B-47 Stratojet on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Boeing B-47 Stratojet (Boeing company designation Model 450) is a retired American long- range, six-engined, turbojet-powered
 The USAF
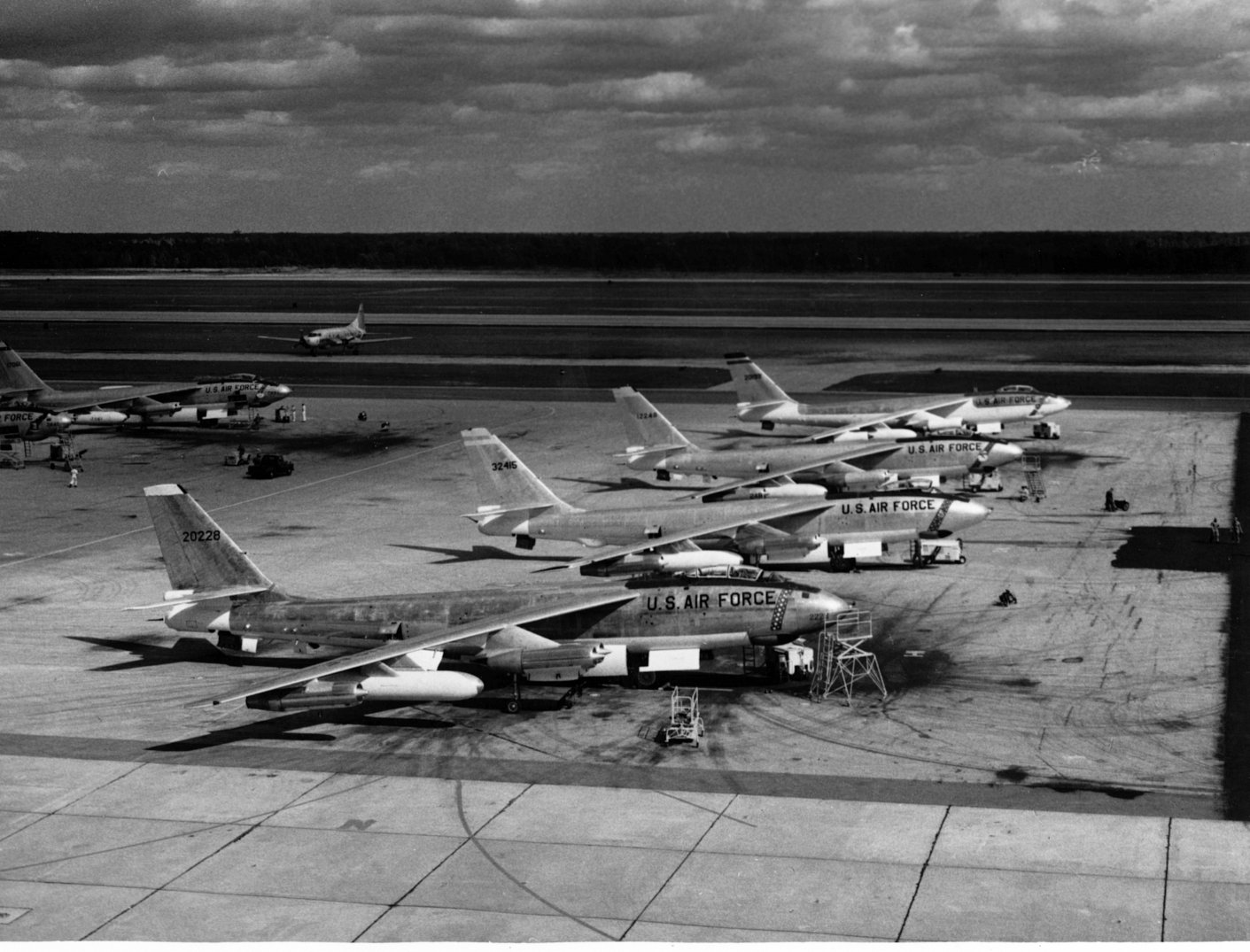
The USAF  Initial mission profiles included the loft bombing of nuclear weapons. As the training for this imposes repeated high stress on the aircraft, the airframe lifetime would have been severely limited by metal fatigue, and this maneuver was eliminated. Improved training led to a good safety record, and few crews felt the aircraft was unsafe or too demanding, but apparently there were some aircrews who had little affection for the B-47. Crew workload was high, having only three crew members to operate it.Fraser November 1949, pp. 141–142. Boeing's
Initial mission profiles included the loft bombing of nuclear weapons. As the training for this imposes repeated high stress on the aircraft, the airframe lifetime would have been severely limited by metal fatigue, and this maneuver was eliminated. Improved training led to a good safety record, and few crews felt the aircraft was unsafe or too demanding, but apparently there were some aircrews who had little affection for the B-47. Crew workload was high, having only three crew members to operate it.Fraser November 1949, pp. 141–142. Boeing's
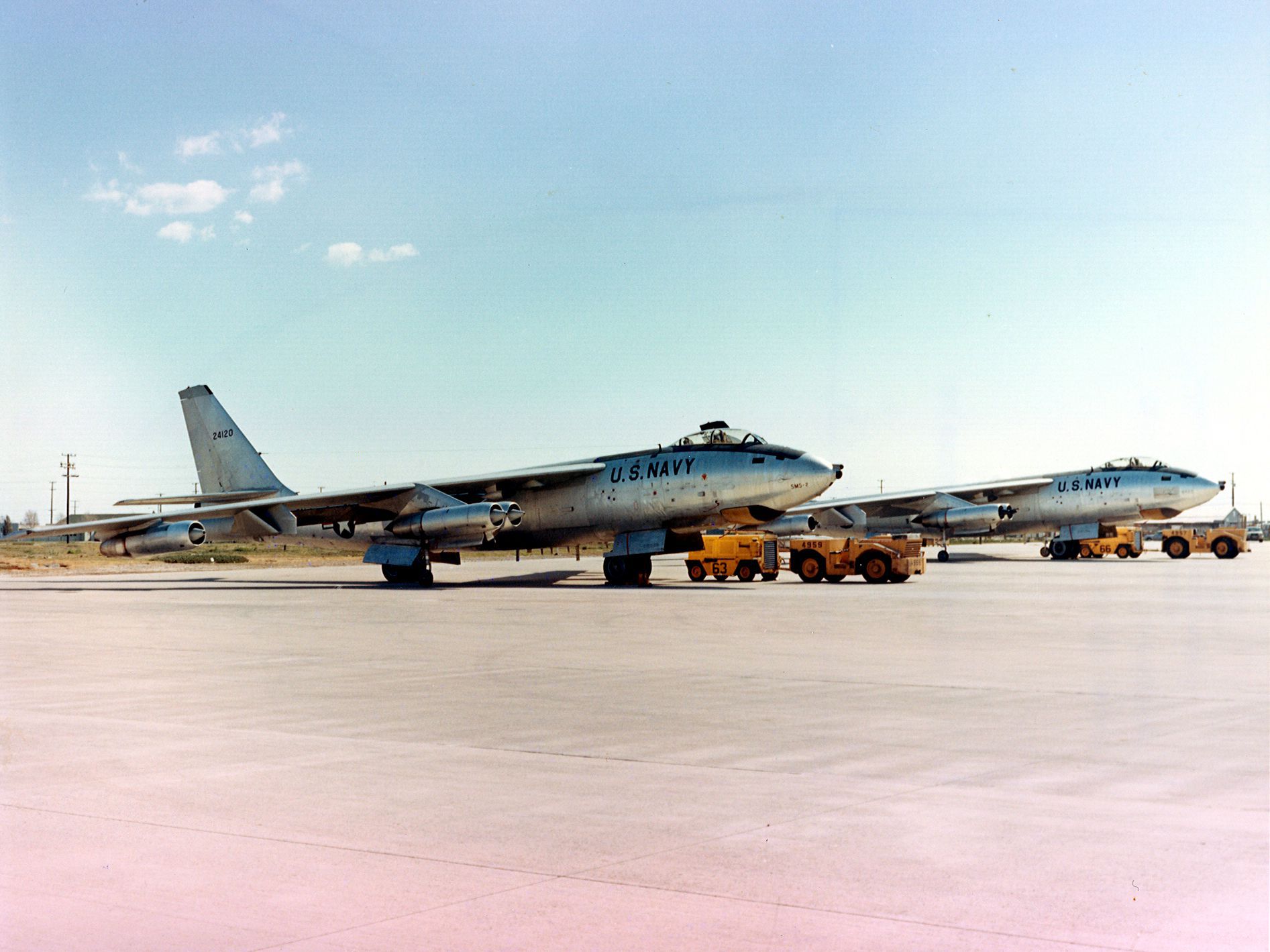
 Stress and fatigue incurred in low-altitude operations led to a number of wing failures and crashes, and an extensive refit program was begun in 1958 to strengthen the wing mountings. The program was known as "Milk Bottle", named after the big connecting pins that were replaced in the wing roots.
One of the more notable mishaps involving a B-47 occurred on 5 February 1958 near Savannah, Georgia, in the so-called
Stress and fatigue incurred in low-altitude operations led to a number of wing failures and crashes, and an extensive refit program was begun in 1958 to strengthen the wing mountings. The program was known as "Milk Bottle", named after the big connecting pins that were replaced in the wing roots.
One of the more notable mishaps involving a B-47 occurred on 5 February 1958 near Savannah, Georgia, in the so-called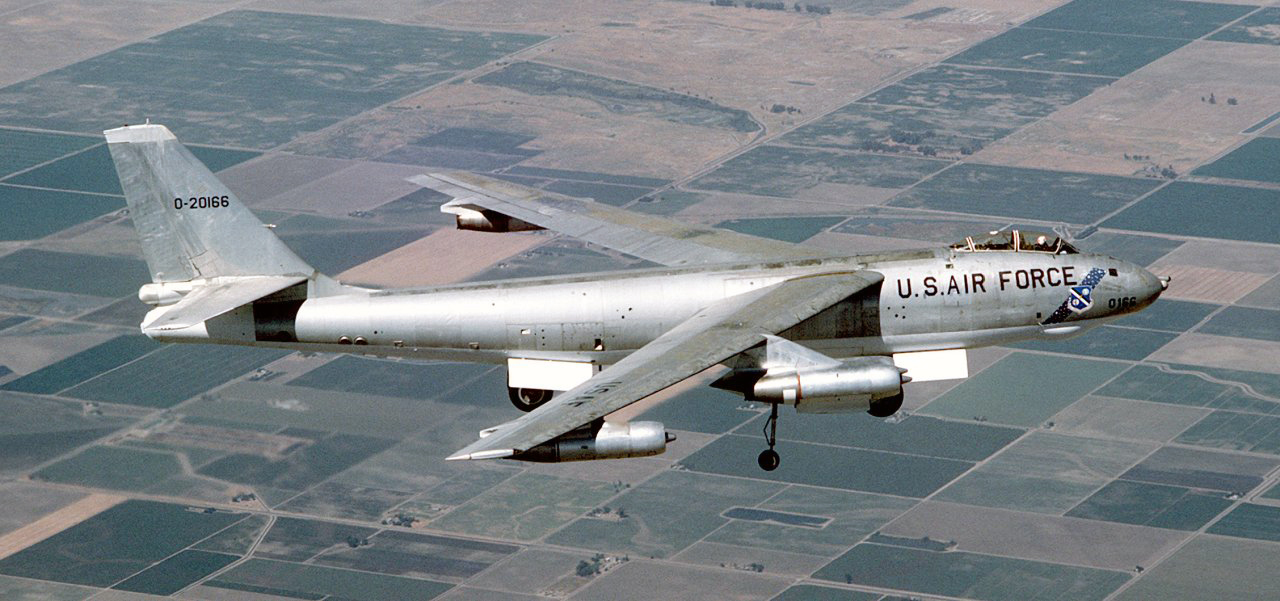  The final recorded flight of a B-47 was on 17 June 1986, when a B-47E was restored to flightworthy condition for a one-time ferry flight. This aircraft was flown from
The final recorded flight of a B-47 was on 17 June 1986, when a B-47E was restored to flightworthy condition for a one-time ferry flight. This aircraft was flown from
 :The first 10 aircraft were designated B-47A and were evaluation aircraft, the first delivered in December 1950. While the XB-47s had been built at Boeing's Seattle plant, all B-47s were built at a government-owned factory in Wichita, Kansas that had previously built B-29s. Their configuration was akin to the XB-47. All were powered by J47-GE-11 turbojets, offering the same thrust as the earlier J47-GE-3, and had built-in rocket-assisted-take-off ( RATO) bottles. Four were fitted with the K-2 bombing and navigation system (BNS), HD-21D autopilot, an analog computer, APS-23 radar, and a Y-4 or Y-4A bombsight. Two were fitted with the tail turret mounting two 20mm cannons; one of them used an Emerson A-2 fire control system (FCS), another a General Electric A-5 FCS. The eight other B-47As lacked defensive armament.
:The B-47As were fitted with ejection seats. The pilot and copilot ejected upward, while the navigator had a downward ejection seat built by
:The first 10 aircraft were designated B-47A and were evaluation aircraft, the first delivered in December 1950. While the XB-47s had been built at Boeing's Seattle plant, all B-47s were built at a government-owned factory in Wichita, Kansas that had previously built B-29s. Their configuration was akin to the XB-47. All were powered by J47-GE-11 turbojets, offering the same thrust as the earlier J47-GE-3, and had built-in rocket-assisted-take-off ( RATO) bottles. Four were fitted with the K-2 bombing and navigation system (BNS), HD-21D autopilot, an analog computer, APS-23 radar, and a Y-4 or Y-4A bombsight. Two were fitted with the tail turret mounting two 20mm cannons; one of them used an Emerson A-2 fire control system (FCS), another a General Electric A-5 FCS. The eight other B-47As lacked defensive armament.
:The B-47As were fitted with ejection seats. The pilot and copilot ejected upward, while the navigator had a downward ejection seat built by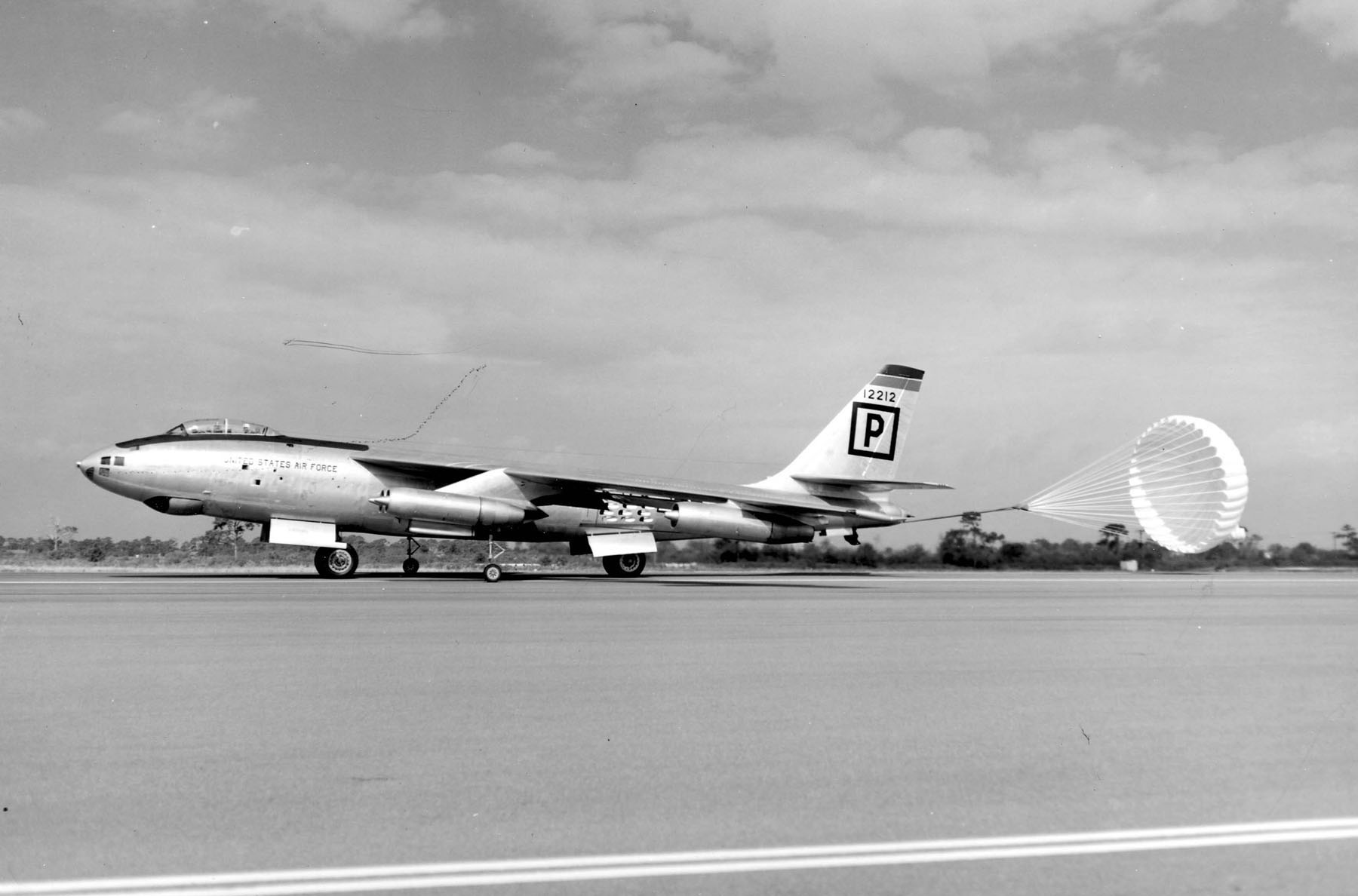  :In November 1949, prior to the B-47A's first flight, the USAF ordered 87 B-47Bs, the first operational model. The first flew on 26 April 1951. A total of 399 were built, including eight assembled by Lockheed and 10 assembled by Douglas using Boeing-built parts. To quickly receive B-47s in quantity, the USAF contracted both Lockheed and Douglas for additional production;Gunston and Gilchrist 1993, p. 44. Lockheed-built aircraft were designated by a "-LM (Lockheed Marietta)" suffix and Douglas-built aircraft given a "-DT (Douglas Tulsa)" suffix. Boeing production was designated by a "-BW (Boeing Wichita)" suffix, except for the Seattle-built XB-47s and B-47As, which had a "-BO" suffix.
:The initial 87 B-47Bs used the same J47-GE-11 engines as the B-47A, subsequent deliveries had uprated J47-GE-23 units with thrust; early aircraft were later retrofitted. It had a built-in RATO system, as used on the B-47A, along with full combat systems. Early aircraft retained the K-2 BNS installed on some B-47As, but most featured the K-4A BNS, incorporating an AN/APS-54 warning radar and an AN/APT-5 electronic countermeasures (ECM) system. The K-4A used a nose-mounted periscopic bombsight. Ejection seats were deleted as a weight reduction measure; a windbreak panel on the main door made for a difficult escape.
:The bomb bay was shorter than the B-47A's as nuclear weapons had shrunk in the interim; the B-47B could carry a larger bombload of up to . All B-47Bs had a tail turret with twin 20 mm (0.79 in) guns and the B-4 radar-guided FCS. Due to issues, this FCS was often replaced with an N-6 optical sight; the copilot could swivel his seat to face backward and sight the guns directly. A nose-mounted in-flight refueling (IFR) receptacle enabled flying boom refueling from KB-50 and KC-97 tankers, requiring the plexiglas nose cone's replacement by a metal nose cone with four small windows, two on either side of the nose. The B-47B was also fitted with a pair of jettisonable external tanks, carried between the inboard and outboard engine assemblies, with a capacity of . Another visible change was the vertical tailplane's squared-off top instead of a rounded top.
:Between 1955 and 1956, Boeing modified surviving B-47Bs from line numbers 235 to 399 to the B-47E standard under program ''High Noon''; this included fitting ejection seats. It was followed by the ''Ebb Tide'' program covering early line numbers from 1 to 234; this included 66 aircraft from the 135 to 234 batch to the same standard as the ''High Noon'' aircraft. Another 30 in the same range had additional modification as drone directors DB-47Bs, and the 1 to 134 range which had the same ''High Noon'' modification, but lacked some non-combat changes. Following these programs, they were sometimes referred to as B-47B-II.
;;YRB-47B
:The USAF considered building a specialized RB-47B reconnaissance variant, but schedule slips ensured that the RB-47E was the first such variant. As an interim measure, 91 B-47B bombers were fitted with a heated pod stowed in the forward bomb bay that housed eight cameras. These were designated YRB-47Bs and were capable of daylight reconnaissance only. Once the RB-47E arrived, they returned to the bomber role.
;;TB-47B
:A total of 66 of the 87 non-combat B-47Bs were re-designated TB-47B in 1953 to alleviate logistics problems due to different engines and systems. Most were used as trainers; some were modified for Air Training Command by Douglas at Tulsa under the ''Field Goal'' program, adding a fourth seat for an instructor and removing the tail turret. They were upgraded to B-47E standard in 1956 under the ''Ebb Tide'' program, joined by 41 more early build aircraft, also designated TB-47B. Used for training through the 1950s.
;;MB-47B
:With the introduction of the
:In November 1949, prior to the B-47A's first flight, the USAF ordered 87 B-47Bs, the first operational model. The first flew on 26 April 1951. A total of 399 were built, including eight assembled by Lockheed and 10 assembled by Douglas using Boeing-built parts. To quickly receive B-47s in quantity, the USAF contracted both Lockheed and Douglas for additional production;Gunston and Gilchrist 1993, p. 44. Lockheed-built aircraft were designated by a "-LM (Lockheed Marietta)" suffix and Douglas-built aircraft given a "-DT (Douglas Tulsa)" suffix. Boeing production was designated by a "-BW (Boeing Wichita)" suffix, except for the Seattle-built XB-47s and B-47As, which had a "-BO" suffix.
:The initial 87 B-47Bs used the same J47-GE-11 engines as the B-47A, subsequent deliveries had uprated J47-GE-23 units with thrust; early aircraft were later retrofitted. It had a built-in RATO system, as used on the B-47A, along with full combat systems. Early aircraft retained the K-2 BNS installed on some B-47As, but most featured the K-4A BNS, incorporating an AN/APS-54 warning radar and an AN/APT-5 electronic countermeasures (ECM) system. The K-4A used a nose-mounted periscopic bombsight. Ejection seats were deleted as a weight reduction measure; a windbreak panel on the main door made for a difficult escape.
:The bomb bay was shorter than the B-47A's as nuclear weapons had shrunk in the interim; the B-47B could carry a larger bombload of up to . All B-47Bs had a tail turret with twin 20 mm (0.79 in) guns and the B-4 radar-guided FCS. Due to issues, this FCS was often replaced with an N-6 optical sight; the copilot could swivel his seat to face backward and sight the guns directly. A nose-mounted in-flight refueling (IFR) receptacle enabled flying boom refueling from KB-50 and KC-97 tankers, requiring the plexiglas nose cone's replacement by a metal nose cone with four small windows, two on either side of the nose. The B-47B was also fitted with a pair of jettisonable external tanks, carried between the inboard and outboard engine assemblies, with a capacity of . Another visible change was the vertical tailplane's squared-off top instead of a rounded top.
:Between 1955 and 1956, Boeing modified surviving B-47Bs from line numbers 235 to 399 to the B-47E standard under program ''High Noon''; this included fitting ejection seats. It was followed by the ''Ebb Tide'' program covering early line numbers from 1 to 234; this included 66 aircraft from the 135 to 234 batch to the same standard as the ''High Noon'' aircraft. Another 30 in the same range had additional modification as drone directors DB-47Bs, and the 1 to 134 range which had the same ''High Noon'' modification, but lacked some non-combat changes. Following these programs, they were sometimes referred to as B-47B-II.
;;YRB-47B
:The USAF considered building a specialized RB-47B reconnaissance variant, but schedule slips ensured that the RB-47E was the first such variant. As an interim measure, 91 B-47B bombers were fitted with a heated pod stowed in the forward bomb bay that housed eight cameras. These were designated YRB-47Bs and were capable of daylight reconnaissance only. Once the RB-47E arrived, they returned to the bomber role.
;;TB-47B
:A total of 66 of the 87 non-combat B-47Bs were re-designated TB-47B in 1953 to alleviate logistics problems due to different engines and systems. Most were used as trainers; some were modified for Air Training Command by Douglas at Tulsa under the ''Field Goal'' program, adding a fourth seat for an instructor and removing the tail turret. They were upgraded to B-47E standard in 1956 under the ''Ebb Tide'' program, joined by 41 more early build aircraft, also designated TB-47B. Used for training through the 1950s.
;;MB-47B
:With the introduction of the  :A four-engined variant of the B-47, the YB-47C, was proposed by Boeing in 1950 to be powered by four Allison J35-A-23 turbojet engines, providing thrust each, in place of the six GE J47s. The J35 was being developed at the time, and was provisionally rated at (with afterburner) or thrust without AB. Thus 4 * 8500 = using that engine, as compared to 6 * = in the production B-47, making it lighter, simpler and more powerful.Jones 1969, . J71-A-5 A contract was signed in January 1950 for the rework of one B-47B. The first flight was projected for April 1951.
:Due to the J35's less-than-expected performance and delays, other engines were considered, such as the proposed Allison J71, however engine problems meant that it was not feasible for the by-then redesignated B-56A. The Pratt & Whitney J57, eventually rated at thrust, was also considered, but was still in development. The Boeing B-52 Stratofortress, which was being concurrently developed, had priority for this engine. Thus, the B-56 was cancelled in December 1952 before the prototype's conversion had started. The donor fuselage intended for the XB-56 was reused as a ground instructional airframe.
:A four-engined variant of the B-47, the YB-47C, was proposed by Boeing in 1950 to be powered by four Allison J35-A-23 turbojet engines, providing thrust each, in place of the six GE J47s. The J35 was being developed at the time, and was provisionally rated at (with afterburner) or thrust without AB. Thus 4 * 8500 = using that engine, as compared to 6 * = in the production B-47, making it lighter, simpler and more powerful.Jones 1969, . J71-A-5 A contract was signed in January 1950 for the rework of one B-47B. The first flight was projected for April 1951.
:Due to the J35's less-than-expected performance and delays, other engines were considered, such as the proposed Allison J71, however engine problems meant that it was not feasible for the by-then redesignated B-56A. The Pratt & Whitney J57, eventually rated at thrust, was also considered, but was still in development. The Boeing B-52 Stratofortress, which was being concurrently developed, had priority for this engine. Thus, the B-56 was cancelled in December 1952 before the prototype's conversion had started. The donor fuselage intended for the XB-56 was reused as a ground instructional airframe.
 ;XB-47D
:Starting in 1951, two XB-47Ds were modified from B-47Bs as experimental platforms, replacing each inboard two-jet pod with a Wright YT49-W-1 turboprop engine spinning a huge four-bladed prop.Natola 2002, pp. 38–42. Engine development issues delayed the XB-47D's first flight until 26 August 1955. Performance was comparable to a conventional B-47, and its reversible propellers shortened the landing roll, but the idea was not pursued.
;B-47E
;XB-47D
:Starting in 1951, two XB-47Ds were modified from B-47Bs as experimental platforms, replacing each inboard two-jet pod with a Wright YT49-W-1 turboprop engine spinning a huge four-bladed prop.Natola 2002, pp. 38–42. Engine development issues delayed the XB-47D's first flight until 26 August 1955. Performance was comparable to a conventional B-47, and its reversible propellers shortened the landing roll, but the idea was not pursued.
;B-47E
 :The designations B-47C and B-47D applied to variants that were never produced, thus the next production model was the definitive B-47E, first flying on 30 January 1953. Four "blocks" or "phases" were built, each incorporating refinements on the previous block; changes sometimes occurred mid-block. The B-47 incorporated the radar-controlled rear tail turret. A total of 1,341 B-47Es were produced; 691 built by Boeing, 386 built by Lockheed, and 264 built by Douglas. Most B-47Bs were rebuilt to B-47E standards and given the designation of B-47B-II, though they were often called B-47Es.
:Early B-47E-Is had J47-GE-25 turbojets with thrust, these were changed to J47-GE-25A engines with water-
:The designations B-47C and B-47D applied to variants that were never produced, thus the next production model was the definitive B-47E, first flying on 30 January 1953. Four "blocks" or "phases" were built, each incorporating refinements on the previous block; changes sometimes occurred mid-block. The B-47 incorporated the radar-controlled rear tail turret. A total of 1,341 B-47Es were produced; 691 built by Boeing, 386 built by Lockheed, and 264 built by Douglas. Most B-47Bs were rebuilt to B-47E standards and given the designation of B-47B-II, though they were often called B-47Es.
:Early B-47E-Is had J47-GE-25 turbojets with thrust, these were changed to J47-GE-25A engines with water- :The B-47E was the basis for several reconnaissance models, the only B-47s to see anything resembling combat. They operated from most airfields that gave access to the USSR and often probed Soviet airspace. Boeing built 240 RB-47Es, similar to the B-47E but with a nose stretched by , giving an arguably more elegant appearance. The long nose accommodated up to 11 cameras, possibly including an O-15 radar camera for low-altitude work, a forward oblique camera for low-altitude work, a K-17 trimetrogon (three-angle) camera for panoramic shots and K-36 telescopic cameras. Cameras were controlled by the "navigator-photographer". Photoflash
:The B-47E was the basis for several reconnaissance models, the only B-47s to see anything resembling combat. They operated from most airfields that gave access to the USSR and often probed Soviet airspace. Boeing built 240 RB-47Es, similar to the B-47E but with a nose stretched by , giving an arguably more elegant appearance. The long nose accommodated up to 11 cameras, possibly including an O-15 radar camera for low-altitude work, a forward oblique camera for low-altitude work, a K-17 trimetrogon (three-angle) camera for panoramic shots and K-36 telescopic cameras. Cameras were controlled by the "navigator-photographer". Photoflash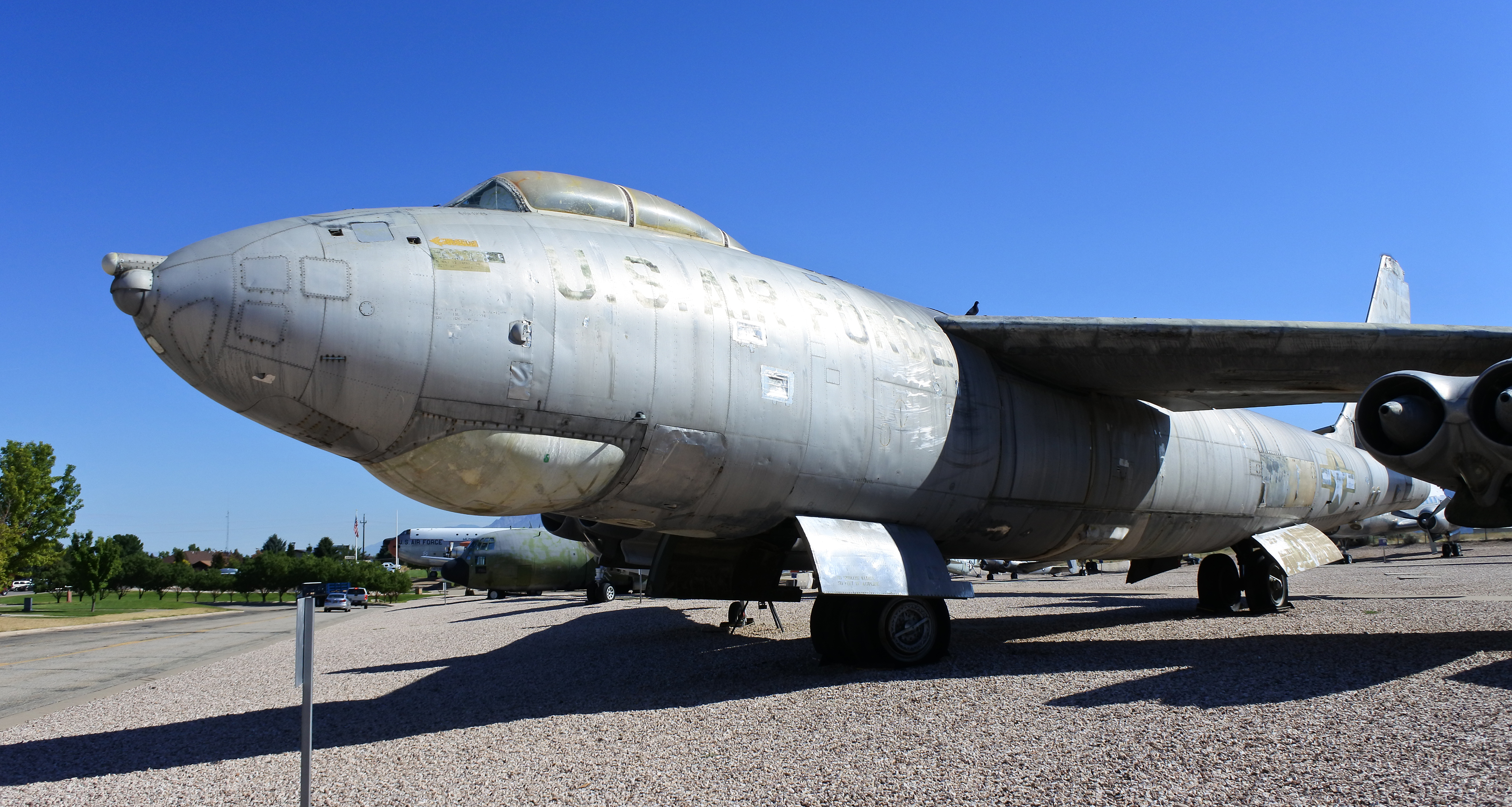  :Following the single WB-47B conversion, in the early 1960s, 34 B-47Es were converted by Lockheed into WB-47Es for weather reconnaissance to replace 44 WB-50D Superfortresses that had suffered several fatal crashes between 1956 and 1960. Stripped of combat gear, they were fitted with nose cameras to photograph cloud formations and a meteorological instrument pod in the bomb bay. Initially assigned to the Air Weather Service of the
:Following the single WB-47B conversion, in the early 1960s, 34 B-47Es were converted by Lockheed into WB-47Es for weather reconnaissance to replace 44 WB-50D Superfortresses that had suffered several fatal crashes between 1956 and 1960. Stripped of combat gear, they were fitted with nose cameras to photograph cloud formations and a meteorological instrument pod in the bomb bay. Initially assigned to the Air Weather Service of the  :A total of 32 RB-47H models were built for electronic intelligence ( ELINT) missions, as well as three more specialized "ERB-47Hs". Featuring a distinctive blunt, rounded nose and sported blisters and pods for intelligence-gathering antennas and gear, they were designed to probe defenses and collect data on radar and communications signals. The bomb bay was replaced by a pressurized compartment, which accommodated "Crows", or Electronic Warfare Officers (EWOs). There were three Crows on board the RB-47H and two on the ERB-47H. A distinctive bulged radome fairing replaced the bomb bay doors. They retained the tail turret and were fitted with jammers and chaff dispensers. A recognizable difference between the RB-47H and ERB-47H was the latter's distinctive antenna fairing under the rounded nose.
:The first RB-47H was delivered in August 1955 to Forbes AFB, Kansas. They received a "Mod 44" or "Silver King" program in 1961 to update electronics systems and was recognizable by a large teardrop pod for ELINT antennas upon a pylon under the belly and offset to one side, as well as a pylon-style antenna under each wing beyond the outboard engine. The EWO compartment was cramped with sitting room only and had both poor noise insulation and climate control, making 12-hour missions uncomfortable and tiring. Successful ejection downward through the belly radome was impossible near the ground. Crews sat bobsled-like on the pilot compartment's floor for takeoff and landing. They then crawled encumbered with Arctic clothing and parachute to and from their compartment along an unpressurized maintenance shelf during a temporary level-off at .
:A total of 32 RB-47H models were built for electronic intelligence ( ELINT) missions, as well as three more specialized "ERB-47Hs". Featuring a distinctive blunt, rounded nose and sported blisters and pods for intelligence-gathering antennas and gear, they were designed to probe defenses and collect data on radar and communications signals. The bomb bay was replaced by a pressurized compartment, which accommodated "Crows", or Electronic Warfare Officers (EWOs). There were three Crows on board the RB-47H and two on the ERB-47H. A distinctive bulged radome fairing replaced the bomb bay doors. They retained the tail turret and were fitted with jammers and chaff dispensers. A recognizable difference between the RB-47H and ERB-47H was the latter's distinctive antenna fairing under the rounded nose.
:The first RB-47H was delivered in August 1955 to Forbes AFB, Kansas. They received a "Mod 44" or "Silver King" program in 1961 to update electronics systems and was recognizable by a large teardrop pod for ELINT antennas upon a pylon under the belly and offset to one side, as well as a pylon-style antenna under each wing beyond the outboard engine. The EWO compartment was cramped with sitting room only and had both poor noise insulation and climate control, making 12-hour missions uncomfortable and tiring. Successful ejection downward through the belly radome was impossible near the ground. Crews sat bobsled-like on the pilot compartment's floor for takeoff and landing. They then crawled encumbered with Arctic clothing and parachute to and from their compartment along an unpressurized maintenance shelf during a temporary level-off at .
 :Operations were generally flown at night and classified Top Secret.Natola 2002, pp. 179–181. The final RB-47H to be retired from service, ''53-4296'', was reactivated and fitted with an F-111-style nose to test avionics for the General Dynamics FB-111 in the early 1970s. It was not given any special designation. It is now on display at the Air Force Armament Museum at Eglin Air Force Base, fitted with a bomber nose.
;YB-47J
:A single B-47E was modified to test the MA-2 BNS for the B-52, and given the designation YB-47J.
;RB-47K
:The RB-47K was a photo and weather reconnaissance variant based on the RB-47E generally used for weather reconnaissance missions, carrying eight dropsonde weather sensors that were released at various checkpoints along its flight path. Data radioed from the dropsondes was logged by the navigator. Fifteen RB-47Ks were built, the variant was in service until 1963.
;EB-47L
:Between 1961 and 1963, 36 B-47Es were modified to carry a communications relay system and were designated EB-47L. Used to support US flying command post aircraft in case of a nuclear attack on the US, the EB-47Ls were only briefly in service as improved communications technologies made them redundant by 1965.
:Operations were generally flown at night and classified Top Secret.Natola 2002, pp. 179–181. The final RB-47H to be retired from service, ''53-4296'', was reactivated and fitted with an F-111-style nose to test avionics for the General Dynamics FB-111 in the early 1970s. It was not given any special designation. It is now on display at the Air Force Armament Museum at Eglin Air Force Base, fitted with a bomber nose.
;YB-47J
:A single B-47E was modified to test the MA-2 BNS for the B-52, and given the designation YB-47J.
;RB-47K
:The RB-47K was a photo and weather reconnaissance variant based on the RB-47E generally used for weather reconnaissance missions, carrying eight dropsonde weather sensors that were released at various checkpoints along its flight path. Data radioed from the dropsondes was logged by the navigator. Fifteen RB-47Ks were built, the variant was in service until 1963.
;EB-47L
:Between 1961 and 1963, 36 B-47Es were modified to carry a communications relay system and were designated EB-47L. Used to support US flying command post aircraft in case of a nuclear attack on the US, the EB-47Ls were only briefly in service as improved communications technologies made them redundant by 1965.
 Twenty-three surviving airframes exist in museum collections; all are located in the United States.
Twenty-three surviving airframes exist in museum collections; all are located in the United States.
 Over the operating history of the B-47, 203 aircraft were lost in crashes, with 464 deaths. This represents approximately 10% of the total number produced.
On 8 February 1954, a B-47 of the 22nd Bomber Wing, March AFB, California, crashed in Stoke Wood, a mile and a half short of the runway at RAF Upper Heyford, England, while on a training run. All three crew were killed.
On 28 February 1955, a crippled B-47 crashed into a trailer park in Lake Charles, Louisiana, killing the three crewmen and two people on the ground.
On 10 March 1956, four B-47s left MacDill Air Force Base in Florida for a non-stop flight to Ben Guerir Air Base in Morocco. After descending through clouds to begin their second round of
Over the operating history of the B-47, 203 aircraft were lost in crashes, with 464 deaths. This represents approximately 10% of the total number produced.
On 8 February 1954, a B-47 of the 22nd Bomber Wing, March AFB, California, crashed in Stoke Wood, a mile and a half short of the runway at RAF Upper Heyford, England, while on a training run. All three crew were killed.
On 28 February 1955, a crippled B-47 crashed into a trailer park in Lake Charles, Louisiana, killing the three crewmen and two people on the ground.
On 10 March 1956, four B-47s left MacDill Air Force Base in Florida for a non-stop flight to Ben Guerir Air Base in Morocco. After descending through clouds to begin their second round of

''Air Force Magazine'', August 2007, Air Force Association. Retrieved 4 June 2009. * Boyne, Walter J. "The Long Reach Of The Stratojet." ''Air Force Magazine'' Vol. 66, issue 71, December 1997. * Bowers, Peter M. "The Boeing B-47" ''Aircraft in Profile, Volume 4''. Windsor, Berkshire, UK: Profile Publications Ltd., 2nd revised and enlarged edition, 1970. . * Bowers, Peter M. ''Boeing Aircraft since 1916''. London: Putnam, 1989. . * Cook, William H. ''The Road to the 707: The Inside Story of Designing the 707.'' Bellevue, Washington: TYC Publishing, 1991. . * Dennison, Robert C. "Stratojet!" ''Air Combat'', July /August 1997. (Dennison is a retired USAF officer and B-47 pilot who works with the B-47 Stratojet Association.) * Fraser, Jim
"I Fly The World's Fastest Bomber."
''Popular Science'', November 1949. Vol. 155, No. 5. pp. 139–142. . * Grant, R.G. and John R. Dailey. ''Flight: 100 Years of Aviation''. Harlow, Essex, UK: DK Adult, 2007. . * Gunston, Bill. ''Bombers of the West''. London: Ian Allan Ltd., 1973, pp. 126–153. . * Gunston, Bill and Peter Gilchrist. ''Jet Bombers: From the Messerschmitt Me 262 to the Stealth B-2''. Osprey, 1993. . * Johnston, A.M. ''Tex Johnston: Jet-Age Test Pilot''. Washington D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Press, 2000. . * Jones, Lloyd S. ''U.S. Bombers, B-1 1928 to B-1 1980s''. Fallbrook, California: Aero Publishers, 1962, second edition 1974. . * Jones, Lloyd S. ''U.S. Bombers: 1928-1980s''. Fallbrook, California: Aero Publishers, Inc., 1981. . * Knaack, Marcelle Size
''Post-World War II Bombers, 1945–1973''(PDF).
Washington, D.C.: Office of Air Force History, 1988. . * Lloyd, Alwyn T. "Boeing's B-47 Stratojet". North Branch Minnesota: Specialty Press, 2005. . * Loftin, Laurence K. Jr
''NASA Scientific and Technical Information Branch'', 2004. * Natola, Mark. "Boeing B-47 Stratojet." ''Schiffer Publishing Ltd'', 2002. . * Peacock, Lindsay. "Stratojet...Progenitor of a Dynasty". '' Air Enthusiast'', Thirty-eight, January–April 1989, pp. 31–44, 63. Bromley, UK: FineScroll. ISSN 0143-5450. * Powers, Francis. "Operation Overflight: A Memoir of the U-2 Incident." ''Potomac Books Inc'', 2004. . * Tegler, Jan. ''B-47 Stratojet: Boeing's Brilliant Bomber''. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2000. . * Yeager, Chuck. "Yeager." ''Bantam Book'', 1985. . * Yenne, Bill. "Variant Briefing: Boeing B-47 Stratojet". ''International Air Power Review'', Volume Six, Autumn/Fall 2002, pp. 156–171. Norwalk, Connecticut: AIRtime Publishing. . ISSN 1473-9917.
National Museum fact sheet Boeing B-56E
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20121206030916/http://www.millionmonkeytheater.com/B-47.html Forgotten Jets – Boeing B-47 Stratojet series– status of all 2,032 produced
B-47 Stratojet Association
{{Authority control B-47 Stratojet Boeing B-47 Boeing B-56 Six-engined jet aircraft Articles containing video clips High-wing aircraft Aircraft first flown in 1947
strategic bomber
A strategic bomber is a medium- to long-range penetration bomber aircraft designed to drop large amounts of air-to-ground weaponry onto a distant target for the purposes of debilitating the enemy's capacity to wage war. Unlike tactical bombers, ...
designed to fly at high subsonic
Subsonic may refer to:
Motion through a medium
* Any speed lower than the speed of sound within a sound-propagating medium
* Subsonic aircraft, a flying machine that flies at air speeds lower than the speed of sound
* Subsonic ammunition, a type o ...
speed and at high altitude to avoid enemy interceptor aircraft. The primary mission of the B-47 was as a nuclear bomber
A bomber is a military combat aircraft designed to attack ground and naval targets by dropping air-to-ground weaponry (such as bombs), launching torpedoes, or deploying air-launched cruise missiles. The first use of bombs dropped from an aircra ...
capable of striking targets within the Soviet Union.
Development of the B-47 can be traced back to a requirement expressed by the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) in 1943 for a reconnaissance bomber that harnessed newly developed jet propulsion. Another key innovation adopted during the development process was the swept wing
A swept wing is a wing that angles either backward or occasionally forward from its root rather than in a straight sideways direction.
Swept wings have been flown since the pioneer days of aviation. Wing sweep at high speeds was first investigate ...
, drawing upon captured German research. With its engines carried in nacelles underneath the wing, the B-47 represented a major innovation in post- World War II combat jet design, and contributed to the development of modern jet airliners. Suitably impressed, in April 1946, the USAAF ordered two prototypes, designated "XB-47"; on 17 December 1947, the first prototype performed its maiden flight. Facing off competition such as the North American XB-45
The North American B-45 Tornado was an early American jet bomber designed and manufactured by aircraft company North American Aviation. It has the distinction of being the first operational jet bomber to enter service with the United States Ai ...
, Convair XB-46 and Martin XB-48, a formal contract for 10 B-47A bombers was signed on 3 September 1948. This would be soon followed by much larger contracts.
During 1951, the B-47 entered operational service with the United States Air Force's Strategic Air Command
Strategic Air Command (SAC) was both a United States Department of Defense Specified Command and a United States Air Force (USAF) Major Command responsible for command and control of the strategic bomber and intercontinental ballistic missile ...
(SAC), becoming a mainstay of its bomber strength by the late 1950s. Over 2,000 were manufactured to meet the Air Force's demands, driven by the tensions of the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
. The B-47 was in service as a strategic bomber until 1965, at which point it had largely been supplanted by more capable aircraft, such as the Boeing B-52 Stratofortress
The Boeing B-52 Stratofortress is an American long-range, subsonic, jet-powered strategic bomber. The B-52 was designed and built by Boeing, which has continued to provide support and upgrades. It has been operated by the United States Air ...
. The B-47 was also adapted to perform a number of other roles and functions, including photographic reconnaissance, electronic intelligence, and weather reconnaissance. While never seeing combat as a bomber, reconnaissance RB-47s would occasionally come under fire near or within Soviet air space. The type remained in service as a reconnaissance aircraft
A reconnaissance aircraft (colloquially, a spy plane) is a military aircraft designed or adapted to perform aerial reconnaissance with roles including collection of imagery intelligence (including using photography), signals intelligence, as ...
until 1969. A few served as flying testbeds up until 1977.
Development
Origins
The B-47 arose from an informal 1943 requirement for a jet-powered reconnaissance bomber, drawn up by the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) to prompt manufacturers to start research into jet bombers. Boeing was among several companies to respond to the request; one of its designs, the Model 424, was basically a scaled-down version of the piston-engined B-29 Superfortress equipped with four jet engines.Peacock 1989, p. 31.Gunston and Gilchrist 1993, pp. 38–39. In 1944, this initial concept evolved into a formal request-for-proposal to design a new bomber with a maximum speed of , a cruise speed of , a range of , and a service ceiling of .Knaack 1988, p. 101.Gunston and Gilchrist 1993, p. 39. In December 1944,North American Aviation
North American Aviation (NAA) was a major American aerospace manufacturer that designed and built several notable aircraft and spacecraft. Its products included: the T-6 Texan trainer, the P-51 Mustang fighter, the B-25 Mitchell bomber, the F ...
, Convair, Boeing and the Glenn Martin Company submitted proposals for the new long-range jet bomber. Wind tunnel testing had shown that the drag from the engine installation of the Model 424 was too high, so Boeing's entry was a revised design, the Model 432, with the four engines buried in the forward fuselage.Peacock 1989, p. 33. The USAAF awarded study contracts to all four companies, requiring that North American and Convair concentrate on four-engined designs (to become B-45 and XB-46), while Boeing and Martin were to build six-engined aircraft (the B-47 and XB-48). The powerplant was to be General Electric's new TG-180 turbojet engine.
Swept wings
In May 1945, the von Kármán mission of the Army Air Forces inspected the secret German aeronautics laboratory near Braunschweig. Von Kármán's team included the chief of the technical staff at Boeing, George S. Schairer. He had heard about the controversial swept-wing theory of R. T. Jones at Langley, but seeing German models of swept-wing aircraft and extensive supersonic wind-tunnel data, the concept was decisively confirmed. He wired his home office: "Stop the bomber design" and changed the wing design.Gunston and Gilchrist 1993, pp. 39–40. Analysis by Boeing engineer Vic Ganzer suggested an optimum sweepback angle of about 35 degrees. Boeing's aeronautical engineers modified the Model 432 with swept wings and tail to produce the "Model 448", which was presented to the USAAF in September 1945. It retained the four TG-180 jet engines in its forward fuselage, with two more TG-180s in the rear fuselage. The flush-mounted air intakes for the rear engines were inadequate while the USAAF considered the engine installation within the fuselage to be a fire hazard.Knaack 1988, p. 102.Gunston and Gilchrist 1993, p. 40. The engines were moved to streamlined pylon-mounted pods under the wings, leading to the next iteration, the ''Model 450'', which featured two TG-180s in a twin pod mounted on a pylon about a third of the way outboard on each wing, plus another engine at each wingtip. The Army Air Force liked this new configuration, so Boeing's engineers refined it, moving the outer engines further inboard to about of the wingspan. The thin wings provided no space for tricycle main gear to retract so it would have needed a considerable bulge in the fuselage aft of the bomb bay for lateral stability. The only way to get a bomb-bay long enough for an A-bomb was to use a "bicycle landing gear", the two main gear assemblies arranged in a tandem configuration and outrigger struts fitted to the inboard engine pods. As the landing gear arrangement maderotation
Rotation, or spin, is the circular movement of an object around a '' central axis''. A two-dimensional rotating object has only one possible central axis and can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. A three-dimensional ...
impossible, it was designed so that the aircraft rested on the ground at the proper angle for takeoff.Bowers 1989, p. 383.Gunston and Gilchrist 1993, p. 42.
Pleased with the refined Model 450 design, in April 1946, the USAAF ordered two prototypes, to be designated "XB-47".Knaack 1988, pp. 102–103. Assembly began in June 1947. The first XB-47 was rolled out on 12 September 1947, a few days before the USAAF became a separate service, the United States Air Force (USAF), on 18 September 1947. According to aviation authors Bill Gunston and Peter Gilchrist, Boeing subjected the first prototype to "one of the most comprehensive ground-test programmes ever undertaken".
Flight test phase
The XB-47 prototype flew its first flight on 17 December 1947 (the anniversary of the Wright Brothers' first four flights on 17 December 1903), with test pilots Robert Robbins and Scott Osler at the controls. It lasted 27 minutes, flying from Boeing Field in Seattle to Moses Lake Airfield in central Washington state.Yenne 2002, p. 158.Peacock 1989, p. 34. While not experiencing major problems, the emergency hot wire system was needed to raise the flaps and the engine fire warning indicators falsely illuminated. Robbins stated that it had good flight characteristics.Natola 2002, pp. 17–24. Robbins had been skeptical about the XB-47, saying that before his first flight he had prayed, "Oh God, please help me through the next two hours." Robbins soon realized that he had an extraordinary aircraft. Chuck Yeager also flew the XB-47, noting it was so aerodynamically clean that he had difficulty landing on the Edwards lakebed.Yeager 1985, pp. 177–178. In February 1949, Russ Schleeh and Joe Howell "broke all coast-to-coast speed records" flying from Moses Lake Air Force Base toAndrews Air Force Base
Andrews Air Force Base (Andrews AFB, AAFB) is the airfield portion of Joint Base Andrews, which is under the jurisdiction of the United States Air Force. In 2009, Andrews Air Force Base merged with Naval Air Facility Washington to form Joint B ...
, averaging .Natola 2002, pp. 34–36. During an early test flight, the canopy came off at high speed, killing pilot Scott Osler; the aircraft was safely landed by the copilot.Boyne, Walter J. "Flying the B-47: An inside look at the USAF's first jet bomber".''Flight Journal'', April 2002. Retrieved 31 March 2010. The accident resulted in a canopy redesign and the hiring of pilot Tex Johnston as chief test pilot.
The second XB-47 (46-066) prototype first flew on 21 July 1948 and, following its delivery to the USAF in December of that year, served as a flying test bed until 1954. Its final destination was Chanute AFB where it was used as a maintenance and familiarization aircraft. The second prototype was equipped with more powerful General Electric J47-GE-3 turbojets with of static thrust each.Yenne 2002, p. 165. The J47 or "TG-190" was a redesigned version of the TG-180/J35. The first prototype was later retrofitted with these engines.
Flight testing of the prototypes was careful and methodical since the design was new in so many ways. They initially suffered from "Dutch roll
Dutch roll is a type of aircraft motion consisting of an out-of-phase combination of "tail-wagging" (yaw) and rocking from side to side (roll). This yaw-roll coupling is one of the basic flight dynamic modes (others include phugoid, short per ...
", an instability that caused it to weave in widening "S" turns, remedied by the addition of a " yaw damper" control system to automatically deflect the rudder to damp out the weaving motion. Wind tunnel tests had shown it would pitch up at maximum speed due to wing stall on the outboard section of the wing. This was confirmed during flight tests so small vanes called " vortex generators" were added to prevent airflow separation.
Both XB-47 prototypes were test flown at Edwards AFB; the first XB-47 (46-065) was disassembled and scrapped in 1954, making the second prototype (46-066) the sole surviving XB-47. Upon retirement, XB-47 (46-066) was restored and placed on display at the Octave Chanute Aerospace Museum in Rantoul, Illinois, remaining there until the museum announced its closure due to financial difficulties in April 2015. In late 2015, the Flight Test Historical Foundation began fundraising to purchase XB-47 (46-066) for relocation to the Flight Test Museum at Edwards AFB. The purchase was completed in August 2016 and on 21 September 2016 the aircraft arrived at Edwards AFB for reassembly, restoration and eventual display at the Flight Test Museum.
X-model competitions
By mid-1948, the USAF's bomber competition had already been through one iteration, pitting the North American XB-45 against the Convair XB-46. The North American design won that round of the competition. As an interim measure, the USAF decided to put the North American bomber into production on a limited basis as the B-45 Tornado. The expectation was that B-45 production would be terminated if either of the remaining two designs in the competition, the Boeing XB-47 and the Martin XB-48, proved superior. It is sometimes claimed that the final production decision was made as a result of Boeing president Bill Allen inviting USAF General K.B. Wolfe, in charge of bomber production, for a ride in the XB-47.Yenne 2002, p. 160. A formal contract for 10 aircraft was signed on 3 September 1948.Knaack 1988, p. 107.Gunston and Gilchrist 1993, pp. 43–44.Production
The total number of B-47s built was 2,042.Design
Overview
The XB-47, which looked nothing like contemporary bombers, was described by Boyne as a "sleek, beautiful outcome that was highly advanced". The 35-degreeswept wing
A swept wing is a wing that angles either backward or occasionally forward from its root rather than in a straight sideways direction.
Swept wings have been flown since the pioneer days of aviation. Wing sweep at high speeds was first investigate ...
s were shoulder-mounted, the inboard turbojet engines mounted in twin pods, at about a third of the span, and the outboard engines singly near the wing tip. This arrangement reduced the bending moment at the wing roots, saving structural weight. The engines' mass acted as counter-flutter
Flutter may refer to:
Technology
* Aeroelastic flutter, a rapid self-feeding motion, potentially destructive, that is excited by aerodynamic forces in aircraft and bridges
* Flutter (American company), a gesture recognition technology company acqu ...
weights.Fraser November 1949, p. 141.
The wing airfoil was identified by Boeing as the BAC 145, also known as the NACA 64A(.225)12 mod airfoil. Wing flexibility was a concern, flexing as much as at the tip;Gunston and Gilchrist 1993, pp. 40–41. major effort was expended to ensure that flight control could be maintained as the wing moved up and down; these worries proved to be mostly unfounded. Its maximum speed was limited to IAS to avoid control reversal, where aileron deflections would cause the wings to twist and produce a roll in the opposite direction to that desired by the pilot. The wings were fitted with a set of Fowler flaps that extended well behind the wing to enhance lift at slow speeds.Natola 2002, pp. 19, 47, 54, 207, 213. The flight control surfaces were powered, augmenting the pilot's inputs and reducing the exertion required to overcome the forces involved.Fraser November 1949, pp. 139–140.
The XB-47 was designed to carry a crew of three in a pressurized forward compartment: a pilot and copilot, in tandem, in a long fighter-style bubble canopy, and a navigator/ bombardier in a compartment in the nose. The copilot doubled as tail gunner (using a remotely controlled, radar-directed tail gun), and the navigator as bombardier.Gunston and Gilchrist 1993, p. 43. The bubble canopy, which provided a high level of visibility to the pilots, pitched up and slid backward; as the cockpit was high off the ground, the crew entered via a door and ladder on the underside of the nose.Fraser November 1949, pp. 140–141. The extreme front of the nose was initially glazed for visual navigation and bomb sighting, but this requirement was soon deleted together with the glazing. Most production versions had a metal nose with no windows. A K-series bombsight provided integrated radar navigation and visual navigation, the optical portion extending through the nose in a small dome. For greater comfort, both heaters and refrigeration systems were present in the cockpit to manage the cockpit environment. There was little vibration compared to prior bombers powered by reciprocating engines.
Engines and performance
During the late 1940s, the bomber was hailed as the fastest of its class in the world.Fraser November 1949, p. 139. The first prototypes were fitted with General Electric J35 turbojets, the production version of the TG-180, with of thrust. Early jet engines did not develop good thrust at low speeds, so to assist take off when heavily loaded, the B-47 had provisions for fitting solid-fuel rocket-assisted takeoff (RATO) rockets, each generating roughly of static thrust.Fraser November 1949, p. 142. Early aircraft had mounts for nine RATO units built into each side of the rear fuselage, arranged in three rows of three bottles. Most of the space within the upper fuselage was taken up by self-sealing fuel tanks, the wing having been deemed unsuitable for storing fuel.Gunston and Gilchrist 1993, pp. 41–43. The performance of the Model 450 was projected to be so good that the bomber would be as fast as fighters then on the drawing board;Gunston and Gilchrist 1993, p. 38. thus the only defensive armament was to be a tail turret with two .50 in (12.7 mm) AN/M2 Browning machine guns, which would in principle be directed by an automaticfire-control system
A fire-control system (FCS) is a number of components working together, usually a gun data computer, a director, and radar, which is designed to assist a ranged weapon system to target, track, and hit a target. It performs the same task as a ...
.Gunston and Gilchrist 1993, pp. 42–43. The two XB-47s were neither fitted with combat equipment nor tail turrets as they were engineering and flight test aircraft only. The total bombload capacity was to be . Production aircraft were to be equipped with modern electronics for navigation, bombing, countermeasures and turret fire control. Navigation was more difficult than on earlier aircraft due to the higher speed involved.Fraser November 1949, p. 140.
One problem with the aircraft was that at higher altitudes, where the pure turbojet engines could produce good fuel economy, the wing was very compromised. At the top of the B-47's envelope, about , it was in " coffin corner".Natola 2002, p. 184. That means that at this level, which produced the most range at most weights due to fuel consumption, there was an envelope of between maximum mach and stall speed. For the B-47 to cross the Atlantic Ocean, it had to be flown this high. Due to its rudimentary autopilot, the pilot had to leave it turned off and spend up to eight hours diligently monitoring the airspeed and adjusting the throttles to avoid going into a stall. For perspective, a modern Boeing 757 has over of difference at even a very heavy weight at . Fuel capacity was enormous, at , more than triple the on the B-29 Superfortress, and meant that maintaining fuel trim to ensure a stable center of gravity was a critical copilot duty.
Drogue chutes
The aircraft was so aerodynamically clean that rapid descent ("penetration") from highcruise
A cruise is any travel on a cruise ship.
Cruise or Cruises may also refer to:
Tourism
* Booze cruise
* Music cruise
* River cruise
Aeronautics and aircraft
* Cruise (aeronautics), a distinct stage of an aircraft's flight
* Aviasouz Cruise, a R ...
altitude to the landing pattern required dragging the deployed rear landing gear. The relatively high wing loading (weight/wing area) required a high landing speed of . To shorten the landing roll, USAF test pilot Major Guy Townsend promoted the addition of a German-invented "ribbon" drag chute ( thrust reversers had not then been developed). For the same reason, the B-47 was the first mass-produced aircraft to be equipped with an anti-skid braking system.
A related problem was that the aircraft's engines would have to be throttled down on landing approach. Since it could take as long as 20 seconds to throttle them back up to full power, the bomber could not easily do a " touch and go" momentary landing. A 16-foot "approach chute" ( drogue parachute) provided aerodynamic drag
In fluid dynamics, drag (sometimes called air resistance, a type of friction, or fluid resistance, another type of friction or fluid friction) is a force acting opposite to the relative motion of any object moving with respect to a surrounding fl ...
so that the aircraft could be flown at approach speeds with the engines throttled at ready-to-spool-up medium power. On the ground, the pilots used the 32-foot "brake chute". The brake chute could be deployed to stop the aircraft from "porpoising", or bouncing, after a hard landing on the front nose gear.Natola 2002, pp. 58–59, 151–153, 206, 211, 219. Training typically included an hour of dragging the approach chute around the landing pattern for multiple practice landings.
Operational history
Early years
 The USAF
The USAF Strategic Air Command
Strategic Air Command (SAC) was both a United States Department of Defense Specified Command and a United States Air Force (USAF) Major Command responsible for command and control of the strategic bomber and intercontinental ballistic missile ...
operated multiple B-47 models (B-47s, EB-47s, RB-47s and YRB-47s) from 1951 through 1965. Upon entry to service, its performance was closer to that of contemporary fighters than SAC's extant B-36 Peacemaker bomber, setting multiple records with ease. It handled well in flight, the controls having a fighter-like light touch. The large bubble canopy enhanced the flying crew's vision and gave a fighter-like feel, but also caused internal temperature variations for the crew. The three-man crew consisted of the commander, copilot and a navigator/bombardier or a crew chief.Natola 2002, pp. 44–45, 136, 156.
In 1953 the B-47 became operational. It was sluggish on takeoff and too fast on landings, an unpleasant combination. If landed at the wrong angle, the B-47 would "porpoise", bouncing fore-and-aft. If the pilot did not lift off for another go-around, instability would quickly cause it to skid onto one wing and cartwheel. Because the wings and surfaces flexed in flight, low-altitude speed restrictions were necessary to ensure effective flight control. The B-47 was regarded as a maintenance "hog". General reliability was good, the only major issuing relating to the avionics, typical of the vacuum tube technology used and the placement of equipment outside the pressurized crew compartment. Much work was done to improve avionics reliability, but avionics remained troublesome throughout the B-47's operational life.
Starting in 1950, several models of the B-47 included a fuel tank inerting system, in which dry ice was sublimed into carbon dioxide vapor while the fuel pumps operated or while the in-flight refueling system was in use. The carbon dioxide was pumped into both the fuel tanks and the fuel system to ensure low oxygen levels throughout. It was implemented largely to reduce the probability of an explosion from static electricity
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material or between materials. The charge remains until it is able to move away by means of an electric current or electrical discharge. Static electricity is na ...
discharges.
 Initial mission profiles included the loft bombing of nuclear weapons. As the training for this imposes repeated high stress on the aircraft, the airframe lifetime would have been severely limited by metal fatigue, and this maneuver was eliminated. Improved training led to a good safety record, and few crews felt the aircraft was unsafe or too demanding, but apparently there were some aircrews who had little affection for the B-47. Crew workload was high, having only three crew members to operate it.Fraser November 1949, pp. 141–142. Boeing's
Initial mission profiles included the loft bombing of nuclear weapons. As the training for this imposes repeated high stress on the aircraft, the airframe lifetime would have been severely limited by metal fatigue, and this maneuver was eliminated. Improved training led to a good safety record, and few crews felt the aircraft was unsafe or too demanding, but apparently there were some aircrews who had little affection for the B-47. Crew workload was high, having only three crew members to operate it.Fraser November 1949, pp. 141–142. Boeing's B-52 Stratofortress
The Boeing B-52 Stratofortress is an American long-range, subsonic, jet-powered strategic bomber. The B-52 was designed and built by Boeing, which has continued to provide support and upgrades. It has been operated by the United States Air ...
, in contrast, generally had six crewmen, five officers and one enlisted, with more internal cabin space.
Prime years
An XB-47 was flown in the 1951 Operation Greenhouse nuclear weapons test. This was followed by a B-47B being flown in the 1952 test,Operation Ivy
Operation Ivy was the eighth series of American nuclear tests, coming after '' Tumbler-Snapper'' and before '' Upshot–Knothole''. The two explosions were staged in late 1952 at Enewetak Atoll in the Pacific Proving Ground in the Marshall Is ...
and the 1954 test, Operation Castle. A B-47E was then flown in the 1956 test, Operation Redwing.Natola 2002, pp. 98–109. "Reflex" missions proved the long-endurance (eighteen hours) and long range capability of the B-47 and aircrews. These were "simulated strike missions against the then Soviet enemy".Natola 2002, pp. 110, 163, 194, 199.
Three B-47s flew cross country from March Air Force Base to the Philadelphia International Airport
Philadelphia International Airport is the primary airport serving Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The airport served 19.6 million passengers annually in 2021, making it the 21st busiest airport in the United States. The airport is located from t ...
as participants in the 1955 Labor Day race. In the 1956 event, three B-47s participated in the G.E. Trophy race for Jet Bombers, flying from Kindley Field
Kindley Air Force Base was a United States Air Force base in Bermuda from 1948–1970, having been operated from 1943 to 1948 by the United States Army Air Forces as ''Kindley Field''.
History
World War II
Prior to American entry into th ...
, Bermuda, to Oklahoma City. One of these set a course speed record of .Natola 2002, pp. 126–131.
By 1956, the USAF had 28 wings of B-47 bombers and five wings of RB-47 reconnaissance aircraft. The B-47 was the first line of America's strategic nuclear deterrent, often operating from forward bases in the UK, Morocco, Spain, Alaska, Greenland and Guam. B-47s were often set up on "one-third" alert, with a third of operational aircraft available sitting on hardstands or an alert ramp adjacent to the runway, loaded with fuel and nuclear weapons, crews on standby, ready to attack the USSR at short notice. Crews were trained to perform " Minimum Interval Take Offs (MITO)",Natola 2002, pp. 36, 44–45, 162, 193. one bomber following another into the air at intervals of as little as 15 seconds to launch as fast as possible. MITO could be hazardous, as the bombers left wingtip vortices and general turbulence behind them; the first generation turbojet engines, fitted with water-injection systems, also created dense black smoke.Natola 2002, p. 180.
The B-47 was the backbone of SAC into 1959, when the B-52 began to assume nuclear alert duties and the number of B-47 bomber wings started to be reduced. B-47 production ceased in 1957, though modifications and rebuilds continued. Operational practice for B-47 bomber operations during this time went from high-altitude bombing to low-altitude strike, which was judged more likely to penetrate Soviet defenses. Crews were trained in "pop-up" attacks, coming in at low level at and then climbing abruptly near the target before releasing a nuclear weapon.Natola 2002, pp. 131–134, 212.
Later years

 Stress and fatigue incurred in low-altitude operations led to a number of wing failures and crashes, and an extensive refit program was begun in 1958 to strengthen the wing mountings. The program was known as "Milk Bottle", named after the big connecting pins that were replaced in the wing roots.
One of the more notable mishaps involving a B-47 occurred on 5 February 1958 near Savannah, Georgia, in the so-called
Stress and fatigue incurred in low-altitude operations led to a number of wing failures and crashes, and an extensive refit program was begun in 1958 to strengthen the wing mountings. The program was known as "Milk Bottle", named after the big connecting pins that were replaced in the wing roots.
One of the more notable mishaps involving a B-47 occurred on 5 February 1958 near Savannah, Georgia, in the so-called 1958 Tybee Island B-47 crash
The Tybee Island mid-air collision was an incident on February 5, 1958, in which the United States Air Force lost a Mark 15 nuclear bomb in the waters off Tybee Island near Savannah, Georgia, United States. During a practice exercise, an F-86 ...
. A B-47 based at Homestead AFB, Florida, was engaged in a simulated combat exercise against an F-86
The North American F-86 Sabre, sometimes called the Sabrejet, is a transonic jet fighter aircraft. Produced by North American Aviation, the Sabre is best known as the United States' first swept-wing fighter that could counter the swept-wing Sov ...
fighter. As was the practice at the time, the B-47 was carrying a single Mark 15 nuclear bomb, without its core. During this exercise, the two aircraft collided. The F-86 crashed after the pilot ejected, while the B-47 suffered substantial damage, including loss of power in one outboard engine. After three unsuccessful landing attempts at Hunter Air Force Base
Hunting is the human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products (fur/ hide, bone/tusks, horn/ antler, ...
, the bomber pilot had to "safe" soft drop the Mark 15 weapon off the coast of Savannah, Georgia near Tybee Island, after which the B-47 landed safely. Despite an extensive nine-month search, the unarmed bomb was never found.
In 1963, the Kennedy administration offered 24 B-47E bombers as an interim Canberra Mk 20 replacement for the Royal Australian Air Force
"Through Adversity to the Stars"
, colours =
, colours_label =
, march =
, mascot =
, anniversaries = RAAF Anniversary Commemoration ...
(RAAF), pending delivery of the much delayed F-111C aircraft. Three B-47E aircraft flew to Australia for demonstration purposes, but RAAF declined the B-47E as technically outdated and too resource-intensive.
During 1963, final phaseout of B-47 bomber wings began, the last were out of SAC service by 1966. The last USAF operational aircraft, WB-47Es assigned to the Air Weather Service
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for ...
, were withdrawn from use in September 1969. Shortly before, a B-47E, USAF Serial Number 53-2280, was used as a testbed for a newly developed fly-by-wire system. The U.S. Navy kept specialized EB-47E test aircraft from USAF inventory in occasional use to support the ''Fleet Electronic Warfare Systems Group (FEWSG)'' until December 1977, being replaced by government owned/contractor operated (GOCO) NKC-135 modified Stratotankers also loaned from the USAF.
 The final recorded flight of a B-47 was on 17 June 1986, when a B-47E was restored to flightworthy condition for a one-time ferry flight. This aircraft was flown from
The final recorded flight of a B-47 was on 17 June 1986, when a B-47E was restored to flightworthy condition for a one-time ferry flight. This aircraft was flown from Naval Air Weapons Station China Lake
Naval Air Weapons Station (NAWS) China Lake is a large military installation in California that supports the research, testing and evaluation programs of the United States Navy. It is part of Navy Region Southwest under Commander, Navy Installat ...
, California, to Castle Air Force Base, California, for static display at the Castle Air Museum, where it presently resides.Natola 2002, pp. 217–219.
Reconnaissance
The only B-47s to see anything close to combat were the aerial reconnaissance variants. The first overflight of Soviet territory with a B-47B, fitted with special radar and cameras in the bomb bay, occurred on 15 October 1952, overflying Soviet airfields in Northeastern Siberia.Natola 2002, pp. 90–97. RB-47s operated from almost every airfield that gave them access to the USSR and routinely probed Soviet airspace. Occasionally, they would avoid confrontations with speed and evasion. At least five aircraft were fired upon and three were shot down. The RB-47s returned fire with their tail turrets, although it is uncertain if they scored any kills; these were the only shots fired in anger by any B-47. On 8 May 1954, after a top secret reconnaissance mission near the Kola Peninsula, a4th Air Division
The 4th Air Division is an inactive United States Air Force unit. Its last assignment was with Fifteenth Air Force, stationed at Francis E. Warren Air Force Base, Wyoming. It was inactivated on 23 August 1988.
As the 4th Bombardment Wing, the u ...
/ 91st Strategic Reconnaissance Wing RB-47E, flown by then-Capt (later Col) Harold "Hal" Austin, overflew the Soviet Union at high altitude, out of reach of MiG-15s. Unknown to USAF intelligence, MiG-17s capable of intercepting it had been stationed nearby. The RB-47E was chased by several MiG-17s, firing upon it with their guns over Soviet and Finnish airspace. While taking damage, the RB-47E escaped over Sweden to its home base at RAF Fairford, Gloucestershire. Its top speed and combat radius
Radius of action, combat radius, or combat range in military terms, refers to the maximum distance a ship, aircraft, or vehicle can travel away from its base along a given course with normal load and return without refueling, allowing for all safet ...
superiority to the fighter jets were decisive factors. The mission marked the first time a jet aircraft equipped with modern aerial photography equipment, K-17 and K-38 cameras, was used for USAF reconnaissance over the Soviet Union. The incident was kept secret by all parties.Natola 2002, pp. 85–89.
Other interceptions resulted in losses. An RB-47 flying from Alaska was scouting the Kamchatka Peninsula on 17 April 1955, when it was intercepted by Soviet MiG-15s in international airspace before disappearing. Between 21 March and 10 May 1956, 16 RB-47Es and five RB-47Hs operating from Thule performed overflights the length of Siberia 156 times under Project HOMERUN. The Soviets filed a complaint with the US government, which attributed the overflights to "navigational difficulties". MiGs intercepted RB-47s on three separate occasions in late 1958: over the Black Sea on 31 October, over the Baltic on 7 November, and over the Sea of Japan on 17 November.
On 1 July 1960, a PVO Strany MiG-19 shot down an RB-47H (AF Serial No. 53-4281) in international airspace over the Barents Sea,Powers 2004, pp. 152, 159. killing four of the crew while two were captured by the Soviets and released in 1961. The co-pilot reported that the MiG-19 jammed his MD-4 FCS (that aimed the tail guns), rendering it defenseless. The last known confrontation between MiGs and RB-47s occurred on 28 April 1965, when an ERB-47H was intercepted by two North Korean MiG-17s over the Sea of Japan. While hit by the MiGs, it returned to Yokota Air Base in Japan with three engines out.Natola 2002, pp. 208–211. A few operated during the Vietnam War on missions such as relaying ELINT data, but were replaced by more efficient and capable Boeing RC-135s. The last RB-47H was retired on 29 December 1967.
The final 15 RB-47s, built from December 1955, were fitted with additional equipment, including the AN/APD " side looking airborne radar" (SLAR) system, and gear to sample the air for fallout from nuclear tests. These were given the designation RB-47K and generally used for weather reconnaissance missions, carrying a load of eight " dropsonde" weather sensors that were released at various checkpoints along the flight path. Data radioed back from the dropsondes was logged by the navigator. The RB-47Ks were in service until 1963.Gunston and Gilchrist 1993, p. 45. The type was succeeded by dedicated reconnaissance aircraft such as the Lockheed U-2.
Variants
:''Section source: Baugher.'' ; XB-47 :Two prototype aircraft, Model 450-1-1 and 450-2-2 respectively,(46-065 and 46-066); powered by six Allison J-35-GE-7 turbojet engines on early flights. The second XB-47 was powered by General Electric J-47-GE-3 engines, the first was retrofitted as such.Lloyd 2005. . ;B-47A :The first 10 aircraft were designated B-47A and were evaluation aircraft, the first delivered in December 1950. While the XB-47s had been built at Boeing's Seattle plant, all B-47s were built at a government-owned factory in Wichita, Kansas that had previously built B-29s. Their configuration was akin to the XB-47. All were powered by J47-GE-11 turbojets, offering the same thrust as the earlier J47-GE-3, and had built-in rocket-assisted-take-off ( RATO) bottles. Four were fitted with the K-2 bombing and navigation system (BNS), HD-21D autopilot, an analog computer, APS-23 radar, and a Y-4 or Y-4A bombsight. Two were fitted with the tail turret mounting two 20mm cannons; one of them used an Emerson A-2 fire control system (FCS), another a General Electric A-5 FCS. The eight other B-47As lacked defensive armament.
:The B-47As were fitted with ejection seats. The pilot and copilot ejected upward, while the navigator had a downward ejection seat built by
:The first 10 aircraft were designated B-47A and were evaluation aircraft, the first delivered in December 1950. While the XB-47s had been built at Boeing's Seattle plant, all B-47s were built at a government-owned factory in Wichita, Kansas that had previously built B-29s. Their configuration was akin to the XB-47. All were powered by J47-GE-11 turbojets, offering the same thrust as the earlier J47-GE-3, and had built-in rocket-assisted-take-off ( RATO) bottles. Four were fitted with the K-2 bombing and navigation system (BNS), HD-21D autopilot, an analog computer, APS-23 radar, and a Y-4 or Y-4A bombsight. Two were fitted with the tail turret mounting two 20mm cannons; one of them used an Emerson A-2 fire control system (FCS), another a General Electric A-5 FCS. The eight other B-47As lacked defensive armament.
:The B-47As were fitted with ejection seats. The pilot and copilot ejected upward, while the navigator had a downward ejection seat built by Stanley Aviation
Stanley Aviation is an aerospace company started by Robert M Stanley, the aviation pioneer, in Buffalo, New York in 1948.
The company has since acquired several other companies and has been most recently acquired by Eaton Corporation.
Stanley is ...
. Minimum safe ejection altitude was about 500 ft (150 m). In the 1950s, there were no suitable "dummies" to test ejection seats, thus live people were used. Several volunteers were injured testing the downward ejection seat. The first person to successfully use it was USAF Colonel Arthur M. Henderson who ejected over Choctawhatchee Bay, near Eglin Air Force Base
Eglin Air Force Base is a United States Air Force (USAF) base in the western Florida Panhandle, located about southwest of Valparaiso in Okaloosa County.
The host unit at Eglin is the 96th Test Wing (formerly the 96th Air Base Wing). The ...
, Florida, on 7 October 1953. Most B-47As were retired by 1952, though one performed flight tests for NACA for a few more years.
;B-47B
 :In November 1949, prior to the B-47A's first flight, the USAF ordered 87 B-47Bs, the first operational model. The first flew on 26 April 1951. A total of 399 were built, including eight assembled by Lockheed and 10 assembled by Douglas using Boeing-built parts. To quickly receive B-47s in quantity, the USAF contracted both Lockheed and Douglas for additional production;Gunston and Gilchrist 1993, p. 44. Lockheed-built aircraft were designated by a "-LM (Lockheed Marietta)" suffix and Douglas-built aircraft given a "-DT (Douglas Tulsa)" suffix. Boeing production was designated by a "-BW (Boeing Wichita)" suffix, except for the Seattle-built XB-47s and B-47As, which had a "-BO" suffix.
:The initial 87 B-47Bs used the same J47-GE-11 engines as the B-47A, subsequent deliveries had uprated J47-GE-23 units with thrust; early aircraft were later retrofitted. It had a built-in RATO system, as used on the B-47A, along with full combat systems. Early aircraft retained the K-2 BNS installed on some B-47As, but most featured the K-4A BNS, incorporating an AN/APS-54 warning radar and an AN/APT-5 electronic countermeasures (ECM) system. The K-4A used a nose-mounted periscopic bombsight. Ejection seats were deleted as a weight reduction measure; a windbreak panel on the main door made for a difficult escape.
:The bomb bay was shorter than the B-47A's as nuclear weapons had shrunk in the interim; the B-47B could carry a larger bombload of up to . All B-47Bs had a tail turret with twin 20 mm (0.79 in) guns and the B-4 radar-guided FCS. Due to issues, this FCS was often replaced with an N-6 optical sight; the copilot could swivel his seat to face backward and sight the guns directly. A nose-mounted in-flight refueling (IFR) receptacle enabled flying boom refueling from KB-50 and KC-97 tankers, requiring the plexiglas nose cone's replacement by a metal nose cone with four small windows, two on either side of the nose. The B-47B was also fitted with a pair of jettisonable external tanks, carried between the inboard and outboard engine assemblies, with a capacity of . Another visible change was the vertical tailplane's squared-off top instead of a rounded top.
:Between 1955 and 1956, Boeing modified surviving B-47Bs from line numbers 235 to 399 to the B-47E standard under program ''High Noon''; this included fitting ejection seats. It was followed by the ''Ebb Tide'' program covering early line numbers from 1 to 234; this included 66 aircraft from the 135 to 234 batch to the same standard as the ''High Noon'' aircraft. Another 30 in the same range had additional modification as drone directors DB-47Bs, and the 1 to 134 range which had the same ''High Noon'' modification, but lacked some non-combat changes. Following these programs, they were sometimes referred to as B-47B-II.
;;YRB-47B
:The USAF considered building a specialized RB-47B reconnaissance variant, but schedule slips ensured that the RB-47E was the first such variant. As an interim measure, 91 B-47B bombers were fitted with a heated pod stowed in the forward bomb bay that housed eight cameras. These were designated YRB-47Bs and were capable of daylight reconnaissance only. Once the RB-47E arrived, they returned to the bomber role.
;;TB-47B
:A total of 66 of the 87 non-combat B-47Bs were re-designated TB-47B in 1953 to alleviate logistics problems due to different engines and systems. Most were used as trainers; some were modified for Air Training Command by Douglas at Tulsa under the ''Field Goal'' program, adding a fourth seat for an instructor and removing the tail turret. They were upgraded to B-47E standard in 1956 under the ''Ebb Tide'' program, joined by 41 more early build aircraft, also designated TB-47B. Used for training through the 1950s.
;;MB-47B
:With the introduction of the
:In November 1949, prior to the B-47A's first flight, the USAF ordered 87 B-47Bs, the first operational model. The first flew on 26 April 1951. A total of 399 were built, including eight assembled by Lockheed and 10 assembled by Douglas using Boeing-built parts. To quickly receive B-47s in quantity, the USAF contracted both Lockheed and Douglas for additional production;Gunston and Gilchrist 1993, p. 44. Lockheed-built aircraft were designated by a "-LM (Lockheed Marietta)" suffix and Douglas-built aircraft given a "-DT (Douglas Tulsa)" suffix. Boeing production was designated by a "-BW (Boeing Wichita)" suffix, except for the Seattle-built XB-47s and B-47As, which had a "-BO" suffix.
:The initial 87 B-47Bs used the same J47-GE-11 engines as the B-47A, subsequent deliveries had uprated J47-GE-23 units with thrust; early aircraft were later retrofitted. It had a built-in RATO system, as used on the B-47A, along with full combat systems. Early aircraft retained the K-2 BNS installed on some B-47As, but most featured the K-4A BNS, incorporating an AN/APS-54 warning radar and an AN/APT-5 electronic countermeasures (ECM) system. The K-4A used a nose-mounted periscopic bombsight. Ejection seats were deleted as a weight reduction measure; a windbreak panel on the main door made for a difficult escape.
:The bomb bay was shorter than the B-47A's as nuclear weapons had shrunk in the interim; the B-47B could carry a larger bombload of up to . All B-47Bs had a tail turret with twin 20 mm (0.79 in) guns and the B-4 radar-guided FCS. Due to issues, this FCS was often replaced with an N-6 optical sight; the copilot could swivel his seat to face backward and sight the guns directly. A nose-mounted in-flight refueling (IFR) receptacle enabled flying boom refueling from KB-50 and KC-97 tankers, requiring the plexiglas nose cone's replacement by a metal nose cone with four small windows, two on either side of the nose. The B-47B was also fitted with a pair of jettisonable external tanks, carried between the inboard and outboard engine assemblies, with a capacity of . Another visible change was the vertical tailplane's squared-off top instead of a rounded top.
:Between 1955 and 1956, Boeing modified surviving B-47Bs from line numbers 235 to 399 to the B-47E standard under program ''High Noon''; this included fitting ejection seats. It was followed by the ''Ebb Tide'' program covering early line numbers from 1 to 234; this included 66 aircraft from the 135 to 234 batch to the same standard as the ''High Noon'' aircraft. Another 30 in the same range had additional modification as drone directors DB-47Bs, and the 1 to 134 range which had the same ''High Noon'' modification, but lacked some non-combat changes. Following these programs, they were sometimes referred to as B-47B-II.
;;YRB-47B
:The USAF considered building a specialized RB-47B reconnaissance variant, but schedule slips ensured that the RB-47E was the first such variant. As an interim measure, 91 B-47B bombers were fitted with a heated pod stowed in the forward bomb bay that housed eight cameras. These were designated YRB-47Bs and were capable of daylight reconnaissance only. Once the RB-47E arrived, they returned to the bomber role.
;;TB-47B
:A total of 66 of the 87 non-combat B-47Bs were re-designated TB-47B in 1953 to alleviate logistics problems due to different engines and systems. Most were used as trainers; some were modified for Air Training Command by Douglas at Tulsa under the ''Field Goal'' program, adding a fourth seat for an instructor and removing the tail turret. They were upgraded to B-47E standard in 1956 under the ''Ebb Tide'' program, joined by 41 more early build aircraft, also designated TB-47B. Used for training through the 1950s.
;;MB-47B
:With the introduction of the hydrogen bomb
A thermonuclear weapon, fusion weapon or hydrogen bomb (H bomb) is a second-generation nuclear weapon design. Its greater sophistication affords it vastly greater destructive power than first-generation nuclear bombs, a more compact size, a lowe ...
, the USAF studied converting a few B-47Bs into MB-47B drones, essentially huge cruise missile
A cruise missile is a guided missile used against terrestrial or naval targets that remains in the atmosphere and flies the major portion of its flight path at approximately constant speed. Cruise missiles are designed to deliver a large warhe ...
s, under the Brass Ring program. Due to impracticality, it was canceled on 1 April 1953.
;;YDB-47B / DB-47B
:There were flight tests through the 1950s for using the B-47B as a launcher for the 31 ft (9.5 m) GAM-63 Rascal missile, and one B-47B was modified into a YDB-47B Rascal launcher. The Rascal never became operational; a total of 74 B-47Bs were modified into DB-74Bs before cancellation.
;;WB-47B
:In 1956, a B-47B was converted into a WB-47B weather reconnaissance model and operated by the Military Air Transportation Service (MATS), one of a few B-47s not operated by SAC. It was used by the Air Weather Service
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for ...
until the mid-1960s.
;;KB-47B
:In 1953, two B-47Bs were modified to test the probe-and-drogue refueling system. The tanker, fitted with British-built tanker kit, was given the designation KB-47G and was known as "Maw" by flightcrews. The receiver aircraft was designated YB-47F and was known as "Paw", though other aircraft (including the YB-52 prototype) were also used as refueling targets. The program was cancelled in 1954 as the KB-47G could not carry a practical fuel load. The idea of fielding B-47 tanker conversions was re-examined, but unfavorable economics meant that it was again discarded in 1957. In parallel to the KB-47, Boeing tested its aerial refueling system aboard its Dash 80, later evolving into the KC-135 Stratotanker, which had greater fuel capacity.
;;Canadair CL-52
:An unusual conversion was the Canadair
Canadair Ltd. was a civil and military aircraft manufacturer in Canada. In 1986, its assets were acquired by Bombardier Aerospace, the aviation division of Canadian transport conglomerate Bombardier Inc.
Canadair's origins lie in the establishm ...
CL-52: a B-47B (USAF S/N 51-2059 RCAF S/N 059X) loaned in 1956 to the Royal Canadian Air Force to test the new, powerful Orenda Iroquois turbojet (rated at dry, afterburning) for the Avro Canada CF-105 Arrow interceptor. Canadair attached the Iroquois engine to the right side of the rear fuselage; due to the large exterior diameter of the engine, no other location was feasible. Flying the CL-52 was reportedly a nightmare. After the Arrow was canceled in early 1959, the B-47B/CL-52, which saw 35 hours of engine flight tests, was returned. Some sources claimed it was bent out of shape; it was scrapped. The CL-52 was the only B-47 to be used by any foreign service.
;YB-47C / RB-47C / B-47Z / B-56
 :A four-engined variant of the B-47, the YB-47C, was proposed by Boeing in 1950 to be powered by four Allison J35-A-23 turbojet engines, providing thrust each, in place of the six GE J47s. The J35 was being developed at the time, and was provisionally rated at (with afterburner) or thrust without AB. Thus 4 * 8500 = using that engine, as compared to 6 * = in the production B-47, making it lighter, simpler and more powerful.Jones 1969, . J71-A-5 A contract was signed in January 1950 for the rework of one B-47B. The first flight was projected for April 1951.
:Due to the J35's less-than-expected performance and delays, other engines were considered, such as the proposed Allison J71, however engine problems meant that it was not feasible for the by-then redesignated B-56A. The Pratt & Whitney J57, eventually rated at thrust, was also considered, but was still in development. The Boeing B-52 Stratofortress, which was being concurrently developed, had priority for this engine. Thus, the B-56 was cancelled in December 1952 before the prototype's conversion had started. The donor fuselage intended for the XB-56 was reused as a ground instructional airframe.
:A four-engined variant of the B-47, the YB-47C, was proposed by Boeing in 1950 to be powered by four Allison J35-A-23 turbojet engines, providing thrust each, in place of the six GE J47s. The J35 was being developed at the time, and was provisionally rated at (with afterburner) or thrust without AB. Thus 4 * 8500 = using that engine, as compared to 6 * = in the production B-47, making it lighter, simpler and more powerful.Jones 1969, . J71-A-5 A contract was signed in January 1950 for the rework of one B-47B. The first flight was projected for April 1951.
:Due to the J35's less-than-expected performance and delays, other engines were considered, such as the proposed Allison J71, however engine problems meant that it was not feasible for the by-then redesignated B-56A. The Pratt & Whitney J57, eventually rated at thrust, was also considered, but was still in development. The Boeing B-52 Stratofortress, which was being concurrently developed, had priority for this engine. Thus, the B-56 was cancelled in December 1952 before the prototype's conversion had started. The donor fuselage intended for the XB-56 was reused as a ground instructional airframe.
 ;XB-47D
:Starting in 1951, two XB-47Ds were modified from B-47Bs as experimental platforms, replacing each inboard two-jet pod with a Wright YT49-W-1 turboprop engine spinning a huge four-bladed prop.Natola 2002, pp. 38–42. Engine development issues delayed the XB-47D's first flight until 26 August 1955. Performance was comparable to a conventional B-47, and its reversible propellers shortened the landing roll, but the idea was not pursued.
;B-47E
;XB-47D
:Starting in 1951, two XB-47Ds were modified from B-47Bs as experimental platforms, replacing each inboard two-jet pod with a Wright YT49-W-1 turboprop engine spinning a huge four-bladed prop.Natola 2002, pp. 38–42. Engine development issues delayed the XB-47D's first flight until 26 August 1955. Performance was comparable to a conventional B-47, and its reversible propellers shortened the landing roll, but the idea was not pursued.
;B-47E
 :The designations B-47C and B-47D applied to variants that were never produced, thus the next production model was the definitive B-47E, first flying on 30 January 1953. Four "blocks" or "phases" were built, each incorporating refinements on the previous block; changes sometimes occurred mid-block. The B-47 incorporated the radar-controlled rear tail turret. A total of 1,341 B-47Es were produced; 691 built by Boeing, 386 built by Lockheed, and 264 built by Douglas. Most B-47Bs were rebuilt to B-47E standards and given the designation of B-47B-II, though they were often called B-47Es.
:Early B-47E-Is had J47-GE-25 turbojets with thrust, these were changed to J47-GE-25A engines with water-
:The designations B-47C and B-47D applied to variants that were never produced, thus the next production model was the definitive B-47E, first flying on 30 January 1953. Four "blocks" or "phases" were built, each incorporating refinements on the previous block; changes sometimes occurred mid-block. The B-47 incorporated the radar-controlled rear tail turret. A total of 1,341 B-47Es were produced; 691 built by Boeing, 386 built by Lockheed, and 264 built by Douglas. Most B-47Bs were rebuilt to B-47E standards and given the designation of B-47B-II, though they were often called B-47Es.
:Early B-47E-Is had J47-GE-25 turbojets with thrust, these were changed to J47-GE-25A engines with water-methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical and the simplest aliphatic alcohol, with the formula C H3 O H (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is a ...
injection, which increased mass flow to temporarily raise thrust to and produce much black smoke when engaged. Jet-Assisted Take Off ( JATO) was installed on early B-47E-Is, integrating 18 JATO bottles, but was removed due to its proximity to fuel tanks. A later JATO system used an external jettisonable "split V" or "horse collar" rack fitted under the rear fuselage, carrying 33 JATO bottles in three rows of 11 bottles;Natola 2002, pp. 31, 36–37, 191, 195. the expendable racks were dropped over specific range areas after takeoff. Early B-47Es had a lower internal fuel capacity of to save weight, which was considered acceptable due to large external tanks and mid-air refueling becoming common practice. A welcome change was the return of ejection seats. The twin .50 in guns (12.7 mm) in the tail turret were replaced with twin 20 mm (0.79 in) cannon for more firepower, backed up by an A-5 FCS in early production and an MD-4 FCS in later production.
:The B-47E-II had only minor changes from later-built B-47E-Is. The B-47E-III featured an ECM suite, consisting of a radar jammer in a bulge under the fuselage plus a chaff
Chaff (; ) is the dry, scaly protective casing of the seeds of cereal grains or similar fine, dry, scaly plant material (such as scaly parts of flowers or finely chopped straw). Chaff is indigestible by humans, but livestock can eat it. In agri ...
dispenser, as well as improved electrical alternators. The B-47E-IV was a major update, featuring stronger landing gear, airframe reinforcement, greater fuel capacity, and an uprated bombload of while the bomb bay was again shortened as nuclear weapons became more compact. Another addition was the MA-7A BNS, which included the AN/APS-64 radar, having a range of up to and could be used as a long range "identification friend or foe
Identification, friend or foe (IFF) is an identification system designed for command and control. It uses a transponder that listens for an ''interrogation'' signal and then sends a ''response'' that identifies the broadcaster. IFF systems usual ...
(IFF) transponder" interrogator to locate other B-47s or tankers, or as a high-resolution ground-targeting radar. The B-47E-IV retained the rarely-used optical bombsight. Most nose windows were deleted; only one remained on each side.
;;TEE TOWN B-47E
:In 1955, 100 B-47E-Is were modified to carry two removable external pods, one mounted on either side of the bomb bay, with each pod containing four AN/ALT-6B jammers. The pods were known as "Tee Town pods" (for Topeka, Kansas, location of Forbes AFB) and so these aircraft were known as "Tee Town B-47s". All retained their bombing capability.
;;EB-47E
:The Tee Town B-47Es led to a specialized ECM conversion, the EB-47E. "Phase IV" or "Blue Cradle" aircraft used a removable cradle housing 16 jammers in the bomb bay, plus radar warning receivers and chaff dispensers. The advanced "Phase V" EB-47E had a pressurized module holding 13 jammers stowed in the bomb bay controlled by two Electronic Warfare Officers (EWOs), also known as "Crows" or "Ravens".Natola 2002, pp. 146, 164–165, 182, 192, 208–211, 214. While the Phase IV jammer was "broadband", covering a wide frequency range to jam radars operating within that range, the Phase V jammer could be selectively tuned to specific radar frequencies, enabling higher jammer power on the most effective frequencies. About 40 B-47Es were converted to EB-47Es; they could not carry bombs but retained tail turrets.
:B-47E ''52-0410'' and ''52-0412'' were converted to EB-47Es in the mid-1960s for the U.S. Navy's Fleet Electronic Warfare Support Group ( FEWSG). Considered to be on indefinite loan, they differed from USAF EB-47Es in that some podded ECM gear was mounted on the external fuel tank pylons. Used as "electronic aggressors" to test ECM systems, they were the last B-47s in service, ''52-0410'' performed its last flight on 20 December 1977.
;;EB-47E(TT)
:Three B-47Es were converted to the specialized EB-47E(TT) "Tell Two" configuration to be used for " telemetry intelligence", picking up radio signals from Soviet missile tests and space launches, being a precursor to the RC-135S Rivet Ball and Cobra Ball. It featured two ECM operators, a "Crow capsule" in the bomb bay loaded with gear, and distinctive antennas below each side of the cockpit. All three aircraft were operated out of Turkey until 1967. Crews often made up stories about their purpose, such as a "return to fighter" defensive system that made air-to-air missiles loop back and attack their own launch fighters.
;;ETB-47E
:As with the B-47B, a few B-47Es were converted to trainers, with a fourth seat for an instructor, and designated ETB-47E. They replaced older TB-47Bs, serving into the early 1960s.
;;DB-47E / YDB-47E
:Two B-47Es were converted to YDB-47Es to support the GAM-63 RASCAL stand-off missile program; two more B-47Es were converted to DB-47Es in preparation for the missile's introduction before it was axed and were reused as drone controller aircraft.
;;JB-47E
:Several B-47Es were assigned to other specialized test duties and given the blanket designation of JB-47E. One was used in the late 1960s to test "fly by wire" control system concepts.
;;JTB-47E
:Two B-47Es were also used for secret flight experiments in the early 1960s and given the designation JTB-47E, and a third modified B-47E was given the designation JRB-47E. They appear to have been test platforms for ECM systems.
;;NB-47E
:A B-47E was loaned to the US Navy to test the GE TF34-2 turbofan for the Lockheed S-3 Viking. It was given the designation NB-47E and performed test flights from 1969 through 1975.
;;QB-47E
:A total of 14 RB-47Es were converted to QB-47E target drones in 1959 and 1960. These aircraft were radio-controlled and included self-destruct charges, arresting gear to assist landings, and carried pods on the external tank pylons to help in scoring weapons tests. Apparently most missiles fired on them were directed for a near-miss, but the QB-47Es were nonetheless eventually whittled down to two survivors that were retired in the early 1970s.
;;RB-47E
: :The B-47E was the basis for several reconnaissance models, the only B-47s to see anything resembling combat. They operated from most airfields that gave access to the USSR and often probed Soviet airspace. Boeing built 240 RB-47Es, similar to the B-47E but with a nose stretched by , giving an arguably more elegant appearance. The long nose accommodated up to 11 cameras, possibly including an O-15 radar camera for low-altitude work, a forward oblique camera for low-altitude work, a K-17 trimetrogon (three-angle) camera for panoramic shots and K-36 telescopic cameras. Cameras were controlled by the "navigator-photographer". Photoflash
:The B-47E was the basis for several reconnaissance models, the only B-47s to see anything resembling combat. They operated from most airfields that gave access to the USSR and often probed Soviet airspace. Boeing built 240 RB-47Es, similar to the B-47E but with a nose stretched by , giving an arguably more elegant appearance. The long nose accommodated up to 11 cameras, possibly including an O-15 radar camera for low-altitude work, a forward oblique camera for low-altitude work, a K-17 trimetrogon (three-angle) camera for panoramic shots and K-36 telescopic cameras. Cameras were controlled by the "navigator-photographer". Photoflash flares
A flare, also sometimes called a fusée, fusee, or bengala in some Latin-speaking countries, is a type of pyrotechnic that produces a bright light or intense heat without an explosion. Flares are used for distress signaling, illumination, o ...
were carried for night photography. While it could be refueled in flight, fuel capacity was increased to a total of .
;;WB-47E
 :Following the single WB-47B conversion, in the early 1960s, 34 B-47Es were converted by Lockheed into WB-47Es for weather reconnaissance to replace 44 WB-50D Superfortresses that had suffered several fatal crashes between 1956 and 1960. Stripped of combat gear, they were fitted with nose cameras to photograph cloud formations and a meteorological instrument pod in the bomb bay. Initially assigned to the Air Weather Service of the
:Following the single WB-47B conversion, in the early 1960s, 34 B-47Es were converted by Lockheed into WB-47Es for weather reconnaissance to replace 44 WB-50D Superfortresses that had suffered several fatal crashes between 1956 and 1960. Stripped of combat gear, they were fitted with nose cameras to photograph cloud formations and a meteorological instrument pod in the bomb bay. Initially assigned to the Air Weather Service of the Military Air Transport Service
The Military Air Transport Service (MATS) is an inactive Department of Defense Unified Command. Activated on 1 June 1948, MATS was a consolidation of the United States Navy's Naval Air Transport Service (NATS) and the United States Air Force's ...
(MATS), they became part of the Military Airlift Command (MAC) upon its establishment. The WB-47Es, the last B-47s in USAF service, were retired in October 1969.
:The 53d Weather Reconnaissance Squadron
The 53rd Weather Reconnaissance Squadron, also known by its nickname, Hurricane Hunters, is a flying unit of the United States Air Force, and "the only Department of Defense organization still flying into tropical storms and hurricanes." Aligne ...
, of the 9th Weather Reconnaissance Wing
The 9th Weather Reconnaissance Wing is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with Air Weather Service at McClellan Air Force Base, California, where it was inactivated on 31 August 1975.
History
Weather re ...
, operated WB-47Es from Hunter Air Force Base
Hunting is the human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products (fur/ hide, bone/tusks, horn/ antler, ...
and Ramey Air Force Base. These assets were transferred to the 57th Weather Reconnaissance Squadron
The 57th Weather Reconnaissance Squadron is an inactive United States Air Force squadron. Its last assignment was with the 9th Weather Reconnaissance Wing at Hickam Air Force Base, Hawaii, where it was inactivated on 10 November 1969.
History ...
for Operation Arc Light, operating from Clark Air Base
Clark Air Base is a Philippine Air Force base on Luzon Island in the Philippines, located west of Angeles City, about northwest of Metro Manila. Clark Air Base was previously a United States military facility, operated by the U.S. Air Forc ...
.Natola 2002, pp. 177–179.
;RB-47H/ERB-47H
 :A total of 32 RB-47H models were built for electronic intelligence ( ELINT) missions, as well as three more specialized "ERB-47Hs". Featuring a distinctive blunt, rounded nose and sported blisters and pods for intelligence-gathering antennas and gear, they were designed to probe defenses and collect data on radar and communications signals. The bomb bay was replaced by a pressurized compartment, which accommodated "Crows", or Electronic Warfare Officers (EWOs). There were three Crows on board the RB-47H and two on the ERB-47H. A distinctive bulged radome fairing replaced the bomb bay doors. They retained the tail turret and were fitted with jammers and chaff dispensers. A recognizable difference between the RB-47H and ERB-47H was the latter's distinctive antenna fairing under the rounded nose.
:The first RB-47H was delivered in August 1955 to Forbes AFB, Kansas. They received a "Mod 44" or "Silver King" program in 1961 to update electronics systems and was recognizable by a large teardrop pod for ELINT antennas upon a pylon under the belly and offset to one side, as well as a pylon-style antenna under each wing beyond the outboard engine. The EWO compartment was cramped with sitting room only and had both poor noise insulation and climate control, making 12-hour missions uncomfortable and tiring. Successful ejection downward through the belly radome was impossible near the ground. Crews sat bobsled-like on the pilot compartment's floor for takeoff and landing. They then crawled encumbered with Arctic clothing and parachute to and from their compartment along an unpressurized maintenance shelf during a temporary level-off at .
:A total of 32 RB-47H models were built for electronic intelligence ( ELINT) missions, as well as three more specialized "ERB-47Hs". Featuring a distinctive blunt, rounded nose and sported blisters and pods for intelligence-gathering antennas and gear, they were designed to probe defenses and collect data on radar and communications signals. The bomb bay was replaced by a pressurized compartment, which accommodated "Crows", or Electronic Warfare Officers (EWOs). There were three Crows on board the RB-47H and two on the ERB-47H. A distinctive bulged radome fairing replaced the bomb bay doors. They retained the tail turret and were fitted with jammers and chaff dispensers. A recognizable difference between the RB-47H and ERB-47H was the latter's distinctive antenna fairing under the rounded nose.
:The first RB-47H was delivered in August 1955 to Forbes AFB, Kansas. They received a "Mod 44" or "Silver King" program in 1961 to update electronics systems and was recognizable by a large teardrop pod for ELINT antennas upon a pylon under the belly and offset to one side, as well as a pylon-style antenna under each wing beyond the outboard engine. The EWO compartment was cramped with sitting room only and had both poor noise insulation and climate control, making 12-hour missions uncomfortable and tiring. Successful ejection downward through the belly radome was impossible near the ground. Crews sat bobsled-like on the pilot compartment's floor for takeoff and landing. They then crawled encumbered with Arctic clothing and parachute to and from their compartment along an unpressurized maintenance shelf during a temporary level-off at .
 :Operations were generally flown at night and classified Top Secret.Natola 2002, pp. 179–181. The final RB-47H to be retired from service, ''53-4296'', was reactivated and fitted with an F-111-style nose to test avionics for the General Dynamics FB-111 in the early 1970s. It was not given any special designation. It is now on display at the Air Force Armament Museum at Eglin Air Force Base, fitted with a bomber nose.
;YB-47J
:A single B-47E was modified to test the MA-2 BNS for the B-52, and given the designation YB-47J.
;RB-47K
:The RB-47K was a photo and weather reconnaissance variant based on the RB-47E generally used for weather reconnaissance missions, carrying eight dropsonde weather sensors that were released at various checkpoints along its flight path. Data radioed from the dropsondes was logged by the navigator. Fifteen RB-47Ks were built, the variant was in service until 1963.
;EB-47L
:Between 1961 and 1963, 36 B-47Es were modified to carry a communications relay system and were designated EB-47L. Used to support US flying command post aircraft in case of a nuclear attack on the US, the EB-47Ls were only briefly in service as improved communications technologies made them redundant by 1965.
:Operations were generally flown at night and classified Top Secret.Natola 2002, pp. 179–181. The final RB-47H to be retired from service, ''53-4296'', was reactivated and fitted with an F-111-style nose to test avionics for the General Dynamics FB-111 in the early 1970s. It was not given any special designation. It is now on display at the Air Force Armament Museum at Eglin Air Force Base, fitted with a bomber nose.
;YB-47J
:A single B-47E was modified to test the MA-2 BNS for the B-52, and given the designation YB-47J.
;RB-47K
:The RB-47K was a photo and weather reconnaissance variant based on the RB-47E generally used for weather reconnaissance missions, carrying eight dropsonde weather sensors that were released at various checkpoints along its flight path. Data radioed from the dropsondes was logged by the navigator. Fifteen RB-47Ks were built, the variant was in service until 1963.
;EB-47L
:Between 1961 and 1963, 36 B-47Es were modified to carry a communications relay system and were designated EB-47L. Used to support US flying command post aircraft in case of a nuclear attack on the US, the EB-47Ls were only briefly in service as improved communications technologies made them redundant by 1965.
Operators
; * United States Air Force * United States Navy ; * Royal Canadian Air Force – 1 B-47B loaned to Canada and converted by Canadair with the designation CL-52 to test the CF-105 Avro Arrow's Orenda engines in 1956; returned to the U.S. Air Force and scrapped (1957)Surviving aircraft
 Twenty-three surviving airframes exist in museum collections; all are located in the United States.
Twenty-three surviving airframes exist in museum collections; all are located in the United States.
Accidents and incidents
 Over the operating history of the B-47, 203 aircraft were lost in crashes, with 464 deaths. This represents approximately 10% of the total number produced.
On 8 February 1954, a B-47 of the 22nd Bomber Wing, March AFB, California, crashed in Stoke Wood, a mile and a half short of the runway at RAF Upper Heyford, England, while on a training run. All three crew were killed.
On 28 February 1955, a crippled B-47 crashed into a trailer park in Lake Charles, Louisiana, killing the three crewmen and two people on the ground.
On 10 March 1956, four B-47s left MacDill Air Force Base in Florida for a non-stop flight to Ben Guerir Air Base in Morocco. After descending through clouds to begin their second round of
Over the operating history of the B-47, 203 aircraft were lost in crashes, with 464 deaths. This represents approximately 10% of the total number produced.
On 8 February 1954, a B-47 of the 22nd Bomber Wing, March AFB, California, crashed in Stoke Wood, a mile and a half short of the runway at RAF Upper Heyford, England, while on a training run. All three crew were killed.
On 28 February 1955, a crippled B-47 crashed into a trailer park in Lake Charles, Louisiana, killing the three crewmen and two people on the ground.
On 10 March 1956, four B-47s left MacDill Air Force Base in Florida for a non-stop flight to Ben Guerir Air Base in Morocco. After descending through clouds to begin their second round of aerial refueling
Aerial refueling, also referred to as air refueling, in-flight refueling (IFR), air-to-air refueling (AAR), and tanking, is the process of transferring aviation fuel from one aircraft (the tanker) to another (the receiver) while both aircraft a ...
over the Mediterranean Sea at 14,000 feet, one of the four aircraft, serial number 52-0534, failed to make contact with the tanker; neither the aircraft, its two nuclear weapon cores, nor its personnel were ever found.
On 28 March 1956, a B-47 exploded near Wichita, Kansas, with an instructor and two student pilots on board. It crashed four miles northeast of the city, killing its crew of three. The office of information services at McConnell Air Force Base said the explosion occurred after takeoff, probably at about 2,000 feet altitude. Wreckage was strewn along the countryside for several miles as the wings sheared off and the fuselage tumbled to earth.
On 27 July 1956, a B-47 of the 307th Bombardment Wing crashed at RAF Lakenheath killing its crew and causing a near radioactive incident when it hit a storage igloo containing three MK-6 nuclear weapons. Although the bombs involved lacked their fissile cores, each carried about 8,000 pounds of high explosives for their trigger mechanism. The crash and ensuing fire did not ignite the high explosives and no detonation occurred.
In November 1956, B-47E serial number 51-2421 of the 96th Bombardment Wing, flying from Altus AFB, crashed on a farm near Hobart, Oklahoma, following engine problems. Four crewmen were killed in the incident.
On 9 October 1957, B-47 serial number 51-2177A, of the 447th Bomb Squadron, 321st Bomb Wing at Pinecastle Air Force Base suffered wing failure and crashed northwest of Orlando, Florida
Orlando () is a city in the U.S. state of Florida and is the county seat of Orange County, Florida, Orange County. In Central Florida, it is the center of the Greater Orlando, Orlando metropolitan area, which had a population of 2,509,831, acco ...
, and west of Winter Park, Florida, while conducting a practice demonstration for the annual Strategic Air Command Bombing Navigation and Reconnaissance Competition at Pinecastle AFB. The wing commander, Colonel Michael Norman Wright McCoy, was killed in the crash; Pinecastle AFB was later renamed McCoy AFB in his honor.
On 4 December 1957, a MacDill Air Force Base B-47 exploded in mid-air over Choctawhatchee Bay, Okaloosa County, Florida. Parts were scattered over a wide underwater area that varied in depth from 20 to 30 feet. Assistance from US Navy divers from the Mine Detection Laboratory, Panama City, Florida, the Underwater Demolition Team No. 21 from Little Creek, Va., the 3201st Boat Squadron, APGC, recovered most of the plane. The three crew were killed.
On 5 February 1958, a B-47 was involved in a mid-air collision with an F-86
The North American F-86 Sabre, sometimes called the Sabrejet, is a transonic jet fighter aircraft. Produced by North American Aviation, the Sabre is best known as the United States' first swept-wing fighter that could counter the swept-wing Sov ...
fighter over Georgia, known as 1958 Tybee Island mid-air collision
The Tybee Island mid-air collision was an incident on February 5, 1958, in which the United States Air Force lost a Mark 15 nuclear bomb in the waters off Tybee Island near Savannah, Georgia, United States. During a practice exercise, an F-86 f ...
.Natola 2002, pp. 77–80.
On 26 February 1958, RB-47E serial number 52-0720 crashed six miles south of Lancaster, OH on approach to Lockbourne AFB, OH, hitting the ground at an angle of 50 degrees. It was determined that the aircraft attained an unusual attitude and/or high speed through disorientation, from which there was no recovery. In actuality, a wheel door had broken away and prevented the control surfaces being fully active.
On 13 March 1958, two B-47s crashed on the same date in separate incidents when the lower wing skin failed at the same structural location. One exploded over southeast Tulsa, Oklahoma, killing one crewman and raining debris over at least 8 square miles, witnessed by thousands of people on the ground. Two of the three men on a training mission from McConnell Air Force Base in Wichita, Kansas, parachuted to safety. The third was trapped in the nose of the plane and died.
On 10 April 1958, a B-47 from Lockbourne Air Force Base, Ohio, exploded mid-flight behind the KC-97G tanker that was to refuel it. The KC-97 was unharmed, but the wreckage fell within a half-mile of a highway and none of the crew survived.
On 15 April 1958, a B-47 from Walker Air Force Base in New Mexico, serial number
A serial number is a unique identifier assigned incrementally or sequentially to an item, to ''uniquely'' identify it.
Serial numbers need not be strictly numerical. They may contain letters and other typographical symbols, or may consist enti ...
52–0562, crashed on takeoff at Pease Air Force Base
Pease, in Middle English, was a noun referring to the vegetable pea; see that article for its etymology. The word survives into modern English in pease pudding.
Pease may also refer to:
People
*Pease family (Darlington), a prominent family in ...
in New Hampshire; all four crewmen were killed.
On 22 November 1958, a B-47B crashed while taking off from Loring Air Force Base in Maine, killing all four crew members on board. The plane belonged to a unit at McCoy Air Force Base in Orlando, Florida. The plane was described as having veered sharply to the right while two-thirds of the way down the runway, eventually crashing 400 feet north of the runway. On 25 November 1958, a KC-135 of the 42d Air Refueling Squadron crashed on takeoff roughly in the same area as the B-47 three days before.
On 4 April 1959, B-47 serial number 52-0320 crashed in the Santa Rita mountains, south of Tucson, Arizona, while attempting to land at Davis-Monthan AFB. All three crew were killed. Investigators noted that a faulty altimeter was a contributing factor.
On 24 April 1959, Captain John S. Lappo, operating from Lockbourne AFB flew a B-47 with two crewmen on board under the Mackinac Bridge in Michigan. Following a general court-martial
A court-martial or court martial (plural ''courts-martial'' or ''courts martial'', as "martial" is a postpositive adjective) is a military court or a trial conducted in such a court. A court-martial is empowered to determine the guilt of me ...
, he was grounded for life.
On 30 December 1959, a B-47B crashed at Torrejón Air Base, Spain one minute after takeoff. All four crew members were killed.
On 31 March 1960, B-47E serial number 52-1414, of the 384th Bomb Wing (SAC), 545th Bombardment Squadron, Little Rock AFB, exploded inflight over Little Rock, Arkansas. Three of the four crew and two civilians on the ground were killed.
On 4 January 1961, B-47 serial number 53-4244, based at Pease Air Force Base, crashed on takeoff; all four crewmen were killed.
On 24 February 1961, a B-47 crashed 10 miles southwest of Hurley, Wisconsin, while on a practice bombing mission from the 40th Bomb Wing at Forbes Air Force Base, Topeka, Kansas. Its four crew were killed. An engine was found 600 yards from the point of impact, indicating it detached prior to the crash.
On 2 May 1961, a B-47 crashed eight miles southwest of Hurley, Wisconsin, only a few miles from the scene of a prior B-47 crash on 24 February 1961. Two of four crew survived. Evidence showed that it was steeply diving when the crash occurred.
In January 1962, a B-47 based at Plattsburgh Air Force Base on a training mission crashed into the side of Wright Peak
Wright Peak is the 16th highest peak in the Adirondack High Peaks, High Peaks of the Adirondack Park, and is located in the MacIntyre Range in the town of North Elba, New York, in Essex County, New York, Essex County, New York (state), New Yor ...
in the High Peaks in the Adirondacks of New York. All four crew were killed. It had veered about 30 miles east due to inclement weather. Wreckage can still be found at the summit, including a landing gear strut and a partial engine.
On 23 July 1962, a B-47 based at Dyess Air Force Base near Abilene, Texas, departed on a training mission through Montana. After crossing into Paradise Valley, it crashed into Emigrant Peak and exploded while turning toward the northwest. All four crew were killed.
On 3 August 1962, B-47 serial number 52-0526, based at Pease Air Force Base, crashed on takeoff; all three crew were killed.
On 22 August 1962, B-47 serial number 52-0553, based at Davis–Monthan Air Force Base near Tucson, Arizona, crashed on a training mission shortly before midnight in the Idaho mountains south of Smiths Ferry; controlled flight into terrain started a forest fire
A wildfire, forest fire, bushfire, wildland fire or rural fire is an unplanned, uncontrolled and unpredictable fire in an area of Combustibility and flammability, combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire ...
, and all three crew were killed.
On 20 February 1963, a B-47 of the 98th Bomb Wing based at Lincoln AFB, Nebraska, crashed in Bashaw Township, approximately three miles north of the town of Comfrey, Minnesota. All four crew were killed. It had just completed a low-altitude simulated bombing run near the town of Heron Lake, Minnesota
Heron Lake is a city in Jackson County, Minnesota, United States. The population was 698 at the 2010 census.
History
Heron Lake was named in 1870 after a local lake where great blue herons were seen.
Heron Lake was named after the Black-Crown ...
, when the sixth engine failed, causing it to crash in a field, resulting in a 25-foot deep by 50-foot wide crater.
On 20 August 1963, a QB-47 veered off course on its landing approach at Eglin Air Force Base and crash landed on a road parallel to the runway. It was used for Bomarc Missile Program tests, normally operated from Eglin Air Force Base Auxiliary Field Number Three (Duke Field
Duke Field , also known as Eglin AFB Auxiliary Field #3, is a military airport located three miles (5 km) south of the central business district of Crestview, in Okaloosa County, Florida, United States.
History
Duke Field was one of the f ...
), approximately north of the main base. Two cars were crushed, killing two occupants and injuring a third.
On 8 December 1964, B-47 serial number 52-0339, based at Pease Air Force Base, crashed in Newington, New Hampshire, shortly after takeoff; all four crewmen were killed.
Specifications (B-47E)
Notable appearances in media
See also
References
Citations
Bibliography
* Boyne, Walter J.br>"Airpower Classics: B-47 Stratojet."''Air Force Magazine'', August 2007, Air Force Association. Retrieved 4 June 2009. * Boyne, Walter J. "The Long Reach Of The Stratojet." ''Air Force Magazine'' Vol. 66, issue 71, December 1997. * Bowers, Peter M. "The Boeing B-47" ''Aircraft in Profile, Volume 4''. Windsor, Berkshire, UK: Profile Publications Ltd., 2nd revised and enlarged edition, 1970. . * Bowers, Peter M. ''Boeing Aircraft since 1916''. London: Putnam, 1989. . * Cook, William H. ''The Road to the 707: The Inside Story of Designing the 707.'' Bellevue, Washington: TYC Publishing, 1991. . * Dennison, Robert C. "Stratojet!" ''Air Combat'', July /August 1997. (Dennison is a retired USAF officer and B-47 pilot who works with the B-47 Stratojet Association.) * Fraser, Jim
"I Fly The World's Fastest Bomber."
''Popular Science'', November 1949. Vol. 155, No. 5. pp. 139–142. . * Grant, R.G. and John R. Dailey. ''Flight: 100 Years of Aviation''. Harlow, Essex, UK: DK Adult, 2007. . * Gunston, Bill. ''Bombers of the West''. London: Ian Allan Ltd., 1973, pp. 126–153. . * Gunston, Bill and Peter Gilchrist. ''Jet Bombers: From the Messerschmitt Me 262 to the Stealth B-2''. Osprey, 1993. . * Johnston, A.M. ''Tex Johnston: Jet-Age Test Pilot''. Washington D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Press, 2000. . * Jones, Lloyd S. ''U.S. Bombers, B-1 1928 to B-1 1980s''. Fallbrook, California: Aero Publishers, 1962, second edition 1974. . * Jones, Lloyd S. ''U.S. Bombers: 1928-1980s''. Fallbrook, California: Aero Publishers, Inc., 1981. . * Knaack, Marcelle Size
''Post-World War II Bombers, 1945–1973''(PDF).
Washington, D.C.: Office of Air Force History, 1988. . * Lloyd, Alwyn T. "Boeing's B-47 Stratojet". North Branch Minnesota: Specialty Press, 2005. . * Loftin, Laurence K. Jr
''NASA Scientific and Technical Information Branch'', 2004. * Natola, Mark. "Boeing B-47 Stratojet." ''Schiffer Publishing Ltd'', 2002. . * Peacock, Lindsay. "Stratojet...Progenitor of a Dynasty". '' Air Enthusiast'', Thirty-eight, January–April 1989, pp. 31–44, 63. Bromley, UK: FineScroll. ISSN 0143-5450. * Powers, Francis. "Operation Overflight: A Memoir of the U-2 Incident." ''Potomac Books Inc'', 2004. . * Tegler, Jan. ''B-47 Stratojet: Boeing's Brilliant Bomber''. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2000. . * Yeager, Chuck. "Yeager." ''Bantam Book'', 1985. . * Yenne, Bill. "Variant Briefing: Boeing B-47 Stratojet". ''International Air Power Review'', Volume Six, Autumn/Fall 2002, pp. 156–171. Norwalk, Connecticut: AIRtime Publishing. . ISSN 1473-9917.
External links
* *National Museum fact sheet Boeing B-56E
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20121206030916/http://www.millionmonkeytheater.com/B-47.html Forgotten Jets – Boeing B-47 Stratojet series– status of all 2,032 produced
B-47 Stratojet Association
{{Authority control B-47 Stratojet Boeing B-47 Boeing B-56 Six-engined jet aircraft Articles containing video clips High-wing aircraft Aircraft first flown in 1947