Avonmouth Dock Railway Station on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Avonmouth railway station is located on the Severn Beach Line and serves the district of Avonmouth in Bristol, England. It is from . Its three letter station code is AVN. The station has two platforms, on either side of two running lines. it is managed by
 The station is located in the Avonmouth district of Bristol, an area of mixed industrial and residential usage. The station sits to the south of the junction of Gloucester Road and Portview Road, the tracks running to parallel to Portview Road and crossing Gloucester Road at a level crossing. The station is on the Severn Beach Line from to , from Temple Meads and from Severn Beach.Railways in the United Kingdom are, for historical reasons, measured in miles and chains. There are 80 chains to the mile. The next station towards Temple Meads is currently , although a new station at
The station is located in the Avonmouth district of Bristol, an area of mixed industrial and residential usage. The station sits to the south of the junction of Gloucester Road and Portview Road, the tracks running to parallel to Portview Road and crossing Gloucester Road at a level crossing. The station is on the Severn Beach Line from to , from Temple Meads and from Severn Beach.Railways in the United Kingdom are, for historical reasons, measured in miles and chains. There are 80 chains to the mile. The next station towards Temple Meads is currently , although a new station at
 All services at Avonmouth are operated by
All services at Avonmouth are operated by
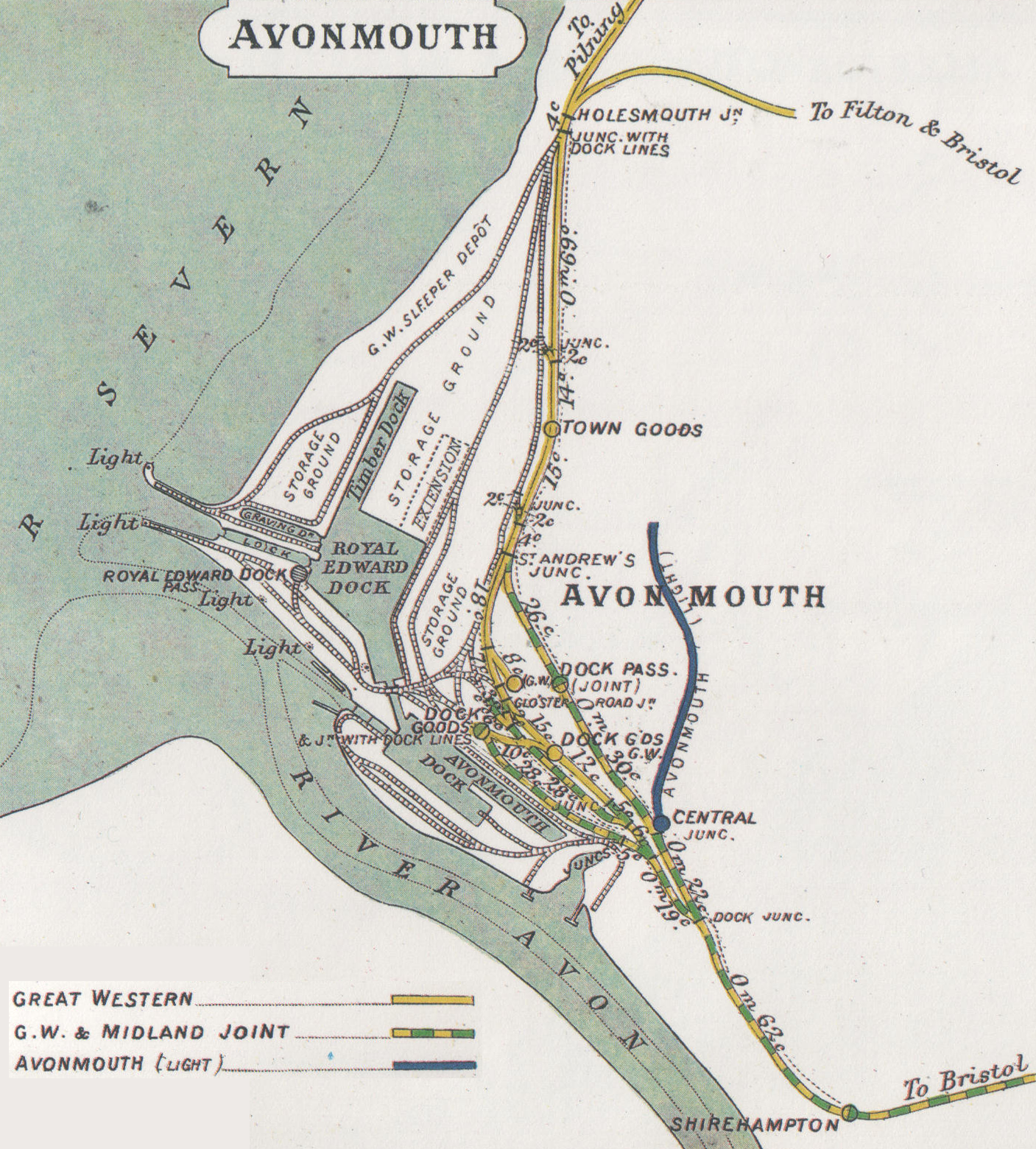 The railways first came to Avonmouth in 1865, when services began on the
The railways first came to Avonmouth in 1865, when services began on the
 When the railways were nationalised in 1948, services at Avonmouth Dock came under the aegis of the Western Region of British Railways. By 1955, service levels had decreased slightly to 28 trains per day from Bristol and 29 return, but the services were at regular intervals. Passenger numbers however dropped sharply in 1961 as the result of a fare increase, and so in 1962 a new reduced timetable was enacted, which lost more passengers. A year later in 1963, the Beeching report suggested the complete withdrawal of services along the line, but ultimately only those beyond Severn Beach or via Henbury were withdrawn. Goods services from the station ended on 20 June 1966, the same day that the station was renamed "Avonmouth". The bay platform was taken out of use and the land later taken for industrial buildings. From 17 July 1967 all staffing was withdrawn from stations along the line, including Avonmouth, with tickets issued by the train guard. The station buildings on the island platform survived into the 1970s, as did the footbridge, but with the exception of the parcels office, all were later demolished. The parcels office was in use in 2006 as a hairdressing salon. The signal box was closed in January 1969, and in September 1973 the wooden level crossing gates were replaced by automatic lifting barriers. By 1974, service had reduced to 19 trains per day in each direction, with no Sunday services to Severn Beach.
When the railways were nationalised in 1948, services at Avonmouth Dock came under the aegis of the Western Region of British Railways. By 1955, service levels had decreased slightly to 28 trains per day from Bristol and 29 return, but the services were at regular intervals. Passenger numbers however dropped sharply in 1961 as the result of a fare increase, and so in 1962 a new reduced timetable was enacted, which lost more passengers. A year later in 1963, the Beeching report suggested the complete withdrawal of services along the line, but ultimately only those beyond Severn Beach or via Henbury were withdrawn. Goods services from the station ended on 20 June 1966, the same day that the station was renamed "Avonmouth". The bay platform was taken out of use and the land later taken for industrial buildings. From 17 July 1967 all staffing was withdrawn from stations along the line, including Avonmouth, with tickets issued by the train guard. The station buildings on the island platform survived into the 1970s, as did the footbridge, but with the exception of the parcels office, all were later demolished. The parcels office was in use in 2006 as a hairdressing salon. The signal box was closed in January 1969, and in September 1973 the wooden level crossing gates were replaced by automatic lifting barriers. By 1974, service had reduced to 19 trains per day in each direction, with no Sunday services to Severn Beach.
 The final remaining station building, the old parcels office, was demolished in 2015. Local rail campaigners, including Friends of Suburban Bristol Railways and MP Charlotte Leslie, petitioned to prevent the demolition, however Network Rail stated that the cost of restoration was too high and that it had become a safety risk.
The final remaining station building, the old parcels office, was demolished in 2015. Local rail campaigners, including Friends of Suburban Bristol Railways and MP Charlotte Leslie, petitioned to prevent the demolition, however Network Rail stated that the cost of restoration was too high and that it had become a safety risk.
Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran ...
, which is the third franchise to be responsible for the station since privatisation
Privatization (also privatisation in British English) can mean several different things, most commonly referring to moving something from the public sector into the private sector. It is also sometimes used as a synonym for deregulation when ...
in 1997. They provide all train services at the station, mainly a train every 30 minutes to and one every hour to .
The station was opened in 1877 by the Bristol Port Railway and Pier
The Bristol Port Railway and Pier (occasionally referred to as the Bristol Port and Pier Railway) was a railway in Bristol, England.
Route
The Bristol Port Railway and Pier company (BPRP) ran from a main terminus at (originally called Clifton), ...
, a railway which ran along the River Avon from to a pier at Avonmouth. The station, originally known as Avonmouth Dock, had a single platform, but was rebuilt with two platforms by the Great Western and Midland
Midland may refer to:
Places Australia
* Midland, Western Australia
Canada
* Midland, Albert County, New Brunswick
* Midland, Kings County, New Brunswick
* Midland, Newfoundland and Labrador
* Midland, Ontario
India
* Midland Ward, Kohima, Nagal ...
Railways in 1885 when they began services via . The station was enhanced numerous times in the early part of the twentieth century, and by 1913 employed 72 staff. Facilities included a goods yard, signal box and engine shed.
The Severn Beach Line declined over the latter half of the twentieth century, with passenger numbers falling significantly. Goods services at Avonmouth ended in 1966, and all staff were withdrawn in 1967. Services had decreased to 10 per day each direction by 2005, but have since increased to a train every 30 minutes to Bristol and hourly to Severn Beach.
Description
Portway Park and Ride
The Portway park and ride site is on the A4 Portway at Shirehampton, to the north-west of Bristol, England, close to junction 18 of the M5 motorway.
History
The site opened in April 2002 with 300 car parking spaces as part of the Bristol par ...
is due to open in the summer of 2022. The next station towards Severn Beach is .
The station is on a north-west/south-east alignment, with two platforms separated by two running lines. The southern "up" platform, adjacent to the "Up Main" line, is used for trains towards Severn Beach. The northern "down" platform, adjacent to the "Down Main" line, is bidirectionally signalled, allowing it to be used by terminating trains and those heading towards Bristol. Both platforms have significant portions of their length fenced off, giving usable lengths of for the southern platform and for the northern.
Facilities at the station are minimal – there is a wooden canopy and bench seating on the northern platform, with a small metal shelter on the southern. Timetable information is provided; help points show next train information and allow users to contact railway staff. There is no ticket office or other means for buying or collecting tickets, however an electronic ticketing
Electronic may refer to:
*Electronics, the science of how to control electric energy in semiconductor
* ''Electronics'' (magazine), a defunct American trade journal
*Electronic storage, the storage of data using an electronic device
*Electronic co ...
trial is to be rolled out at the station. There is a car park with six spaces, as well as stands for four bicycles. The nearest bus stops are away on Avonmouth Road.
The line through Avonmouth has a speed limit of for locomotive-hauled trains and for diesel multiple units. The line, which is not electrified, handles less than 5 million train tonnes per year, has a loading gauge
A loading gauge is a diagram or physical structure that defines the maximum height and width dimensions in railway vehicles and their loads. Their purpose is to ensure that rail vehicles can pass safely through tunnels and under bridges, and ke ...
of W6 and a route availability of 7. , more than 110,000 passengers used Avonmouth station, making it the 1,635th busiest station in the country and the sixth busiest within the Bristol unitary authority area
A unitary authority is a local government, local authority responsible for all local government functions within its area or performing additional functions that elsewhere are usually performed by a higher level of sub-national government or the ...
. This was an increase of 175% from the 2002–03 financial year, and reflected a general rise in usage of the Severn Beach Line.Annual estimated passenger usage based on sales of tickets in stated financial year(s) which end or originate at Avonmouth, from Office of Rail and Road statistics. Methodology may vary year on year. The 2014-15 estimates of station usage saw a further increase of 8% to 120,000 making it the 1,614th busiest station in the country.
Services
Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran ...
using ''Turbo'' DMUs
A diesel multiple unit or DMU is a multiple-unit train powered by on-board diesel engines. A DMU requires no separate locomotive, as the engines are incorporated into one or more of the carriages. Diesel-powered single-unit railcars are also ...
.
The typical off-peak service in trains per hour is:
* 2 tph to of which 1 continues to
* 1 tph to
On Sundays, there is an hourly service between Bristol Temple Meads and Severn Beach with one train per day to and from Weston-super-Mare.
Services previously ran every 40 minutes to Bristol and every two hours to Severn Beach but were increased to half-hourly to Bristol and hourly to Severn Beach in the December 2021 timetable change.
History
Construction and early operations
 The railways first came to Avonmouth in 1865, when services began on the
The railways first came to Avonmouth in 1865, when services began on the Bristol Port Railway and Pier
The Bristol Port Railway and Pier (occasionally referred to as the Bristol Port and Pier Railway) was a railway in Bristol, England.
Route
The Bristol Port Railway and Pier company (BPRP) ran from a main terminus at (originally called Clifton), ...
(BPRP), a self-contained railway which ran along the north bank of the River Avon to a deep water pier on the Severn Estuary. The BPRP line ran through the site of the current station and beyond to a terminus at the first Avonmouth station. The BPRP ran into trouble by 1871 when the terminal pier at Avonmouth became difficult to use due to a build-up of silt. With no prospect of a proper dock being funded without a connection to the national rail network, the Clifton Extension Railway (CER) was approved. This was a joint venture by the BPRP, Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran ...
(GWR) and Midland Railway (MR) which ran from Sneyd Park Junction, south of , via , to join up with the national network at Narroways Hill Junction. The link opened in 1877, but initially only for goods trains. The route from Sneyd Park Junction to Clifton Down was subsequently cleared for passenger use on 3 August 1878, but the Midland and Great Western Railways did not think the BPRP track was in a suitable condition and so refused to run any passenger trains beyond Clifton Down.
The station, originally known as Avonmouth Dock, was opened in 1877, shortly after the opening of the Avonmouth Docks in February that year. It was built on, or very near to, the site of a halt built in 1868 for the Docks' construction workers. The local area was still mostly rural – there were a few buildings around the station area, as well as the docks, with the closest extent of the Bristol conurbation away at Shirehampton. The station cost £275 to build, and was merely a platform on the south side of the single track, served by eight trains per day between and the BPRP's Avonmouth terminus, increasing to ten per day from 1887. The Great Western and Midland Railways considered the station inadequate for the passenger numbers expected, and so purchased additional land to enhance the station with extra tracks. The new station comprised a wide island platform – the northern face on the original through line, the southern face being for a new terminal line. The station, now known as Avonmouth Dock Joint, was constructed using mainly wood and corrugated iron. It was opened on 1 September 1885, coinciding with the beginning of passenger services beyond Clifton Down. The Great Western initially offered six trains per day each direction between Avonmouth Dock and . Fearing competition, the BPRP did not allow passengers to use GWR services between its stations. The Midland Railway did not run any passenger services beyond Clifton Down, apart from a one-month trial service in September 1885. Despite the increased traffic the BPRP suffered financially, and was taken over by the CER in 1890. The BPRP's Avonmouth terminus closed to the public in 1902, after which all trains terminated at Avonmouth Dock.
Early twentieth century
The station went through numerous enhancements in the first part of the twentieth century. A new platform canopy and urinal were provided in 1900 at a cost of £250. Further improvements followed in 1902 at a cost of £80; and in August 1904 significant enhancements to the station buildings and an extension of the platform cost a total of £1,570. A turntable was constructed in December 1903; with asignal box
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The ''IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' ...
, known as Avonmouth Dock Passenger, installed at the end of the platform. Dedicated goods staff were employed from the start of 1904, with that year also seeing the installation of a run-around loop
A headshunt (or escape track in the United States) is a short length of track provided to release locomotives at terminal platforms, or to allow shunting to take place clear of main lines.
Terminal headshunt
A 'terminal headshunt' is a short l ...
for the terminal platform. A small engine shed was added in January 1905. In 1910, some passenger trains once again began to run beyond Avonmouth Dock, continuing towards on the newly opened Henbury Loop Line
The Henbury Loop Line, also known as the Filton to Avonmouth Line, is a railway line following the boundary between Bristol and South Gloucestershire between the Severn Beach Line at Hallen Marsh Junction, Avonmouth and the Cross Country Rout ...
, which allowed goods trains to the docks to avoid the steep Clifton Down Tunnel
Clifton Down is an area of public open space in Bristol, England, north of the village of Clifton. With its neighbour Durdham Down to the northeast, it constitutes the large area known as The Downs, much used for leisure including walking and t ...
. Other trains arrived from London via the loop, connecting with steamer services to Canada and Jamaica. At this point there were 17 trains from Bristol to Avonmouth Dock and 15 back each day; increasing to 21 and 19 respectively by 1920. The station was well-staffed, with 25 station staff and 47 goods staff in 1913. Positions included stationmaster; booking clerks; posters; and outdoor porters, who took goods to ships in the docks.
During the First World War, an Army Remount Service
The Army Remount Service was the body responsible for the purchase and training of horses and mules as remounts for the British Army between 1887 and 1942.
Origins
Prior to 1887, the purchase of horses was the responsibility of individual regi ...
depot was located near Shirehampton. Over the course of the war, Avonmouth Dock Joint handled 35,000 animals, mainly horses and mules, en route to the depot. July 1917 saw the introduction of platform tickets, to capitalise on people using the station to bid farewell to friends heading overseas, or to welcome those returning. The platform was lengthened to in December 1917. A second through track was added in 1918, and so a new cinder-covered platform was built on the north side of the line. The two platforms were linked by a footbridge and a level crossing. The cost of the new platform and the lengthening works was £7,420.
After the war, construction of the Bristol Portway along the Avon Gorge necessitated the closure of the line from Sneyd Park Junction to Hotwells, with trains along it ceasing on 3 July 1922. By this point there were nine trains per day from Hotwells, and eight return. To compensate for the loss of service, the Great Western provided an additional four trains daily from Avonmouth Dock to Bristol and six return. In 1923, grouping
Grouping may refer to:
* Muenchian grouping
* Principles of grouping
* Railways Act 1921, also known as Grouping Act, a reorganisation of the British railway system
* Grouping (firearms), the pattern of multiple shots from a sidearm
See also ...
resulted in the Midland Railway being absorbed into the London, Midland and Scottish Railway
The London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMSIt has been argued that the initials LMSR should be used to be consistent with LNER, GWR and SR. The London, Midland and Scottish Railway's corporate image used LMS, and this is what is generally u ...
(LMS), and the line continued in a joint arrangement between the Great Western and the LMS. The engine shed was closed in 1924.
By the mid-1920s, the station was proving inadequate for the passenger numbers, and so work began on a comprehensive rebuild in 1926. The new buildings were made of brick; with a large, four-chimneyed building containing most of the facilities; as well as a separate parcels office. The northern platform had a wooden awning built, which is still in place today.
From 1928 many services to Avonmouth Dock were extended to . By 1947, just before the railways were nationalised
Nationalization (nationalisation in British English) is the process of transforming privately-owned assets into public assets by bringing them under the public ownership of a national government or state. Nationalization usually refers to pri ...
, there were 33 services each direction between Avonmouth Dock and Temple Meads, with 18 on Sundays. Some trains made circular trips to and from Temple Meads via Clifton Down and Henbury or .
British Rail and privatisation
 When the railways were nationalised in 1948, services at Avonmouth Dock came under the aegis of the Western Region of British Railways. By 1955, service levels had decreased slightly to 28 trains per day from Bristol and 29 return, but the services were at regular intervals. Passenger numbers however dropped sharply in 1961 as the result of a fare increase, and so in 1962 a new reduced timetable was enacted, which lost more passengers. A year later in 1963, the Beeching report suggested the complete withdrawal of services along the line, but ultimately only those beyond Severn Beach or via Henbury were withdrawn. Goods services from the station ended on 20 June 1966, the same day that the station was renamed "Avonmouth". The bay platform was taken out of use and the land later taken for industrial buildings. From 17 July 1967 all staffing was withdrawn from stations along the line, including Avonmouth, with tickets issued by the train guard. The station buildings on the island platform survived into the 1970s, as did the footbridge, but with the exception of the parcels office, all were later demolished. The parcels office was in use in 2006 as a hairdressing salon. The signal box was closed in January 1969, and in September 1973 the wooden level crossing gates were replaced by automatic lifting barriers. By 1974, service had reduced to 19 trains per day in each direction, with no Sunday services to Severn Beach.
When the railways were nationalised in 1948, services at Avonmouth Dock came under the aegis of the Western Region of British Railways. By 1955, service levels had decreased slightly to 28 trains per day from Bristol and 29 return, but the services were at regular intervals. Passenger numbers however dropped sharply in 1961 as the result of a fare increase, and so in 1962 a new reduced timetable was enacted, which lost more passengers. A year later in 1963, the Beeching report suggested the complete withdrawal of services along the line, but ultimately only those beyond Severn Beach or via Henbury were withdrawn. Goods services from the station ended on 20 June 1966, the same day that the station was renamed "Avonmouth". The bay platform was taken out of use and the land later taken for industrial buildings. From 17 July 1967 all staffing was withdrawn from stations along the line, including Avonmouth, with tickets issued by the train guard. The station buildings on the island platform survived into the 1970s, as did the footbridge, but with the exception of the parcels office, all were later demolished. The parcels office was in use in 2006 as a hairdressing salon. The signal box was closed in January 1969, and in September 1973 the wooden level crossing gates were replaced by automatic lifting barriers. By 1974, service had reduced to 19 trains per day in each direction, with no Sunday services to Severn Beach.
British Rail
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most of the overground rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. It was formed from the nationalisation of the Big Four British rai ...
was split into business-led sectors in the 1980s, at which time operations at Avonmouth passed to Regional Railways. At this time, all trains ran to Severn Beach, but the service pattern was irregular. This changed in 1995 when an hourly timetable was introduced for peak times, but northbound services were terminated at Avonmouth.
When the railway was privatised in 1997, local services were franchised to Wales & West, which was succeeded by Wessex Trains, an arm of National Express, in 2001. Following action by Friends of Severn Beach Railway and a string of protests, services had increased to 10 per day in each direction by 2005, with Bristol City Council providing a subsidy to Wessex Trains. The Wessex franchise was amalgamated with the Great Western franchise into the Greater Western franchise from 2006, and responsibility passed to First Great Western, a subsidiary company of FirstGroup, subsequently rebranded as Great Western Railway in 2015. A minimum service requirement was written into the franchise agreement, ensuring an hourly service along the line, and this has since been increased to three trains every two hours (25 trains per day). Sunday services to Severn Beach were restored in 2010.
 The final remaining station building, the old parcels office, was demolished in 2015. Local rail campaigners, including Friends of Suburban Bristol Railways and MP Charlotte Leslie, petitioned to prevent the demolition, however Network Rail stated that the cost of restoration was too high and that it had become a safety risk.
The final remaining station building, the old parcels office, was demolished in 2015. Local rail campaigners, including Friends of Suburban Bristol Railways and MP Charlotte Leslie, petitioned to prevent the demolition, however Network Rail stated that the cost of restoration was too high and that it had become a safety risk.
Future
First Great Western declined a contractual option to continue the Greater Western passenger franchise (of which services at Avonmouth are a part) beyond 2013, citing a desire for a longer-term contract due to the impending upgrade to the Great Western Main Line. The franchise was put out to tender, but the process was halted and later scrapped due to the fallout from the collapse of the InterCity West Coast franchise competition. A two-year franchise extension until September 2015 was agreed in October 2013, and subsequently extended until March 2019. With the coming upgrade to the Great Western Main Line, the main line from London to Bristol is due to be electrified by 2016. However, the electrification will not extend beyond the main lines, so Avonmouth will continue to be served by diesel trains. Stephen Williams, MP forBristol West
Bristol West is a borough constituency represented in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom since 2015 by Thangam Debbonaire of the Labour Party (UK), Labour Party. It mostly covers ...
; and the group Friends of Suburban Bristol Railways
Friends of Suburban Bristol Railways (FoSBR) is a Bristol-based campaign group, calling for better rail transport in the Bristol area.
Formation
FoSBR was formed in 1995 as ''Friends of Severn Beach Railway'', to protest against the potential ...
support the electrification being extended to the Severn Beach Line.
Improved services at Avonmouth are called for as part of the Greater Bristol Metro
MetroWest, formerly known as the Greater Bristol Metro, is a project to improve the rail services in Bristol, England, and the surrounding region. It was first proposed at First Great Western's Stakeholder Event in March 2008. The aim of the p ...
scheme, a rail transport plan which aims to enhance transport capacity in the Bristol area. There is an aspiration for half-hourly services, with trains towards Bristol terminating alternately at and , however due to the large sections of the Severn Beach Line which are single-track, and to the congested main line from Temple Meads, such frequency is not currently feasible. The enhancement scheme was given the go-ahead in July 2012 as part of the City Deal, whereby local councils would be given greater control over money by the government. There are also calls for the reopening of the Henbury Loop Line
The Henbury Loop Line, also known as the Filton to Avonmouth Line, is a railway line following the boundary between Bristol and South Gloucestershire between the Severn Beach Line at Hallen Marsh Junction, Avonmouth and the Cross Country Rout ...
, which could allow a direct service from Avonmouth to . Plans for a loop were rejected by the West of England Joint Transport Board, however
Bristol City Councillors voted to send the decision back to the board for further discussion.
See also
*Public transport in Bristol
The majority of public transport users in the Bristol Urban Area are transported by bus, although rail has experienced growth and does play an important part, particularly in peak hours. There were plans for a light rail system, however this has n ...
Notes
References
Notes to references
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Avonmouth Railway Station Railway stations in Bristol DfT Category F1 stations Former Clifton Extension Railway stations Railway stations in Great Britain opened in 1885 Railway stations served by Great Western Railway Railway station Severn Beach Line Bristol Port Railway and Pier