The autism spectrum, often referred to as just autism or in the context of a professional diagnosis autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a
neurodevelopmental condition (or conditions) characterized by difficulties in
social interaction
A social relation or also described as a social interaction or social experience is the fundamental unit of analysis within the social sciences, and describes any voluntary or involuntary interpersonal relationship between two or more individuals ...
, verbal and
nonverbal communication, and the presence of repetitive behavior and restricted interests. Other common signs include unusual responses to
sensory stimuli.
Autism is generally understood as a ''
spectrum disorder'', which means that it can manifest differently in each person: any given autistic individual is likely to show some, but not all, of the characteristics associated with it, and the person may exhibit them to varying degrees.
Some autistic people remain
nonspeaking over the course of their lifespan, while others have relatively unimpaired
spoken language. There is large variation in the level of support people require, and the same person may present differently at varying times. Historically, autism was divided into sub-categories, but there were persistent questions over the validity of these divisions, and the most recent editions of the main diagnostic manuals list ASD as a single disorder.
While
psychiatry traditionally classifies autism as a
neurodevelopmental disorder
Neurodevelopmental disorders are a group of disorders that affect the development of the nervous system, leading to abnormal brain function which may affect emotion, learning ability, self-control, and memory. The effects of neurodevelopmental ...
, many autistic people, most autistic advocates and a rapidly increasing number of researchers see autism as part of
neurodiversity, the natural diversity in human thinking, and experience, with strengths, differences, and weaknesses.
On this view, promoted by the
autism rights movement, autism is not pathological, but this does not preclude autistic individuals from being disabled or having high support needs. This relatively positive and holistic view of autism has led to a certain degree of friction between autistic individuals, advocates, charities, researchers and practitioners.
Scientists are still trying to determine
what causes autism; it is
highly heritable and believed to be mainly genetic, but there are many genes involved, and environmental factors may also be relevant. It is unclear why autism frequently co-occurs with
attention deficit hyperactivity disorder,
epilepsy,
intellectual disability, amongst other conditions. There are ongoing disagreements about what should be included as part of the autism diagnosis, whether meaningful sub-types of autism exist,
and the significance of autism-associated traits in the wider population. The combination of broader criteria and increased awareness has led to a trend of steadily increasing estimates of
autism prevalence, causing a common misconception that there is an autism epidemic and perpetuating the controversial myth that it is
caused by vaccines.
While autistic people remain autistic throughout their lives, various interventions can help them in different ways. Autistic people with high support needs often benefit from
finding and learning other modes of communication and
making their environments more accessible.
Classification
Spectrum model
It is now known that autism is a highly variable
neurodevelopmental disorder
Neurodevelopmental disorders are a group of disorders that affect the development of the nervous system, leading to abnormal brain function which may affect emotion, learning ability, self-control, and memory. The effects of neurodevelopmental ...
which is generally thought to cover a broad and deep
spectrum
A spectrum (plural ''spectra'' or ''spectrums'') is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary, without gaps, across a continuum. The word was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of color ...
, manifesting very differently from one individual to another. Some have high support needs, may be
non-speaking, and experience developmental delays; this is more likely with other co-existing diagnoses. Other individuals have relatively low support needs; they may have more typical speech-language and intellectual skills but atypical social/conversation skills, narrowly focused interests, and wordy,
pedantic communication. They may still require significant support in some areas of their lives. The spectrum model should not be understood as a continuum running from mild to severe, but instead means that autism can present very differently in each individual. How a person presents can depend on context, and may vary over time.
ICD
The
World Health Organization's
International Classification of Diseases (11th Revision)
ICD-11, regarded as the global standard, was released in June 2018 and came into full effect as of January 2022.
It describes ASD as follows:
ICD-11 was produced by professionals from 55 countries out of the 90 countries involved and is the most widely used reference worldwide. Clinicians use the ICD as a reference for diagnosis and reporting but researchers, particularly in the US, continue to use the ''
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (
DSM-5-TR from 2022,
DSM-5
The ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition'' (DSM-5), is the 2013 update to the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'', the taxonomic and diagnostic tool published by the American Psychiatric ...
from 2013, or their predecessors) as some material is not included in the ICD (the ICD is broader in scope, covering general as well as mental health). There remain differences, for example
Rett syndrome was included in ASD in the DSM-5 but in the ICD-11 it was excluded and placed in the chapter for Developmental Anomalies. Both the ICD and the DSM have been under revision and there has been collaborative work towards a convergence of the two since 1980 (when
DSM-3 was published and
ICD-9 was current), including more rigorous biological assessment - in place of historical experience - and a simplification of the system of classification.
DSM
The
American Psychiatric Association
The American Psychiatric Association (APA) is the main professional organization of psychiatrists and trainee psychiatrists in the United States, and the largest psychiatric organization in the world. It has more than 37,000 members are invol ...
's ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, Text Revision'' (
DSM-5-TR), released in 2022, is the current version of the DSM. The fifth edition,
DSM-5
The ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition'' (DSM-5), is the 2013 update to the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'', the taxonomic and diagnostic tool published by the American Psychiatric ...
, released in May 2013, was the first to define ASD as a single diagnosis, which is continued in DSM-5-TR. ASD encompasses previous diagnoses which included
Asperger syndrome,
childhood disintegrative disorder,
PDD-NOS
A pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified (Including atypical autism) (PDD-NOS) is one of four disorders which were collapsed into the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder in the DSM-5 and also was one of the five disorders cl ...
, and the range of diagnoses which included the word ''autism''. Rather than distinguishing between these diagnoses, the DSM-5 and DSM-5-TR adopt a dimensional approach to diagnosing disorders that fall underneath the autism spectrum umbrella in one diagnostic category. Within this category, the DSM-5 and the DSM includes a framework that differentiates each individual by dimensions of symptom severity, as well as by associated features (i.e., the presence of other disorders or factors which likely contribute to the symptoms, other neurodevelopmental or mental disorders, intellectual disability, or language impairment). The symptom domains are social communication and restricted, repetitive behaviors, with the option of a separate severity - the negative impact of the symptoms on the individual - being specified for each domain, rather than an overall severity. Prior to the DSM-5, the DSM separated social deficits and communication deficits into two domains. Further, the DSM-5 changed to an onset age in the early developmental period, with a note that symptoms may manifest later when social demands exceed capabilities, rather than the previous, more restricted 3 years of age.
These changes continue in the DSM-5-TR.
Features and characteristics
For many autistic individuals, characteristics usually first appear during infancy or childhood and generally follow a steady course without
remission
Remission often refers to:
*Forgiveness
Remission may also refer to:
Healthcare and science
*Remission (medicine), the state of absence of disease activity in patients with a chronic illness, with the possibility of return of disease activity
*R ...
(different developmental timelines described in more detail below).
Autistic people may be severely impaired in some respects but average, or even superior, in others.
Clinicians consider assessment for ASD when a patient shows:
* regular difficulties in social interaction or communication
* restricted or repetitive behaviors (often called "
stimming")
* resistance to changes or restricted interests
These features are typically assessed with the following, when appropriate:
* problems in obtaining or sustaining employment or education
* difficulties in initiating or sustaining social relationships
* connections with mental health or learning disability services
* a history of neurodevelopmental conditions (including learning disabilities and
ADHD) or mental health conditions.
There are many signs associated with ASD; the presentation varies widely:
:
Atypical eating is also common, but it does not need to be present to make a diagnosis.
[ This paper represents a consensus of representatives from nine professional and four parent organizations in the US.]
Some autistic people can exhibit notable ability, for example in mathematics, music or artistic reproduction, which in exceptional cases is usually referred to as
savant syndrome.
[ , volume = 70 , issue = 2 , pages = 201–210 , date = April 2018 , pmid = 29691585 ] More generally, autistic people tend to show a 'spiky skills profile', with strong abilities in some areas contrasting with much weaker abilities in others.
Developmental course
There are two possible developmental courses of ASD. One course of development is more gradual in nature, with symptoms appearing fairly early in life and persisting.
A second course of development is characterized by normal or near-normal development before onset of regression or loss of skills, which is known as regressive autism.
Gradual autism development
Most parents report that the onset of autism features appear within the first or second year of life.
This course of development is fairly gradual, in that parents typically report concerns in development over the first two years of life and diagnosis can be made around 3–4 years of age.
Overt features gradually begin after the age of six months, become established by age two or three years, and tend to continue through adulthood, although often in more muted form.
Some of the early signs of ASDs in this course include decreased attention at faces, failure to obviously respond when name is called, failure to show interests by showing or pointing, and delayed imaginative play.
Regressive autism development
Regressive autism occurs when a child appears to develop typically but then starts to lose
speech
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses Phonetics, phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words (that is, all English words sound different from all French words, even if ...
and social skills and is subsequently diagnosed with ASD.
Other terms used to describe regression in children with autism are ''autism with regression'', ''autistic regression'', ''setback-type autism'', and ''acquired autistic syndrome''.
Within the regressive autism developmental course, there are two patterns. The first pattern is when developmental losses occur in the first 15 months to 3 years.
The second pattern, childhood disintegrative disorder (a diagnosis now included under ASD), is characterized by regression after normal development in the first 3 to 4, or even up to 9 years of life.
After the regression, the child follows the standard pattern of autistic neurological development. The term ''regressive autism'' refers to the appearance that neurological development has reversed; it is actually only the affected developmental skills, rather than the neurology as a whole, that regresses.
Usually, the apparent onset of regressive autism can be surprising and distressing to parents, who often initially suspect severe hearing loss. Attribution of regression to environmental stress factors may result in a delay in diagnosis.
There is no standard definition for regression.
Some children show a mixture of features, with some early delays and some later losses; and there is evidence of a continuous spectrum of behaviors, rather than, or in addition to, a black-and-white distinction, between autism with and without regression.
There are several intermediate types of development, which do not neatly fit into either the traditional early onset or the regressive categories, including mixtures of early deficits, failures to progress, subtle diminishment, and obvious losses.
Regression may occur in a variety of domains, including communication, social, cognitive, and self-help skills; however, the most common regression is loss of language.
Some children lose social development instead of language; some lose both.
Skill loss may be quite rapid, or may be slow and preceded by a lengthy period of no skill progression; the loss may be accompanied by reduced social play or increased irritability.
The temporarily acquired skills typically amount to a few words of spoken language, and may include some rudimentary social perception.
The prevalence of regression varies depending on the definition used.
If regression is defined strictly to require loss of language, it is less common; if defined more broadly, to include cases where language is preserved but social interaction is diminished, it is more common.
Although regressive autism is often thought to be a less common (compared with gradual course of autism onset described above), this remains an area of ongoing debate; some evidence suggests that a pattern of regressive autism may be more common than previously thought. There are some who believe that regressive autism is simply early-onset autism which was recognized at a later date. Researchers have conducted studies to determine whether regressive autism is a distinct subset of ASD, but the results of these studies have contradicted one another.
Differential outcomes
There continues to be a debate over the differential outcomes based on these two developmental courses. Some studies suggest that regression is associated with poorer outcomes and others report no differences between those with early gradual onset and those who experience a regression period.
While there is conflicting evidence surrounding language outcomes in autism, some studies have shown that cognitive and language abilities at age may help predict language proficiency and production after age 5. Overall, the literature stresses the importance of early intervention in achieving positive longitudinal outcomes.
Social and communication skills
In social contexts, autistic people may respond and behave differently than individuals without ASD.
Impairments in social skills present many challenges for autistic individuals. Deficits in social skills may lead to problems with friendships, romantic relationships, daily living, and vocational success.
One study that examined the outcomes of autistic adults found that, compared to the general population, autistic people were less likely to be married, but it is unclear whether this outcome was due to deficits in social skills or intellectual impairment, or some other reason. A factor to this is likely discrimination against autistic people which is perpetuated by myths; for example: the myth that autistic people have no empathy.
Prior to 2013, deficits in social function and communication were considered two separate symptom domains of autism. The current social communication domain criteria for autism diagnosis require individuals to have deficits across three social skills: social-emotional reciprocity, nonverbal communication, and developing and sustaining relationships.
A range of social-emotional reciprocity difficulties (an individual's ability to naturally engage in social interactions) may be present. Autistic individuals may lack mutual sharing of interests, for example many autistic children prefer not to play or interact with others. They may lack awareness or understanding of other people's thoughts or feelings – a child may get too close to peers (entering their
personal space) without noticing that this makes them uncomfortable. They may also engage in atypical behaviors to gain attention, for example a child may push a peer to gain attention before starting a conversation.
Older children and adults with ASD
perform worse on tests of face and emotion recognition than non-autistic individuals, although this may be partly due to a
lower ability to define a person's own emotions.
Autistic people experience deficits in their ability to develop, maintain, and understand relationships, as well as difficulties adjusting behavior to fit social contexts. ASD presents with impairments in
pragmatic communication skills, such as difficulty initiating a conversation or failure to consider the interests of the listener to sustain a conversation.
The ability to be focused exclusively on one topic in communication is known as
monotropism, and can be compared to "tunnel vision". It is common for autistic individuals to communicate strong interest in a specific topic, speaking in lesson-like monologues about their passion instead of enabling reciprocal communication with whomever they are speaking to.
What may look like self-involvement or indifference toward others stems from a struggle to recognize or remember that other people have their own personalities, perspectives, and interests.
Another difference in pragmatic communication skills is that autistic people may not recognize the need to control the volume of their voice in different social settings – for example, they may speak loudly in libraries or movie theaters.
Autistic people display atypical nonverbal behaviors or have difficulties with
nonverbal communication. They may make infrequent
eye contact – an autistic child may not make eye contact when called by name, or they may avoid making eye contact with an observer. Aversion of gaze can also be seen in
anxiety disorders, however poor eye contact in autistic children is not due to shyness or anxiety; rather, it is overall diminished in quantity. Autistic individuals may struggle with both production and understanding of facial expressions. They often do not know how to recognize emotions from others' facial expressions, or they may not respond with the appropriate facial expressions. They may have trouble recognizing subtle expressions of emotion and identifying what various emotions mean for the conversation.
A defining feature is that autistic people have social impairments and often lack the intuition about others that many people take for granted.
Temple Grandin, an autistic woman involved in autism activism, described her inability to understand the
social communication of
neurotypicals, or people with typical
neural development
The development of the nervous system, or neural development (neurodevelopment), refers to the processes that generate, shape, and reshape the nervous system of animals, from the earliest stages of embryonic development to adulthood. The fie ...
, as leaving her feeling "like an anthropologist on Mars". They may also not pick up on
body language or social cues such as eye contact and facial expressions if they provide more information than the person can process at that time. They struggle with understanding the context and subtext of conversational or printed situations, and have trouble forming resulting conclusions about the content. This also results in a lack of social awareness and atypical language expression.
How facial expressions differ between those on the autism spectrum and neurotypical individuals is not clear. Further, at least half of autistic children have unusual
prosody.
Autistic people may also experience difficulties with verbal communication. Differences in communication may be present from the first year of life, and may include delayed onset of
babbling, unusual gestures, diminished responsiveness, and vocal patterns that are not synchronized with the caregiver. In the second and third years, autistic children have less frequent and less diverse babbling, consonants, words, and word combinations; their gestures are less often integrated with words. Autistic children are less likely to make requests or share experiences, and are more likely to simply repeat others' words (
echolalia).
seems to be necessary for functional speech, and deficits in joint attention seem to distinguish infants with ASD.
For example, they may look at a pointing hand instead of the object to which the hand is pointing,
and they consistently fail to point at objects in order to comment on or share an experience.
Autistic children may have difficulty with imaginative play and with developing symbols into language.
Some autistic linguistic behaviors include repetitive or rigid language, and restricted interests in conversation. For example, a child might repeat words or insist on always talking about the same subject.
Echolalia may also be present in autistic individuals, for example by responding to a question by repeating the inquiry instead of answering.
Language impairment is also common in autistic children, but is not part of a diagnosis.
Many autistic children develop language skills at an uneven pace where they easily acquire some aspects of communication, while never fully developing others,
such as in some cases of
hyperlexia. In some cases, individuals remain
completely nonverbal throughout their lives. The CDC estimated that around 40% of autistic children don't speak at all, although the accompanying levels of literacy and nonverbal communication skills vary.
Restricted and repetitive behaviors

ASD includes a wide variety of characteristics. Some of these include behavioral characteristics which widely range from slow development of social and learning skills to difficulties creating connections with other people. Autistic individuals may experience these challenges with forming connections due to anxiety or depression, which they are more likely to experience, and as a result isolate themselves.
Other behavioral characteristics include abnormal responses to sensations (such as sights, sounds, touch, taste and smell) and problems keeping a consistent speech rhythm. The latter problem influences an individual's social skills, leading to potential problems in how they are understood by communication partners. Behavioral characteristics displayed by autistic people typically influence development, language, and social competence. Behavioral characteristics of autistic people can be observed as perceptual disturbances, disturbances of development rate, relating, speech and language, and motility.
The second core symptom of autism spectrum is a pattern of restricted and repetitive behaviors, activities, and interests. In order to be diagnosed with ASD under DSM-5 or DSM-5-TR, a person must have at least two of the following behaviors:
*
Repetitive behaviors – Repetitive behaviors such as rocking, hand flapping, finger flicking, head banging, or repeating phrases or sounds.
These behaviors may occur constantly or only when the person gets stressed, anxious or upset.
*Resistance to change – A strict adherence to routines such as eating certain foods in a specific order, or taking the same path to school every day.
The child may have a meltdown if there is any change or disruption to their routine.
*Restricted interests – An excessive interest in a particular activity, topic, or hobby, and devoting all their attention to it. For example, young children might completely focus on things that spin and ignore everything else. Older children might try to learn everything about a single topic, such as the weather or sports, and
perseverate or talk about it constantly.
*Sensory reactivity – An unusual reaction to certain sensory inputs such as having a negative reaction to specific sounds or textures, being fascinated by lights or movements or having an apparent indifference to pain or heat.
Autistic individuals can display many forms of repetitive or restricted behavior, which the Repetitive Behavior Scale-Revised (RBS-R) categorizes as follows.
*
Stereotyped behaviors: Repetitive movements, such as hand flapping, head rolling, or body rocking.
*
Compulsive behaviors: Time-consuming behaviors intended to reduce anxiety, that an individual feels compelled to perform repeatedly or according to rigid rules, such as placing objects in a specific order, checking things, or handwashing.
* Sameness: Resistance to change; for example, insisting that the furniture not be moved or refusing to be interrupted.
*
Ritualistic behavior: Unvarying pattern of daily activities, such as an unchanging menu or a dressing ritual. This is closely associated with sameness and an independent validation has suggested combining the two factors.
* Restricted interests: Interests or fixations that are abnormal in theme or intensity of focus, such as preoccupation with a single television program, toy, or game.
*
Self-injury
Self-harm is intentional behavior that is considered harmful to oneself. This is most commonly regarded as direct injury of one's own skin tissues usually without a suicidal intention. Other terms such as cutting, self-injury and self-mutilatio ...
: Behaviors such as eye-poking,
skin-picking, hand-biting and head-banging.
Self-injury
Self-injurious behaviors (SIB) are relatively common in autistic people, and can include head-banging, self-cutting, self-biting, and hair-pulling.
Some of these behaviors can result in serious injury or death.
Following are theories about the cause of self-injurious behavior in children
with developmental delay, including autistic individuals:
* Frequency and/or continuation of self-injurious behavior can be influenced by environmental factors (e.g. reward in return for halting self-injurious behavior). However this theory is not applicable to younger children with autism. There is some evidence that frequency of self-injurious behavior can be reduced by removing or modifying environmental factors that reinforce this behavior.
* Higher rates of self-injury are also noted in socially isolated individuals with autism. Studies have shown that socialization skills are related factors to self injurious behavior for individuals with autism.
* Self-injury could be a response to modulate
pain perception
Nociception (also nocioception, from Latin ''nocere'' 'to harm or hurt') is the sensory nervous system's process of encoding noxious stimuli. It deals with a series of events and processes required for an organism to receive a painful stimulus, co ...
when chronic pain or other health problems that cause pain are present.
* An abnormal
basal ganglia connectivity may predispose to self-injurious behavior.
Other features
Autistic individuals may have symptoms that do not contribute to the official diagnosis, but that can affect the individual or the family.
Some individuals with ASD show unusual abilities, ranging from
splinter skills (such as the memorization of trivia) to the rare talents of
autistic savants. One study describes how some individuals with ASD show superior skills in perception and attention, relative to the general population.
Sensory
Sensory may refer to:
Biology
* Sensory ecology, how organisms obtain information about their environment
* Sensory neuron, nerve cell responsible for transmitting information about external stimuli
* Sensory perception, the process of acquiri ...
abnormalities are found in over 90% of autistic people, and are considered core features by some.
Differences between the previously recognized disorders under the autism spectrum are greater for under-responsivity (for example, walking into things) than for over-responsivity (for example, distress from loud noises) or for sensation seeking (for example, rhythmic movements). An estimated 60–80% of autistic people have motor signs that include
poor muscle tone
Hypotonia is a state of low muscle tone (the amount of tension or resistance to stretch in a muscle), often involving reduced muscle strength. Hypotonia is not a specific medical disorder, but a potential manifestation of many different diseases ...
,
poor motor planning, and
toe walking;
deficits in motor coordination are pervasive across ASD and are greater in autism proper. Unusual eating behavior occurs in about three-quarters of children with ASD, to the extent that it was formerly a diagnostic indicator. Selectivity is the most common problem, although eating rituals and food refusal also occur.
There is tentative evidence that
gender dysphoria
Gender dysphoria (GD) is the distress a person experiences due to a mismatch between their gender identitytheir personal sense of their own genderand their sex assigned at birth. The diagnostic label gender identity disorder (GID) was used unt ...
occurs more frequently in autistic people (see
Autism and LGBT identities). As well as that, a 2021 anonymized online survey of 16–90 year-olds revealed that autistic males are more likely to identify as bisexual, while autistic females are more likely to identify as homosexual.
Gastrointestinal problems are one of the most commonly
co-occurring medical conditions in autistic people.
These are linked to greater social impairment, irritability, language impairments, mood changes, and behavior and sleep problems.
Parents of children with ASD have higher levels of
stress.
Siblings of children with ASD report greater admiration and less conflict with the affected sibling than siblings of unaffected children and were similar to siblings of children with
Down syndrome in these aspects of the sibling relationship. However, they reported lower levels of closeness and intimacy than siblings of children with Down syndrome; siblings of individuals with ASD have greater risk of negative well-being and poorer sibling relationships as adults.
Causes
It had mostly long been presumed that there is a common cause at the genetic, cognitive, and neural levels for the social and non-social components of ASD's symptoms, described as a triad in the classic autism criteria.
However, there is increasing suspicion that autism is instead a complex disorder whose core aspects have distinct causes that often co-occur.
While it is unlikely that a single cause for ASD exists,
many risk factors identified in the research literature may contribute to ASD development. These risk factors include genetics, prenatal and perinatal factors (meaning factors during pregnancy or very early infancy),
neuroanatomical
Neuroanatomy is the study of the structure and organization of the nervous system. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defi ...
abnormalities, and environmental factors. It is possible to identify general factors, but much more difficult to pinpoint specific factors. Given the current state of knowledge, prediction can only be of a global nature and therefore requires the use of general markers.
Biological subgroups
Research into causes has been hampered by the inability to identify biologically meaningful subgroups within the autistic population and by the traditional boundaries between the disciplines of
psychiatry,
psychology,
neurology and
pediatrics
Pediatrics ( also spelled ''paediatrics'' or ''pædiatrics'') is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, adolescents, and young adults. In the United Kingdom, paediatrics covers many of their youth until th ...
. Newer technologies such as
fMRI and
diffusion tensor imaging can help identify biologically relevant
phenotypes (observable traits) that can be viewed on
brain scans, to help further
neurogenetic
Neurogenetics studies the role of genetics in the development and function of the nervous system. It considers neural characteristics as phenotypes (i.e. manifestations, measurable or not, of the genetic make-up of an individual), and is mainly bas ...
studies of autism; one example is lowered activity in the
fusiform face area of the brain, which is associated with impaired perception of people versus objects.
It has been proposed to classify autism using genetics as well as behavior. (For more, see
Brett Abrahams)
Genetics
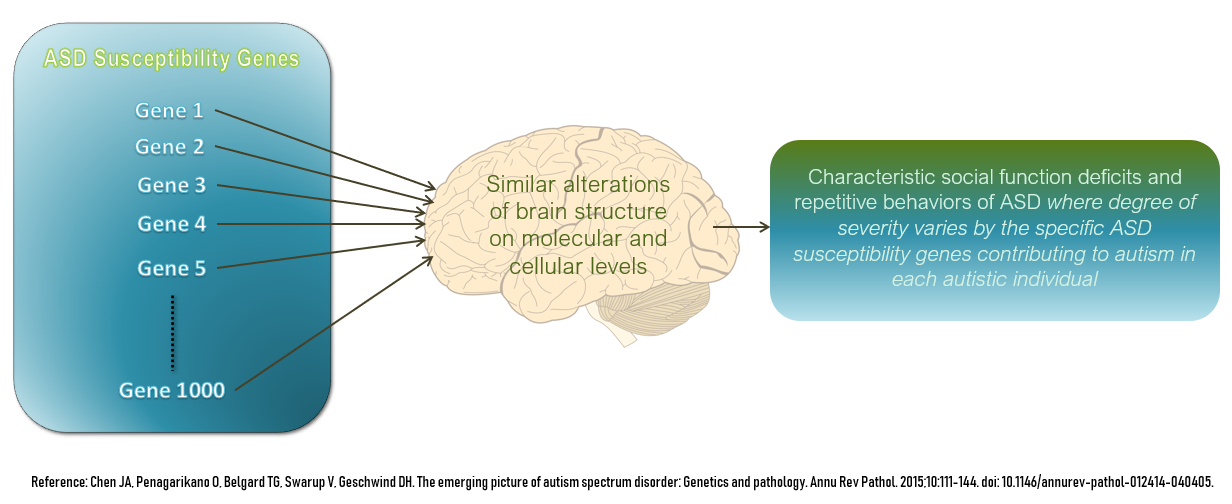
Autism has a strong genetic basis, although the
genetics of autism are complex and it is unclear whether ASD is explained more by rare
mutations with major effects, or by rare multi-gene interactions of common genetic variants.
Complexity arises due to interactions among multiple genes, the environment, and
epigenetic factors which do not change
DNA sequencing but are heritable and influence
gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. The ...
.
Many genes have been associated with autism through sequencing the genomes of affected individuals and their parents.
However, most of the mutations that increase autism risk have not been identified. Typically, autism cannot be traced to a
Mendelian (single-gene) mutation or to a single
chromosome abnormality
A chromosomal abnormality, chromosomal anomaly, chromosomal aberration, chromosomal mutation, or chromosomal disorder, is a missing, extra, or irregular portion of chromosomal DNA. These can occur in the form of numerical abnormalities, where the ...
, and none of the genetic syndromes associated with ASD have been shown to selectively cause ASD.
Numerous candidate genes have been located, with only small effects attributable to any particular gene.
Most loci individually explain less than 1% of cases of autism.
, it appeared that between 74% and 93% of ASD risk is heritable.
After an older child is diagnosed with ASD, 7–20% of subsequent children are likely to be as well.
If parents have one autistic child, they have a 2% to 8% chance of having a second child who is also autistic. If the autistic child is an identical twin the other will be affected 36 to 95 percent of the time. If they are fraternal twins the other will only be affected up to 31 percent of the time. The large number of autistic individuals with unaffected family members may result from spontaneous
structural variation, such as
deletions,
duplications or
inversions in genetic material during
meiosis. Hence, a substantial fraction of autism cases may be traceable to genetic causes that are highly heritable but not inherited: that is, the mutation that causes the autism is not present in the parental genome.
, understanding of genetic risk factors had shifted from a focus on a few
allele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chro ...
s to an understanding that genetic involvement in ASD is probably diffuse, depending on a large number of variants, some of which are common and have a small effect, and some of which are rare and have a large effect. The most common gene disrupted with large effect rare variants appeared to be
CHD8, but less than 0.5% of autistic people have such a mutation. The gene CHD8 encodes the protein chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 8, which is a
chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important ...
regulator enzyme that is essential during fetal development, CHD8 is an ATP dependent enzyme.
The protein contains an Snf2 helicase domain that is responsible for the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP.
CHD8 encodes for a DNA helicase that function as a transcription repressor by remodeling chromatin structure by altering the position of nucleosomes. CHD8 negatively regulates Wnt signaling. Wnt signaling is important in the vertebrate early development and morphogenesis. It is believed that CHD8 also recruits the linker histone H1 and causes the repression of β-catenin and p53 target genes.
The importance of CHD8 can be observed in studies where CHD8-knockout mice died after 5.5 embryonic days because of widespread p53 induced apoptosis. Some studies have determined the role of CHD8 in autism spectrum disorder (ASD). CHD8 expression significantly increases during human mid-fetal development.
The chromatin remodeling activity and its interaction with transcriptional regulators have shown to play an important role in ASD aetiology.
The developing mammalian brain has a conserved CHD8 target regions that are associated with ASD risk genes. The knockdown of CHD8 in human neural stem cells results in dysregulation of ASD risk genes that are targeted by CHD8. Recently CD8 has been associated to the regulation of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), and the regulation of X chromosome inactivation (XCI) initiation, via regulation of Xist long non-coding RNA, the master regulator of XCI, though competitive binding to Xist regulatory regions.
Some ASD is associated with clearly genetic conditions, like
fragile X syndrome; however, only around 2% of autistic people have fragile X.
Hypotheses from
evolutionary psychiatry suggest that these genes persist because they are linked to human inventiveness, intelligence or systemising.
Current research suggests that genes that increase susceptibility to ASD are ones that control
protein synthesis
Protein biosynthesis (or protein synthesis) is a core biological process, occurring inside Cell (biology), cells, homeostasis, balancing the loss of cellular proteins (via Proteolysis, degradation or Protein targeting, export) through the product ...
in
neuronal cells in response to cell needs, activity and adhesion of neuronal cells,
synapse
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell.
Synapses are essential to the transmission of nervous impulses from ...
formation and remodeling, and excitatory to inhibitory
neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neuro ...
balance. Therefore, despite up to 1000 different genes thought to contribute to increased risk of ASD, all of them eventually affect normal neural development and connectivity between different functional areas of the brain in a similar manner that is characteristic of an ASD brain. Some of these genes are known to modulate production of the
GABA neurotransmitter which is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the nervous system. These GABA-related genes are under-expressed in an ASD brain. On the other hand, genes controlling expression of
glial and immune cells in the brain e.g.
astrocyte
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" + , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of e ...
s and
microglia
Microglia are a type of neuroglia (glial cell) located throughout the brain and spinal cord. Microglia account for about 7% of cells found within the brain. As the resident macrophage cells, they act as the first and main form of active immune de ...
, respectively, are over-expressed which correlates with increased number of glial and immune cells found in postmortem ASD brains. Some genes under investigation in ASD pathophysiology are those that affect the
mTOR signaling pathway which supports cell growth and survival.
All these genetic variants contribute to the development of the autistic spectrum; however, it cannot be guaranteed that they are determinants for the development.
ASD may be under-diagnosed in women and girls due to an assumption that it is primarily a male condition, but genetic phenomena such as
imprinting and
X linkage
Sex linked describes the sex-specific patterns of inheritance and presentation when a gene mutation (allele) is present on a sex chromosome (allosome) rather than a non-sex chromosome (autosome). In humans, these are termed X-linked recessive, ...
have the ability to raise the frequency and severity of conditions in males, and theories have been put forward for a genetic reason why males are diagnosed more often, such as the
imprinted brain hypothesis
The imprinted brain hypothesis is an unsubstantiated hypothesis in evolutionary psychology regarding the causes of autism spectrum and schizophrenia spectrum disorders, first presented by Bernard Crespi and Christopher Badcock in 2008. It claims ...
and the
extreme male brain theory.
Early life
Several prenatal and perinatal complications have been reported as possible risk factors for autism. These risk factors include maternal
gestational diabetes, maternal and paternal age over 30, bleeding during pregnancy after the first trimester, use of certain prescription medication (e.g.
valproate) during pregnancy, and
meconium
Meconium is the earliest stool of a mammalian infant resulting from defecation. Unlike later feces, meconium is composed of materials ingested during the time the infant spends in the uterus: intestinal epithelial cells, lanugo, mucus, amniotic ...
in the
amniotic fluid. While research is not conclusive on the relation of these factors to autism, each of these factors has been identified more frequently in children with autism, compared to their siblings who do not have autism, and other typically developing youth.
While it is unclear if any single factors during the prenatal phase affect the risk of autism,
complications during pregnancy may be a risk.
Low
vitamin D levels in early development have been hypothesized as a risk factor for autism.
There are also studies being done to test if certain types of regressive autism have an
autoimmune basis.
Maternal nutrition and inflammation during preconception and pregnancy influences fetal neurodevelopment.
Intrauterine growth restriction is associated with ASD, in both term and preterm infants.
Maternal inflammatory and
autoimmune diseases may damage fetal tissues, aggravating a genetic problem or damaging the nervous system.
Exposure to air pollution during child pregnancy, especially
heavy metals
upright=1.2, Crystals of osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">lead.html" ;"title="osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead
Heavy metals are generally defined as ...
and particulates, may increase the risk of autism.
Environmental factors that have been claimed without evidence to contribute to or exacerbate autism include certain foods,
infectious disease
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable d ...
s,
solvents,
PCBs,
phthalates and
phenols used in plastic products,
pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are meant to control pests. This includes herbicide, insecticide, nematicide, molluscicide, piscicide, avicide, rodenticide, bactericide, insect repellent, animal repellent, microbicide, fungicide, and lampri ...
s,
brominated flame retardants,
alcohol, smoking,
illicit drugs,
vaccines,
and
prenatal stress. Some, such as the MMR vaccine, have been completely disproven.
Disproven vaccine hypothesis
Parents may first become aware of ASD symptoms in their child around the time of a routine vaccination. This has led to unsupported and disproven theories blaming
vaccine "overload", a
vaccine preservative, or the
MMR vaccine
The MMR vaccine is a vaccine against measles, mumps, and rubella (German measles), abbreviated as ''MMR''. The first dose is generally given to children around 9 months to 15 months of age, with a second dose at 15 months to 6 years of age, ...
for causing autism spectrum disorder.
In 1998, British physician and academic
Andrew Wakefield led a
fraudulent, litigation-funded study that suggested that the
MMR vaccine
The MMR vaccine is a vaccine against measles, mumps, and rubella (German measles), abbreviated as ''MMR''. The first dose is generally given to children around 9 months to 15 months of age, with a second dose at 15 months to 6 years of age, ...
may cause autism.
This conjecture suggested that autism results from brain damage caused either by the MMR vaccine itself, or by
thimerosal, a vaccine preservative.
No convincing scientific evidence supports these claims.
They are biologically implausible,
and further evidence continues to refute them, including the observation that the rate of autism continues to climb despite elimination of thimerosal from routine childhood vaccines.
A 2014 meta-analysis examined ten major studies on autism and vaccines involving 1.25 million children worldwide; it concluded that neither the MMR vaccine, which has never contained thimerosal, nor the vaccine components thimerosal or
mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
, lead to the development of ASDs.
Despite this, misplaced parental concern has led to lower rates of
childhood immunizations,
outbreaks of previously controlled childhood diseases in some countries, and the preventable deaths of several children.
[Vaccines and autism:
*
*
*
*
* ]
Etiological hypotheses
Several hypotheses have been presented that try to explain how and why autism develops by integrating known causes (genetic and environmental effects) and findings (neurobiological and somatic). Some are more comprehensive, such as the Pathogenetic Triad,
which proposes and operationalizes three core features (an autistic personality, cognitive compensation, neuropathological burden) that interact to cause autism, and the
Intense World Theory,
which explains autism through a hyper-active neurobiology that leads to an increased perception, attention, memory, and emotionality. There are also simpler hypotheses that explain only individual parts of the neurobiology or phenotype of autism, such as
mind-blindness (a decreased ability for
Theory of Mind), the
weak central coherence theory, or the
extreme male brain and
empathising-systemising theory.
Evolutionary hypotheses
Research exploring the
evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
ary benefits of autism and associated genes has suggested that autistic people may have played a "unique role in technological spheres and understanding of natural systems" in the course of human development. It has been suggested that it may have arisen as "a slight trade off for other traits that are seen as highly advantageous", providing "advantages in tool making and mechanical thinking", with speculation that the condition may "reveal itself to be the result of a
balanced polymorphism, like
sickle cell anemia, that is advantageous in a certain mixture of genes and disadvantageous in specific combinations".
In 2011, a paper in ''
Evolutionary Psychology'' proposed that autistic traits, including increased abilities for spatial intelligence, concentration and memory, could have been
naturally selected
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. C ...
to enable self-sufficient
foraging in a more (although not completely) solitary environment, referred to as the "Solitary Forager Hypothesis". A 2016 paper examines Asperger syndrome as "an alternative
prosocial adaptive strategy" which may have developed as a result of the emergence of "collaborative morality" in the context of small-scale
hunter-gathering
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, ...
, i.e. where "a positive social reputation for making a contribution to group wellbeing and survival" becomes more important than complex social understanding.
Conversely, some multidisciplinary research suggests that
recent human evolution may be a driving force in the rise of a number of medical conditions in recent human populations, including autism. Studies in
evolutionary medicine indicate that as biological evolution becomes outpaced by cultural evolution, disorders linked to bodily dysfunction increase in prevalence due to a lack of contact with pathogens and negative environmental conditions that once widely affected ancestral populations. Because natural selection primarily favors reproduction over health and longevity, the lack of this impetus to adapt to certain harmful circumstances creates a tendency for genes in descendant populations to over-express themselves, which may cause a wide array of maladies, ranging from
mental disorders
A mental disorder, also referred to as a mental illness or psychiatric disorder, is a behavioral or mental pattern that causes significant distress or impairment of personal functioning. Such features may be persistent, relapsing and remitti ...
to
autoimmune diseases.
Pathophysiology
Autism's symptoms result from maturation-related changes in various systems of the brain.
How autism occurs is not yet well understood. Its mechanism can be divided into two areas: the
pathophysiology
Pathophysiology ( physiopathology) – a convergence of pathology with physiology – is the study of the disordered physiological processes that cause, result from, or are otherwise associated with a disease or injury. Pathology is the ...
of brain structures and processes associated with autism, and the
neuropsychological
Neuropsychology is a branch of psychology concerned with how a person's cognition and behavior are related to the brain and the rest of the nervous system. Professionals in this branch of psychology often focus on how injuries or illnesses of ...
linkages between brain structures and behaviors.
The behaviors appear to have multiple pathophysiologies.
There is evidence that
gut–brain axis abnormalities may be involved.
A 2015 review proposed that immune,
gastrointestinal inflammation, malfunction of the
autonomic nervous system,
gut flora
Gut microbiota, gut microbiome, or gut flora, are the microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses that live in the digestive tracts of animals. The gastrointestinal metagenome is the aggregate of all the genomes of the gut mi ...
alterations, and food
metabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism.
The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, c ...
s may cause brain neuroinflammation and dysfunction.
A 2016 review concludes that
enteric nervous system abnormalities might play a role in neurological disorders such as autism. Neural connections and the immune system are a pathway that may allow diseases originated in the intestine spread to the brain.
Several lines of evidence point to
synaptic dysfunction as a cause of autism.
Some rare mutations may lead to autism by disrupting some synaptic pathways, such as those involved with
cell adhesion.
All known
teratogens (agents that cause
birth defects) related to the risk of autism appear to act during the first eight weeks from
conception, and though this does not exclude the possibility that autism can be initiated or affected later, there is strong evidence that autism arises very early in development.
In general, neuroanatomical studies support the concept that autism may involve a combination of brain enlargement in some areas and reduction in others.
These studies suggest that autism may be caused by abnormal neuronal growth and pruning during the early stages of prenatal and postnatal brain development, leaving some areas of the brain with too many neurons and other areas with too few neurons.
Some research has reported an overall brain enlargement in autism, while others suggest abnormalities in several areas of the brain, including the
frontal lobe, the
mirror neuron system, the
limbic system
The limbic system, also known as the paleomammalian cortex, is a set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, immediately beneath the medial temporal lobe of the cerebrum primarily in the forebrain.Schacter, Daniel L. 2012. ''Ps ...
, the
temporal lobe, and the
corpus callosum.
In
functional neuroimaging studies, when performing
theory of mind and facial emotion response tasks, the
median
In statistics and probability theory, the median is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a data sample, a population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as "the middle" value. The basic fe ...
person on the autism spectrum exhibits less activation in the primary and secondary somatosensory
cortices of the brain than the median member of a properly sampled
control population. This finding coincides with reports demonstrating abnormal patterns of cortical thickness and
grey matter volume in those regions of autistic peoples' brains.
Brain connectivity
Brains of autistic individuals have been observed to have abnormal connectivity and the degree of these abnormalities directly correlates with the severity of autism. Following are some observed abnormal connectivity patterns in autistic individuals:
* Decreased connectivity ''between'' different specialized regions of the brain (e.g. lower neuron density in
corpus callosum) and relative over-connectivity ''within'' specialized regions of the brain by adulthood. Connectivity between different regions of the brain ('long-range' connectivity) is important for integration and global processing of information and comparing incoming sensory information with the existing model of the world within the brain. Connections within each specialized regions ('short-range' connections) are important for processing individual details and modifying the existing model of the world within the brain to more closely reflect incoming sensory information. In infancy, children at high risk for autism that were later diagnosed with autism were observed to have abnormally high long-range connectivity which then decreased through childhood to eventual long-range ''under-connectivity'' by adulthood.
[
* Abnormal preferential processing of information by the left hemisphere of the brain vs. preferential processing of information by right hemisphere in neurotypical individuals. The left hemisphere is associated with processing information related to details whereas the right hemisphere is associated with processing information in a more global and integrated sense that is essential for pattern recognition. For example, visual information like face recognition is normally processed by the right hemisphere which tends to integrate all information from an incoming sensory signal, whereas an ASD brain preferentially processes visual information in the left hemisphere where information tends to be processed for local details of the face rather than the overall configuration of the face. This left lateralization negatively impacts both facial recognition and spatial skills.][
* Increased functional connectivity within the left hemisphere which directly correlates with severity of autism. This observation also supports preferential processing of details of individual components of sensory information over global processing of sensory information in an ASD brain.][
* Prominent abnormal connectivity in the frontal and occipital regions. In autistic individuals low connectivity in the frontal cortex was observed from infancy through adulthood. This is in contrast to long-range connectivity which is high in infancy and low in adulthood in ASD.][ Abnormal neural organization is also observed in the Broca's area which is important for speech production.][
]
Neuropathology
Listed below are some characteristic findings in ASD brains on molecular and cellular levels regardless of the specific genetic variation or mutation contributing to autism in a particular individual:
*Limbic system
The limbic system, also known as the paleomammalian cortex, is a set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, immediately beneath the medial temporal lobe of the cerebrum primarily in the forebrain.Schacter, Daniel L. 2012. ''Ps ...
with smaller neurons that are more densely packed together. Given that the limbic system is the main center of emotions and memory in the human brain, this observation may explain social impairment in ASD.[
*Fewer and smaller Purkinje neurons in the cerebellum. New research suggest a role of the cerebellum in emotional processing and language.][
*Increased number of ]astrocyte
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" + , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of e ...
s and microglia
Microglia are a type of neuroglia (glial cell) located throughout the brain and spinal cord. Microglia account for about 7% of cells found within the brain. As the resident macrophage cells, they act as the first and main form of active immune de ...
in the cerebral cortex. These cells provide metabolic and functional support to neurons and act as immune cells in the nervous system, respectively.[
*Increased brain size in early childhood causing macrocephaly in 15–20% of ASD individuals. The brain size however normalizes by mid-childhood. This variation in brain size in not uniform in the ASD brain with some parts like the frontal and temporal lobes being larger, some like the parietal and occipital lobes being normal sized, and some like cerebellar vermis, corpus callosum, and basal ganglia being smaller than neurotypical individuals.][
*]Cell adhesion molecule
Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) are a subset of cell surface proteins that are involved in the binding of cells with other cells or with the extracellular matrix (ECM), in a process called cell adhesion. In essence, CAMs help cells stick to each ...
s that are essential to formation and maintenance of connections between neurons, neuroligins found on postsynaptic neurons that bind presynaptic cell adhesion molecules, and proteins that anchor cell adhesion molecules to neurons are all found to be mutated in ASD.[
]
Gut-immune-brain axis
46% to 84% of autistic individuals have GI-related problems like reflux, diarrhea, constipation, inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of inflammation, inflammatory conditions of the colon (anatomy), colon and small intestine, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis being the principal types. Crohn's disease affects the small intestine a ...
, and food allergies. It has been observed that the makeup of gut bacteria in autistic people is different than that of neurotypical individuals which has raised the question of influence of gut bacteria on ASD development via inducing an inflammatory state.[
*The immune system is thought to be the intermediary that modulates the influence of gut bacteria on the brain. Some ASD individuals have a dysfunctional immune system with higher numbers of some types of immune cells, biochemical messengers and modulators, and autoimmune antibodies. Increased inflammatory ]biomarker
In biomedical contexts, a biomarker, or biological marker, is a measurable indicator of some biological state or condition. Biomarkers are often measured and evaluated using blood, urine, or soft tissues to examine normal biological processes, p ...
s correlate with increased severity of ASD symptoms and there is some evidence to support a state of chronic brain inflammation in ASD.gut microbiota
Gut microbiota, gut microbiome, or gut flora, are the microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses that live in the digestive tracts of animals. The gastrointestinal metagenome is the aggregate of all the genomes of the gut m ...
. Additionally, immunoglobulin A antibodies that are central to gut immunity were also found in elevated levels in ASD populations. Some of these antibodies may attack proteins that support myelination of the brain, a process that is important for robust transmission of neural signal in many nerves.immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells and objects such ...
during pregnancy (by gut bacteria, bacterial toxins, an infection, or non-infectious causes) and gut bacteria in the mother that induce increased levels of Th17, a pro-inflammatory immune cell, have been associated with an increased risk of autism. Some maternal IgG antibodies that cross the placenta to provide passive immunity to the fetus can also attack the fetal brain.
Mirror neuron system
The mirror neuron system consists of a network of brain areas that have been associated with empathy
Empathy is the capacity to understand or feel what another person is experiencing from within their frame of reference, that is, the capacity to place oneself in another's position. Definitions of empathy encompass a broad range of social, cog ...
processes in humans.
Social brain interconnectivity
A number of discrete brain regions and networks among regions that are involved in dealing with other people have been discussed together under the rubric of the social brain. , there is a consensus that autism spectrum is likely related to problems with interconnectivity among these regions and networks, rather than problems with any specific region or network.
Temporal lobe
Functions of the temporal lobe are related to many of the deficits observed in individuals with ASDs, such as receptive language, social cognition, joint attention, action observation, and empathy. The temporal lobe also contains the superior temporal sulcus and the fusiform face area, which may mediate facial processing. It has been argued that dysfunction in the superior temporal sulcus underlies the social deficits that characterize autism. Compared to typically developing individuals, one study found that individuals with so-called high-functioning autism had reduced activity in the fusiform face area when viewing pictures of faces.
Mitochondria
ASD could be linked to mitochondrial disease, a basic cellular abnormality with the potential to cause disturbances in a wide range of body systems.mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial D ...
abnormalities.
Serotonin
Serotonin
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vas ...
is a major neurotransmitter in the nervous system and contributes to formation of new neurons (neurogenesis
Neurogenesis is the process by which nervous system cells, the neurons, are produced by neural stem cells (NSCs). It occurs in all species of animals except the porifera (sponges) and placozoans. Types of NSCs include neuroepithelial cells (NECs) ...
), formation of new connections between neurons ( synaptogenesis), remodeling of synapses, and survival and migration of neurons, processes that are necessary for a developing brain and some also necessary for learning in the adult brain. 45% of ASD individuals have been found to have increased blood serotonin levels.[ It has been hypothesized that increased activity of serotonin in the developing brain may facilitate the onset of ASD, with an association found in six out of eight studies between the use of ]selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a class of drugs that are typically used as antidepressants in the treatment of major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and other psychological conditions.
SSRIs increase the extracellul ...
s (SSRIs) by the pregnant mother and the development of ASD in the child exposed to SSRI in the antenatal environment. The study could not definitively conclude SSRIs caused the increased risk for ASD due to the biases found in those studies, and the authors called for more definitive, better conducted studies. Confounding by indication has since then been shown to be likely. However, it is also hypothesized that SSRIs may help reduce symptoms of ASD and even positively affect brain development in some ASD patients.
Diagnosis
 Autism spectrum disorder is a clinical diagnosis that is typically made by a physician based off reported and directly observed behavior in the affected individual. According to the updated diagnostic criteria in the DSM-5-TR, in order to receive a diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder, one must present with “persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction” and “restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities.”
Autism spectrum disorder is a clinical diagnosis that is typically made by a physician based off reported and directly observed behavior in the affected individual. According to the updated diagnostic criteria in the DSM-5-TR, in order to receive a diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder, one must present with “persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction” and “restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities.”hearing impairment
Hearing loss is a partial or total inability to hear. Hearing loss may be present at birth or acquired at any time afterwards. Hearing loss may occur in one or both ears. In children, hearing problems can affect the ability to acquire spoken l ...
, a specific language impairment
Specific language impairment (SLI) (the term developmental language disorder is preferred by some) is diagnosed when a child's language does not develop normally and the difficulties cannot be accounted for by generally slow development, physical ...
psychotic disorders
Psychosis is a condition of the mind that results in difficulties determining what is real and what is not real. Symptoms may include delusions and hallucinations, among other features. Additional symptoms are incoherent speech and behavior t ...
. Furthermore, the presence of autism can make it harder to diagnose coexisting psychiatric disorders such as depression.
Ideally the diagnosis of ASD should be given by a team of clinicians (e.g. pediatricians, child psychiatrists, child neurologists) based on information provided from the affected individual, caregivers, other medical professionals and from direct observation.pediatrician
Pediatrics ( also spelled ''paediatrics'' or ''pædiatrics'') is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, adolescents, and young adults. In the United Kingdom, paediatrics covers many of their youth until the ...
or primary care physician taking a developmental history and performing a physical exam. If warranted, the physician may refer the individual to an ASD specialist who will observe and assess cognitive, communication, family, and other factors using standardized tools, and taking into account any associated medical conditions.Metabolic
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
and neuroimaging tests are also not routinely performed for diagnosis of ASD.neuropsychologists
Neuropsychology is a branch of psychology concerned with how a person's cognition and behavior are related to the brain and the rest of the nervous system. Professionals in this branch of psychology often focus on how injuries or illnesses of ...
, and psychiatrists).
Screening
About half of parents of children with ASD notice their child's atypical behaviors by age 18 months, and about four-fifths notice by age 24 months.Checklist for Autism in Toddlers
The Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (CHAT) is a psychological questionnaire designed to evaluate risk for autism spectrum disorder in children ages 18–24 months. The 14-question test is filled out by the parent and a pediatrician or physician ...
(CHAT), on children aged 18–30 months suggests that it is best used in a clinical setting and that it has low sensitivity
Sensitivity may refer to:
Science and technology Natural sciences
* Sensitivity (physiology), the ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli
** Sensory processing sensitivity in humans
* Sensitivity and specificity, statisti ...
(many false-negatives) but good specificity (few false-positives).
Misdiagnosis
There is a significant level of misdiagnosis of autism in neurodevelopmentally typical children; 18–37% of children diagnosed with ASD eventually lose their diagnosis. This high rate of lost diagnosis cannot be accounted for by successful ASD treatment alone. The most common reason parents reported as the cause of lost ASD diagnosis was new information about the child (73.5%), such as a replacement diagnosis. Other reasons included a diagnosis given so the child could receive ASD treatment (24.2%), ASD treatment success or maturation (21%), and parents disagreeing with the initial diagnosis (1.9%).specific language impairment
Specific language impairment (SLI) (the term developmental language disorder is preferred by some) is diagnosed when a child's language does not develop normally and the difficulties cannot be accounted for by generally slow development, physical ...
, social communication disorder, anxiety disorder, reactive attachment disorder, cognitive impairment, visual impairment, hearing loss and normal behavioral variation. Some behavioral variations that resemble autistic traits are repetitive behaviors, sensitivity to change in daily routines, focused interests, and toe-walking. These are considered normal behavioral variations when they do not cause impaired function. Boys are more likely to exhibit repetitive behaviors especially when excited, tired, bored, or stressed. Some ways of distinguishing typical behavioral variations from autistic behaviors are the ability of the child to suppress these behaviors and the absence of these behaviors during sleep.
Comorbidity
ASDs tend to be highly comorbid with other disorders.Tuberous sclerosis
Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) is a rare multisystem autosomal dominant genetic disease that causes non-cancerous tumours to grow in the brain and on other vital organs such as the kidneys, heart, liver, eyes, lungs and skin. A combination ...
, an autosomal dominant genetic condition in which non-malignant tumors grow in the brain and on other vital organs, is present in 1–4% of individuals with ASDs.Down
Down most often refers to:
* Down, the relative direction opposed to up
* Down (gridiron football), in American/Canadian football, a period when one play takes place
* Down feather, a soft bird feather used in bedding and clothing
* Downland, a ty ...
, Prader-Willi, Angelman, Williams syndrome and SYNGAP1-related intellectual disability SYNGAP1-related intellectual disability is a monogenetic developmental and epileptic encephalopathy that affects the central nervous system. Symptoms include intellectual disability, epilepsy, autism, sensory processing deficits, hypotonia and unst ...
.
* Learning disabilities are also highly comorbid in individuals with an ASD. Approximately 25–75% of individuals with an ASD also have some degree of a learning disability.schizoid personality disorder
Schizoid personality disorder (, often abbreviated as SzPD or ScPD) is a personality disorder characterized by a lack of interest in social relationships, a tendency toward a solitary or sheltered lifestyle, secretiveness, emotional coldnes ...
, which is characterized by a lack of interest in social relationships, a tendency towards a solitary or sheltered lifestyle, secretiveness, emotional coldness, detachment and apathy.Genetic disorder
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorde ...
s - about 10–15% of autism cases have an identifiable Mendelian (single-gene) condition, chromosome abnormality
A chromosomal abnormality, chromosomal anomaly, chromosomal aberration, chromosomal mutation, or chromosomal disorder, is a missing, extra, or irregular portion of chromosomal DNA. These can occur in the form of numerical abnormalities, where the ...
, or other genetic syndromes.
* Several metabolic defects, such as phenylketonuria, are associated with autistic symptoms.nocturnal awakenings
Middle-of-the-night insomnia (MOTN) is characterized by having difficulty returning to sleep after waking up during the night or very early in the morning. This kind of insomnia (sleeplessness) is different from initial or sleep-onset insomnia, wh ...
, and early morning awakenings. Sleep problems are associated with difficult behaviors and family stress, and are often a focus of clinical attention over and above the primary ASD diagnosis.
Management
There is no treatment as such for autism, and many sources advise that this is not an appropriate goal, although treatment of co-occurring conditions remains an important goal. There is no cure for autism as of 2022, nor can any of the known treatments significantly reduce brain mutations caused by autism, although those who require little-to-no support are more likely to experience a lessening of symptoms over time.
Non-pharmacological interventions
Intensive, sustained special education or remedial education programs and behavior therapy early in life can help children acquire self-care, social, and job skills. Available approaches include applied behavior analysis, developmental models, structured teaching, speech and language therapy, social skills
A social skill is any competence facilitating interaction and communication with others where social rules and relations are created, communicated, and changed in verbal and nonverbal ways. The process of learning these skills is called social ...
therapy, and occupational therapy
Occupational therapy (OT) is a global healthcare profession. It involves the use of assessment and intervention to develop, recover, or maintain the meaningful activities, or ''occupations'', of individuals, groups, or communities. The field of ...
.Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology
The ''Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology'' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed journal covering child and adolescent mental health. It was established in 1971 as the ''Journal of Clinical Child Psychology'', obtaining its current name in 2 ...
'' has deemed two early childhood interventions as "well-established": individual comprehensive ABA, and focused teacher-implemented ABA combined with DSP.Cochrane Cochrane may refer to:
Places Australia
*Cochrane railway station, Sydney, a railway station on the closed Ropes Creek railway line
Canada
* Cochrane, Alberta
* Cochrane Lake, Alberta
* Cochrane District, Ontario
** Cochrane, Ontario, a town wit ...
review found no evidence that early intensive behavioral intervention (EIBI) is effective in reducing behavioral problems associated with autism in most autistic children but did help improve IQ and language skills. The Cochrane review did acknowledge that this may be due to the low quality of studies currently available on EIBI and therefore providers should recommend EIBI based on their clinical judgement and the family's preferences. No adverse effects of EIBI treatment were found.[
Generally speaking, treatment of ASD focuses on behavioral and educational interventions to target its two core symptoms: social communication deficits and restricted, repetitive behaviors.]Melatonin
Melatonin is a natural product found in plants and animals. It is primarily known in animals as a hormone released by the pineal gland in the brain at night, and has long been associated with control of the sleep–wake cycle.
In vertebrates ...
for example can be used for sleep problems.
While there are a number of parent-mediated behavioral therapies to target social communication deficits in children with autism, there is uncertainty regarding the efficacy of interventions to treat RRBs.
Education
 Educational interventions often used include applied behavior analysis (ABA), developmental models, structured teaching, speech and language therapy and
Educational interventions often used include applied behavior analysis (ABA), developmental models, structured teaching, speech and language therapy and social skills
A social skill is any competence facilitating interaction and communication with others where social rules and relations are created, communicated, and changed in verbal and nonverbal ways. The process of learning these skills is called social ...
therapy.discrete trial training
Discrete trial training (DTT) is a technique used by practitioners of applied behavior analysis (ABA) that was developed by Ivar Lovaas at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA). DTT uses direct instruction and reinforcers to create clea ...
—the structured and intensive form of ABA.
Pharmacological interventions
Medications may be used to treat ASD symptoms that interfere with integrating a child into home or school when behavioral treatment fails.anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil
Turmoil may refer to:
* ''Turmoil'' (1984 video game), a 1984 video game released by Bug-Byte
* ''Turmoil'' (2016 video game), a 2016 indie oil tycoon video ...
.stimulant
Stimulants (also often referred to as psychostimulants or colloquially as uppers) is an overarching term that covers many drugs including those that increase activity of the central nervous system and the body, drugs that are pleasurable and inv ...
s, and antipsychotic
Antipsychotics, also known as neuroleptics, are a class of psychotropic medication primarily used to manage psychosis (including delusions, hallucinations, paranoia or disordered thought), principally in schizophrenia but also in a range o ...
s.atypical antipsychotic
The atypical antipsychotics (AAP), also known as second generation antipsychotics (SGAs) and serotonin–dopamine antagonists (SDAs), are a group of antipsychotic drugs (antipsychotic drugs in general are also known as major tranquilizers and ne ...
drugs risperidone and aripiprazole are FDA-approved for treating associated aggressive and self-injurious behaviors.
Alternative medicine
A multitude of researched alternative therapies have also been implemented. Many have resulted in harm to autistic people.mindfulness
Mindfulness is the practice of purposely bringing one's attention to the present-moment experience without evaluation, a skill one develops through meditation or other training. Mindfulness derives from ''sati'', a significant element of Hind ...
-based interventions for improving mental health.
Although popularly used as an alternative treatment for autistic people, there is no good evidence to recommend a gluten- and casein-free diet as a standard treatment.calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
and vitamin D; however, suboptimal bone development in ASD has also been associated with lack of exercise and gastrointestinal disorders.pseudoscientific
Pseudoscience consists of statements, beliefs, or practices that claim to be both scientific and factual but are incompatible with the scientific method. Pseudoscience is often characterized by contradictory, exaggerated or unfalsifiable claim ...
mixture of homeopathy
Homeopathy or homoeopathy is a pseudoscientific system of alternative medicine. It was conceived in 1796 by the German physician Samuel Hahnemann. Its practitioners, called homeopaths, believe that a substance that causes symptoms of a dis ...
, supplements, and 'vaccine detoxing'.
Results of a systematic review on interventions to address health outcomes among autistic adults found emerging evidence to support mindfulness
Mindfulness is the practice of purposely bringing one's attention to the present-moment experience without evaluation, a skill one develops through meditation or other training. Mindfulness derives from ''sati'', a significant element of Hind ...
-based interventions for improving mental health. This includes decreasing stress, anxiety, ruminating thoughts, anger, and aggression.
Prevention
While infection with rubella
Rubella, also known as German measles or three-day measles, is an infection caused by the rubella virus. This disease is often mild, with half of people not realizing that they are infected. A rash may start around two weeks after exposure and ...
during pregnancy causes fewer than 1% of cases of autism,
Prognosis
There is currently no evidence of a cure for autism.independent living
Independent living (IL), as seen by its advocates, is a philosophy, a way of looking at society and disability, and a worldwide movement of disabled people working for equal opportunities, self-determination, and self-respect. In the context o ...
is unlikely with severe autism.
Many autistic people face significant obstacles in transitioning to adulthood. Compared to the general population, autistic people are more likely to be unemployed and to have never had a job. About half of people in their 20s with autism are not employed. Some autistic adults are unable to live independently.
Academic performance
The number of students identified and served as eligible for autism services in the United States has increased from 5,413 children in 1991–1992 to 370,011 children in the 2010–2011 academic school year.United States Department of Health and Human Services
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the U.S. federal government created to protect the health of all Americans and providing essential human services. Its motto ...
reported approximately 1 in 68 children are diagnosed with ASD at age 8 although onset is typically between ages 2 and 4.teacher
A teacher, also called a schoolteacher or formally an educator, is a person who helps students to acquire knowledge, competence, or virtue, via the practice of teaching.
''Informally'' the role of teacher may be taken on by anyone (e.g. w ...
s, school psychologists, and other school professionals.
Employment
In the United States, about half of people in their 20s with autism are unemployed, and one third of those with graduate degrees may be unemployed.
Epidemiology
 The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that about 1 in 100 children have autism. The number of people diagnosed has increased considerably since the 1990s, which may be partly due to increased recognition of the condition.
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that about 1 in 100 children have autism. The number of people diagnosed has increased considerably since the 1990s, which may be partly due to increased recognition of the condition.
United States
In the United States it is estimated to affect more than 2% of children (about 1.5 million) . According to the latest CDC prevalence reports, 1 in 44 children (2.3%) in the United States had a diagnosis of ASD in 2018. Prevalence is estimated at 6 per 1,000 for ASDs as a whole.
History
 A few examples of autistic symptoms and treatments were described long before autism was named. The '' Table Talk'' of
A few examples of autistic symptoms and treatments were described long before autism was named. The '' Table Talk'' of Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Protestant Reformation and the namesake of Luther ...
, compiled by his notetaker, Mathesius, contains the story of a 12-year-old boy who may have been severely autistic. The earliest well-documented case of autism is that of Hugh Blair of Borgue, as detailed in a 1747 court case in which his brother successfully petitioned to annul Blair's marriage to gain Blair's inheritance.
The Wild Boy of Aveyron, a feral child found in 1798, showed several signs of autism. He was non-verbal during his teenage years, and his case was widely popular among society for its time. Such cases brought awareness to autism, and more research was conducted on the natural dimensions of human behavior. The medical student Jean Itard
Jean Marc Gaspard Itard (24 April 1774, Oraison, Alpes-de-Haute-Provence – 5 July 1838, Paris) was a French physician born in Provence. He is perhaps best known for his work with Victor of Aveyron.
Biography
Itard, without a university e ...
treated him with a behavioral program designed to help him form social attachments and to induce speech via imitation.Swiss
Swiss may refer to:
* the adjectival form of Switzerland
* Swiss people
Places
* Swiss, Missouri
* Swiss, North Carolina
*Swiss, West Virginia
* Swiss, Wisconsin
Other uses
*Swiss-system tournament, in various games and sports
*Swiss Internation ...
psychiatrist Eugen Bleuler in 1910 as he was defining symptoms of schizophrenia. He derived it from the and used it to mean morbid self-admiration, referring to "autistic withdrawal of the patient to his fantasies, against which any influence from outside becomes an intolerable disturbance". A Soviet child psychiatrist, Grunya Sukhareva, described a similar syndrome in Russian in 1925, and in German in 1926.
Clinical development and diagnoses
 Autism spectrum disorder, as it is known today, can be traced back to the late 1930s, when two separate psychiatrists – Leo Kanner of Johns Hopkins Hospital and Hans Asperger of the Vienna University Hospital – used the word ''autism'' to describe the patients they were studying in their own clinical research and practice. The word ''autism'' first took its modern sense in German, when Asperger adopted Bleuler's terminology ''autistic psychopaths'' in a 1938 lecture in German about child psychology. Asperger was investigating an ASD which was later known as Asperger syndrome, although it did not become widely recognized as a separate diagnosis until 1981; it has since been eliminated from the lexicon.
Autism spectrum disorder, as it is known today, can be traced back to the late 1930s, when two separate psychiatrists – Leo Kanner of Johns Hopkins Hospital and Hans Asperger of the Vienna University Hospital – used the word ''autism'' to describe the patients they were studying in their own clinical research and practice. The word ''autism'' first took its modern sense in German, when Asperger adopted Bleuler's terminology ''autistic psychopaths'' in a 1938 lecture in German about child psychology. Asperger was investigating an ASD which was later known as Asperger syndrome, although it did not become widely recognized as a separate diagnosis until 1981; it has since been eliminated from the lexicon.[ Reprinted in ] Almost all the characteristics described in Kanner's first paper on the subject, notably "autistic aloneness" and "insistence on sameness", are still regarded as typical of autistic spectrum disorder.
Terminology and distinction from schizophrenia
As late as the mid-1970s there was little evidence of a genetic role in autism, however by 2007 it was recognised as one of the most heritable psychiatric conditions. Although the rise of parent organizations and the destigmatization of childhood ASD have affected how ASD is viewed,medical specialists
A medical specialty is a branch of medical practice that is focused on a defined group of patients, diseases, skills, or philosophy. Examples include those branches of medicine that deal exclusively with children ( paediatrics), cancer (oncology), ...
express beliefs consistent with outdated autism research.
It took until 1980 for the DSM-III to differentiate autism from childhood schizophrenia. In 1987, the DSM-III-R provided a checklist for diagnosing autism. In May 2013, the DSM-5 was released, updating the classification for pervasive developmental disorders. The grouping of disorders, including PDD-NOS, autism, Asperger syndrome, Rett syndrome, and CDD, has been removed and replaced with the general term of Autism Spectrum Disorders. The two categories that exist are impaired social communication and/or interaction, and restricted and/or repetitive behaviors.
The Internet has helped autistic individuals bypass nonverbal cues and emotional sharing that they find difficult to deal with, and has given them a way to form online communities and work remotely. Societal and cultural aspects of autism have developed: some in the community seek a cure, while others believe that autism is simply another way of being.
Society and culture
An autistic culture has emerged, accompanied by the autistic rights
The autism spectrum, often referred to as just autism or in the context of a professional diagnosis autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a neurodevelopmental condition (or conditions) characterized by difficulti ...
and neurodiversity movements who argue autism should be accepted as a difference to be accommodated instead of cured,World Autism Awareness Day
World Autism Awareness Day is an internationally recognized day annually on April 2nd, encouraging Member States of the United Nations to take measures to raise awareness about autistic individuals throughout the world. It was designated by the ...
, Autism Sunday
Autism Sunday, also known as the International Day of Prayer for autism spectrum disorders, is an event observed annually on the second Sunday of February.
History
Autism Sunday was first held in 2002 during Autism Awareness Year in the United ...
, Autistic Pride Day
Autistic Pride Day is a pride celebration for autistic people held on 18 June each year. Autistic pride recognises the importance of pride for autistic people and its role in bringing about positive changes in the broader society.
Although Au ...
, Autreat, and others. Social-science scholars study those with autism in hopes to learn more about "autism as a culture, transcultural comparisons ... and research on social movements." Many autistic individuals have been successful in their fields.
Neurodiversity movement
Some autistic people, as well as a number of researchers, have advocated a shift in attitudes toward the view that autism spectrum disorder is a difference, rather than a disease that must be treated or cured.[ A preliminary, freely readable draft, with slightly different wording in the quoted text, is in: ] Critics have bemoaned the entrenchment of some of these groups' opinions.social movement
A social movement is a loosely organized effort by a large group of people to achieve a particular goal, typically a social or political one. This may be to carry out a social change, or to resist or undo one. It is a type of group action and may ...
s within the context of disability rights, emphasizing the concept of neurodiversity, which describes the autism spectrum as a result of natural variations in the human brain rather than a disorder to be cured.
Caregivers
Families who care for an autistic child face added stress from a number of different causes. Parents may struggle to understand the diagnosis and to find appropriate care options. Parents often take a negative view of the diagnosis, and may struggle emotionally. More than half of parents over the age of 50 are still living with their child, as about 85% of autistic people have difficulties living independently.
Broader autism phenotype
The broader autism phenotype (BAP) describes individuals who may not have ASD but do have autistic traits, such as avoiding eye contact and stimming.
See also
* Autism spectrum disorders in the media
Autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) or autism spectrum conditions (ASCs) describe a range of conditions classified as neurodevelopmental disorders in the DSM-5, used by the American Psychiatric Association. As with many neurodivergent people and condi ...
* Extraordinary Attorney Woo
* List of films about autism
This is a list of autism-related films:
Fiction
Non-fiction
ReferencesMost Popular "Autism" Titles (Sorted by Release Date, descending): 507at IMDb
IMDb (an abbreviation of Internet Movie Database) is an online database of informat ...
* Social narrative
References
Sources
*
*
Further reading
* Gabovitch, Elaine; Dutra, Courtney; Lauer, Emily. (2016)
''The Healthy People 2020 Roadmap for Massachusetts Children & Youth with ASD/DD: Understanding Needs and Measuring Outcomes'' (Report)
Worcester: UMASS Chan Medical School. Retrieved 30 June 2022.
* Matson JL, Dempsey T (2008). "Stereotypy in Adults with Autism Spectrum Disorders: Relationship and Diagnostic Fidelity". ''Journal of Developmental and Physical Disabilities, 20''(2) 155–165. doi 10.1007/s10882-007-9086-0. S2CID 143874013.
*
* eISSN 1873-3379
*
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Autism spectrum
Developmental psychology
Developmental neuroscience
Learning disabilities
Spectrum disorders
 ASD includes a wide variety of characteristics. Some of these include behavioral characteristics which widely range from slow development of social and learning skills to difficulties creating connections with other people. Autistic individuals may experience these challenges with forming connections due to anxiety or depression, which they are more likely to experience, and as a result isolate themselves.
Other behavioral characteristics include abnormal responses to sensations (such as sights, sounds, touch, taste and smell) and problems keeping a consistent speech rhythm. The latter problem influences an individual's social skills, leading to potential problems in how they are understood by communication partners. Behavioral characteristics displayed by autistic people typically influence development, language, and social competence. Behavioral characteristics of autistic people can be observed as perceptual disturbances, disturbances of development rate, relating, speech and language, and motility.
The second core symptom of autism spectrum is a pattern of restricted and repetitive behaviors, activities, and interests. In order to be diagnosed with ASD under DSM-5 or DSM-5-TR, a person must have at least two of the following behaviors:
* Repetitive behaviors – Repetitive behaviors such as rocking, hand flapping, finger flicking, head banging, or repeating phrases or sounds. These behaviors may occur constantly or only when the person gets stressed, anxious or upset.
*Resistance to change – A strict adherence to routines such as eating certain foods in a specific order, or taking the same path to school every day. The child may have a meltdown if there is any change or disruption to their routine.
*Restricted interests – An excessive interest in a particular activity, topic, or hobby, and devoting all their attention to it. For example, young children might completely focus on things that spin and ignore everything else. Older children might try to learn everything about a single topic, such as the weather or sports, and perseverate or talk about it constantly.
*Sensory reactivity – An unusual reaction to certain sensory inputs such as having a negative reaction to specific sounds or textures, being fascinated by lights or movements or having an apparent indifference to pain or heat.
Autistic individuals can display many forms of repetitive or restricted behavior, which the Repetitive Behavior Scale-Revised (RBS-R) categorizes as follows.
* Stereotyped behaviors: Repetitive movements, such as hand flapping, head rolling, or body rocking.
* Compulsive behaviors: Time-consuming behaviors intended to reduce anxiety, that an individual feels compelled to perform repeatedly or according to rigid rules, such as placing objects in a specific order, checking things, or handwashing.
* Sameness: Resistance to change; for example, insisting that the furniture not be moved or refusing to be interrupted.
* Ritualistic behavior: Unvarying pattern of daily activities, such as an unchanging menu or a dressing ritual. This is closely associated with sameness and an independent validation has suggested combining the two factors.
* Restricted interests: Interests or fixations that are abnormal in theme or intensity of focus, such as preoccupation with a single television program, toy, or game.
*
ASD includes a wide variety of characteristics. Some of these include behavioral characteristics which widely range from slow development of social and learning skills to difficulties creating connections with other people. Autistic individuals may experience these challenges with forming connections due to anxiety or depression, which they are more likely to experience, and as a result isolate themselves.
Other behavioral characteristics include abnormal responses to sensations (such as sights, sounds, touch, taste and smell) and problems keeping a consistent speech rhythm. The latter problem influences an individual's social skills, leading to potential problems in how they are understood by communication partners. Behavioral characteristics displayed by autistic people typically influence development, language, and social competence. Behavioral characteristics of autistic people can be observed as perceptual disturbances, disturbances of development rate, relating, speech and language, and motility.
The second core symptom of autism spectrum is a pattern of restricted and repetitive behaviors, activities, and interests. In order to be diagnosed with ASD under DSM-5 or DSM-5-TR, a person must have at least two of the following behaviors:
* Repetitive behaviors – Repetitive behaviors such as rocking, hand flapping, finger flicking, head banging, or repeating phrases or sounds. These behaviors may occur constantly or only when the person gets stressed, anxious or upset.
*Resistance to change – A strict adherence to routines such as eating certain foods in a specific order, or taking the same path to school every day. The child may have a meltdown if there is any change or disruption to their routine.
*Restricted interests – An excessive interest in a particular activity, topic, or hobby, and devoting all their attention to it. For example, young children might completely focus on things that spin and ignore everything else. Older children might try to learn everything about a single topic, such as the weather or sports, and perseverate or talk about it constantly.
*Sensory reactivity – An unusual reaction to certain sensory inputs such as having a negative reaction to specific sounds or textures, being fascinated by lights or movements or having an apparent indifference to pain or heat.
Autistic individuals can display many forms of repetitive or restricted behavior, which the Repetitive Behavior Scale-Revised (RBS-R) categorizes as follows.
* Stereotyped behaviors: Repetitive movements, such as hand flapping, head rolling, or body rocking.
* Compulsive behaviors: Time-consuming behaviors intended to reduce anxiety, that an individual feels compelled to perform repeatedly or according to rigid rules, such as placing objects in a specific order, checking things, or handwashing.
* Sameness: Resistance to change; for example, insisting that the furniture not be moved or refusing to be interrupted.
* Ritualistic behavior: Unvarying pattern of daily activities, such as an unchanging menu or a dressing ritual. This is closely associated with sameness and an independent validation has suggested combining the two factors.
* Restricted interests: Interests or fixations that are abnormal in theme or intensity of focus, such as preoccupation with a single television program, toy, or game.
*  Autism has a strong genetic basis, although the genetics of autism are complex and it is unclear whether ASD is explained more by rare mutations with major effects, or by rare multi-gene interactions of common genetic variants. Complexity arises due to interactions among multiple genes, the environment, and epigenetic factors which do not change DNA sequencing but are heritable and influence
Autism has a strong genetic basis, although the genetics of autism are complex and it is unclear whether ASD is explained more by rare mutations with major effects, or by rare multi-gene interactions of common genetic variants. Complexity arises due to interactions among multiple genes, the environment, and epigenetic factors which do not change DNA sequencing but are heritable and influence  Autism spectrum disorder is a clinical diagnosis that is typically made by a physician based off reported and directly observed behavior in the affected individual. According to the updated diagnostic criteria in the DSM-5-TR, in order to receive a diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder, one must present with “persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction” and “restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities.” These behaviors must begin in early childhood and affect one's ability to perform everyday tasks. Furthermore, the symptoms must not be fully explainable by intellectual developmental disorder or global developmental delay.
There are several factors that make autism spectrum disorder difficult to diagnose. First off, there are no standardized imaging, molecular or genetic tests that can be used to diagnose ASD. Additionally, there is a lot of variety in how ASD affects individuals. The behavioral manifestations of ASD depend on one's developmental stage, age of presentation, current support, and individual variability. Lastly, there are multiple conditions that may present similarly to autism spectrum disorder, including intellectual disability,
Autism spectrum disorder is a clinical diagnosis that is typically made by a physician based off reported and directly observed behavior in the affected individual. According to the updated diagnostic criteria in the DSM-5-TR, in order to receive a diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder, one must present with “persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction” and “restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities.” These behaviors must begin in early childhood and affect one's ability to perform everyday tasks. Furthermore, the symptoms must not be fully explainable by intellectual developmental disorder or global developmental delay.
There are several factors that make autism spectrum disorder difficult to diagnose. First off, there are no standardized imaging, molecular or genetic tests that can be used to diagnose ASD. Additionally, there is a lot of variety in how ASD affects individuals. The behavioral manifestations of ASD depend on one's developmental stage, age of presentation, current support, and individual variability. Lastly, there are multiple conditions that may present similarly to autism spectrum disorder, including intellectual disability,  Educational interventions often used include applied behavior analysis (ABA), developmental models, structured teaching, speech and language therapy and
Educational interventions often used include applied behavior analysis (ABA), developmental models, structured teaching, speech and language therapy and  The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that about 1 in 100 children have autism. The number of people diagnosed has increased considerably since the 1990s, which may be partly due to increased recognition of the condition.
While rates of ASD are consistent across cultures, they vary greatly by gender, with boys diagnosed far more frequently than girls: 1 in 70 boys, but only 1 in 315 girls at eight years of age. Girls, however, are more likely to have associated cognitive impairment, suggesting that less severe forms of ASD are likely being missed in girls and women. Prevalence differences may be a result of gender differences in expression of clinical symptoms, with women and girls with autism showing less atypical behaviors and, therefore, less likely to receive an ASD diagnosis.
Using DSM-5 criteria, 92% of the children diagnosed per DSM-IV with one of the disorders which is now considered part of ASD will still meet the diagnostic criteria of ASD. However, if both ASD and the social (pragmatic) communication disorder categories of DSM-5 are combined, the prevalence of autism is mostly unchanged from the prevalence per the DSM-IV criteria. The best estimate for prevalence of ASD is 0.7% or 1 child in 143 children. Relatively mild forms of autism, such as Aspergers as well as other developmental disorders, are included in the DSM-5 diagnostic criteria. ASD rates were constant between 2014 and 2016 but twice the rate compared to the time period between 2011 and 2014 (1.25 vs 2.47%). A Canadian meta-analysis from 2019 confirmed these effects as the profiles of people diagnosed with autism became less and less different from the profiles of the general population. In the US, the rates for diagnosed ASD have been steadily increasing since 2000 when records began being kept. While it remains unclear whether this trend represents a true rise in incidence, it likely reflects changes in ASD diagnostic criteria, improved detection, and increased public awareness of autism. In 2012, the NHS estimated that the overall prevalence of autism among adults aged 18 years and over in the UK was 1.1%. A 2016 survey in the United States reported a rate of 25 per 1,000 children for ASD. It is important to note that rates of autism are poorly understood in many low- and middle-income countries, which affects the accuracy of global ASD prevalence estimates, but it is thought that most autistic individuals live in low- and middle-income countries.
In the UK, from 1998 to 2018, the autism diagnoses increased by 787%. This increase is largely attributable to changes in diagnostic practices, referral patterns, availability of services, age at diagnosis, and public awareness (particularly among women), though unidentified environmental risk factors cannot be ruled out. The available evidence does not rule out the possibility that autism's true prevalence has increased; a real increase would suggest directing more attention and funding toward psychosocial factors and changing environmental factors instead of continuing to focus on genetics. It has been established that vaccination is not a risk factor for autism and is not a cause of any increase in autism prevalence rates, if any change in the rate of autism exists at all.
Males have higher likelihood of being diagnosed with ASD than females. The sex ratio averages 4.3:1 and is greatly modified by cognitive impairment: it may be close to 2:1 with intellectual disability and more than 5.5:1 without. Several theories about the higher prevalence in males have been investigated, but the cause of the difference is unconfirmed; one theory is that females are underdiagnosed.
The risk of developing autism is greater with older fathers than with older mothers; two potential explanations are the known increase in mutation burden in older sperm, and the hypothesis that men marry later if they carry genetic liability and show some signs of autism. Most professionals believe that race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic background do not affect the occurrence of autism.
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that about 1 in 100 children have autism. The number of people diagnosed has increased considerably since the 1990s, which may be partly due to increased recognition of the condition.
While rates of ASD are consistent across cultures, they vary greatly by gender, with boys diagnosed far more frequently than girls: 1 in 70 boys, but only 1 in 315 girls at eight years of age. Girls, however, are more likely to have associated cognitive impairment, suggesting that less severe forms of ASD are likely being missed in girls and women. Prevalence differences may be a result of gender differences in expression of clinical symptoms, with women and girls with autism showing less atypical behaviors and, therefore, less likely to receive an ASD diagnosis.
Using DSM-5 criteria, 92% of the children diagnosed per DSM-IV with one of the disorders which is now considered part of ASD will still meet the diagnostic criteria of ASD. However, if both ASD and the social (pragmatic) communication disorder categories of DSM-5 are combined, the prevalence of autism is mostly unchanged from the prevalence per the DSM-IV criteria. The best estimate for prevalence of ASD is 0.7% or 1 child in 143 children. Relatively mild forms of autism, such as Aspergers as well as other developmental disorders, are included in the DSM-5 diagnostic criteria. ASD rates were constant between 2014 and 2016 but twice the rate compared to the time period between 2011 and 2014 (1.25 vs 2.47%). A Canadian meta-analysis from 2019 confirmed these effects as the profiles of people diagnosed with autism became less and less different from the profiles of the general population. In the US, the rates for diagnosed ASD have been steadily increasing since 2000 when records began being kept. While it remains unclear whether this trend represents a true rise in incidence, it likely reflects changes in ASD diagnostic criteria, improved detection, and increased public awareness of autism. In 2012, the NHS estimated that the overall prevalence of autism among adults aged 18 years and over in the UK was 1.1%. A 2016 survey in the United States reported a rate of 25 per 1,000 children for ASD. It is important to note that rates of autism are poorly understood in many low- and middle-income countries, which affects the accuracy of global ASD prevalence estimates, but it is thought that most autistic individuals live in low- and middle-income countries.
In the UK, from 1998 to 2018, the autism diagnoses increased by 787%. This increase is largely attributable to changes in diagnostic practices, referral patterns, availability of services, age at diagnosis, and public awareness (particularly among women), though unidentified environmental risk factors cannot be ruled out. The available evidence does not rule out the possibility that autism's true prevalence has increased; a real increase would suggest directing more attention and funding toward psychosocial factors and changing environmental factors instead of continuing to focus on genetics. It has been established that vaccination is not a risk factor for autism and is not a cause of any increase in autism prevalence rates, if any change in the rate of autism exists at all.
Males have higher likelihood of being diagnosed with ASD than females. The sex ratio averages 4.3:1 and is greatly modified by cognitive impairment: it may be close to 2:1 with intellectual disability and more than 5.5:1 without. Several theories about the higher prevalence in males have been investigated, but the cause of the difference is unconfirmed; one theory is that females are underdiagnosed.
The risk of developing autism is greater with older fathers than with older mothers; two potential explanations are the known increase in mutation burden in older sperm, and the hypothesis that men marry later if they carry genetic liability and show some signs of autism. Most professionals believe that race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic background do not affect the occurrence of autism.
 A few examples of autistic symptoms and treatments were described long before autism was named. The '' Table Talk'' of
A few examples of autistic symptoms and treatments were described long before autism was named. The '' Table Talk'' of  Autism spectrum disorder, as it is known today, can be traced back to the late 1930s, when two separate psychiatrists – Leo Kanner of Johns Hopkins Hospital and Hans Asperger of the Vienna University Hospital – used the word ''autism'' to describe the patients they were studying in their own clinical research and practice. The word ''autism'' first took its modern sense in German, when Asperger adopted Bleuler's terminology ''autistic psychopaths'' in a 1938 lecture in German about child psychology. Asperger was investigating an ASD which was later known as Asperger syndrome, although it did not become widely recognized as a separate diagnosis until 1981; it has since been eliminated from the lexicon. In English, Kanner first used ''autism'' in its modern sense when he introduced the label ''early infantile autism'' in a 1943 report of 11 children with striking behavioral similarities; his publication was named ''Autistic Disturbances of Affective Contact''. Reprinted in Almost all the characteristics described in Kanner's first paper on the subject, notably "autistic aloneness" and "insistence on sameness", are still regarded as typical of autistic spectrum disorder. It is not known whether Kanner derived the term independently of Hans Asperger.
Kanner's reuse of ''autism'' led to decades of confused terminology like ''infantile schizophrenia'', and child psychiatry's focus on maternal deprivation led to misconceptions of autism as an infant's response to " refrigerator mothers". Starting in the late 1960s, autism was established as a ''separate'' syndrome from schizophrenia. Leo Kanner was the first person to describe autism as a neurodevelopmental disorder in 1943 by calling it ''infantile autism'' and therefore ''rejected'' the refrigerator mother theory.
The discussion of autism prior to the twentieth century brought about much controversy. Without researchers being able to meet a consensus on the varying forms of condition, there was a lack of research being conducted on the disorder. Discussing the syndrome and its complexity frustrated researchers at the time. Controversies have surrounded various claims regarding the etiology of autism. In the 1950s, the refrigerator mother theory emerged as an explanation for autism despite no scientific evidence behind it. The hypothesis was based on the idea that autistic behaviors stem from the emotional "frigidity," lack of warmth, and cold, distant, rejecting demeanor of a child's mother. Parents of children with an ASD experienced blame, guilt and self-doubt, especially as the theory was embraced by the medical establishment and went largely unchallenged into the mid-1960s. The "refrigerator mother" theory has since been refuted in the scientific literature, including a 2015 systematic review which showed absolutely no association between caregiver interaction and language outcomes in ASD patients. Another controversial claim suggested that watching ''extensive'' amounts of television may cause autism. This hypothesis was largely based on research suggesting that the increasing rates of autism in the 1970s and 1980s were linked to the growth of cable television at the time.
Autism spectrum disorder, as it is known today, can be traced back to the late 1930s, when two separate psychiatrists – Leo Kanner of Johns Hopkins Hospital and Hans Asperger of the Vienna University Hospital – used the word ''autism'' to describe the patients they were studying in their own clinical research and practice. The word ''autism'' first took its modern sense in German, when Asperger adopted Bleuler's terminology ''autistic psychopaths'' in a 1938 lecture in German about child psychology. Asperger was investigating an ASD which was later known as Asperger syndrome, although it did not become widely recognized as a separate diagnosis until 1981; it has since been eliminated from the lexicon. In English, Kanner first used ''autism'' in its modern sense when he introduced the label ''early infantile autism'' in a 1943 report of 11 children with striking behavioral similarities; his publication was named ''Autistic Disturbances of Affective Contact''. Reprinted in Almost all the characteristics described in Kanner's first paper on the subject, notably "autistic aloneness" and "insistence on sameness", are still regarded as typical of autistic spectrum disorder. It is not known whether Kanner derived the term independently of Hans Asperger.
Kanner's reuse of ''autism'' led to decades of confused terminology like ''infantile schizophrenia'', and child psychiatry's focus on maternal deprivation led to misconceptions of autism as an infant's response to " refrigerator mothers". Starting in the late 1960s, autism was established as a ''separate'' syndrome from schizophrenia. Leo Kanner was the first person to describe autism as a neurodevelopmental disorder in 1943 by calling it ''infantile autism'' and therefore ''rejected'' the refrigerator mother theory.
The discussion of autism prior to the twentieth century brought about much controversy. Without researchers being able to meet a consensus on the varying forms of condition, there was a lack of research being conducted on the disorder. Discussing the syndrome and its complexity frustrated researchers at the time. Controversies have surrounded various claims regarding the etiology of autism. In the 1950s, the refrigerator mother theory emerged as an explanation for autism despite no scientific evidence behind it. The hypothesis was based on the idea that autistic behaviors stem from the emotional "frigidity," lack of warmth, and cold, distant, rejecting demeanor of a child's mother. Parents of children with an ASD experienced blame, guilt and self-doubt, especially as the theory was embraced by the medical establishment and went largely unchallenged into the mid-1960s. The "refrigerator mother" theory has since been refuted in the scientific literature, including a 2015 systematic review which showed absolutely no association between caregiver interaction and language outcomes in ASD patients. Another controversial claim suggested that watching ''extensive'' amounts of television may cause autism. This hypothesis was largely based on research suggesting that the increasing rates of autism in the 1970s and 1980s were linked to the growth of cable television at the time.