Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
is a
neurodevelopmental disorder
Neurodevelopmental disorders are a group of mental conditions negatively affecting the development of the nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord. According to the American Psychiatric Association Diagnostic and Statistical Manu ...
characterised by symptoms of
inattention
Attention or focus, is the concentration of awareness on some phenomenon to the exclusion of other stimuli. It is the selective concentration on discrete information, either subjectively or objectively. William James (1890) wrote that "Attent ...
, hyperactivity,
impulsivity
In psychology, impulsivity (or impulsiveness) is a tendency to act on a whim, displaying behavior characterized by little or no forethought, reflection, or consideration of the consequences. Impulsive actions are typically "poorly conceived, pre ...
, and
emotional dysregulation
Emotional dysregulation is characterized by an inability to flexibly respond to and manage emotional states, resulting in intense and prolonged emotional reactions that deviate from social norms, given the nature of the environmental stimuli enc ...
that are excessive and pervasive, impairing in multiple contexts, and
developmentally inappropriate. ADHD symptoms arise from
executive dysfunction
In psychology and neuroscience, executive dysfunction, or executive function deficit, is a disruption to the efficacy of the executive functions, which is a group of cognitive processes that regulate, control, and manage other cognitive processe ...
.
Impairments resulting from deficits in self-regulation such as
time management
Time management is the process of planning and exercising conscious control of time spent on specific activities—especially to increase effectiveness, efficiency and productivity.
Time management involves demands relating to work, social ...
,
inhibition, task initiation, and sustained attention can include poor professional performance, relationship difficulties, and numerous health risks,
collectively predisposing to a diminished
quality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
and a reduction in life expectancy.
As a consequence, the disorder costs society hundreds of billions of US dollars each year, worldwide. It is associated with other
mental disorder
A mental disorder, also referred to as a mental illness, a mental health condition, or a psychiatric disability, is a behavioral or mental pattern that causes significant distress or impairment of personal functioning. A mental disorder is ...
s as well as non-psychiatric disorders, which can cause additional impairment.
While ADHD involves a lack of sustained attention to tasks,
inhibitory deficits also can lead to difficulty interrupting an already ongoing response pattern, manifesting in the perseveration of actions despite a change in context whereby the individual intends the termination of those actions. This symptom is known colloquially as
hyperfocus
Hyperfocus is an intense form of mind, mental attention, concentration or creative visualization, visualization that focuses consciousness on a subject, topic, or task. In some individuals, various subjects or topics may also include daydreams, c ...
and is related to risks such as
addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to use a drug or engage in a behavior that produces natural reward, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use can ...
and types of offending behaviour.
ADHD can be difficult to tell apart from other conditions.
ADHD represents the extreme lower end of the continuous dimensional trait (bell curve) of executive functioning and self-regulation, which is supported by twin, brain imaging and molecular genetic studies.
The precise causes of ADHD are unknown in most individual cases.
[ Meta-analyses have shown that the disorder is primarily genetic with a heritability rate of 70–80%,]traumatic brain injury
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity ranging from mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI/concussion) to severe traumati ...
,
Signs and symptoms
Inattention, hyperactivity (restlessness in adults), disruptive behaviour, and impulsivity are common in ADHD.DSM-5-TR
The ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition'' (DSM-5), is the 2013 update to the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'', the taxonomy (general), taxonomic and diagnostic tool published by the ...
), symptoms must be present for six months or more to a degree that is much greater than others of the same age.[ This requires at least six symptoms of either inattention or hyperactivity/impulsivity for those under 17 and at least five symptoms for those 17 years or older.][ The symptoms must be present in at least two settings (e.g., social, school, work, or home), and must directly interfere with or reduce quality of functioning.][ Additionally, several symptoms must have been present before age 12 as per DSM-5 criteria.][ However, research indicates the age of onset should not be interpreted as a prerequisite for diagnosis given contextual exceptions.]
Presentations
ADHD is divided into three primary presentations:
Characteristics in childhood
Difficulties managing anger are more common in children with ADHD, as are delays in speech, language and motor development.handwriting
Handwriting in Italian schools (XXth - XXIst century)
Handwriting is the personal and unique style of writing with a writing instrument, such as a pen or pencil in the hand. Handwriting includes both block and cursive styles and is separa ...
is more common in children with ADHD.dyslexia
Dyslexia (), previously known as word blindness, is a learning disability that affects either reading or writing. Different people are affected to different degrees. Problems may include difficulties in spelling words, reading quickly, wri ...
or dysgraphia
Dysgraphia is a neurological disorder and learning disability that concerns impairments in written expression, which affects the ability to write, primarily handwriting, but also coherence. It is a specific learning disability (SLD) as well as a ...
. There is significant overlap in the symptomatologies of ADHD, dyslexia, and dysgraphia,
Emotional dysregulation
Although not listed as an official symptom, emotional dysregulation
Emotional dysregulation is characterized by an inability to flexibly respond to and manage emotional states, resulting in intense and prolonged emotional reactions that deviate from social norms, given the nature of the environmental stimuli enc ...
or mood lability is generally understood to be a common symptom of ADHD.
Relationship difficulties
People with ADHD of all ages are more likely to have problems with social skills
A social skill is any competence facilitating interaction and communication with others where social rules and relations are created, communicated, and changed in verbal and nonverbal ways. The process of learning these skills is called socia ...
, such as social interaction and forming and maintaining friendships. This is true for all presentations. About half of children and adolescents with ADHD experience social rejection
Social rejection occurs when an individual is deliberately excluded from a social relationship or social interaction. The topic includes ''interpersonal rejection'' (or peer rejection), ''romantic rejection'', and ''familial estrangement''. A pe ...
by their peers compared to 10–15% of non-ADHD children and adolescents. People with attention deficits are prone to having difficulty processing verbal and nonverbal language which can negatively affect social interaction. They may also drift off during conversations, miss social cues, and have trouble learning social skills.
Hyperfocus
An association between ADHD and hyperfocus, a state characterised by intense and narrow concentration on a specific stimulus, object or task for a prolonged period of time,
IQ test performance
Certain studies have found that people with ADHD tend to have lower scores on intelligence quotient
An intelligence quotient (IQ) is a total score derived from a set of standardized tests or subtests designed to assess human intelligence. Originally, IQ was a score obtained by dividing a person's mental age score, obtained by administering ...
(IQ) tests.
Causes
ADHD arises from brain maldevelopment especially in the prefrontal executive networks that can arise either from genetic factors (different gene variants and mutations for building and regulating such networks) or from acquired disruptions to the development of these networks and regions involved in executive functioning and self-regulation.
Genetics
Literature review
A literature review is an overview of previously published works on a particular topic. The term can refer to a full scholarly paper or a section of a scholarly work such as books or articles. Either way, a literature review provides the rese ...
s published in ''Biological Psychiatry
Biological psychiatry or biopsychiatry is an approach to psychiatry that aims to understand mental disorder in terms of the biology, biological function of the nervous system. It is interdisciplinary in its approach and draws on sciences such as ...
'' and in '' Molecular Psychiatry'' have found the average heritability
Heritability is a statistic used in the fields of Animal husbandry, breeding and genetics that estimates the degree of ''variation'' in a phenotypic trait in a population that is due to genetic variation between individuals in that population. T ...
estimate of ADHD to be from 0.74 to 0.8, based on family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
, twin studies
Twin studies are studies conducted on Identical twin, identical or Fraternal twin, fraternal twins. They aim to reveal the importance of environmental and genetics, genetic influences for traits, phenotypes, and disorders. Twin research is consid ...
, and adoption studies.Simon Baron-Cohen
Sir Simon Philip Baron-Cohen (born 15 August 1958) is a British clinical psychologist and professor of developmental psychopathology at the University of Cambridge. He is the director of the university's Autism Research Centre and a Fellow of ...
's suggestion for the sex ratio in the epidemiology of autism as an analogue.Natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the Heredity, heritable traits characteristic of a population over generation ...
has been acting against the genetic variants for ADHD over the course of at least 45,000 years, indicating that it was not an adaptive trait in ancient times. The disorder may remain at a stable rate by the balance of genetic mutations and removal rate (natural selection) across generations; over thousands of years, these genetic variants become more stable, decreasing disorder prevalence. Throughout human evolution, the executive functions involved in ADHD likely provide the capacity to bind contingencies across time thereby directing behaviour toward future over immediate events so as to maximise future social consequences for humans.
ADHD has a high heritability
Heritability is a statistic used in the fields of Animal husbandry, breeding and genetics that estimates the degree of ''variation'' in a phenotypic trait in a population that is due to genetic variation between individuals in that population. T ...
of 74%, meaning that 74% of the presence of ADHD in the population is due to genetic factors. There are multiple gene variants which each slightly increase the likelihood of a person having ADHD; it is polygenic
A polygene is a member of a group of non- epistatic genes that interact additively to influence a phenotypic trait, thus contributing to multiple-gene inheritance (polygenic inheritance, multigenic inheritance, quantitative inheritance), a type ...
and thus arises through the accumulation of many genetic risks each having a very small effect.MAOA
Monoamine oxidase A, also known as MAO-A, is an enzyme (Enzyme classification, E.C. 1.4.3.4) that in humans is encoded by the ''MAOA'' gene. This gene is one of two neighboring gene family members that encode mitochondrial enzymes which catalyze ...
, COMT, and DBH.BDNF
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), or abrineurin, is a protein found in the and the periphery. that, in humans, is encoded by the ''BDNF'' gene. BDNF is a member of the neurotrophin family of growth factors, which are related to the cano ...
.dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. It is an amine synthesized ...
and is associated with ADHD. The DRD4 receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily related ...
that inhibits adenylyl cyclase
Adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1, also commonly known as adenyl cyclase and adenylyl cyclase, abbreviated AC) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP diphosphate-lyase (cyclizing; 3′,5′-cyclic-AMP-forming). It catalyzes the following reaction:
:A ...
. The DRD4–7R mutation results in a wide range of behavioural phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (physical form and structure), its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological propert ...
s, including ADHD symptoms reflecting split attention. The DRD4 gene is both linked to novelty seeking and ADHD. The genes GFOD1 and CDH13 show strong genetic associations with ADHD. CDH13's association with Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism, also known as autism spectrum disorder (ASD), is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by differences or difficulties in social communication and interaction, a preference for predictability and routine, sensory processing di ...
(ASD), schizophrenia
Schizophrenia () is a mental disorder characterized variously by hallucinations (typically, Auditory hallucination#Schizophrenia, hearing voices), delusions, thought disorder, disorganized thinking and behavior, and Reduced affect display, f ...
, bipolar disorder, and depression make it an interesting candidate causative gene.zebrafish
The zebrafish (''Danio rerio'') is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the family Danionidae of the order Cypriniformes. Native to South Asia, it is a popular aquarium fish, frequently sold under the trade name zebra danio (an ...
, knockout of this gene causes a loss of dopaminergic function in the ventral diencephalon
In the human brain, the diencephalon (or interbrain) is a division of the forebrain (embryonic ''prosencephalon''). It is situated between the telencephalon and the midbrain (embryonic ''mesencephalon''). The diencephalon has also been known as t ...
and the fish display a hyperactive/impulsive phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (physical form and structure), its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological propert ...
.genetic variation
Genetic variation is the difference in DNA among individuals or the differences between populations among the same species. The multiple sources of genetic variation include mutation and genetic recombination. Mutations are the ultimate sources ...
to be used as a tool for diagnosis, more validating studies need to be performed. However, smaller studies have shown that genetic polymorphism
A gene is said to be polymorphic if more than one allele occupies that gene's locus within a population. In addition to having more than one allele at a specific locus, each allele must also occur in the population at a rate of at least 1% to ge ...
s in genes related to catecholaminergic neurotransmission or the SNARE
SNARE proteins – "Soluble NSF attachment protein, SNAP REceptors" – are a large protein family consisting of at least 24 members in yeasts and more than 60 members in mammalian and plant cells.
The primary role of SNARE proteins is to m ...
complex of the synapse
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that allows a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or a target effector cell. Synapses can be classified as either chemical or electrical, depending o ...
can reliably predict a person's response to stimulant medication.
Environment
In addition to genetics, some environmental factors might play a role in causing ADHD.fetal alcohol spectrum disorder
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASDs) are a group of conditions that can occur in a person who is exposed to alcohol during gestation. FASD affects 1 in 20 Americans, but is highly misdiagnosed and underdiagnosed.
The several forms of the ...
s which can include ADHD-like symptoms.lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
or polychlorinated biphenyls
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are organochlorine compounds with the formula C12 H10−''x'' Cl''x''; they were once widely used in the manufacture of carbonless copy paper, as heat transfer fluids, and as dielectric and coolant fluids f ...
, may develop problems which resemble ADHD.organophosphate
In organic chemistry, organophosphates (also known as phosphate esters, or OPEs) are a class of organophosphorus compounds with the general structure , a central phosphate molecule with alkyl or aromatic substituents. They can be considered ...
insecticide
Insecticides are pesticides used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. The major use of insecticides is in agriculture, but they are also used in home and garden settings, i ...
s chlorpyrifos and dialkyl phosphate is associated with an increased risk; however, the evidence is not conclusive.Nicotine
Nicotine is a natural product, naturally produced alkaloid in the nightshade family of plants (most predominantly in tobacco and ''Duboisia hopwoodii'') and is widely used recreational drug use, recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As ...
exposure during pregnancy may be an environmental risk.
Extreme premature birth
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is betwee ...
, very low birth weight, and extreme neglect, abuse, or social deprivation also increase the riskmeasles
Measles (probably from Middle Dutch or Middle High German ''masel(e)'', meaning "blemish, blood blister") is a highly contagious, Vaccine-preventable diseases, vaccine-preventable infectious disease caused by Measles morbillivirus, measles v ...
, varicella zoster encephalitis
Encephalitis is inflammation of the Human brain, brain. The severity can be variable with symptoms including reduction or alteration in consciousness, aphasia, headache, fever, confusion, a stiff neck, and vomiting. Complications may include se ...
, rubella
Rubella, also known as German measles or three-day measles, is an infection caused by the rubella virus. This disease is often mild, with half of people not realizing that they are infected. A rash may start around two weeks after exposure and ...
, enterovirus 71).traumatic brain injury
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity ranging from mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI/concussion) to severe traumati ...
later develop ADHDEuropean Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
has put in place regulatory measures based on these concerns.allergies
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include Allergic rhinitis, hay fever, Food allergy, food al ...
to certain foods may worsen ADHD symptoms.
Pathophysiology
Current models of ADHD suggest that it is associated with functional impairments in some of the brain's neurotransmitter systems, particularly those involving dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. It is an amine synthesized ...
and norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic compound, organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and human body, body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The ...
.ventral tegmental area
The ventral tegmental area (VTA) (tegmentum is Latin for ''covering''), also known as the ventral tegmental area of Tsai, or simply ventral tegmentum, is a group of neurons located close to the midline on the floor of the midbrain. The VTA is th ...
and locus coeruleus project to diverse regions of the brain and govern a variety of cognitive processes.dopamine pathway
Dopaminergic pathways (dopamine pathways, dopaminergic projections) in the human brain are involved in both physiological and behavioral processes including motion, movement, cognition, executive functions, Reward system, reward, motivation, and N ...
s and norepinephrine pathways which project to the prefrontal cortex
In mammalian brain anatomy, the prefrontal cortex (PFC) covers the front part of the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex. It is the association cortex in the frontal lobe. The PFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA11, BA12, ...
and striatum
The striatum (: striata) or corpus striatum is a cluster of interconnected nuclei that make up the largest structure of the subcortical basal ganglia. The striatum is a critical component of the motor and reward systems; receives glutamat ...
are directly responsible for modulating executive function
In cognitive science and neuropsychology, executive functions (collectively referred to as executive function and cognitive control) are a set of cognitive processes that support goal-directed behavior, by regulating thoughts and actions thro ...
(cognitive control of behaviour), motivation, reward perception, and motor function;pathophysiology
Pathophysiology (or physiopathology) is a branch of study, at the intersection of pathology and physiology, concerning disordered physiological processes that cause, result from, or are otherwise associated with a disease or injury. Pathology is ...
of ADHD.
Brain structure
 In children with ADHD, there is a general reduction of volume in certain brain structures, with a proportionally greater decrease in the volume in the left-sided prefrontal cortex.
In children with ADHD, there is a general reduction of volume in certain brain structures, with a proportionally greater decrease in the volume in the left-sided prefrontal cortex.amygdala
The amygdala (; : amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek language, Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is a paired nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclear complex present in the Cerebral hemisphere, cerebral hemispheres of vertebrates. It is c ...
, caudate, hippocampus
The hippocampus (: hippocampi; via Latin from Ancient Greek, Greek , 'seahorse'), also hippocampus proper, is a major component of the brain of humans and many other vertebrates. In the human brain the hippocampus, the dentate gyrus, and the ...
, and putamen
The putamen (; from Latin, meaning "nutshell") is a subcortical nucleus (neuroanatomy), nucleus with a rounded structure, in the basal ganglia nuclear group. It is located at the base of the forebrain and above the midbrain.
The putamen and c ...
appears smaller in individuals with ADHD compared with controls. Structural MRI studies have also revealed differences in white matter, with marked differences in inter-hemispheric asymmetry between ADHD and typically developing youths.
Functional MRI (fMRI) studies have revealed a number of differences between ADHD and control brains. Mirroring what is known from structural findings, fMRI studies have shown evidence for a higher connectivity between subcortical and cortical regions, such as between the caudate and prefrontal cortex. The degree of hyperconnectivity between these regions correlated with the severity of inattention or hyperactivity
Neurotransmitter pathways
Previously, it had been suggested that the elevated number of dopamine transporter
The dopamine transporter (DAT, also sodium-dependent dopamine transporter) is a membrane-spanning protein coded for in humans by the ''SLC6A3'' gene (also known as ''DAT1''), that pumps the neurotransmitter dopamine out of the synaptic cleft ba ...
s in people with ADHD was part of the pathophysiology, but it appears the elevated numbers may be due to adaptation following exposure to stimulant medication.glutamatergic
Glutamatergic means "related to glutamate". A glutamatergic agent (or drug) is a chemical that directly modulates the excitatory amino acid (glutamate/aspartate) system in the body or brain. Examples include excitatory amino acid receptor agonist ...
, or cholinergic pathways.
Executive function and motivation
ADHD arises from a core deficit in executive functions (e.g., attentional control
Attentional control, commonly referred to as concentration, refers to an individual's capacity to choose what they pay attention to and what they ignore. It is also known as endogeny, endogenous attention or executive functions, executive attenti ...
, inhibitory control
Inhibitory control, also known as response inhibition, is a cognitive process – and, more specifically, an executive function – that permits an individual to inhibit their impulses and natural, habitual, or dominant behavioral re ...
, and working memory
Working memory is a cognitive system with a limited capacity that can Memory, hold information temporarily. It is important for reasoning and the guidance of decision-making and behavior. Working memory is often used synonymously with short-term m ...
), which are a set of cognitive processes that are required to successfully select and monitor behaviours that facilitate the attainment of one's chosen goals.procrastination
Procrastination is the act of unnecessarily delaying or postponing something despite knowing that there could be negative consequences for doing so. It is a common human experience involving delays in everyday chores or even putting off tasks such ...
control, maintaining concentration, paying attention, ignoring distractions, regulating emotions, and remembering details.
Paradoxical reaction to neuroactive substances
Another sign of the structurally altered signal processing in the central nervous system in this group of people is the conspicuously common paradoxical reaction ( of patients). These are unexpected reactions in the opposite direction as with a normal effect, or otherwise significant different reactions. These are reactions to neuroactive substances such as local anesthetic
A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of all sensation (including pain) in a specific body part without loss of consciousness, providing local anesthesia, as opposed to a general anesthetic, which eliminates all sensati ...
at the dentist, sedative
A sedative or tranquilliser is a substance that induces sedation by reducing irritability or Psychomotor agitation, excitement. They are central nervous system (CNS) Depressant, depressants and interact with brain activity, causing its decelera ...
, caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine chemical classification, class and is the most commonly consumed Psychoactive drug, psychoactive substance globally. It is mainly used for its eugeroic (wakefulness pr ...
, antihistamine
Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic (not patented) drug that can be bought without a prescription and provides ...
, weak neuroleptics and central and peripheral painkillers. Since the causes of ''paradoxical reactions'' are at least partly genetic, it may be useful in critical situations, for example before operations, to ask whether such abnormalities may also exist in family members.
Diagnosis
ADHD is diagnosed by an assessment of a person's behavioural and mental development, including ruling out the effects of drugs, medications, and other medical or psychiatric problems as explanations for the symptoms.Vanderbilt ADHD diagnostic rating scale
The Vanderbilt ADHD Diagnostic Rating Scale (VADRS) is a psychological assessment tool for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms and their effects on behavior and academic performance in children ages 6–12. This measure was ...
.Vanderbilt ADHD diagnostic rating scale
The Vanderbilt ADHD Diagnostic Rating Scale (VADRS) is a psychological assessment tool for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms and their effects on behavior and academic performance in children ages 6–12. This measure was ...
, are used in the screening and evaluation of ADHD.biomarker
In biomedical contexts, a biomarker, or biological marker, is a measurable indicator of some biological state or condition. Biomarkers are often measured and evaluated using blood, urine, or soft tissues to examine normal biological processes, ...
s such as blood or urine samples, electroencephalogram
Electroencephalography (EEG)
is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The bio signals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neoc ...
(EEG) markers, and neuroimaging
Neuroimaging is the use of quantitative (computational) techniques to study the neuroanatomy, structure and function of the central nervous system, developed as an objective way of scientifically studying the healthy human brain in a non-invasive ...
such as MRIs, in diagnosis for ADHD remains unclear; studies showed great variability, did not assess test-retest reliability, and were not independently replicable.neurodevelopmental disorder
Neurodevelopmental disorders are a group of mental conditions negatively affecting the development of the nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord. According to the American Psychiatric Association Diagnostic and Statistical Manu ...
antisocial personality disorder
Antisocial personality disorder (ASPD) is a personality disorder defined by a chronic pattern of behavior that disregards the rights and well-being of others. People with ASPD often exhibit behavior that conflicts with social norms, leading to ...
.neurological disorder
Neurological disorders represent a complex array of medical conditions that fundamentally disrupt the functioning of the nervous system. These disorders affect the brain, spinal cord, and nerve networks, presenting unique diagnosis, treatment, and ...
.
Classification
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual
As with many other psychiatric disorders, a formal diagnosis should be made by a qualified professional based on a set number of criteria. In the United States, these criteria are defined by the American Psychiatric Association
The American Psychiatric Association (APA) is the main professional organization of psychiatrists and trainee psychiatrists in the United States, and the largest psychiatric organization in the world. It has more than 39,200 members who are in ...
in the DSM. Based on the DSM-5 criteria published in 2013 and the DSM-5-TR criteria published in 2022, there are three presentations of ADHD:
# ADHD, predominantly inattentive presentation, presents with symptoms including being easily distracted, forgetful, daydreaming, disorganisation, poor sustained attention, and difficulty completing tasks.
# ADHD, predominantly hyperactive-impulsive presentation, presents with excessive fidgeting and restlessness, hyperactivity, and difficulty waiting and remaining seated.
# ADHD, combined presentation, is a combination of the first two presentations.
This subdivision is based on presence of at least six (in children) or five (in older teenagers and adults) out of nine long-term (lasting at least six months) symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity–impulsivity, or both.
International Classification of Diseases
In the eleventh revision of the (ICD-11
The ICD-11 is the eleventh revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD). It replaces the ICD-10 as the global standard for recording health information and causes of death. The ICD is developed and annually updated by the World H ...
) by the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
, the disorder is classified as Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (code 6A05). The defined subtypes are ''predominantly inattentive presentation'' (6A05.0); ''predominantly hyperactive-impulsive presentation'' (6A05.1); and ''combined presentation'' (6A05.2). However, the ICD-11 includes two residual categories for individuals who do not entirely match any of the defined subtypes: ''other specified presentation'' (6A05.Y) where the clinician includes detail on the individual's presentation; and ''presentation unspecified'' (6A05.Z) where the clinician does not provide detail.ICD-10
ICD-10 is the 10th revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), a medical classification list by the World Health Organization (WHO). It contains codes for diseases, signs and symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social cir ...
), the symptoms of ''hyperkinetic disorder'' were analogous to ADHD in the ICD-11. When a conduct disorder (as defined by ICD-10)
Social construct theory
The social construct theory of ADHD suggests that, because the boundaries between normal and abnormal behaviour are socially constructed (i.e. jointly created and validated by all members of society, and in particular by physician
A physician, medical practitioner (British English), medical doctor, or simply doctor is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through the Medical education, study, Med ...
s, parents, teachers, and others), it then follows that subjective valuations and judgements determine which diagnostic criteria are used and thus, the number of people affected. Thomas Szasz
Thomas Stephen Szasz ( ; ; 15 April 1920 – 8 September 2012) was a Hungarian-American academic and psychiatrist. He served for most of his career as professor of psychiatry at the State University of New York Upstate Medical University. A dis ...
, a supporter of this theory, has argued that ADHD was "invented and then given a name".
Adults
Adults with ADHD are diagnosed under the same criteria, including that their signs must have been present by the age of six to twelve. The individual is the best source for information in diagnosis, however others may provide useful information about the individual's symptoms currently and in childhood; a family history of ADHD also adds weight to a diagnosis.alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
as a coping mechanism.gambling
Gambling (also known as betting or gaming) is the wagering of something of Value (economics), value ("the stakes") on a Event (probability theory), random event with the intent of winning something else of value, where instances of strategy (ga ...
are common.
Differential diagnosis
The DSM provides differential diagnoses – potential alternate explanations for specific symptoms. Assessment and investigation of clinical history determines which is the most appropriate diagnosis. The DSM-5 suggests oppositional defiant disorder
Oppositional defiant disorder (ODD) is listed in the DSM-5 under ''Disruptive, impulse-control, and conduct disorders'' and defined as "a pattern of angry/irritable mood, argumentative/defiant behavior, or vindictiveness." This behavior is usu ...
, intermittent explosive disorder, and other disorders such as stereotypic movement disorder and Tourette syndrome
Tourette syndrome (TS), or simply Tourette's, is a common neurodevelopmental disorder that begins in childhood or adolescence. It is characterized by multiple movement (motor) tics and at least one vocal (phonic) tic. Common tics are blinkin ...
, in addition to specific learning disorder, intellectual disability
Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability (in the United Kingdom), and formerly mental retardation (in the United States), Rosa's Law, Pub. L. 111-256124 Stat. 2643(2010).Archive is a generalized neurodevelopmental ...
, autism
Autism, also known as autism spectrum disorder (ASD), is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by differences or difficulties in social communication and interaction, a preference for predictability and routine, sensory processing d ...
, reactive attachment disorder, anxiety disorder
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental disorders characterized by significant and uncontrollable feelings of anxiety and fear such that a person's social, occupational, and personal functions are significantly impaired. Anxiety may cause phys ...
s, depressive disorders, bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder (BD), previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that each last from days to weeks, and in ...
, disruptive mood dysregulation disorder, substance use disorder
Substance use disorder (SUD) is the persistent use of drugs despite substantial harm and adverse consequences to self and others. Related terms include ''substance use problems'' and ''problematic drug or alcohol use''. Along with substance-ind ...
, personality disorder
Personality disorders (PD) are a class of mental health conditions characterized by enduring maladaptive patterns of behavior, cognition, and inner experience, exhibited across many contexts and deviating from those accepted by the culture. ...
s, psychotic disorders
In psychopathology, psychosis is a condition in which a person is unable to distinguish, in their experience of life, between what is and is not real. Examples of psychotic symptoms are delusions, hallucinations, and disorganized or incoh ...
, medication-induced symptoms, and neurocognitive disorders. Many but not all of these are also common comorbidities of ADHD.post-traumatic stress disorder
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental disorder that develops from experiencing a Psychological trauma, traumatic event, such as sexual assault, domestic violence, child abuse, warfare and its associated traumas, natural disaster ...
.irritability
Irritability is the excitatory ability that living organisms have to respond to changes in their environment. The term is used for both the physiological reaction to stimuli and for the pathological, abnormal or excessive sensitivity to stimul ...
in addition to low-mood and self-esteem as a result of symptom expression might be confusable with dysthymia
Dysthymia ( ), known as persistent depressive disorder (PDD) in the DSM-5-TR and dysthymic disorder in ICD-11, is a psychiatric condition marked by symptoms that are similar to those of major depressive disorder, but which persist for at leas ...
and bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder (BD), previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that each last from days to weeks, and in ...
as well as with borderline personality disorder
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is a personality disorder characterized by a pervasive, long-term pattern of significant interpersonal relationship instability, an acute fear of Abandonment (emotional), abandonment, and intense emotiona ...
, however they are comorbid at a significantly increased rate relative to the general population.Obstructive sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common sleep-related breathing disorder and is characterized by recurrent episodes of complete or partial airway obstruction, obstruction of the respiratory tract#Upper respiratory tract, upper airway lea ...
can also cause ADHD-like symptoms.learning disabilities
Learning disability, learning disorder, or learning difficulty (British English) is a condition in the brain that causes difficulties comprehending or processing information and can be caused by several different factors. Given the "difficulty ...
may feel distractable and agitated when asked to engage in tasks that require the impaired skill (e.g., reading, math), but not in other situations. A person with an intellectual disability
Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability (in the United Kingdom), and formerly mental retardation (in the United States), Rosa's Law, Pub. L. 111-256124 Stat. 2643(2010).Archive is a generalized neurodevelopmental ...
may develop symptoms that overlap with ADHD when placed in a school environment that is inappropriate for their needs. The type of inattention implicated in ADHD, of poor persistence and sustained attention, differs substantially from selective or oriented inattention seen in cognitive disengagement syndrome (CDS), as well as from rumination, reexperiencing or mind blanking seen in anxiety disorders or PTSD.
In mood disorders, ADHD-like symptoms may be limited to manic or depressive states of an episodic nature. Symptoms overlapping with ADHD in psychotic disorders
In psychopathology, psychosis is a condition in which a person is unable to distinguish, in their experience of life, between what is and is not real. Examples of psychotic symptoms are delusions, hallucinations, and disorganized or incoh ...
may be limited to psychotic states. Substance use disorder
Substance use disorder (SUD) is the persistent use of drugs despite substantial harm and adverse consequences to self and others. Related terms include ''substance use problems'' and ''problematic drug or alcohol use''. Along with substance-ind ...
, some medications, and certain medical conditions may cause symptoms to appear later in life, while ADHD, as a neurodevelopmental disorder
Neurodevelopmental disorders are a group of mental conditions negatively affecting the development of the nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord. According to the American Psychiatric Association Diagnostic and Statistical Manu ...
, requires for them to have been present since childhood.
Furthermore, a careful understanding of the nature of the symptoms may help establish the difference between ADHD and other disorders.personality disorder
Personality disorders (PD) are a class of mental health conditions characterized by enduring maladaptive patterns of behavior, cognition, and inner experience, exhibited across many contexts and deviating from those accepted by the culture. ...
s, but not necessarily such features as a fear of abandonment, an unstable sense of self, narcissistic tendencies, aggressiveness, or other personality features.
Comorbidities
Psychiatric comorbidities
In children, ADHD occurs with other disorders about two-thirds of the time.Autism spectrum disorder
Autism, also known as autism spectrum disorder (ASD), is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by differences or difficulties in social communication and interaction, a preference for predictability and routine, sensory processing di ...
(ASD), co-occurring at a rate of 21% in those with ADHD, affects social skills, ability to communicate, behaviour, and interests.Learning disabilities
Learning disability, learning disorder, or learning difficulty (British English) is a condition in the brain that causes difficulties comprehending or processing information and can be caused by several different factors. Given the "difficulty ...
have been found to occur in about 20–30% of children with ADHD. Learning disabilities can include developmental speech and language disorders, and academic skills disorders.Tourette syndrome
Tourette syndrome (TS), or simply Tourette's, is a common neurodevelopmental disorder that begins in childhood or adolescence. It is characterized by multiple movement (motor) tics and at least one vocal (phonic) tic. Common tics are blinkin ...
Oppositional defiant disorder
Oppositional defiant disorder (ODD) is listed in the DSM-5 under ''Disruptive, impulse-control, and conduct disorders'' and defined as "a pattern of angry/irritable mood, argumentative/defiant behavior, or vindictiveness." This behavior is usu ...
(ODD) occurs in about 25% of children with an inattentive presentation and 50% of those with a combined presentation.antisocial personality disorder
Antisocial personality disorder (ASPD) is a personality disorder defined by a chronic pattern of behavior that disregards the rights and well-being of others. People with ASPD often exhibit behavior that conflicts with social norms, leading to ...
in adulthood.limbic system
The limbic system, also known as the paleomammalian cortex, is a set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, immediately beneath the medial temporal lobe of the cerebrum primarily in the forebrain.Schacter, Daniel L. 2012. ''P ...
, and increase the size of one's orbitofrontal cortex
The orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) is a prefrontal cortex region in the frontal lobes of the brain which is involved in the cognitive process of decision-making. In non-human primates it consists of the association cortex areas Brodmann area 11, 1 ...
, whereas ADHD was shown to reduce connections in the cerebellum
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or eve ...
and prefrontal cortex
In mammalian brain anatomy, the prefrontal cortex (PFC) covers the front part of the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex. It is the association cortex in the frontal lobe. The PFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA11, BA12, ...
more broadly. Conduct disorder involves more impairment in motivation control than ADHD.Borderline personality disorder
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is a personality disorder characterized by a pervasive, long-term pattern of significant interpersonal relationship instability, an acute fear of Abandonment (emotional), abandonment, and intense emotiona ...
has also been noted to co-occur with ADHD,Anxiety disorder
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental disorders characterized by significant and uncontrollable feelings of anxiety and fear such that a person's social, occupational, and personal functions are significantly impaired. Anxiety may cause phys ...
s have been found to occur more commonly in the ADHD population, as have mood disorder
A mood disorder, also known as an affective disorder, is any of a group of conditions of mental and behavioral disorder where the main underlying characteristic is a disturbance in the person's mood. The classification is in the ''Diagnostic ...
s (especially bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder (BD), previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that each last from days to weeks, and in ...
and major depressive disorder
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive depression (mood), low mood, low self-esteem, and anhedonia, loss of interest or pleasure in normally ...
).insomnia
Insomnia, also known as sleeplessness, is a sleep disorder where people have difficulty sleeping. They may have difficulty falling asleep, or staying asleep for as long as desired. Insomnia is typically followed by daytime sleepiness, low ene ...
is the most common sleep disorder with behavioural therapy being the preferred treatment.Melatonin
Melatonin, an indoleamine, is a natural compound produced by various organisms, including bacteria and eukaryotes. Its discovery in 1958 by Aaron B. Lerner and colleagues stemmed from the isolation of a substance from the pineal gland of cow ...
is sometimes used in children who have sleep onset insomnia.Restless legs syndrome
Restless legs syndrome (RLS), also known as Willis–Ekbom disease (WED), is a neurological disorder, usually chronic, that causes an overwhelming urge to move one's legs. There is often an unpleasant feeling in the legs that improves temporaril ...
has been found to be more common in those with ADHD and is often due to iron deficiency anemia.substance use disorder
Substance use disorder (SUD) is the persistent use of drugs despite substantial harm and adverse consequences to self and others. Related terms include ''substance use problems'' and ''problematic drug or alcohol use''. Along with substance-ind ...
s.alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
or cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae that is widely accepted as being indigenous to and originating from the continent of Asia. However, the number of species is disputed, with as many as three species be ...
.eating disorder
An eating disorder is a mental disorder defined by abnormal eating behaviors that adversely affect a person's health, physical or mental health, mental health. These behaviors may include eating too much food or too little food. Types of eatin ...
compared to those without ADHD; conversely, individuals with eating disorders are two times more likely to have ADHD than those without eating disorders.
Trauma
ADHD, trauma, and adverse childhood experiences are also comorbid, which could in part be potentially explained by the similarity in presentation between different diagnoses. The symptoms of ADHD and PTSD can have significant behavioural overlap—in particular, motor restlessness, difficulty concentrating, distractibility, irritability/anger, emotional constriction or dysregulation, poor impulse control, and forgetfulness are common in both.
Non-psychiatric
Some non-psychiatric conditions are also comorbidities of ADHD. This includes epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of Non-communicable disease, non-communicable Neurological disorder, neurological disorders characterized by a tendency for recurrent, unprovoked Seizure, seizures. A seizure is a sudden burst of abnormal electrical activit ...
,asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
and sleep disorders,migraine
Migraine (, ) is a complex neurological disorder characterized by episodes of moderate-to-severe headache, most often unilateral and generally associated with nausea, and light and sound sensitivity. Other characterizing symptoms may includ ...
headaches, but have no increased risk of tension-type headaches. Children with ADHD may also experience headaches as a result of medication.systematic review
A systematic review is a scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from published studies on ...
of 82 studies that all confirmed or implied elevated accident-proneness in ADHD patients, and whose data suggested that the type of accidents or injuries—and overall risk—changes over the lifespan of ADHD patients. In January 2014, '' Accident Analysis & Prevention'' published a meta-analysis
Meta-analysis is a method of synthesis of quantitative data from multiple independent studies addressing a common research question. An important part of this method involves computing a combined effect size across all of the studies. As such, th ...
of 16 studies examining the relative risk of traffic collision
A traffic collision, also known as a motor vehicle collision, or car crash, occurs when a vehicle collides with another vehicle, pedestrian, animal, road debris, or other moving or stationary obstruction, such as a tree, pole or building. Tr ...
s for drivers with ADHD, finding an overall relative risk estimate of 1.36 without controlling for exposure, a relative risk estimate of 1.29 when controlling for publication bias
In published academic research, publication bias occurs when the outcome of an experiment or research study biases the decision to publish or otherwise distribute it. Publishing only results that show a Statistical significance, significant find ...
, a relative risk estimate of 1.23 when controlling for exposure, and a relative risk estimate of 1.86 for ADHD drivers with oppositional defiant disorder
Oppositional defiant disorder (ODD) is listed in the DSM-5 under ''Disruptive, impulse-control, and conduct disorders'' and defined as "a pattern of angry/irritable mood, argumentative/defiant behavior, or vindictiveness." This behavior is usu ...
or conduct disorder comorbidities.
Problematic digital media use
Suicide risk
Systematic reviews in 2017 and 2020 found strong evidence that ADHD is associated with increased suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death.
Risk factors for suicide include mental disorders, physical disorders, and substance abuse. Some suicides are impulsive acts driven by stress (such as from financial or ac ...
risk across all age groups, as well as growing evidence that an ADHD diagnosis in childhood or adolescence represents a significant future suicidal risk factor.
Rejection sensitive dysphoria
Rejection sensitive dysphoria, while not a formal diagnosis, is also a common symptom of ADHD, estimated to affect a majority of people with ADHD. Others posit that rejection sensitivity stems from early attachment relationships and parental rejection;
Management
The management of ADHD typically involves counseling
Counseling is the professional guidance of the individual by utilizing psychological methods especially in collecting case history data, using various techniques of the personal interview, and testing interests and aptitudes.
This is a list of c ...
or medications, either alone or in combination. While there are various options of treatment to improve ADHD symptoms, medication therapies substantially improve long-term outcomes, and while eliminating some elevated risks such as obesity,positive reinforcement
Positive is a property of positivity and may refer to:
Mathematics and science
* Positive formula, a logical formula not containing negation
* Positive number, a number that is greater than 0
* Plus sign, the sign "+" used to indicate a posit ...
improves task performance.[ Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ] Data also suggest that combining medication with cognitive behavioral therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a form of psychotherapy that aims to reduce symptoms of various mental health conditions, primarily depression, PTSD, and anxiety disorders.
Cognitive behavioral therapy focuses on challenging and chang ...
(CBT) can have positive effects: although CBT is substantially less effective, it can help address problems that reside after medication has been optimised.
Behavioural therapies
There is good evidence for the use of behavioural therapies in ADHD. They are the recommended first-line treatment in those who have mild symptoms or who are preschool-aged.cognitive behavioral therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a form of psychotherapy that aims to reduce symptoms of various mental health conditions, primarily depression, PTSD, and anxiety disorders.
Cognitive behavioral therapy focuses on challenging and chang ...
, interpersonal psychotherapy, family therapy
Family therapy (also referred to as family counseling, family systems therapy, marriage and family therapy, couple and family therapy) is a branch of psychotherapy focused on families and couples in intimate relationships to nurture change and ...
, school-based interventions, social skills training, behavioural peer intervention, organisation training,Neurofeedback
Neurofeedback is a form of biofeedback that uses electrical potentials in the brain to reinforce desired brain states through operant conditioning. This process is non-invasive neurotherapy and typically collects brain activity data using elect ...
has greater treatment effects than non-active controls for up to 6 months and possibly a year following treatment, and may have treatment effects comparable to active controls (controls proven to have a clinical effect) over that time period. Despite efficacy in research, there is insufficient regulation of neurofeedback practice, leading to ineffective applications and false claims regarding innovations. Parent training may improve a number of behavioural problems including oppositional and non-compliant behaviours.
Digital interventions
Several clinical trials have investigated the efficacy of digital therapeutics, particularly Akili Interactive Labs's video game-based digital therapeutic AKL-T01, marketed as EndeavourRx. The pediatric STARS-ADHD randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, controlled trial demonstrated that AKL-T01 significantly improved performance on the Test of Variables of Attention, an objective measure of attention and inhibitory control, compared to a control group after four weeks of at-home use.Nature Portfolio
Nature Portfolio (formerly known as Nature Publishing Group and Nature Research) is a division of the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature that publishes academic journals, magazines, online databases, and services in scien ...
's npj Digital Medicine evaluated AKL-T01 as an adjunctive treatment for children with ADHD who were either on stimulant medication or not on stimulant pharmacotherapy. Results showed improvements in ADHD-related impairment (measured by the Impairment Rating Scale) and ADHD symptoms after 4 weeks of treatment, with effects persisting during a 4-week pause and further improving with an additional treatment period.
Medication
The medications for ADHD appear to alleviate symptoms via their effects on the pre-frontal executive, striatal and related regions and networks in the brain; usually by increasing neurotransmission of norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic compound, organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and human body, body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The ...
and dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. It is an amine synthesized ...
.
Stimulants
Methylphenidate
Methylphenidate, sold under the brand names Ritalin ( ) and Concerta ( ) among others, is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It may be taken Oral adm ...
and amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from Alpha and beta carbon, alpha-methylphenethylamine, methylphenethylamine) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, an ...
or its derivatives are often first-line treatments for ADHD.Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and ...
studies suggest that long-term treatment with amphetamine or methylphenidate decreases abnormalities in brain structure and function found in subjects with ADHD.scientific consensus
Scientific consensus is the generally held judgment, position, and opinion of the majority or the supermajority of scientists in a particular field of study at any particular time.
Consensus is achieved through scholarly communication at confer ...
that methylphenidate is safe and highly effective for treating ADHD.insomnia
Insomnia, also known as sleeplessness, is a sleep disorder where people have difficulty sleeping. They may have difficulty falling asleep, or staying asleep for as long as desired. Insomnia is typically followed by daytime sleepiness, low ene ...
for ADHD patients taking stimulants has been measured at between 11 and 45 per cent for different medications,emotional lability
In medicine and psychology, emotional lability is a Medical sign, sign or symptom typified by exaggerated changes in mood or affect (psychology), affect in quick succession. Sometimes the emotions expressed outwardly are very different from how th ...
, may also lead to discontinuation.Stimulant psychosis
Stimulant psychosis is a mental disorder characterized by psychotic symptoms such as hallucinations, paranoid ideation, delusions, disorganized thinking, and grossly disorganized behaviour. It typically occurs following an overdose or several ...
and mania
Mania, also known as manic syndrome, is a Psychiatry, psychiatric Abnormality (behavior), behavioral syndrome defined as a state of Abnormality (behavior), abnormally elevated arousal, affect (psychology), affect, and energy level. During a mani ...
are rare at therapeutic doses, appearing to occur in approximately 0.1% of individuals, within the first several weeks after starting amphetamine therapy.cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumati ...
(CVD) across age groups, although the study suggests further investigation is warranted for patients with preexisting CVD as well as long-term medication use. Regular monitoring has been recommended in those on long-term treatment.nicotine
Nicotine is a natural product, naturally produced alkaloid in the nightshade family of plants (most predominantly in tobacco and ''Duboisia hopwoodii'') and is widely used recreational drug use, recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As ...
and other nicotinic agonists as treatments for ADHD have shown favorable results; however, no nicotinic drug has been approved for ADHD treatment. Caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine chemical classification, class and is the most commonly consumed Psychoactive drug, psychoactive substance globally. It is mainly used for its eugeroic (wakefulness pr ...
was formerly used as a second-line treatment for ADHD but research indicates it has no significant effects in reducing ADHD symptoms. Caffeine appears to help with alertness, arousal and reaction time but not the type of inattention implicated in ADHD (sustained attention/persistence). Pseudoephedrine and ephedrine
Ephedrine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant and sympathomimetic agent that is often used to prevent hypotension, low blood pressure during anesthesia. It has also been used for asthma, narcolepsy, and obesity but is not the preferred ...
do not affect ADHD symptoms.Modafinil
Modafinil, sold under the brand name Provigil among others, is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant and wakefulness-promoting agent, eugeroic (wakefulness promoter) medication used primarily to treat narcolepsy, a sleep disorder characteri ...
has shown some efficacy in reducing the severity of ADHD in children and adolescents. It may be prescribed off-label to treat ADHD.
Non-stimulants
Two non-stimulant medications, atomoxetine
Atomoxetine, formerly sold under the brand name Strattera, is a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (sNRI) medication used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and, to a lesser extent, cognitive disengagement syndr ...
and viloxazine, are approved by the FDA and in other countries for the treatment of ADHD.
Atomoxetine
Atomoxetine, formerly sold under the brand name Strattera, is a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (sNRI) medication used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and, to a lesser extent, cognitive disengagement syndr ...
, due to its lack of addiction liability, may be preferred in those who are at risk of recreational or compulsive stimulant use, although evidence is lacking to support its use over stimulants for this reason.Meta-analyses
Meta-analysis is a method of synthesis of quantitative data from multiple independent studies addressing a common research question. An important part of this method involves computing a combined effect size across all of the studies. As such, th ...
and systematic review
A systematic review is a scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from published studies on ...
s have found that atomoxetine has comparable efficacy, equal tolerability and response rate (75%) to methylphenidate
Methylphenidate, sold under the brand names Ritalin ( ) and Concerta ( ) among others, is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It may be taken Oral adm ...
in children and adolescents. In adults, efficacy and discontinuation rates are equivalent.Amantadine
Amantadine, sold under the brand name Gocovri among others, is a medication used to treat dyskinesia associated with parkinsonism and influenza caused by type A influenzavirus, though its use for the latter is no longer recommended because ...
was shown to induce similar improvements in children treated with methylphenidate
Methylphenidate, sold under the brand names Ritalin ( ) and Concerta ( ) among others, is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It may be taken Oral adm ...
, with less frequent side effects. A 2021 retrospective study showed that amantadine may serve as an effective adjunct to stimulants for ADHD–related symptoms and appears to be a safer alternative to second- or third-generation antipsychotics.
Bupropion is also used off-label by some clinicians due to research findings. It is effective, but modestly less than atomoxetine and methylphenidate.
There is little evidence on the effects of medication on social behaviours.clonidine
Clonidine, sold under the brand name Catapres among others, is an α2A-adrenergic receptor agonist medication used to treat high blood pressure, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), drug withdrawal (e.g., alcohol, opioids, or nic ...
, are approved by the FDA and in other countries for the treatment of ADHD (effective in children and adolescents but effectiveness has still not been shown for adults).
Guidelines
Guidelines on when to use medications vary by country. The United Kingdom's National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) is an executive non-departmental public body of the Department of Health and Social Care (United Kingdom), Department of Health and Social Care.
As the national health technolog ...
recommends use for children only in severe cases, though for adults medication is a first-line treatment.
Exercise
Exercise does not reduce the symptoms of ADHD.
Diet
Dietary modifications are not recommended by the American Academy of Pediatrics
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) is the largest professional association of pediatricians in the United States. It is headquartered in Itasca, Illinois, and maintains an office in Washington, D.C. The AAP has published hundreds of poli ...
, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) is an executive non-departmental public body of the Department of Health and Social Care (United Kingdom), Department of Health and Social Care.
As the national health technolog ...
, or the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality due to insufficient evidence.free fatty acid
In chemistry, in particular in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, f ...
supplementation or decreased consumption of artificial food colouring.elimination diet
An elimination diet, also known as exclusion diet, is a diagnostic procedure used to identify foods that an individual cannot consume without adverse effects. Adverse effects may be due to food allergy, food intolerance, other physiological mechan ...
results in a small overall benefit in a minority of children, such as those with allergies.gluten-free diet
A gluten-free diet (GFD) is a nutritional plan that strictly excludes gluten, which is a mixture of prolamin proteins found in wheat (and all of its species and hybrids, such as spelt, kamut, and triticale), as well as barley, rye, and oats ...
as standard ADHD treatment is not advised.zinc deficiency
Zinc deficiency is defined either as insufficient body levels of zinc to meet the needs of the body, or as a zinc blood level below the normal range. However, since a decrease in blood concentration is only detectable after long-term or severe ...
(which is rare outside of developing countries), zinc supplementation is not recommended as treatment for ADHD.
Prognosis
About 30–50% of people diagnosed in childhood continue to have ADHD in adulthood, with 2.58% of adults estimated to have ADHD which began in childhood.coping
Coping refers to conscious or unconscious strategies used to reduce and manage unpleasant emotions. Coping strategies can be cognitions or behaviors and can be individual or social. To cope is to deal with struggles and difficulties in life. It ...
mechanisms as they mature, thus compensating to some extent for their previous symptoms.smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is combusted, and the resulting smoke is typically inhaled to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream of a person. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, whi ...
, alcohol misuse, and face other health challenges such as depression, self-harm, or personality disorder
Personality disorders (PD) are a class of mental health conditions characterized by enduring maladaptive patterns of behavior, cognition, and inner experience, exhibited across many contexts and deviating from those accepted by the culture. ...
s.
Epidemiology
 ADHD is estimated to affect about 6–7% of people aged 18 and under when diagnosed via the DSM-IV criteria.
ADHD is estimated to affect about 6–7% of people aged 18 and under when diagnosed via the DSM-IV criteria.[. Both DSM-IV-TR and ICD-10 criteria were used.]
ADHD is diagnosed approximately twice as often in boys as in girls,New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of ...
'' article.non-White
The term "person of color" (: people of color or persons of color; abbreviated POC) is used to describe any person who is not considered "white". In its current meaning, the term originated in, and is associated with, the United States. From th ...
children in the US are less likely than White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no chroma). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully (or almost fully) reflect and scatter all the visible wa ...
children to be diagnosed or treated for ADHD, a finding that is often explained by bias among health professionals, as well as parents who may be reluctant to acknowledge that their child has ADHD. Crosscultural differences in diagnosis of ADHD can also be attributed to the long-lasting effects of harmful, racially targeted medical practices. Medical pseudosciences, particularly those that targeted Black populations during the period of slavery in the US, lead to a distrust of medical practices within certain communities. The combination of ADHD symptoms often being regarded as misbehaviour rather than as a psychiatric condition, and the use of drugs to regulate ADHD, result in a hesitancy to trust a diagnosis of ADHD. Cases of misdiagnosis in ADHD can also occur due to stereotyping of people of color. Due to ADHD's subjectively determined symptoms, medical professionals may diagnose individuals based on stereotyped behaviour or misdiagnose due to cultural differences in symptom presentation.CDC
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency under the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and is headquartered in Atlanta, ...
's Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report reports around 15.5 million U.S. adults have attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, with many facing challenges in accessing treatment. One-third of diagnosed individuals had received a prescription for a stimulant drug in the past year but nearly three-quarters of them reported difficulties filling the prescription due to medication shortages.
History
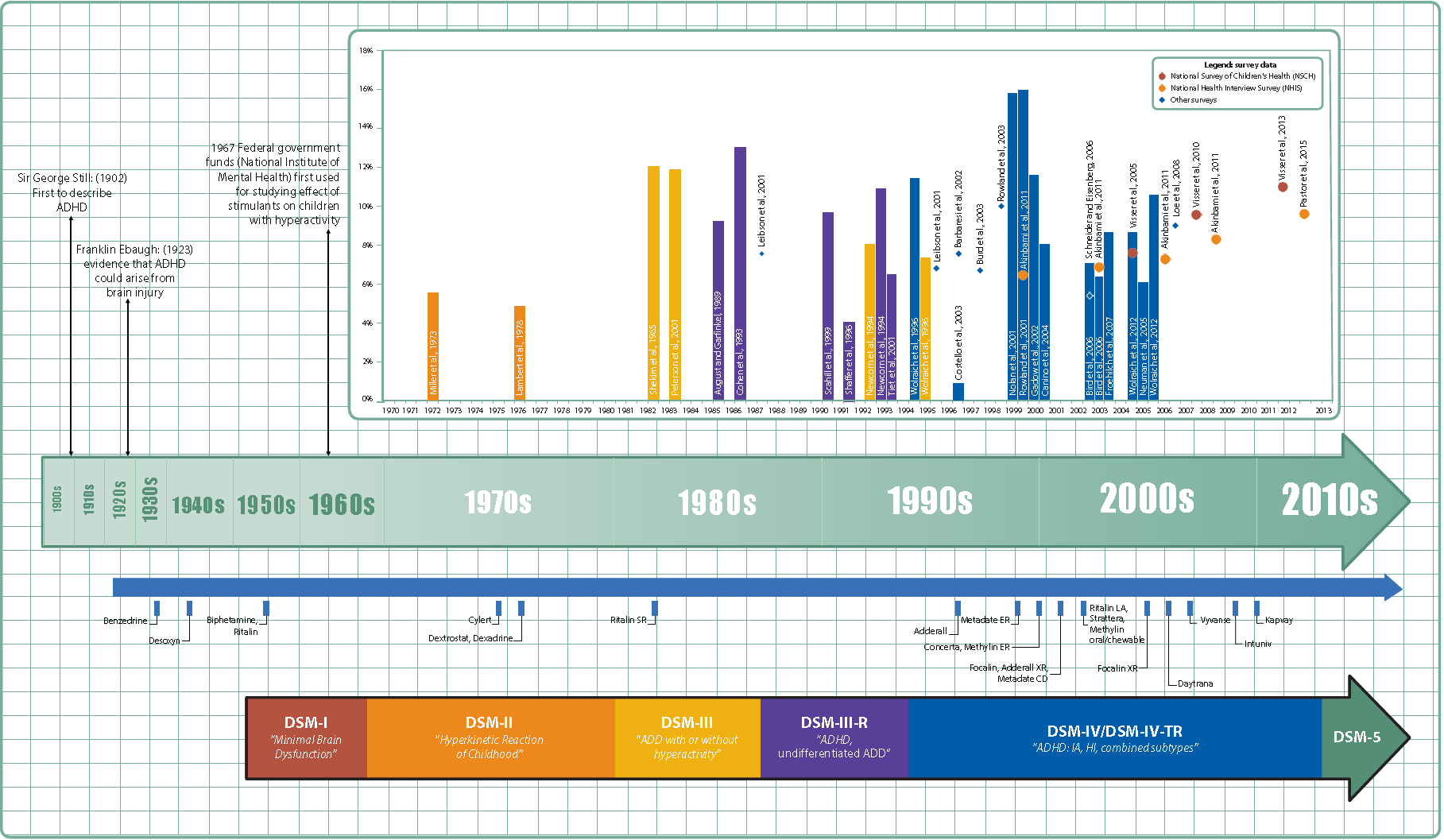 ADHD was officially known as attention deficit disorder (ADD) from 1980 to 1987; prior to the 1980s, it was known as hyperkinetic reaction of childhood. Symptoms similar to those of ADHD have been described in medical literature dating back to the 18th century. Sir Alexander Crichton describes "mental restlessness" in his book ''An inquiry into the nature and origin of mental derangement'' written in 1798. He made observations about children showing signs of being inattentive and having the "fidgets". The first clear description of ADHD is credited to George Still in 1902 during a series of lectures he gave to the Royal College of Physicians of London.
ADHD was officially known as attention deficit disorder (ADD) from 1980 to 1987; prior to the 1980s, it was known as hyperkinetic reaction of childhood. Symptoms similar to those of ADHD have been described in medical literature dating back to the 18th century. Sir Alexander Crichton describes "mental restlessness" in his book ''An inquiry into the nature and origin of mental derangement'' written in 1798. He made observations about children showing signs of being inattentive and having the "fidgets". The first clear description of ADHD is credited to George Still in 1902 during a series of lectures he gave to the Royal College of Physicians of London.[ Prior to the DSM, terms included ''minimal brain damage'' in the 1930s.
ADHD, its diagnosis, and its treatment have been controversial since the 1970s.]frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a Sulcus (neur ...
s) were involved in ADHD. A genetic component was identified and ADHD was acknowledged to be a persistent, long-term disorder which lasted from childhood into adulthood.
Research directions
Possible positive traits
Possible positive traits of ADHD are a new avenue of research, and therefore limited.
A 2020 review found that creativity may be associated with ADHD symptoms, particularly divergent thinking
Divergent thinking is a thought process used to generate creative ideas by exploring many possible solutions. It typically occurs in a spontaneous, free-flowing, "non-linear" manner, such that many ideas are generated in an emergent cognitive fa ...
and quantity of creative achievements, but not with the disorder of ADHD itself – i.e. it has not been found to be increased in people diagnosed with the disorder, only in people with subclinical symptoms or those that possess traits associated with the disorder. Divergent thinking is the ability to produce creative solutions which differ significantly from each other and consider the issue from multiple perspectives. Those with ADHD symptoms could be advantaged in this form of creativity as they tend to have diffuse attention, allowing rapid switching between aspects of the task under consideration; flexible associative memory, allowing them to remember and use more distantly related ideas which is associated with creativity; and impulsivity, allowing them to consider ideas which others may not have.
Possible biomarkers for diagnosis
Reviews of ADHD biomarker
In biomedical contexts, a biomarker, or biological marker, is a measurable indicator of some biological state or condition. Biomarkers are often measured and evaluated using blood, urine, or soft tissues to examine normal biological processes, ...
s have noted that platelet monoamine oxidase
Monoamine oxidases (MAO) () are a family of enzymes that catalyze the oxidation of monoamines, employing oxygen to clip off their amine group. They are found bound to the outer membrane of mitochondria in most cell types of the body. The fi ...
expression, urinary norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic compound, organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and human body, body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The ...
, urinary MHPG, and urinary phenethylamine
Phenethylamine (PEA) is an organic compound, natural monoamine alkaloid, and trace amine, which acts as a central nervous system stimulant in humans. In the brain, phenethylamine regulates monoamine neurotransmission by binding to trace ami ...
levels consistently differ between ADHD individuals and non-ADHD controls. These parameters could serve as prognostic biomarkers for ADHD, but more research is needed to establish their prognostic utility. Urinary and blood plasma
Blood plasma is a light Amber (color), amber-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are absent, but which contains Blood protein, proteins and other constituents of whole blood in Suspension (chemistry), suspension. It makes up ...
phenethylamine concentrations are lower in ADHD individuals relative to controls.amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from Alpha and beta carbon, alpha-methylphenethylamine, methylphenethylamine) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, an ...
and methylphenidate
Methylphenidate, sold under the brand names Ritalin ( ) and Concerta ( ) among others, is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It may be taken Oral adm ...
, increase phenethylamine biosynthesis
Biosynthesis, i.e., chemical synthesis occurring in biological contexts, is a term most often referring to multi-step, enzyme-Catalysis, catalyzed processes where chemical substances absorbed as nutrients (or previously converted through biosynthe ...
in treatment-responsive individuals with ADHD.
See also
* Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder controversies
* Directed attention fatigue – a temporary state sharing many of the symptoms of ADHD
* Self-medication
Self-medication, sometime called do-it-yourself (DIY) medicine, is a human behavior in which an individual uses a substance or any exogenous influence to self-administer treatment for physical or psychological conditions, for example headaches or ...
References
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
* National Institute of Mental Health
NIMH Pages About Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD).
National Institutes of Health (NIH), U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
{{Authority control
1987 neologisms
Ailments of unknown cause
Amphetamine
Attention disorders
Learning disabilities
Methylphenidate
Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate (full)
Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate
 In children with ADHD, there is a general reduction of volume in certain brain structures, with a proportionally greater decrease in the volume in the left-sided prefrontal cortex. The posterior parietal cortex also shows thinning in individuals with ADHD compared to controls. Other brain structures in the prefrontal-striatal-cerebellar and prefrontal-striatal-thalamic circuits have also been found to differ between people with and without ADHD.
The subcortical volumes of the accumbens,
In children with ADHD, there is a general reduction of volume in certain brain structures, with a proportionally greater decrease in the volume in the left-sided prefrontal cortex. The posterior parietal cortex also shows thinning in individuals with ADHD compared to controls. Other brain structures in the prefrontal-striatal-cerebellar and prefrontal-striatal-thalamic circuits have also been found to differ between people with and without ADHD.
The subcortical volumes of the accumbens,  ADHD is estimated to affect about 6–7% of people aged 18 and under when diagnosed via the DSM-IV criteria. When diagnosed via the ICD-10 criteria, rates in this age group are estimated around 1–2%. Rates are similar between countries and differences in rates depend mostly on how it is diagnosed. Children in North America appear to have a higher rate of ADHD than children in Africa and the Middle East; this is believed to be due to differing methods of diagnosis rather than a difference in underlying frequency. (The same publication which describes this difference also notes that the difference may be rooted in the available studies from these respective regions, as far more studies were from North America than from Africa and the Middle East.) it was estimated to affect 84.7 million people globally.. Both DSM-IV-TR and ICD-10 criteria were used.
ADHD is diagnosed approximately twice as often in boys as in girls, and 1.6 times more often in men than in women, although the disorder is overlooked in girls or diagnosed in later life because their symptoms sometimes differ from diagnostic criteria. In 2014, Keith Conners, one of the early advocates for recognition of the disorder, spoke out against overdiagnosis in a ''
ADHD is estimated to affect about 6–7% of people aged 18 and under when diagnosed via the DSM-IV criteria. When diagnosed via the ICD-10 criteria, rates in this age group are estimated around 1–2%. Rates are similar between countries and differences in rates depend mostly on how it is diagnosed. Children in North America appear to have a higher rate of ADHD than children in Africa and the Middle East; this is believed to be due to differing methods of diagnosis rather than a difference in underlying frequency. (The same publication which describes this difference also notes that the difference may be rooted in the available studies from these respective regions, as far more studies were from North America than from Africa and the Middle East.) it was estimated to affect 84.7 million people globally.. Both DSM-IV-TR and ICD-10 criteria were used.
ADHD is diagnosed approximately twice as often in boys as in girls, and 1.6 times more often in men than in women, although the disorder is overlooked in girls or diagnosed in later life because their symptoms sometimes differ from diagnostic criteria. In 2014, Keith Conners, one of the early advocates for recognition of the disorder, spoke out against overdiagnosis in a '' ADHD was officially known as attention deficit disorder (ADD) from 1980 to 1987; prior to the 1980s, it was known as hyperkinetic reaction of childhood. Symptoms similar to those of ADHD have been described in medical literature dating back to the 18th century. Sir Alexander Crichton describes "mental restlessness" in his book ''An inquiry into the nature and origin of mental derangement'' written in 1798. He made observations about children showing signs of being inattentive and having the "fidgets". The first clear description of ADHD is credited to George Still in 1902 during a series of lectures he gave to the Royal College of Physicians of London.
The terminology used to describe the condition has changed over time and has included: ''minimal brain dysfunction'' in the DSM-I (1952), ''hyperkinetic reaction of childhood'' in the DSM-II (1968), and ''attention-deficit disorder with or without hyperactivity'' in the DSM-III (1980). In 1987, the symptoms of inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity were collectively combined to define the new diagnosis of ADHD, and in 1994 the DSM-IV in split the diagnosis into three subtypes: ADHD inattentive type, ADHD hyperactive-impulsive type, and ADHD combined type. These terms were kept in the DSM-5 in 2013 and in the DSM-5-TR in 2022. Prior to the DSM, terms included ''minimal brain damage'' in the 1930s.
ADHD, its diagnosis, and its treatment have been controversial since the 1970s. For example, positions differ on whether ADHD is within the normal range of behaviour, and to degree to which ADHD is a genetic condition. Other areas of controversy include the use of stimulant medications in children, the method of diagnosis, and the possibility of overdiagnosis. In 2009, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence states that the current treatments and methods of diagnosis are based on the dominant view of the academic literature.
Once neuroimaging studies were possible, studies in the 1990s provided support for the pre-existing theory that neurological differences (particularly in the
ADHD was officially known as attention deficit disorder (ADD) from 1980 to 1987; prior to the 1980s, it was known as hyperkinetic reaction of childhood. Symptoms similar to those of ADHD have been described in medical literature dating back to the 18th century. Sir Alexander Crichton describes "mental restlessness" in his book ''An inquiry into the nature and origin of mental derangement'' written in 1798. He made observations about children showing signs of being inattentive and having the "fidgets". The first clear description of ADHD is credited to George Still in 1902 during a series of lectures he gave to the Royal College of Physicians of London.
The terminology used to describe the condition has changed over time and has included: ''minimal brain dysfunction'' in the DSM-I (1952), ''hyperkinetic reaction of childhood'' in the DSM-II (1968), and ''attention-deficit disorder with or without hyperactivity'' in the DSM-III (1980). In 1987, the symptoms of inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity were collectively combined to define the new diagnosis of ADHD, and in 1994 the DSM-IV in split the diagnosis into three subtypes: ADHD inattentive type, ADHD hyperactive-impulsive type, and ADHD combined type. These terms were kept in the DSM-5 in 2013 and in the DSM-5-TR in 2022. Prior to the DSM, terms included ''minimal brain damage'' in the 1930s.
ADHD, its diagnosis, and its treatment have been controversial since the 1970s. For example, positions differ on whether ADHD is within the normal range of behaviour, and to degree to which ADHD is a genetic condition. Other areas of controversy include the use of stimulant medications in children, the method of diagnosis, and the possibility of overdiagnosis. In 2009, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence states that the current treatments and methods of diagnosis are based on the dominant view of the academic literature.
Once neuroimaging studies were possible, studies in the 1990s provided support for the pre-existing theory that neurological differences (particularly in the