|
Modified Checklist For Autism In Toddlers
The Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (M-CHAT) is a psychological questionnaire that evaluates risk for autism spectrum disorder in children ages 16–30 months. The 20-question test is filled out by the parent, and a follow-up portion is available for children who are classified as medium- to high-risk for autism spectrum disorder. Children who score in the medium to high-risk zone may not necessarily meet criteria for a diagnosis. The checklist is designed so that primary care physicians can interpret it immediately and easily. The M-CHAT has shown fairly good reliability and validity in assessing child autism symptoms in recent studies. Question breakdown, scoring, and interpretation The first section of the M-CHAT identifies 20 behavioral characteristics of the autism spectrum and asks if the child has experienced any of them. If the parent reports a sufficient number of characteristics for the child in this section, a follow-up form outlining specific questions pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
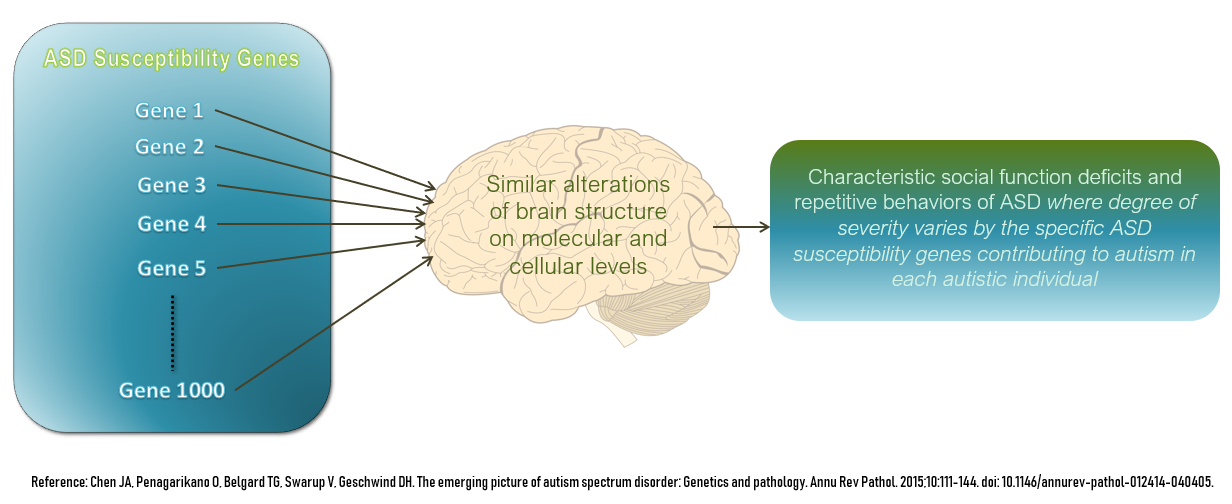
Autism Spectrum Disorder
The autism spectrum, often referred to as just autism or in the context of a professional diagnosis autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a neurodevelopmental disorder, neurodevelopmental condition (or conditions) characterized by difficulties in Social relation, social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication, and the presence of repetitive behavior and restricted interests. Other common signs include unusual responses to Multisensory integration, sensory stimuli. Autism is generally understood as a ''spectrum disorder'', which means that it can manifest differently in each person: any given autistic individual is likely to show some, but not all, of the characteristics associated with it, and the person may exhibit them to varying degrees. Some autistic people remain nonverbal autism, nonspeaking over the course of their lifespan, while others have relatively unimpaired spoken language. There is large variation in the level of support peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reliability (psychometrics)
In statistics and psychometrics, reliability is the overall consistency of a measure. A measure is said to have a high reliability if it produces similar results under consistent conditions:"It is the characteristic of a set of test scores that relates to the amount of random error from the measurement process that might be embedded in the scores. Scores that are highly reliable are precise, reproducible, and consistent from one testing occasion to another. That is, if the testing process were repeated with a group of test takers, essentially the same results would be obtained. Various kinds of reliability coefficients, with values ranging between 0.00 (much error) and 1.00 (no error), are usually used to indicate the amount of error in the scores." For example, measurements of people's height and weight are often extremely reliable.The Marketing Accountability Standards Board (MASB) endorses this definition as part of its ongoinCommon Language: Marketing Activities and Metrics Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Test Validity
Test validity is the extent to which a test (such as a chemical test, chemical, physical test, physical, or test (assessment), scholastic test) accuracy and precision, accurately measures what it is supposed to measure. In the fields of psychological testing and test (assessment), educational testing, "validity refers to the degree to which evidence and theory support the interpretations of test scores entailed by proposed uses of tests".American Educational Research Association, American Psychological Association, & National Council on Measurement in Education. (1999) ''Standards for educational and psychological testing''. Washington, DC: American Educational Research Association. Although classical models divided the concept into various "validities" (such as content validity, criterion validity, and construct validity),Guion, R. M. (1980). On trinitarian doctrines of validity. ''Professional Psychology, 11'', 385-398. the currently dominant view is that validity is a single unitar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autism Spectrum
The autism spectrum, often referred to as just autism or in the context of a professional diagnosis autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a neurodevelopmental condition (or conditions) characterized by difficulties in social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication, and the presence of repetitive behavior and restricted interests. Other common signs include unusual responses to sensory stimuli. Autism is generally understood as a ''spectrum disorder'', which means that it can manifest differently in each person: any given autistic individual is likely to show some, but not all, of the characteristics associated with it, and the person may exhibit them to varying degrees. Some autistic people remain nonspeaking over the course of their lifespan, while others have relatively unimpaired spoken language. There is large variation in the level of support people require, and the same person may present differently at varying times. Historically, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Validity (statistics)
Validity is the main extent to which a concept, conclusion or measurement is well-founded and likely corresponds accurately to the real world. The word "valid" is derived from the Latin validus, meaning strong. The validity of a measurement tool (for example, a test in education) is the degree to which the tool measures what it claims to measure. Validity is based on the strength of a collection of different types of evidence (e.g. face validity, construct validity, etc.) described in greater detail below. In psychometrics, validity has a particular application known as test validity: "the degree to which evidence and theory support the interpretations of test scores" ("as entailed by proposed uses of tests"). It is generally accepted that the concept of scientific validity addresses the nature of reality in terms of statistical measures and as such is an epistemological and philosophical issue as well as a question of measurement. The use of the term in logic is narrower, relati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reliability (statistics)
In statistics and psychometrics, reliability is the overall consistency of a measure. A measure is said to have a high reliability if it produces similar results under consistent conditions:"It is the characteristic of a set of test scores that relates to the amount of random error from the measurement process that might be embedded in the scores. Scores that are highly reliable are precise, reproducible, and consistent from one testing occasion to another. That is, if the testing process were repeated with a group of test takers, essentially the same results would be obtained. Various kinds of reliability coefficients, with values ranging between 0.00 (much error) and 1.00 (no error), are usually used to indicate the amount of error in the scores." For example, measurements of people's height and weight are often extremely reliable.The Marketing Accountability Standards Board (MASB) endorses this definition as part of its ongoinCommon Language: Marketing Activities and Metrics Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-report Inventories
A self-report inventory is a type of psychological test in which a person fills out a survey or questionnaire with or without the help of an investigator. Self-report inventories often ask direct questions about personal interests, values, symptoms, behaviors, and traits or personality types. Inventories are different from tests in that there is no objectively correct answer; responses are based on opinions and subjective perceptions. Most self-report inventories are brief and can be taken or administered within five to 15 minutes, although some, such as the Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI), can take several hours to fully complete. They are popular because they can be inexpensive to give and to score, and their scores can often show good reliability. There are three major approaches to developing self-report inventories: theory-guided, factor analysis, and criterion-keyed. Theory-guided inventories are constructed around a theory of personality or a prototyp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Checklist For Autism In Toddlers
The Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (CHAT) is a psychological questionnaire designed to evaluate risk for autism spectrum disorder in children ages 18–24 months. The 14-question test is filled out by the parent and a pediatrician or physician and takes approximately 5 minutes to complete. The CHAT has shown good reliability and validity in assessing child autism risk in recent studies. Some research has identified barriers, such as socioeconomic status and parent education level, to the validation of both the CHAT and the Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (M-CHAT) as a reliable and valid screener for children of all backgrounds. History and development The CHAT was initially developed in the early 1990s to screen for autism in children as young as 18 months. Prior to this point, diagnosis of autism was rare in children younger than 3 years old. Additionally, no specialized screening tool had been developed to detect early signs of autism in young children. This c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autism
The autism spectrum, often referred to as just autism or in the context of a professional diagnosis autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a neurodevelopmental condition (or conditions) characterized by difficulties in social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication, and the presence of repetitive behavior and restricted interests. Other common signs include unusual responses to sensory stimuli. Autism is generally understood as a ''spectrum disorder'', which means that it can manifest differently in each person: any given autistic individual is likely to show some, but not all, of the characteristics associated with it, and the person may exhibit them to varying degrees. Some autistic people remain nonspeaking over the course of their lifespan, while others have relatively unimpaired spoken language. There is large variation in the level of support people require, and the same person may present differently at varying times. Historically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pervasive Developmental Disorders
The diagnostic category pervasive developmental disorders (PDD), as opposed to specific developmental disorders (SDD), is a group of disorders characterized by delays in the development of multiple basic functions including socialization and communication. The pervasive developmental disorders include autism, Asperger syndrome, pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified (PDD-NOS, i.e., all autism spectrum disorders SD, childhood disintegrative disorder (CDD), overactive disorder associated with mental retardation and stereotyped movements, and Rett syndrome. The first four of these disorders are commonly called the autism spectrum disorders; the last disorder is much rarer, and is sometimes placed in the autism spectrum and sometimes not. The terminology PDD and ASD is often used interchangeably and varies depending on location. The two have overlapping definitions but are defined differently by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th edit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autism Screening And Assessment Tools
The autism spectrum, often referred to as just autism or in the context of a professional diagnosis autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a neurodevelopmental disorder, neurodevelopmental condition (or conditions) characterized by difficulties in Social relation, social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication, and the presence of repetitive behavior and restricted interests. Other common signs include unusual responses to Multisensory integration, sensory stimuli. Autism is generally understood as a ''spectrum disorder'', which means that it can manifest differently in each person: any given autistic individual is likely to show some, but not all, of the characteristics associated with it, and the person may exhibit them to varying degrees. Some autistic people remain nonverbal autism, nonspeaking over the course of their lifespan, while others have relatively unimpaired spoken language. There is large variation in the level of support peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |