associated with Bahamian cuisine, which reflects Caribbean, African and European influences. Some settlements have festivals associated with the traditional crop or food of that area, such as the "Pineapple Fest" in Gregory Town, Eleuthera or the "Crab Fest" on Andros. Other significant traditions include story telling.
Bahamians have created a rich literature of poetry, short stories, plays and short fictional works. Common themes in these works are (1) an awareness of change, (2) a striving for sophistication, (3) a search for identity, (4) nostalgia for the old ways and (5) an appreciation of beauty. Some major writers are Susan Wallace, Percival Miller, Robert Johnson, Raymond Brown, O.M. Smith, William Johnson, Eddie Minnis and Winston Saunders
Winston Vernon Saunders, CMG (3 October 1941 – 25 November 2006) was a Bahamian educator, lawyer, actor, playwright and cultural director.
Early life
In his youth, Saunders attended Government High School in Nassau, Bahamas, later becoming h ...
.
Bahamas culture is rich with beliefs, traditions, folklore and legend. The best-known folklore and legends in The Bahamas include the lusca and chickcharney
The chickcharney (also known as the chickcharnie or chickcharnee) is a legendary creature in the folklore of Andros Island in the Bahama Islands. It is said to live in the forests, is furry or feathered, and about tall, with an ugly appearance r ...
creatures of Andros, Pretty Molly on Exuma Bahamas and the Lost City of Atlantis on Bimini Bahamas.
Symbols
Forward, Upward, Onward Together.The national flower of The Bahamas is the
yellow elder
''Tecoma stans'' is a species of flowering perennial shrub in the trumpet vine family, Bignoniaceae, that is native to the Americas. Common names include yellow trumpetbush, yellow bells, yellow elder, ginger-thomas. ''Tecoma stans'' is the o ...
, as it is endemic to the Bahama islands and it blooms throughout the year.
Selection of the yellow elder over many other flowers was made through the combined popular vote of members of all four of New Providence's garden clubs of the 1970s—the Nassau Garden Club, the Carver Garden Club, the International Garden Club and the YWCA Garden Club. They reasoned that other flowers grown there—such as the bougainvillea, hibiscus and poinciana—had already been chosen as the national flowers of other countries. The yellow elder, on the other hand, was unclaimed by other countries (although it is now also the national flower of the United States Virgin Islands) and also the yellow elder is native to the family islands.
Sport
 Sport is a significant part of Bahamian culture. The national sport is
Sport is a significant part of Bahamian culture. The national sport is cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by striki ...
, which has been played in The Bahamas from 1846 and is the oldest sport played in the country today. The Bahamas Cricket Association
Bahamas Cricket Association is the official governing body of the sport of cricket in The Bahamas. Bahamas Cricket Association is The Bahamas's representative at the International Cricket Council and is an associate member and has been a member ...
was formed in 1936, and from the 1940s to the 1970s, cricket was played amongst many Bahamians. Bahamas is not a part of the West Indies Cricket Board, so players are not eligible to play for the West Indies cricket team. The late 1970s saw the game begin to decline in the country as teachers, who had previously come from the United Kingdom with a passion for cricket, were replaced by teachers who had been trained in the United States. The Bahamian physical education teachers had no knowledge of the game and instead taught track and field, basketball, baseball, softball, volleyball and Association football where primary and high schools compete against each other. Today cricket is still enjoyed by a few locals and immigrants in the country, usually from Jamaica, Guyana
Guyana ( or ), officially the Cooperative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern mainland of South America. Guyana is an indigenous word which means "Land of Many Waters". The capital city is Georgetown. Guyana is bordered by the ...
, Trinidad and Barbados. Cricket is played on Saturdays and Sundays at Windsor Park and Haynes Oval in Nassau, Bahamas
Nassau ( ) is the capital and largest city of the Bahamas. With a population of 274,400 as of 2016, or just over 70% of the entire population of the Bahamas, Nassau is commonly defined as a primate city, dwarfing all other towns in the country. ...
. Whiles the main and only cricket grounds on Grand Bahama
Grand Bahama is the northernmost of the islands of the Bahamas, with the town of West End located east of Palm Beach, Florida. It is the third largest island in the Bahamas island chain of approximately 700 islands and 2,400 cays. The island is ...
is the Lucaya Cricket Oval.
The only other sporting event that began before cricket was horse racing
Horse racing is an equestrian performance sport, typically involving two or more horses ridden by jockeys (or sometimes driven without riders) over a set distance for competition. It is one of the most ancient of all sports, as its basic p ...
, which started in 1796. The most popular spectator sports are those imported from the United States, such as basketball, American football, and baseball, rather than from the British Isles, due to the country's close proximity to the United States, unlike their other Caribbean counterparts, where cricket, soccer
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 players who primarily use their feet to propel the ball around a rectangular field called a pitch. The objective of the game is ...
, and netball have proven to be more popular.
Over the years American football has become much more popular than soccer. Leagues for teens and adults have been developed by the Bahamas American Football Federation. However soccer, as it is commonly known in the country, is still a very popular sport amongst high school pupils. Leagues are governed by the Bahamas Football Association. In 2013 the Bahamian government has been working closely with Tottenham Hotspur of London to promote the sport in the country as well as promoting The Bahamas in the European market. In 2013, 'Spurs' became the first Premier League club to play an exhibition match in The Bahamas, facing the Jamaica men's national team. Joe Lewis, the owner of the club, is based in The Bahamas.
Other popular sports are swimming, tennis and boxing, where Bahamians have enjoyed some degree of success at the international level. Other sports such as golf, rugby league, rugby union, beach soccer
Beach soccer, also known as beach football, sand football or beasal, is a variant of association football played on a beach or some form of sand.
Whilst football has been played informally on beaches, the introduction of ''beach soccer'' was an a ...
, and netball are considered growing sports. Athletics, commonly known as 'track and field' in the country, is the most successful sport by far amongst Bahamians. Bahamians have a strong tradition in the sprints
Sprint may refer to:
Aerospace
*Spring WS202 Sprint, a Canadian aircraft design
*Sprint (missile), an anti-ballistic missile
Automotive and motorcycle
* Alfa Romeo Sprint, automobile produced by Alfa Romeo between 1976 and 1989
*Chevrolet Sprint ...
and jumps. Track and field is probably the most popular spectator sport in the country next to basketball due to their success over the years. Triathlons are gaining popularity in Nassau and the Family Islands.
The Bahamas first participated at the Olympic Games in 1952, and has sent athletes to compete in every Summer Olympic Games
The Summer Olympic Games (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques d'été), also known as the Games of the Olympiad, and often referred to as the Summer Olympics, is a major international multi-sport event normally held once every four years. The inau ...
since then, except when they participated in the American-led boycott of the 1980 Summer Olympics
The 1980 Summer Olympics boycott was one part of a number of actions initiated by the United States to protest against the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan. The Soviet Union, which hosted the 1980 Summer Olympics in Moscow, and its allies late ...
. The nation has never participated in any Winter Olympic Games. Bahamian athletes have won a total of sixteen medals, all in athletics and sailing. The Bahamas has won more Olympic medals than any other country with a population under one million.
The Bahamas were hosts of the first men's senior FIFA tournament to be staged in the Caribbean, the 2017 FIFA Beach Soccer World Cup
The 2017 FIFA Beach Soccer World Cup was the ninth edition of the FIFA Beach Soccer World Cup, the premier international beach soccer championship contested by the men's national teams of the member associations of FIFA. Overall, this was the 19t ...
. The Bahamas also hosted the first 3 editions of the IAAF World Relays. The nation also hosted the 2017 Commonwealth Youth Games
The 2017 Commonwealth Youth Games, officially known as the VI Commonwealth Youth Games, and commonly known as Bahamas 2017, or Nassau 2017, was the sixth edition of the Commonwealth Youth Games which started in 2000. The games were held from 19 to ...
, along with annual events Bahamas Bowl and Battle 4 Atlantis
The Battle 4 Atlantis is an early-season college basketball tournament. It takes place at Atlantis Paradise Island on Paradise Island in The Bahamas, on the week of the US holiday of Thanksgiving. For sponsorship purposes, the tournament is o ...
.
See also
*Outline of the Bahamas
The location of The Bahamas
An enlargeable relief map of the Commonwealth of The Bahamas
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to The Bahamas:
Commonwealth of The Bahamas – sovereign island coun ...
*Index of Bahamas-related articles
Index (or its plural form indices) may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities
* Index (''A Certain Magical Index''), a character in the light novel series ''A Certain Magical Index''
* The Index, an item on a Halo megastru ...
References
Citations
Sources
* *Further reading
;General history *Cash Philip ''et al.'' (Don Maples, Alison Packer). ''The Making of The Bahamas: A History for Schools''. London: Collins, 1978. *Miller, Hubert W. ''The Colonization of The Bahamas, 1647–1670, The William and Mary Quarterly'' 2 no.1 (January 1945): 33–46. *Craton, Michael. ''A History of The Bahamas''. London: Collins, 1962. *Craton, Michael and Saunders, Gail. ''Islanders in the Stream: A History of the Bahamian People''. Athens: University of Georgia Press, 1992 *Collinwood, Dean. "Columbus and the Discovery of Self", ''Weber Studies'', Vol. 9 No. 3 (Fall) 1992: 29–44. *Dodge, Steve. ''Abaco: The History of an Out Island and its Cays'', Tropic Isle Publications, 1983. *Dodge, Steve. ''The Compleat Guide to Nassau'', White Sound Press, 1987. *Boultbee, Paul G. ''The Bahamas.'' Oxford: ABC-Clio Press, 1990. *Wood, David E., comp., ''A Guide to Selected Sources to the History of the Seminole Settlements of Red Bays, Andros, 1817–1980'', Nassau: Department of Archives ;Economic history *Johnson, Howard. ''The Bahamas in Slavery and Freedom''. Kingston: Ian Randle Publishing, 1991. *Johnson, Howard. ''The Bahamas from Slavery to Servitude, 1783–1933''. Gainesville: University of Florida Press, 1996. *Alan A. Block. ''Masters of Paradise'', New Brunswick and London, Transaction Publishers, 1998. *Storr, Virgil H. ''Enterprising Slaves and Master Pirates: Understanding Economic Life in the Bahamas''. New York: Peter Lang, 2004. ;Social history *Johnson, Wittington B. ''Race Relations in the Bahamas, 1784–1834: The Nonviolent Transformation from a Slave to a Free Society'', Fayetteville: University of Arkansas, 2000. *Shirley, Paul. "Tek Force Wid Force", ''History Today'' 54, no. 41 (April 2004): 30–35. *Saunders, Gail. ''The Social Life in the Bahamas 1880s–1920s''. Nassau: Media Publishing, 1996. *Saunders, Gail. ''Bahamas Society After Emancipation''. Kingston: Ian Randle Publishing, 1990. *Curry, Jimmy. ''Filthy Rich Gangster/First Bahamian Movie''. Movie Mogul Pictures: 1996. *Curry, Jimmy. ''To the Rescue/First Bahamian Rap/Hip Hop Song''. Royal Crown Records, 1985. *Collinwood, Dean. ''The Bahamas Between Worlds'', White Sound Press, 1989. *Collinwood, Dean and Steve Dodge. ''Modern Bahamian Society'', Caribbean Books, 1989. *Dodge, Steve, Robert McIntire and Dean Collinwood. ''The Bahamas Index'', White Sound Press, 1989. *Collinwood, Dean. "The Bahamas", in ''The Whole World Handbook 1992–1995'', 12th ed., New York: St. Martin's Press, 1994. *Collinwood, Dean. "The Bahamas", chapters in Jack W. Hopkins, ed., ''Latin American and Caribbean Contemporary Record'', Vols. 1,2,3,4, Holmes and Meier Publishers, 1983, 1984, 1985, 1986. *Collinwood, Dean. "Problems of Research and Training in Small Islands with a Social Science Faculty", in ''Social Science in Latin America and the Caribbean'', UNESCO, No. 48, 1982. *Collinwood, Dean and Rick Phillips, "The National Literature of the New Bahamas", ''Weber Studies'', Vol.7, No. 1 (Spring) 1990: 43–62. *Collinwood, Dean. "Writers, Social Scientists and Sexual Norms in the Caribbean", ''Tsuda Review'', No. 31 (November) 1986: 45–57. *Collinwood, Dean. "Terra Incognita: Research on the Modern Bahamian Society", ''Journal of Caribbean Studies'', Vol. 1, Nos. 2–3 (Winter) 1981: 284–297. *Collinwood, Dean and Steve Dodge. "Political Leadership in the Bahamas", The Bahamas Research Institute, No.1, May 1987.External links
* * *The Bahamas
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' *
The Bahamas
from the BBC News
Key Development Forecasts for The Bahamas
from
International Futures
International Futures (IFs) is a global integrated assessment modelling, integrated assessment model designed to help with thinking strategically and systematically about key global systems (economic, demographic, education, health, environment, ...
Maps of the Bahamas from the American Geographical Society Library
newspaper, 1849–1922, as
Open Access
Open access (OA) is a set of principles and a range of practices through which research outputs are distributed online, free of access charges or other barriers. With open access strictly defined (according to the 2001 definition), or libre op ...
from the Digital Library of the Caribbean
{{DEFAULTSORT:Bahamas
1970s establishments in the Caribbean
1973 establishments in North America
Countries in the Caribbean
Countries in North America
Archipelagoes of the Atlantic Ocean
English-speaking countries and territories
Former English colonies
Island countries
Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations
Member states of the Caribbean Community
Member states of the United Nations
Populated places established in 1647
Small Island Developing States
States and territories established in 1973