|
Acklins
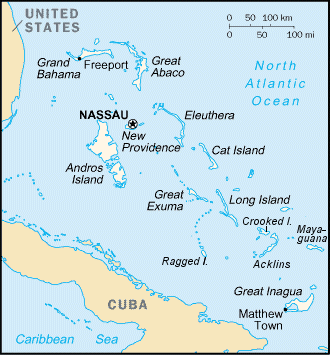
Acklins is an island and district of the Bahamas. It is one of a group of islands arranged along a large, shallow lagoon called the Bight of Acklins, of which the largest are Crooked Island () in the north and Acklins () in the southeast, and the smaller are Long Cay (once known as Fortune Island, ()) in the northwest, and Castle Island in the south. Etymology The indigenous Lucayan people called the Acklins as ''Yabaque'', meaning "large western land". History The islands were settled by American Loyalists in the late 1780s who set up cotton plantations maintained by over 1,000 slaves. After the abolition of slavery in the British Empire the plantations became uneconomical, and the replacement income from sponge diving has now dwindled as well with the rest of the natural sponge industry after the advent of synthetics. The inhabitants now live by fishing and small-scale farming. Although Acklins Island has relatively few historical landmarks, there are some notewo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucayan People
The Lucayan people ( ) were the original residents of The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands before the European colonisation of the Americas. They were a branch of the Taínos who inhabited most of the Caribbean islands at the time. The Lucayans were the first Indigenous Americans encountered by Christopher Columbus (in October 1492). Shortly after contact, the Spanish kidnapped and enslaved Lucayans with the displacement culminating in the complete eradication of the Lucayan people from the Bahamas by 1520. The name "Lucayan" is an Anglicization of the Spanish ''Lucayos'', itself a hispanicization derived from the Lucayan ''Lukku-Cairi'', which the people used for themselves, meaning "people of the islands". The Taíno word for "island", ''cairi'', became ''cayo'' in Spanish and " cay" in English pelled "key" in American English Some crania and artifacts of " Ciboney type" were reportedly found on Andros Island, but if some Ciboney did reach the Bahamas ahead of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts Of The Bahamas
Local government in the Bahamas exists at two levels: 32 districts and 41 towns. The boundaries of districts are defined by the First Schedule of The Bahamas Local Government Act 1996 (as amended by law and declarations of the Minister responsible for Family Island Affairs), defined with reference to parliamentary constituency boundaries. The Second Schedule lists 13 districts which are divided into town areas. Towns are governed by directly elected town committees. Second Schedule districts are governed by nine-person district councils composed of the chairs of the town committees, and if numerically required, additional people elected by the town committees. The 19 Third Schedule districts are unitary authorities which cannot be divided into towns. They are governed by nine-person district councils which are directly elected by voters. The powers of Second Schedule and Third Schedule councils are slightly different, and the Third Schedule district known as the City of Free ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plana Cays
The Plana Cays are a group of two small uninhabited islands in the southern Bahama Islands, located east of Acklins Island and west of Mayaguana Island. The indigenous Lucayan people called the islands ''Amaguaya'', meaning "toward the middle lands". The eastern cay was the last natural habitat of the Bahamian Hutia, a species of rabbit-sized rodent Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the Order (biology), order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and Mandible, lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal specie .... It was thought to be extinct until 1966, when a population was found on the Plana Cays by biologist Garrett Clough. Hutias have since been transplanted from the Plana Cays to other parts of the Bahamas. The Plana Cays have been suggested as the first landfall of Christopher Columbus in the New World. References * Acklins Uninhabited islands of the Bahamas {{Bahamas-g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring Point, Bahamas
Spring Point is a town in Acklins, Bahamas and serves as its capital. As of 2010, it had a population of 36. This town's primary transport methods are boat and airplane, with Spring Point Airport serving its area. Data current as of October 2006. Source: DAFIF. References Populated places in the Bahamas {{Bahamas-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crooked Island, Bahamas
Crooked Island is an island and district, part of a group of Bahamian islands defining a large, shallow lagoon called the Bight of Acklins, of which the largest are Crooked Island in the north and Acklins in the south-east, and the smaller are Long Cay (once known as Fortune Island) in the north-west, and Castle Island in the south. Etymology The indigenous Lucayan people called the island ''Jumento'', meaning "upper land of the middle distance". Meanwhile, the Spaniard explorers had named the island ''Isabella''. History The islands were settled by American Loyalists in the late 1780s who set cotton plantations using over 1,000 slaves. After the abolition of slavery in the British Empire these became uneconomical, and the replacement income from sponge diving has now dwindled as well. The inhabitants now live by fishing and small-scale farming. It is believed that the first Post Office in the Bahamas was at Pitts Town on Crooked Island. Population The main town in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring Point Airport
Spring Point Airport is an airport serving Spring Point on Acklins Island in The Bahamas. Bahamasair flies to Spring Point Airport, and it is the only airline that flies here. Facilities The airport resides at an elevation of above mean sea level. It has one runway designated 13/31 with an asphalt Asphalt most often refers to: * Bitumen, also known as "liquid asphalt cement" or simply "asphalt", a viscous form of petroleum mainly used as a binder in asphalt concrete * Asphalt concrete, a mixture of bitumen with coarse and fine aggregates, u ... surface measuring . Airlines and destinations References External links * * Airports in the Bahamas Acklins {{Bahamas-struct-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MICAL (Bahamas Parliament Constituency)
Mayaguana, Inagua, Crooked Island, Acklins and Long Cay, abbreviated as MICAL, is a parliamentary constituency represented in the House of Assembly of the Bahamas. Geography The constituency name is an acronym An acronym is a type of abbreviation consisting of a phrase whose only pronounced elements are the initial letters or initial sounds of words inside that phrase. Acronyms are often spelled with the initial Letter (alphabet), letter of each wor ... of the five islands it contains that form the south-eastern tip of the Bahamas: Mayaguana, Inagua, Crooked Island, Acklins, and Long Cay. The constituency is geographically large and rural. Members of Parliament Election results References See also * List of National Assembly constituencies of The Bahamas Constituencies of the Bahamas Year of establishment missing {{Bahamas-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Cay
Long Cay (formerly known as Fortune Island; ; ; ) is an 8-square-mile (21 km2) island in the Bahamas in an atoll that includes Acklins Island and Crooked Island. Since 1999, it has also been one of the Third Schedule districts of The Bahamas. , its population was 29. Coordinates = 2235 North and 7422 West. Geography Long Cay lies to the west of a shallow lagoon called the Bight of Acklins and is an extension of the western arm of Crooked Island, separated from it by a channel about one mile wide. The main town is Albert Town, now largely a ghost town. Douglas Town was another former settlement only about 500 meters from Albert Town. Great Salt Pond lies in the middle of the island. The southernmost point is known as Windsor Point, called ''Cabo Hermoso'' by Christopher Columbus. History On 19 October 1492, Long Cay was discovered by Columbus on his first voyage to the New World, and he named it Isabela. Albert Town became a port in the sponge and salt industries and a port of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samana Cay
Samana Cay is a now uninhabited island in the Bahamas believed by some researchers to have been the location of Christopher Columbus's first landfall in the Americas on October 12, 1492. It is an islet in the eastern Bahamas, northeast of Acklins Island. About long and up to wide with an area of about it is bound by reefs. The verdant cay has long been uninhabited, but figurines, pottery shards, and other artifacts discovered there in the mid-1980s have been ascribed to Lucayan Indians, who lived on the cay around the time of Columbus's voyages. The indigenous people of the island on which Columbus first landed called it "Guanahani." Samana Cay was first proposed to be Guanahani by Gustavus Fox in 1882, but the predominant theory gives the honour to San Salvador Island. However, in 1986, Joseph Judge of ''National Geographic Magazine'' made different calculations based on extracts from Columbus's logs and argued for Samana Cay as the location, but his methodology has also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahamas
The Bahamas, officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an archipelagic and island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean. It contains 97 per cent of the archipelago's land area and 88 per cent of its population. It comprises more than 3,000 islands, cays and islets in the Atlantic Ocean, and is located north of Cuba and north-west of the island of Hispaniola (split between the Dominican Republic and Haiti) and the Turks and Caicos Islands, southeast of the U.S. state of Florida and east of the Florida Keys. The capital and largest city is Nassau on the island of New Providence. The Royal Bahamas Defence Force describes the Bahamas' territory as encompassing of ocean space. The Bahama islands were inhabited by the Arawak and Lucayans, a branch of the Arawakan- speaking Taíno, for many centuries. Christopher Columbus was the first European to see the islands, making his first landfall in the "New World" in 1492 when he landed on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahamian Hutia
The Bahamian hutia or Ingraham's hutia (''Geocapromys ingrahami'') is a small, furry, rat-like mammal found only in the Bahamas. About the size of a rabbit, it lives in burrows in forests or shrubland, emerging at night to feed on leaves, fruit, and other plant matter. It was believed extinct until rediscovery in 1964, and it remains the focus of conservation efforts. The Bahamian hutia is a member of the hutia subfamily ( Capromyinae), a group of rodents native to the Caribbean, many of which are endangered or extinct. Description The Bahamian hutia is a rat-like rodent with a short tail and a body-length of up to . Its fur varies in colour and can be black, brown, grey, white or reddish. Distribution and habitat The Bahamian hutia is endemic to the Bahamas. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forest, subtropical or tropical dry shrubland, and rocky areas. It was believed to be extinct until 1966, when biologist Garrett Clough found a relict populati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |