Atlantic 55 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five
 The oldest known mentions of an "Atlantic" sea come from Stesichorus around mid-sixth century BC (Sch. A. R. 1. 211): (Greek: ; English: 'the Atlantic sea'; etym. 'Sea of
The oldest known mentions of an "Atlantic" sea come from Stesichorus around mid-sixth century BC (Sch. A. R. 1. 211): (Greek: ; English: 'the Atlantic sea'; etym. 'Sea of
 The
The
 Surface water temperatures, which vary with latitude, current systems, and season and reflect the latitudinal distribution of solar energy, range from below to over . Maximum temperatures occur north of the equator, and minimum values are found in the polar regions. In the middle latitudes, the area of maximum temperature variations, values may vary by .
From October to June the surface is usually covered with sea ice in the
Surface water temperatures, which vary with latitude, current systems, and season and reflect the latitudinal distribution of solar energy, range from below to over . Maximum temperatures occur north of the equator, and minimum values are found in the polar regions. In the middle latitudes, the area of maximum temperature variations, values may vary by .
From October to June the surface is usually covered with sea ice in the
 North of the North Atlantic Gyre, the cyclonic
North of the North Atlantic Gyre, the cyclonic
 Climate is influenced by the temperatures of the surface waters and water currents as well as winds. Because of the ocean's great capacity to store and release heat, maritime climates are more moderate and have less extreme seasonal variations than inland climates.
Climate is influenced by the temperatures of the surface waters and water currents as well as winds. Because of the ocean's great capacity to store and release heat, maritime climates are more moderate and have less extreme seasonal variations than inland climates.
 Every winter, the
Every winter, the
 The same development can be seen in Europe. In
The same development can be seen in Europe. In
 The Norse settlement of the
The Norse settlement of the
 Christopher Columbus Voyages of Christopher Columbus, reached the Americas in 1492 under Spanish flag. Six years later Vasco da Gama reached India under the Portuguese flag, by navigating south around the Cape of Good Hope, thus proving that the Atlantic and Indian Oceans are connected. In 1500, in his voyage to India following Vasco da Gama, Pedro Alvares Cabral reached Brazil, taken by the currents of the South Atlantic Gyre. Following these explorations, Spain and Portugal quickly Colonization of the Americas, conquered and colonized large territories in the New World and forced the Amerindian population into slavery in order to exploit the vast quantities of silver and gold they found. Spain and Portugal monopolized this trade in order to keep other European nations out, but conflicting interests nevertheless led to a series of Spanish-Portuguese wars. A peace treaty mediated by the Pope divided the conquered territories into Spanish and Portuguese sectors while keeping other colonial powers away. England, France, and the Dutch Republic enviously watched the Spanish and Portuguese wealth grow and allied themselves with Piracy in the Atlantic World, pirates such as Henry Mainwaring and Alexandre Exquemelin. They could explore the convoys leaving the Americas because prevailing winds and currents made the transport of heavy metals slow and predictable.
Christopher Columbus Voyages of Christopher Columbus, reached the Americas in 1492 under Spanish flag. Six years later Vasco da Gama reached India under the Portuguese flag, by navigating south around the Cape of Good Hope, thus proving that the Atlantic and Indian Oceans are connected. In 1500, in his voyage to India following Vasco da Gama, Pedro Alvares Cabral reached Brazil, taken by the currents of the South Atlantic Gyre. Following these explorations, Spain and Portugal quickly Colonization of the Americas, conquered and colonized large territories in the New World and forced the Amerindian population into slavery in order to exploit the vast quantities of silver and gold they found. Spain and Portugal monopolized this trade in order to keep other European nations out, but conflicting interests nevertheless led to a series of Spanish-Portuguese wars. A peace treaty mediated by the Pope divided the conquered territories into Spanish and Portuguese sectors while keeping other colonial powers away. England, France, and the Dutch Republic enviously watched the Spanish and Portuguese wealth grow and allied themselves with Piracy in the Atlantic World, pirates such as Henry Mainwaring and Alexandre Exquemelin. They could explore the convoys leaving the Americas because prevailing winds and currents made the transport of heavy metals slow and predictable.
 In the colonies of the Americas, depredation, smallpox and others diseases, and slavery quickly reduced the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous population of the Americas to the extent that the Atlantic slave trade had to be introduced to replace them — a trade that became the norm and an integral part of the colonization. Between the 15th century and 1888, when Slavery in Brazil, Brazil became the last part of the Americas to end the slave trade, an estimated ten million Africans were exported as slaves, most of them destined for agricultural labour. The slave trade was officially abolished in the Slavery in the British Isles, British Empire and the Slavery in the United States, United States in 1808, and slavery itself was abolished in the British Empire in 1838 and in the United States in 1865 after the American Civil War, Civil War.
From Columbus to the Industrial Revolution Trans-Atlantic trade, including colonialism and slavery, became crucial for Western Europe. For European countries with direct access to the Atlantic (including Britain, France, the Netherlands, Portugal, and Spain) 1500–1800 was a period of sustained growth during which these countries grew richer than those in Eastern Europe and Asia. Colonialism evolved as part of the Trans-Atlantic trade, but this trade also strengthened the position of merchant groups at the expense of monarchs. Growth was more rapid in non-absolutist countries, such as Britain and the Netherlands, and more limited in Absolute monarchy, absolutist monarchies, such as Portugal, Spain, and France, where profit mostly or exclusively benefited the monarchy and its allies.
Trans-Atlantic trade also resulted in increasing urbanization: in European countries facing the Atlantic, urbanization grew from 8% in 1300, 10.1% in 1500, to 24.5% in 1850; in other European countries from 10% in 1300, 11.4% in 1500, to 17% in 1850. Likewise, GDP doubled in Atlantic countries but rose by only 30% in the rest of Europe. By end of the 17th century, the volume of the Trans-Atlantic trade had surpassed that of the Mediterranean trade.
The Atlantic Ocean became the scene of one of the longest continuous naval military camapaigns throughout World War II, from 1939 to 1945.
In the colonies of the Americas, depredation, smallpox and others diseases, and slavery quickly reduced the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous population of the Americas to the extent that the Atlantic slave trade had to be introduced to replace them — a trade that became the norm and an integral part of the colonization. Between the 15th century and 1888, when Slavery in Brazil, Brazil became the last part of the Americas to end the slave trade, an estimated ten million Africans were exported as slaves, most of them destined for agricultural labour. The slave trade was officially abolished in the Slavery in the British Isles, British Empire and the Slavery in the United States, United States in 1808, and slavery itself was abolished in the British Empire in 1838 and in the United States in 1865 after the American Civil War, Civil War.
From Columbus to the Industrial Revolution Trans-Atlantic trade, including colonialism and slavery, became crucial for Western Europe. For European countries with direct access to the Atlantic (including Britain, France, the Netherlands, Portugal, and Spain) 1500–1800 was a period of sustained growth during which these countries grew richer than those in Eastern Europe and Asia. Colonialism evolved as part of the Trans-Atlantic trade, but this trade also strengthened the position of merchant groups at the expense of monarchs. Growth was more rapid in non-absolutist countries, such as Britain and the Netherlands, and more limited in Absolute monarchy, absolutist monarchies, such as Portugal, Spain, and France, where profit mostly or exclusively benefited the monarchy and its allies.
Trans-Atlantic trade also resulted in increasing urbanization: in European countries facing the Atlantic, urbanization grew from 8% in 1300, 10.1% in 1500, to 24.5% in 1850; in other European countries from 10% in 1300, 11.4% in 1500, to 17% in 1850. Likewise, GDP doubled in Atlantic countries but rose by only 30% in the rest of Europe. By end of the 17th century, the volume of the Trans-Atlantic trade had surpassed that of the Mediterranean trade.
The Atlantic Ocean became the scene of one of the longest continuous naval military camapaigns throughout World War II, from 1939 to 1945.
 The Atlantic harbors petroleum and gas fields, fish, marine mammals (Pinniped, seals and whales), sand and gravel aggregates, placer deposits, polymetallic nodules, and precious stones.
Gold deposits are a mile or two under water on the ocean floor, however, the deposits are also encased in rock that must be mined through. Currently, there is no cost-effective way to mine or extract gold from the ocean to make a profit.
Various international treaties attempt to reduce pollution caused by environmental threats such as oil spills, marine debris, and the incineration of toxic wastes at sea.
The Atlantic harbors petroleum and gas fields, fish, marine mammals (Pinniped, seals and whales), sand and gravel aggregates, placer deposits, polymetallic nodules, and precious stones.
Gold deposits are a mile or two under water on the ocean floor, however, the deposits are also encased in rock that must be mined through. Currently, there is no cost-effective way to mine or extract gold from the ocean to make a profit.
Various international treaties attempt to reduce pollution caused by environmental threats such as oil spills, marine debris, and the incineration of toxic wastes at sea.
 ;North-East Atlantic:
North-East Atlantic is schematically limited to the 42°00' west longitude except around Greenland and at south to 36°00' north latitude; and 68°30' east longitude at the east, according to FAO fisheries definition and include various seas and/or subareas:
;North-East Atlantic:
North-East Atlantic is schematically limited to the 42°00' west longitude except around Greenland and at south to 36°00' north latitude; and 68°30' east longitude at the east, according to FAO fisheries definition and include various seas and/or subareas:  ;North-West Atlantic : In the North-West Atlantic landings have decreased from 4.2 million tons in the early 1970s to 1.9 million tons in 2013. During the 21st century some species have shown weak signs of recovery, including Greenland halibut, yellowtail flounder, Atlantic halibut, haddock, spiny dogfish, while other stocks shown no such signs, including cod, Witch (righteye flounder), witch flounder, and redfish. Stocks of invertebrates, in contrast, remain at record levels of abundance. 31% of stocks are overfished in the North-west Atlantic.
;North-West Atlantic : In the North-West Atlantic landings have decreased from 4.2 million tons in the early 1970s to 1.9 million tons in 2013. During the 21st century some species have shown weak signs of recovery, including Greenland halibut, yellowtail flounder, Atlantic halibut, haddock, spiny dogfish, while other stocks shown no such signs, including cod, Witch (righteye flounder), witch flounder, and redfish. Stocks of invertebrates, in contrast, remain at record levels of abundance. 31% of stocks are overfished in the North-west Atlantic.
 In 1497, John Cabot became the first Western European since the Vikings to explore mainland North America and one of his major discoveries was the abundant resources of Atlantic cod off Newfoundland. Referred to as "Newfoundland Currency" this discovery yielded some 200 million tons of fish over five centuries. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries new fisheries started to exploit haddock, mackerel, and lobster. From the 1950s to the 1970s the introduction of European and Asian distant-water fleets in the area dramatically increased the fishing capacity and the number of exploited species. It also expanded the exploited areas from near-shore to the open sea and to great depths to include deep-water species such as Sebastes, redfish, Greenland halibut, witch flounder, and Grenadiers (fish), grenadiers. Overfishing in the area was recognised as early as the 1960s but, because this was occurring on international waters, it took until the late 1970s before any attempts to regulate was made. In the early 1990s, this finally resulted in the collapse of the Atlantic northwest cod fishery. The population of a number of deep-sea fishes also collapsed in the process, including American plaice, redfish, and Greenland halibut, together with flounder and grenadier.
;Eastern Central Atlantic : In the Eastern Central Atlantic small pelagic fishes constitute about 50% of landings with sardine reaching 0.6–1.0 million tons per year. Pelagic fish stocks are considered fully fished or overfished, with sardines south of Cape Bojador the notable exception. Almost half of the stocks are fished at biologically unsustainable levels. Total catches have been fluctuating since the 1970s; reaching 3.9 million tons in 2013 or slightly less than the peak production in 2010.
In 1497, John Cabot became the first Western European since the Vikings to explore mainland North America and one of his major discoveries was the abundant resources of Atlantic cod off Newfoundland. Referred to as "Newfoundland Currency" this discovery yielded some 200 million tons of fish over five centuries. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries new fisheries started to exploit haddock, mackerel, and lobster. From the 1950s to the 1970s the introduction of European and Asian distant-water fleets in the area dramatically increased the fishing capacity and the number of exploited species. It also expanded the exploited areas from near-shore to the open sea and to great depths to include deep-water species such as Sebastes, redfish, Greenland halibut, witch flounder, and Grenadiers (fish), grenadiers. Overfishing in the area was recognised as early as the 1960s but, because this was occurring on international waters, it took until the late 1970s before any attempts to regulate was made. In the early 1990s, this finally resulted in the collapse of the Atlantic northwest cod fishery. The population of a number of deep-sea fishes also collapsed in the process, including American plaice, redfish, and Greenland halibut, together with flounder and grenadier.
;Eastern Central Atlantic : In the Eastern Central Atlantic small pelagic fishes constitute about 50% of landings with sardine reaching 0.6–1.0 million tons per year. Pelagic fish stocks are considered fully fished or overfished, with sardines south of Cape Bojador the notable exception. Almost half of the stocks are fished at biologically unsustainable levels. Total catches have been fluctuating since the 1970s; reaching 3.9 million tons in 2013 or slightly less than the peak production in 2010.
 ;Western Central Atlantic: In the Western Central Atlantic, catches have been decreasing since 2000 and reached 1.3 million tons in 2013. The most important species in the area, Gulf menhaden, reached a million tons in the mid-1980s but only half a million tons in 2013 and is now considered fully fished. Round sardinella was an important species in the 1990s but is now considered overfished. Groupers and Lutjanidae, snappers are overfished and northern brown shrimp and Eastern oyster, American cupped oyster are considered fully fished approaching overfished. 44% of stocks are being fished at unsustainable levels.
;Western Central Atlantic: In the Western Central Atlantic, catches have been decreasing since 2000 and reached 1.3 million tons in 2013. The most important species in the area, Gulf menhaden, reached a million tons in the mid-1980s but only half a million tons in 2013 and is now considered fully fished. Round sardinella was an important species in the 1990s but is now considered overfished. Groupers and Lutjanidae, snappers are overfished and northern brown shrimp and Eastern oyster, American cupped oyster are considered fully fished approaching overfished. 44% of stocks are being fished at unsustainable levels.
 ;South-East Atlantic: In the South-East Atlantic catches have decreased from 3.3 million tons in the early 1970s to 1.3 million tons in 2013. Horse mackerel and hake are the most important species, together representing almost half of the landings. Off South Africa and Namibia Merluccius paradoxus, deep-water hake and Merluccius capensis, shallow-water Cape hake have recovered to sustainable levels since regulations were introduced in 2006 and the states of Southern African pilchard and Southern African anchovy, anchovy have improved to fully fished in 2013.
;South-West Atlantic: In the South-West Atlantic, a peak was reached in the mid-1980s and catches now fluctuate between 1.7 and 2.6 million tons. The most important species, the Illex argentinus, Argentine shortfin squid, which reached half a million tons in 2013 or half the peak value, is considered fully fished to overfished. Another important species was the Brazilian sardinella, with a production of 100,000 tons in 2013 it is now considered overfished. Half the stocks in this area are being fished at unsustainable levels: Whitehead's round herring has not yet reached fully fished but Cunene horse mackerel is overfished. The sea snail Haliotis midae, perlemoen abalone is targeted by illegal fishing and remain overfished.
;South-East Atlantic: In the South-East Atlantic catches have decreased from 3.3 million tons in the early 1970s to 1.3 million tons in 2013. Horse mackerel and hake are the most important species, together representing almost half of the landings. Off South Africa and Namibia Merluccius paradoxus, deep-water hake and Merluccius capensis, shallow-water Cape hake have recovered to sustainable levels since regulations were introduced in 2006 and the states of Southern African pilchard and Southern African anchovy, anchovy have improved to fully fished in 2013.
;South-West Atlantic: In the South-West Atlantic, a peak was reached in the mid-1980s and catches now fluctuate between 1.7 and 2.6 million tons. The most important species, the Illex argentinus, Argentine shortfin squid, which reached half a million tons in 2013 or half the peak value, is considered fully fished to overfished. Another important species was the Brazilian sardinella, with a production of 100,000 tons in 2013 it is now considered overfished. Half the stocks in this area are being fished at unsustainable levels: Whitehead's round herring has not yet reached fully fished but Cunene horse mackerel is overfished. The sea snail Haliotis midae, perlemoen abalone is targeted by illegal fishing and remain overfished.
map
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
Cartage.org.lb (archived)
"Map of Atlantic Coast of North America from the Chesapeake Bay to Florida"
from 1639 via the Library of Congress {{Authority control Atlantic Ocean, Oceans History of the Atlantic Ocean, Landforms of the Atlantic Ocean, Articles containing video clips Oceans surrounding Antarctica
ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wo ...
s, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by the ...
" of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
and Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
from the "New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 3 ...
" of the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
in the European perception of the World
In its most general sense, the term "world" refers to the totality of entities, to the whole of reality or to everything that is. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the worl ...
.
The Atlantic Ocean occupies an elongated, S-shaped basin extending longitudinally between Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
and Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
to the east, and North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
and South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southe ...
to the west. As one component of the interconnected World Ocean, it is connected in the north to the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, a ...
, to the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
in the southwest, the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by th ...
in the southeast, and the Southern Ocean
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the World Ocean, generally taken to be south of 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. With a size of , it is regarded as the second-small ...
in the south (other definitions describe the Atlantic as extending southward to Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest contine ...
). The Atlantic Ocean is divided in two parts, by the Equatorial Counter Current, with the North(ern) Atlantic Ocean and the South(ern) Atlantic Ocean split at about 8°N.
Scientific explorations of the Atlantic include the ''Challenger'' expedition, the German ''Meteor'' expedition, Columbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhatt ...
's Lamont–Doherty Earth Observatory
The Lamont–Doherty Earth Observatory (LDEO) is the scientific research center of the Columbia Climate School, and a unit of The Earth Institute at Columbia University. It focuses on climate and earth sciences and is located on a 189-acre (64 h ...
and the United States Navy Hydrographic Office.
Toponymy
 The oldest known mentions of an "Atlantic" sea come from Stesichorus around mid-sixth century BC (Sch. A. R. 1. 211): (Greek: ; English: 'the Atlantic sea'; etym. 'Sea of
The oldest known mentions of an "Atlantic" sea come from Stesichorus around mid-sixth century BC (Sch. A. R. 1. 211): (Greek: ; English: 'the Atlantic sea'; etym. 'Sea of Atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geographic ...
') and in '' The Histories'' of Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known f ...
around 450 BC (Hdt. 1.202.4): (Greek: ; English: 'Sea of Atlas' or 'the Atlantic sea') where the name refers to "the sea beyond the pillars of Heracles
The Pillars of Hercules ( la, Columnae Herculis, grc, Ἡράκλειαι Στῆλαι, , ar, أعمدة هرقل, Aʿmidat Hiraql, es, Columnas de Hércules) was the phrase that was applied in Antiquity to the promontories that flank t ...
" which is said to be part of the sea that surrounds all land. In these uses, the name refers to Atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geographic ...
, the Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
in Greek mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical co ...
, who supported the heavens and who later appeared as a frontispiece in Medieval maps and also lent his name to modern atlases
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geographic ...
. On the other hand, to early Greek sailors and in Ancient Greek mythological literature such as the ''Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; grc, Ἰλιάς, Iliás, ; "a poem about Ilium") is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odysse ...
'' and the ''Odyssey
The ''Odyssey'' (; grc, Ὀδύσσεια, Odýsseia, ) is one of two major Ancient Greek literature, ancient Greek Epic poetry, epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by moder ...
'', this all-encompassing ocean was instead known as Oceanus
In Greek mythology, Oceanus (; grc-gre, , Ancient Greek pronunciation: , also Ὠγενός , Ὤγενος , or Ὠγήν ) was a Titan son of Uranus and Gaia, the husband of his sister the Titan Tethys, and the father of the river gods a ...
, the gigantic river that encircled the world; in contrast to the enclosed seas well known to the Greeks: the Mediterranean and the Black Sea. In contrast, the term "Atlantic" originally referred specifically to the Atlas Mountains
The Atlas Mountains are a mountain range in the Maghreb in North Africa. It separates the Sahara Desert from the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean; the name "Atlantic" is derived from the mountain range. It stretches around through Moroc ...
in Morocco and the sea off the Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar ( ar, مضيق جبل طارق, Maḍīq Jabal Ṭāriq; es, Estrecho de Gibraltar, Archaic: Pillars of Hercules), also known as the Straits of Gibraltar, is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Medi ...
and the North African coast. The Greek word has been reused by scientists for the huge Panthalassa ocean that surrounded the supercontinent Pangaea hundreds of millions of years ago.
The term "Aethiopian Ocean
Aethiopian, Æthiopian, Æthiopic or Ethiopian Sea or Ocean ( la, Æthiopicum Mare or ''Oceanus Æthiopicus''; ar, البحر الأثيوبي) was the name given to the southern half of the Atlantic Ocean in classical geographical works. The na ...
", derived from Ancient Ethiopia
Ethiopia is one of the oldest countries in Africa, the emergence of Ethiopian civilization dates back thousands of years. Due to migration and imperial expansion, it grew to include many other primarily Afro-Asiatic languages, Afro-Asiatic-spea ...
, was applied to the Southern Atlantic as late as the mid-19th century. During the Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafarin ...
, the Atlantic was also known to English cartographers as the Great Western Ocean.
The pond is a term often used by British and American speakers in reference to the Northern Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
, as a form of meiosis
Meiosis (; , since it is a reductional division) is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, such as sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately resu ...
, or ironic understatement. It is used mostly when referring to events or circumstances "on this side of the pond" or "on the other side of the pond", rather than to discuss the ocean itself. The term dates to 1640, first appearing in print in pamphlet released during the reign of Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
, and reproduced in 1869 in Nehemiah Wallington's ''Historical Notices of Events Occurring Chiefly in The Reign of Charles I'', where "great Pond" is used in reference to the Atlantic Ocean by Francis Windebank, Charles I's Secretary of State.
Extent and data
TheInternational Hydrographic Organization
The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) is an intergovernmental organisation representing hydrography. , the IHO comprised 98 Member States.
A principal aim of the IHO is to ensure that the world's seas, oceans and navigable waters a ...
(IHO) defined the limits of the oceans and seas in 1953, but some of these definitions have been revised since then and some are not used by various authorities, institutions, and countries, see for example the CIA World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print version is available ...
. Correspondingly, the extent and number of oceans and seas vary.
The Atlantic Ocean is bounded on the west by North and South America. It connects to the Arctic Ocean through the Denmark Strait, Greenland Sea
The Greenland Sea is a body of water that borders Greenland to the west, the Svalbard archipelago to the east, Fram Strait and the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Norwegian Sea and Iceland to the south. The Greenland Sea is often defined as p ...
, Norwegian Sea
The Norwegian Sea ( no, Norskehavet; is, Noregshaf; fo, Norskahavið) is a marginal sea, grouped with either the Atlantic Ocean or the Arctic Ocean, northwest of Norway between the North Sea and the Greenland Sea, adjoining the Barents Sea to ...
and Barents Sea
The Barents Sea ( , also ; no, Barentshavet, ; russian: Баренцево море, Barentsevo More) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located off the northern coasts of Norway and Russia and divided between Norwegian and Russian territo ...
. To the east, the boundaries of the ocean proper are Europe: the Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar ( ar, مضيق جبل طارق, Maḍīq Jabal Ṭāriq; es, Estrecho de Gibraltar, Archaic: Pillars of Hercules), also known as the Straits of Gibraltar, is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Medi ...
(where it connects with the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
—one of its marginal seas—and, in turn, the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
, both of which also touch upon Asia) and Africa.
In the southeast, the Atlantic merges into the Indian Ocean. The 20° East meridian, running south from Cape Agulhas to Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest contine ...
defines its border. In the 1953 definition it extends south to Antarctica, while in later maps it is bounded at the 60° parallel by the Southern Ocean.
The Atlantic has irregular coasts indented by numerous bays, gulfs and seas. These include the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
, Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
, Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico ...
, Davis Strait, Denmark Strait, part of the Drake Passage, Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of ...
, Labrador Sea
The Labrador Sea (French: ''mer du Labrador'', Danish: ''Labradorhavet'') is an arm of the North Atlantic Ocean between the Labrador Peninsula and Greenland. The sea is flanked by continental shelf, continental shelves to the southwest, northwest, ...
, Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
, North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
, Norwegian Sea
The Norwegian Sea ( no, Norskehavet; is, Noregshaf; fo, Norskahavið) is a marginal sea, grouped with either the Atlantic Ocean or the Arctic Ocean, northwest of Norway between the North Sea and the Greenland Sea, adjoining the Barents Sea to ...
, almost all of the Scotia Sea, and other tributary water bodies. Including these marginal seas the coast line of the Atlantic measures compared to for the Pacific.
Including its marginal seas, the Atlantic covers an area of or 23.5% of the global ocean and has a volume of or 23.3% of the total volume of the earth's oceans. Excluding its marginal seas, the Atlantic covers and has a volume of . The North Atlantic covers (11.5%) and the South Atlantic (11.1%). The average depth is and the maximum depth, the Milwaukee Deep
Milwaukee Deep, also known as the Milwaukee Depth, is part of the Puerto Rico Trench. Together with the surrounding area, known as Brownson Deep, the Milwaukee Deep forms an elongated depression that constitutes the floor of the trench. As the ...
in the Puerto Rico Trench, is .
Biggest seas in Atlantic Ocean
Top large seas: #Sargasso Sea
The Sargasso Sea () is a region of the Atlantic Ocean bounded by four currents forming an ocean gyre. Unlike all other regions called seas, it has no land boundaries. It is distinguished from other parts of the Atlantic Ocean by its charac ...
- 3.5 million km2
# Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico ...
- 2.754 million km2
# Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
- 2.510 million km2
# Gulf of Guinea
The Gulf of Guinea is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean from Cape Lopez in Gabon, north and west to Cape Palmas in Liberia. The intersection of the Equator and Prime Meridian (zero degrees latitude and longitude) is in the ...
- 2.35 million km2
# Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of ...
- 1.550 million km2
# Norwegian Sea
The Norwegian Sea ( no, Norskehavet; is, Noregshaf; fo, Norskahavið) is a marginal sea, grouped with either the Atlantic Ocean or the Arctic Ocean, northwest of Norway between the North Sea and the Greenland Sea, adjoining the Barents Sea to ...
- 1.383 million km2
# Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay ( crj, text=ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, translit=Wînipekw; crl, text=ᐐᓂᐹᒄ, translit=Wînipâkw; iu, text=ᑲᖏᖅᓱᐊᓗᒃ ᐃᓗᐊ, translit=Kangiqsualuk ilua or iu, text=ᑕᓯᐅᔭᕐᔪᐊᖅ, translit=Tasiujarjuaq; french: b ...
- 1.23 million km2
# Greenland Sea
The Greenland Sea is a body of water that borders Greenland to the west, the Svalbard archipelago to the east, Fram Strait and the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Norwegian Sea and Iceland to the south. The Greenland Sea is often defined as p ...
- 1.205 million km2
# Argentine Sea - 1 million km2
# Labrador Sea
The Labrador Sea (French: ''mer du Labrador'', Danish: ''Labradorhavet'') is an arm of the North Atlantic Ocean between the Labrador Peninsula and Greenland. The sea is flanked by continental shelf, continental shelves to the southwest, northwest, ...
- 841,000 km2
# Irminger Sea - 780,000 km2
# Baffin Bay
Baffin Bay ( Inuktitut: ''Saknirutiak Imanga''; kl, Avannaata Imaa; french: Baie de Baffin), located between Baffin Island and the west coast of Greenland, is defined by the International Hydrographic Organization as a marginal sea of the Arct ...
- 689,000 km2
# North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
- 575,000 km2
# Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
- 436,000 km2
# Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
- 377,000 km2
# Libyan Sea - 350,000 km2
# Levantine Sea
The Levantine Sea (Arabic: بحر الشام, tr, Levanten Denizi, el, Θάλασσα του Λεβάντε) is the easternmost part of the Mediterranean Sea.
Geography
The Levantine Sea is bordered by Turkey in the north and north-east co ...
- 320,000 km2
# Celtic Sea - 300,000 km2
# Tyrrhenian Sea
The Tyrrhenian Sea (; it, Mar Tirreno , french: Mer Tyrrhénienne , sc, Mare Tirrenu, co, Mari Tirrenu, scn, Mari Tirrenu, nap, Mare Tirreno) is part of the Mediterranean Sea off the western coast of Italy. It is named for the Tyrrhenian pe ...
- 275,000 km2
# Gulf of Saint Lawrence - 226,000 km2
# Bay of Biscay
The Bay of Biscay (), known in Spain as the Gulf of Biscay ( es, Golfo de Vizcaya, eu, Bizkaiko Golkoa), and in France and some border regions as the Gulf of Gascony (french: Golfe de Gascogne, oc, Golf de Gasconha, br, Pleg-mor Gwaskogn), ...
- 223,000 km2
# Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek language, Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish language, Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It ...
- 214,000 km2
# Ionian Sea
The Ionian Sea ( el, Ιόνιο Πέλαγος, ''Iónio Pélagos'' ; it, Mar Ionio ; al, Deti Jon ) is an elongated bay of the Mediterranean Sea. It is connected to the Adriatic Sea to the north, and is bounded by Southern Italy, including C ...
- 169,000 km2
# Balearic Sea
The Balearic Sea ( endotoponym: ''Mar Balear'' in Catalan and Spanish) is a body of water in the Mediterranean Sea between the Balearic Islands and the mainland of Spain. The Ebro River flows into this small sea.
Islands and archipelagoes
Th ...
- 150,000 km2
# Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
- 138,000 km2
# Gulf of Bothnia
The Gulf of Bothnia (; fi, Pohjanlahti; sv, Bottniska viken) is divided into the Bothnian Bay and Bothnian Sea, and it is the northernmost arm of the Baltic Sea, between Finland's west coast ( East Bothnia) and the Sweden's east coast (West ...
- 116,300 km2
# Sea of Crete
300px, Map of the Sea of Crete
The Sea of Crete (, ''Kritiko Pelagos''), or Cretan Sea, is a sea, part of the Aegean Sea, located in its southern extremity, with a total surface area of . The sea stretches to the north of the island of Crete, eas ...
- 95,000 km2
# Gulf of Maine
The Gulf of Maine is a large gulf of the Atlantic Ocean on the east coast of North America. It is bounded by Cape Cod at the eastern tip of Massachusetts in the southwest and by Cape Sable Island at the southern tip of Nova Scotia in the northeast ...
- 93,000 km2
# Ligurian Sea
The Ligurian Sea ( it, Mar Ligure; french: Mer Ligurienne; lij, Mâ Ligure) is an arm of the Mediterranean Sea. It lies between the Italian Riviera (Liguria) and the island of Corsica. The sea is thought to have been named after the ancient L ...
- 80,000 km2
# English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
- 75,000 km2
# James Bay
James Bay (french: Baie James; cr, ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, Wînipekw, dirty water) is a large body of water located on the southern end of Hudson Bay in Canada. Both bodies of water extend from the Arctic Ocean, of which James Bay is the southernmost par ...
- 68,300 km2
# Bothnian Sea
The Bothnian Sea ( sv, Bottenhavet; fi, Selkämeri) links the Bothnian Bay (also called the Bay of Bothnia) with the Baltic proper. Kvarken is situated between the two. Together, the Bothnian Sea and Bay make up a larger geographical entity, t ...
- 66,000 km2
# Gulf of Sidra
The Gulf of Sidra ( ar, خليج السدرة, Khalij as-Sidra, also known as the Gulf of Sirte ( ar, خليج سرت, Khalij Surt, is a body of water in the Mediterranean Sea on the northern coast of Libya, named after the oil port of Sidra or ...
- 57,000 km2
# Sea of the Hebrides - 47,000 km2
# Irish Sea
The Irish Sea or , gv, Y Keayn Yernagh, sco, Erse Sie, gd, Muir Èireann , Ulster-Scots: ''Airish Sea'', cy, Môr Iwerddon . is an extensive body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the Ce ...
- 46,000 km2
# Sea of Azov
The Sea of Azov ( Crimean Tatar: ''Azaq deñizi''; russian: Азовское море, Azovskoye more; uk, Азовське море, Azovs'ke more) is a sea in Eastern Europe connected to the Black Sea by the narrow (about ) Strait of Kerch, ...
- 39,000 km2
# Bothnian Bay - 36,800 km2
# Gulf of Venezuela
The Gulf of Venezuela is a gulf of the Caribbean Sea bounded by the Venezuelan states of Zulia and Falcón and by La Guajira Department, Colombia. The western side is formed by the Guajira Peninsula. A strait connects it with Maracaibo Lake to ...
- 17,840 km2
# Bay of Campeche
The Bay of Campeche ( es, Bahía de Campeche), or Campeche Sound, is a bight (geography), bight in the southern area of the Gulf of Mexico, forming the north side of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec. It is surrounded on three sides by the Mexico, Mexic ...
- 16,000 km2
# Gulf of Lion
The Gulf of Lion or Gulf of Lions ( French: ''golfe du Lion'', Spanish: ''golfo de León'', Italian: ''Golfo del Leone'', Occitan: ''golf del/dau Leon'', Catalan: ''golf del Lleó'', Medieval Latin: ''sinus Leonis'', ''mare Leonis'', Classical L ...
- 15,000 km2
# Sea of Marmara - 11,350 km2
# Wadden Sea
The Wadden Sea ( nl, Waddenzee ; german: Wattenmeer; nds, Wattensee or ; da, Vadehavet; fy, Waadsee, longname=yes; frr, di Heef) is an intertidal zone in the southeastern part of the North Sea. It lies between the coast of northwestern conti ...
- 10,000 km2
# Archipelago Sea
The Archipelago Sea ( fi, Saaristomeri, sv, Skärgårdshavet) is a part of the Baltic Sea between the Gulf of Bothnia, the Gulf of Finland and the Sea of Åland, within Finnish territorial waters. By some definitions it contains the largest ar ...
- 8,300 km2
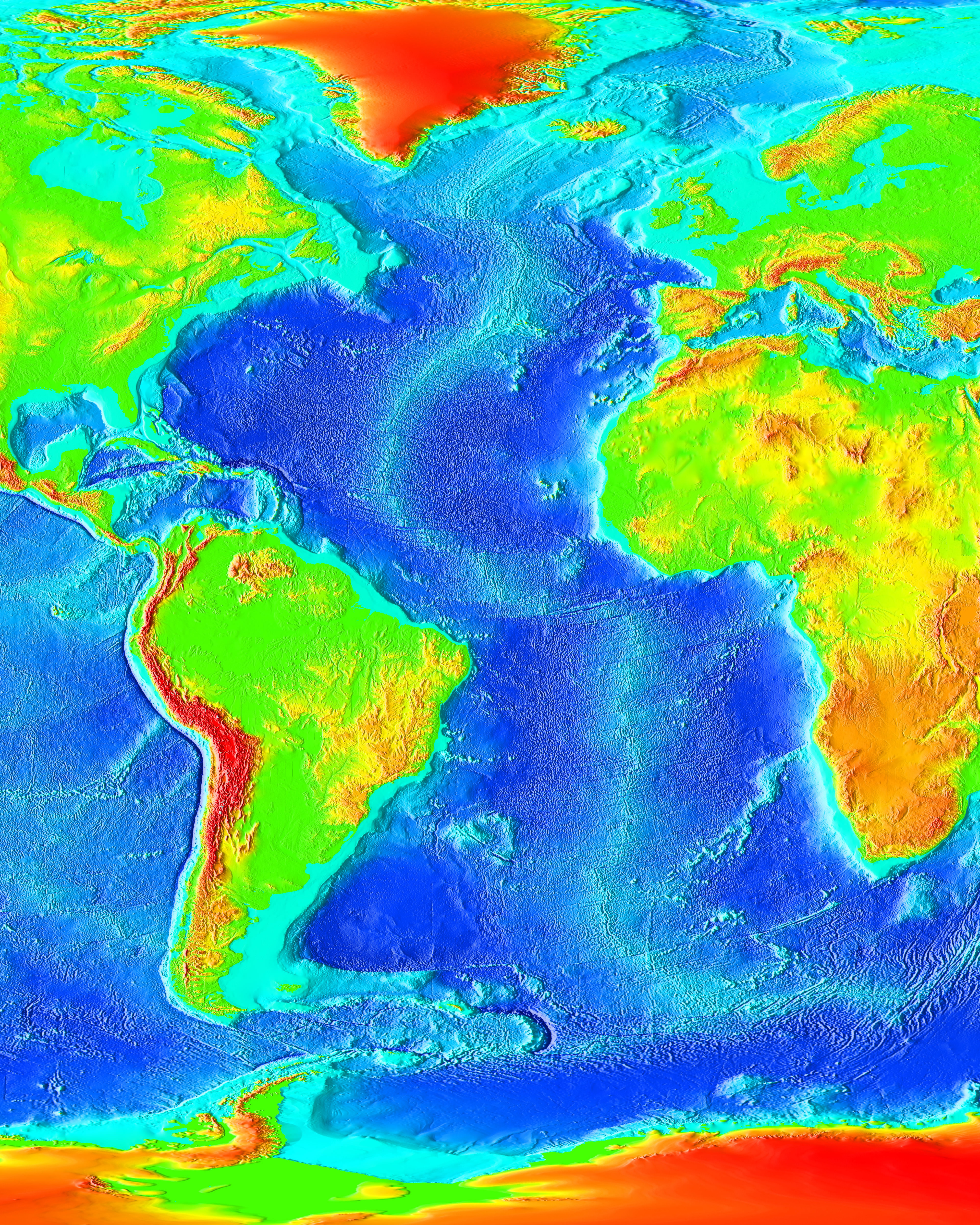
Bathymetry
 The
The bathymetry
Bathymetry (; ) is the study of underwater depth of ocean floors (''seabed topography''), lake floors, or river floors. In other words, bathymetry is the underwater equivalent to hypsometry or topography. The first recorded evidence of water de ...
of the Atlantic is dominated by a submarine mountain range called the Mid-Atlantic Ridge
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is a mid-ocean ridge (a divergent or constructive plate boundary) located along the floor of the Atlantic Ocean, and part of the longest mountain range in the world. In the North Atlantic, the ridge separates the North Ame ...
(MAR). It runs from 87°N or south of the North Pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. It is called the True North Pole to distinguish from the Mag ...
to the subantarctic Bouvet Island at 54°S.
Mid-Atlantic Ridge
The MAR divides the Atlantic longitudinally into two halves, in each of which a series of basins are delimited by secondary, transverse ridges. The MAR reaches above along most of its length, but is interrupted by larger transform faults at two places: theRomanche Trench
The Romanche Trench, also called the ''Romanche Furrow'' or ''Romanche Gap'', is the third deepest of the major trenches of the Atlantic Ocean, after the Puerto Rico Trench and the South Sandwich Trench. It bisects the Mid-Atlantic Ridge (MAR) ju ...
near the Equator and the Gibbs Fracture Zone
Charlie-Gibbs Fracture Zone is a system of two parallel fracture zones. It is the most prominent interruption of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between the Azores and Iceland. It can be traced over more than 2000 kilometers, all the way from north-eas ...
at 53°N. The MAR is a barrier for bottom water, but at these two transform faults deep water currents can pass from one side to the other.
The MAR rises above the surrounding ocean floor and its rift valley is the divergent boundary
In plate tectonics, a divergent boundary or divergent plate boundary (also known as a constructive boundary or an extensional boundary) is a linear feature that exists between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other. Divergent b ...
between the North American
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Ca ...
and Eurasian
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago ...
plates in the North Atlantic and the South American and African
African or Africans may refer to:
* Anything from or pertaining to the continent of Africa:
** People who are native to Africa, descendants of natives of Africa, or individuals who trace their ancestry to indigenous inhabitants of Africa
*** Ethn ...
plates in the South Atlantic. The MAR produces basaltic volcanoes in Eyjafjallajökull, Iceland, and pillow lava on the ocean floor. The depth of water at the apex of the ridge is less than in most places, while the bottom of the ridge is three times as deep.
The MAR is intersected by two perpendicular ridges: the Azores–Gibraltar Transform Fault
The Azores–Gibraltar Transform Fault (AGFZ), also called a fault zone and a fracture zone, is a major seismic zone in the Eastern Atlantic Ocean between the Azores and the Strait of Gibraltar. It is the product of the complex interaction between ...
, the boundary between the Nubian
Nubian may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Nubia, a region along the Nile river in Southern Egypt and northern Sudan.
*Nubian people
*Nubian languages
*Anglo-Nubian goat, a breed of goat
* Nubian ibex
* , several ships of the Britis ...
and Eurasian plates, intersects the MAR at the Azores Triple Junction, on either side of the Azores microplate, near the 40°N. A much vaguer, nameless boundary, between the North American
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Ca ...
and South American plates, intersects the MAR near or just north of the Fifteen-Twenty Fracture Zone, approximately at 16°N.
In the 1870s, the ''Challenger'' expedition discovered parts of what is now known as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, or:
The remainder of the ridge was discovered in the 1920s by the German ''Meteor'' expedition using echo-sounding equipment. The exploration of the MAR in the 1950s led to the general acceptance of seafloor spreading and plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large ...
.
Most of the MAR runs under water but where it reaches the surfaces it has produced volcanic islands. While nine of these have collectively been nominated a World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
for their geological value, four of them are considered of "Outstanding Universal Value" based on their cultural and natural criteria: Þingvellir, Iceland; Landscape of the Pico Island Vineyard Culture, Portugal; Gough and Inaccessible Islands, United Kingdom; and Brazilian Atlantic Islands: Fernando de Noronha and Atol das Rocas Reserves, Brazil.
Ocean floor
Continental shelves in the Atlantic are wide off Newfoundland, southernmost South America, and north-eastern Europe. In the western Atlanticcarbonate platform
A carbonate platform is a sedimentary body which possesses topographic relief, and is composed of autochthonic calcareous deposits. Platform growth is mediated by sessile organisms whose skeletons build up the reef or by organisms (usually microb ...
s dominate large areas, for example, the Blake Plateau
The Blake Plateau lies in the western Atlantic Ocean off the southeastern United States coasts of North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia and Florida. The Blake Plateau lies between the North American continental shelf and the deep ocean basin ...
and Bermuda Rise.
The Atlantic is surrounded by passive margins except at a few locations where active margin
Active may refer to:
Music
* ''Active'' (album), a 1992 album by Casiopea
* Active Records, a record label
Ships
* ''Active'' (ship), several commercial ships by that name
* HMS ''Active'', the name of various ships of the British Royal ...
s form deep trenches: the Puerto Rico Trench ( maximum depth) in the western Atlantic and South Sandwich Trench () in the South Atlantic. There are numerous submarine canyons off north-eastern North America, western Europe, and north-western Africa. Some of these canyons extend along the continental rises and farther into the abyssal plains as deep-sea channels.
In 1922, a historic moment in cartography and oceanography occurred. The USS ''Stewart'' used a Navy Sonic Depth Finder to draw a continuous map across the bed of the Atlantic. This involved little guesswork because the idea of sonar is straightforward with pulses being sent from the vessel, which bounce off the ocean floor, then return to the vessel. The deep ocean floor is thought to be fairly flat with occasional deeps, abyssal plain
An abyssal plain is an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor, usually found at depths between and . Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth's surface. T ...
s, trenches, seamount
A seamount is a large geologic landform that rises from the ocean floor that does not reach to the water's surface (sea level), and thus is not an island, islet or cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abru ...
s, basins
Basin may refer to:
Geography and geology
* Depression (geology)
** Back-arc basin, a submarine feature associated with island arcs and subduction zones
** Debris basin, designed to prevent damage from debris flow
** Drainage basin (hydrology), a ...
, plateaus, canyons, and some guyots. Various shelves along the margins of the continents constitute about 11% of the bottom topography with few deep channels cut across the continental rise.
The mean depth between 60°N
The 60th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 60 degrees north of Earth's equator. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean.
Although it lies approximately twice as far away from the Equator as ...
and 60°S is , or close to the average for the global ocean, with a modal depth between .
In the South Atlantic the Walvis Ridge and Rio Grande Rise form barriers to ocean currents.
The Laurentian Abyss The Laurentian Fan or Laurentian Abyss is an underwater depression off the eastern coast of Canada in the Atlantic Ocean. Not a trench, but more of an "underwater valley", it is estimated to be at most ~19,685 feet (3.7 miles; 6.0 km) in depth. The ...
is found off the eastern coast of Canada.
Water characteristics
 Surface water temperatures, which vary with latitude, current systems, and season and reflect the latitudinal distribution of solar energy, range from below to over . Maximum temperatures occur north of the equator, and minimum values are found in the polar regions. In the middle latitudes, the area of maximum temperature variations, values may vary by .
From October to June the surface is usually covered with sea ice in the
Surface water temperatures, which vary with latitude, current systems, and season and reflect the latitudinal distribution of solar energy, range from below to over . Maximum temperatures occur north of the equator, and minimum values are found in the polar regions. In the middle latitudes, the area of maximum temperature variations, values may vary by .
From October to June the surface is usually covered with sea ice in the Labrador Sea
The Labrador Sea (French: ''mer du Labrador'', Danish: ''Labradorhavet'') is an arm of the North Atlantic Ocean between the Labrador Peninsula and Greenland. The sea is flanked by continental shelf, continental shelves to the southwest, northwest, ...
, Denmark Strait, and Baltic Sea.
The Coriolis effect circulates North Atlantic water in a clockwise direction, whereas South Atlantic water circulates counter-clockwise. The south tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravity, gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide t ...
s in the Atlantic Ocean are semi-diurnal; that is, two high tides occur every 24 lunar hours. In latitudes above 40° North some east–west oscillation, known as the North Atlantic oscillation
The North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) is a weather phenomenon over the North Atlantic Ocean of fluctuations in the difference of atmospheric pressure at sea level (SLP) between the Icelandic Low and the Azores High. Through fluctuations in the ...
, occurs.
Salinity
On average, the Atlantic is the saltiest major ocean; surface watersalinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal ...
in the open ocean ranges from 33 to 37 parts per thousand (3.3–3.7%) by mass and varies with latitude and season. Evaporation, precipitation, river inflow and sea ice
Sea ice arises as seawater freezes. Because ice is less dense than water, it floats on the ocean's surface (as does fresh water ice, which has an even lower density). Sea ice covers about 7% of the Earth's surface and about 12% of the world's oce ...
melting influence surface salinity values. Although the lowest salinity values are just north of the equator (because of heavy tropical rainfall), in general, the lowest values are in the high latitudes and along coasts where large rivers enter. Maximum salinity values occur at about 25° north and south
South is one of the cardinal directions or Points of the compass, compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Pro ...
, in subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical zone, geographical and Köppen climate classification, climate zones to the Northern Hemisphere, north and Southern Hemisphere, south of the tropics. Geographically part of the Geographical z ...
regions with low rainfall and high evaporation.
The high surface salinity in the Atlantic, on which the Atlantic thermohaline circulation is dependent, is maintained by two processes: the Agulhas Leakage/Rings, which brings salty Indian Ocean waters into the South Atlantic, and the "Atmospheric Bridge", which evaporates subtropical Atlantic waters and exports it to the Pacific.
Water masses
The Atlantic Ocean consists of four major, upper water masses with distinct temperature and salinity. The Atlantic Subarctic Upper Water in the northernmost North Atlantic is the source for Subarctic Intermediate Water and North Atlantic Intermediate Water. North Atlantic Central Water can be divided into the Eastern and Western North Atlantic central Water since the western part is strongly affected by the Gulf Stream and therefore the upper layer is closer to underlying fresher subpolar intermediate water. The eastern water is saltier because of its proximity to Mediterranean Water. North Atlantic Central Water flows into South Atlantic Central Water at 15°N. There are five intermediate waters: four low-salinity waters formed at subpolar latitudes and one high-salinity formed through evaporation. Arctic Intermediate Water, flows from north to become the source for North Atlantic Deep Water south of the Greenland-Scotland sill. These two intermediate waters have different salinity in the western and eastern basins. The wide range of salinities in the North Atlantic is caused by the asymmetry of the northern subtropical gyre and the large number of contributions from a wide range of sources: Labrador Sea, Norwegian-Greenland Sea, Mediterranean, and South Atlantic Intermediate Water. The North Atlantic Deep Water (NADW) is a complex of four water masses, two that form by deep convection in the open ocean — Classical and Upper Labrador Sea Water — and two that form from the inflow of dense water across the Greenland-Iceland-Scotland sill — Denmark Strait and Iceland-Scotland Overflow Water. Along its path across Earth the composition of the NADW is affected by other water masses, especially Antarctic Bottom Water and Mediterranean Overflow Water. The NADW is fed by a flow of warm shallow water into the northern North Atlantic which is responsible for the anomalous warm climate in Europe. Changes in the formation of NADW have been linked to global climate changes in the past. Since man-made substances were introduced into the environment, the path of the NADW can be traced throughout its course by measuring tritium and radiocarbon from nuclear weapon tests in the 1960s andCFCs
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are fully or partly halogenated hydrocarbons that contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), chlorine (Cl), and fluorine (F), produced as volatile derivatives of methane, ethane, and propan ...
.
Gyres
The clockwise warm-waterNorth Atlantic Gyre
The North Atlantic Gyre of the Atlantic Ocean is one of five great oceanic gyres. It is a circular ocean current, with offshoot eddies and sub-gyres, across the North Atlantic from the Intertropical Convergence Zone (calms or doldrums) to the part ...
occupies the northern Atlantic, and the counter-clockwise warm-water South Atlantic Gyre appears in the southern Atlantic.
In the North Atlantic, surface circulation is dominated by three inter-connected currents: the Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Current, North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida a ...
which flows north-east from the North American coast at Cape Hatteras; the North Atlantic Current, a branch of the Gulf Stream which flows northward from the Grand Banks
The Grand Banks of Newfoundland are a series of underwater plateaus south-east of the island of Newfoundland on the North American continental shelf. The Grand Banks are one of the world's richest fishing grounds, supporting Atlantic cod, swordf ...
; and the Subpolar Front, an extension of the North Atlantic Current, a wide, vaguely defined region separating the subtropical gyre from the subpolar gyre. This system of currents transport warm water into the North Atlantic, without which temperatures in the North Atlantic and Europe would plunge dramatically.
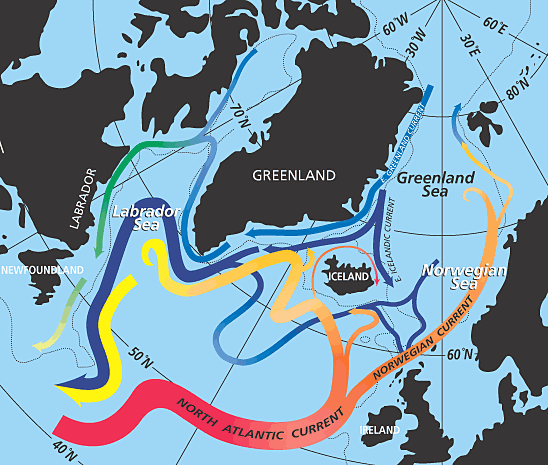
 North of the North Atlantic Gyre, the cyclonic
North of the North Atlantic Gyre, the cyclonic North Atlantic Subpolar Gyre
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north'' is ...
plays a key role in climate variability. It is governed by ocean currents from marginal seas and regional topography, rather than being steered by wind, both in the deep ocean and at sea level.
The subpolar gyre forms an important part of the global thermohaline circulation. Its eastern portion includes eddying branches of the North Atlantic Current which transport warm, saline waters from the subtropics to the north-eastern Atlantic. There this water is cooled during winter and forms return currents that merge along the eastern continental slope of Greenland where they form an intense (40–50 Sv) current which flows around the continental margins of the Labrador Sea
The Labrador Sea (French: ''mer du Labrador'', Danish: ''Labradorhavet'') is an arm of the North Atlantic Ocean between the Labrador Peninsula and Greenland. The sea is flanked by continental shelf, continental shelves to the southwest, northwest, ...
. A third of this water becomes part of the deep portion of the North Atlantic Deep Water (NADW). The NADW, in its turn, feeds the meridional overturning circulation (MOC), the northward heat transport of which is threatened by anthropogenic climate change. Large variations in the subpolar gyre on a decade-century scale, associated with the North Atlantic oscillation
The North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) is a weather phenomenon over the North Atlantic Ocean of fluctuations in the difference of atmospheric pressure at sea level (SLP) between the Icelandic Low and the Azores High. Through fluctuations in the ...
, are especially pronounced in Labrador Sea Water, the upper layers of the MOC.
The South Atlantic is dominated by the anti-cyclonic southern subtropical gyre. The South Atlantic Central Water
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþaz ...
originates in this gyre, while Antarctic Intermediate Water
Antarctic Intermediate Water (AAIW) is a cold, relatively low salinity water mass found mostly at intermediate depths in the Southern Ocean. The AAIW is formed at the ocean surface in the Antarctic Convergence zone or more commonly called the Ant ...
originates in the upper layers of the circumpolar region, near the Drake Passage and the Falkland Islands. Both these currents receive some contribution from the Indian Ocean. On the African east coast, the small cyclonic Angola Gyre
, national_anthem = " Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordina ...
lies embedded in the large subtropical gyre.
The southern subtropical gyre is partly masked by a wind-induced Ekman layer. The residence time of the gyre is 4.4–8.5 years. North Atlantic Deep Water flows southward below the thermocline of the subtropical gyre.
Sargasso Sea
The Sargasso Sea in the western North Atlantic can be defined as the area where two species of ''Sargassum
''Sargassum'' is a genus of brown (class Phaeophyceae) macroalgae (seaweed) in the order Fucales. Numerous species are distributed throughout the temperate and tropical oceans of the world, where they generally inhabit shallow water and coral re ...
'' (''S. fluitans'' and ''natans'') float, an area wide and encircled by the Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Current, North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida a ...
, North Atlantic Drift, and North Equatorial Current
The North Equatorial Current (NEC) is a westward wind-driven current mostly located near the equator, but the location varies from different oceans. The NEC in the Pacific and the Atlantic is about 5°-20°N, while the NEC in the Indian Ocean is v ...
. This population of seaweed probably originated from Tertiary ancestors on the European shores of the former Tethys Ocean and has, if so, maintained itself by vegetative growth
Vegetative phase change is the juvenile-to- adult transition in plants.
This transition is distinct from the reproductive transition and is most prolonged and pronounced in woody species. Manipulating phase change may be an important avenue for ...
, floating in the ocean for millions of years.
Other species endemic to the Sargasso Sea include the sargassum fish, a predator with algae-like appendages which hovers motionless among the ''Sargassum''. Fossils of similar fishes have been found in fossil bays of the former Tethys Ocean, in what is now the Carpathian
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The range stretches ...
region, that were similar to the Sargasso Sea. It is possible that the population in the Sargasso Sea migrated to the Atlantic as the Tethys closed at the end of the Miocene around 17 Ma. The origin of the Sargasso fauna and flora remained enigmatic for centuries. The fossils found in the Carpathians in the mid-20th century often called the "quasi-Sargasso assemblage", finally showed that this assemblage originated in the Carpathian Basin from where it migrated over Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
to the Central Atlantic where it evolved into modern species of the Sargasso Sea.
The location of the spawning ground for European eels remained unknown for decades. In the early 19th century it was discovered that the southern Sargasso Sea is the spawning ground for both the European
European, or Europeans, or Europeneans, may refer to:
In general
* ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to Europe
** Ethnic groups in Europe
** Demographics of Europe
** European cuisine, the cuisines of Europe ...
and American eel
The American eel (''Anguilla rostrata'') is a facultative catadromous fish found on the eastern coast of North America. Freshwater eels are fish belonging to the elopomorph superorder, a group of phylogenetically ancient teleosts. The America ...
and that the former migrate more than and the latter . Ocean currents such as the Gulf Stream transport eel larvae from the Sargasso Sea to foraging areas in North America, Europe, and Northern Africa. Recent but disputed research suggests that eels possibly use Earth's magnetic field
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. The magnetic f ...
to navigate through the ocean both as larvae and as adults.
Climate
 Climate is influenced by the temperatures of the surface waters and water currents as well as winds. Because of the ocean's great capacity to store and release heat, maritime climates are more moderate and have less extreme seasonal variations than inland climates.
Climate is influenced by the temperatures of the surface waters and water currents as well as winds. Because of the ocean's great capacity to store and release heat, maritime climates are more moderate and have less extreme seasonal variations than inland climates. Precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
can be approximated from coastal weather data and air temperature from water temperatures.
The oceans are the major source of the atmospheric moisture that is obtained through evaporation. Climatic zones vary with latitude; the warmest zones stretch across the Atlantic north of the equator. The coldest zones are in high latitudes, with the coldest regions corresponding to the areas covered by sea ice. Ocean currents influence the climate by transporting warm and cold waters to other regions. The winds that are cooled or warmed when blowing over these currents influence adjacent land areas.
The Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Current, North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida a ...
and its northern extension towards Europe, the North Atlantic Drift is thought to have at least some influence on climate. For example, the Gulf Stream helps moderate winter temperatures along the coastline of southeastern North America, keeping it warmer in winter along the coast than inland areas. The Gulf Stream also keeps extreme temperatures from occurring on the Florida Peninsula. In the higher latitudes, the North Atlantic Drift, warms the atmosphere over the oceans, keeping the British Isles and north-western Europe mild and cloudy, and not severely cold in winter, like other locations at the same high latitude. The cold water currents contribute to heavy fog off the coast of eastern Canada (the Grand Banks of Newfoundland
The Grand Banks of Newfoundland are a series of underwater plateaus south-east of the island of Newfoundland on the North American continental shelf. The Grand Banks are one of the world's richest fishing grounds, supporting Atlantic cod, swordf ...
area) and Africa's north-western coast. In general, winds transport moisture and air over land areas.
Natural hazards
 Every winter, the
Every winter, the Icelandic Low
The Icelandic Low is a semi-permanent centre of low atmospheric pressure found between Iceland and southern Greenland and extending in the Northern Hemisphere winter into the Barents Sea. In the summer, it weakens and splits into two centres, one ...
produces frequent storms. Iceberg
An iceberg is a piece of freshwater ice more than 15 m long that has broken off a glacier or an ice shelf and is floating freely in open (salt) water. Smaller chunks of floating glacially-derived ice are called "growlers" or "bergy bits". The ...
s are common from early February to the end of July across the shipping lanes near the Grand Banks of Newfoundland
The Grand Banks of Newfoundland are a series of underwater plateaus south-east of the island of Newfoundland on the North American continental shelf. The Grand Banks are one of the world's richest fishing grounds, supporting Atlantic cod, swordf ...
. The ice season is longer in the polar regions, but there is little shipping in those areas.
Hurricanes are a hazard in the western parts of the North Atlantic during the summer and autumn. Due to a consistently strong wind shear and a weak Intertropical Convergence Zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. It encircles Earth near the thermal e ...
, South Atlantic tropical cyclone
South Atlantic tropical cyclones are unusual weather events that occur in the Southern Hemisphere. Strong wind shear, which disrupts the formation of cyclones, as well as a lack of weather disturbances favorable for development in the South Atl ...
s are rare.
Geology and plate tectonics
The Atlantic Ocean is underlain mostly by densemafic
A mafic mineral or rock is a silicate mineral or igneous rock rich in magnesium and iron. Most mafic minerals are dark in color, and common rock-forming mafic minerals include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Common mafic rocks include ...
oceanic crust made up of basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
and gabbro
Gabbro () is a phaneritic (coarse-grained), mafic intrusive igneous rock formed from the slow cooling of magnesium-rich and iron-rich magma into a holocrystalline mass deep beneath the Earth's surface. Slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro is che ...
and overlain by fine clay, silt and siliceous ooze on the abyssal plain. The continental margins and continental shelf mark lower density, but greater thickness felsic
In geology, felsic is a modifier describing igneous rocks that are relatively rich in elements that form feldspar and quartz.Marshak, Stephen, 2009, ''Essentials of Geology,'' W. W. Norton & Company, 3rd ed. It is contrasted with mafic rocks, whi ...
continental rock that is often much older than that of the seafloor. The oldest oceanic crust in the Atlantic is up to 145 million years and situated off the west coast of Africa and east coast of North America, or on either side of the South Atlantic.
In many places, the continental shelf and continental slope are covered in thick sedimentary layers. For instance, on the North American side of the ocean, large carbonate deposits formed in warm shallow waters such as Florida and the Bahamas, while coarse river outwash sands and silt are common in shallow shelf areas like the Georges Bank
Georges Bank (formerly known as St. Georges Bank) is a large elevated area of the sea floor between Cape Cod, Massachusetts (United States), and Cape Sable Island, Nova Scotia (Canada). It separates the Gulf of Maine from the Atlantic Ocean.
Th ...
. Coarse sand, boulders, and rocks were transported into some areas, such as off the coast of Nova Scotia or the Gulf of Maine
The Gulf of Maine is a large gulf of the Atlantic Ocean on the east coast of North America. It is bounded by Cape Cod at the eastern tip of Massachusetts in the southwest and by Cape Sable Island at the southern tip of Nova Scotia in the northeast ...
during the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
ice ages.
Central Atlantic
The break-up of Pangaea began in the Central Atlantic, between North America and Northwest Africa, where rift basins opened during the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic. This period also saw the first stages of the uplift of the Atlas Mountains. The exact timing is controversial with estimates ranging from 200 to 170 Ma. The opening of the Atlantic Ocean coincided with the initial break-up of the supercontinent Pangaea, both of which were initiated by the eruption of the Central Atlantic Magmatic Province (CAMP), one of the most extensive and voluminous large igneous provinces in Earth's history associated with the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, one of Earth's majorextinction event
An extinction event (also known as a mass extinction or biotic crisis) is a widespread and rapid decrease in the biodiversity on Earth. Such an event is identified by a sharp change in the diversity and abundance of multicellular organisms. I ...
s.
Theoliitic dikes
Dyke (UK) or dike (US) may refer to:
General uses
* Dyke (slang), a slang word meaning "lesbian"
* Dike (geology), a subvertical sheet-like intrusion of magma or sediment
* Dike (mythology), ''Dikē'', the Greek goddess of moral justice
* Dikes, ...
, sills, and lava flows from the CAMP eruption at 200 Ma have been found in West Africa, eastern North America, and northern South America. The extent of the volcanism has been estimated to of which covered what is now northern and central Brazil.
The formation of the Central American Isthmus closed the Central American Seaway
The Central American Seaway (also known as the Panamanic Seaway, Inter-American Seaway and Proto-Caribbean Seaway) was a body of water that once separated North America from South America. It formed during the Jurassic (200–154 Ma) during the br ...
at the end of the Pliocene 2.8 Ma ago. The formation of the isthmus resulted in the migration and extinction of many land-living animals, known as the Great American Interchange
The Great American Biotic Interchange (commonly abbreviated as GABI), also known as the Great American Interchange and the Great American Faunal Interchange, was an important late Cenozoic paleozoogeographic biotic interchange event in which lan ...
, but the closure of the seaway resulted in a "Great American Schism" as it affected ocean currents, salinity, and temperatures in both the Atlantic and Pacific. Marine organisms on both sides of the isthmus became isolated and either diverged or went extinct.
Geologically, the Northern Atlantic is the area delimited to the south by two conjugate margins, Newfoundland and Iberia, and to the north by the Arctic Eurasian Basin. The opening of the Northern Atlantic closely followed the margins of its predecessor, the
Iapetus Ocean
The Iapetus Ocean (; ) was an ocean that existed in the late Neoproterozoic and early Paleozoic eras of the geologic timescale (between 600 and 400 million years ago). The Iapetus Ocean was situated in the southern hemisphere, between the paleoco ...
, and spread from the Central Atlantic in six stages: Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
–Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
, Porcupine
Porcupines are large rodents with coats of sharp spines, or quills, that protect them against predation. The term covers two families of animals: the Old World porcupines of family Hystricidae, and the New World porcupines of family, Erethizont ...
–North America, Eurasia–Greenland, Eurasia–North America. Active and inactive spreading systems in this area are marked by the interaction with the Iceland hotspot
The Iceland hotspot is a hotspot which is partly responsible for the high volcanic activity which has formed the Iceland Plateau and the island of Iceland.
Iceland is one of the most active volcanic regions in the world, with eruptions occur ...
.
Seafloor spreading led to the extension of the crust and formations of troughs and sedimentary basins. The Rockall Trough opened between 105 and 84 million years ago although along the rift failed along with one leading into the Bay of Biscay
The Bay of Biscay (), known in Spain as the Gulf of Biscay ( es, Golfo de Vizcaya, eu, Bizkaiko Golkoa), and in France and some border regions as the Gulf of Gascony (french: Golfe de Gascogne, oc, Golf de Gasconha, br, Pleg-mor Gwaskogn), ...
.
Spreading began opening the Labrador Sea
The Labrador Sea (French: ''mer du Labrador'', Danish: ''Labradorhavet'') is an arm of the North Atlantic Ocean between the Labrador Peninsula and Greenland. The sea is flanked by continental shelf, continental shelves to the southwest, northwest, ...
around 61 million years ago, continuing until 36 million years ago. Geologists distinguish two magmatic phases. One from 62 to 58 million years ago predates the separation of Greenland from northern Europe while the second from 56 to 52 million years ago happened as the separation occurred.
Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its s ...
began to form 62 million years ago due to a particularly concentrated mantle plume. Large quantities of basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
erupted at this time period are found on Baffin Island, Greenland, the Faroe Islands, and Scotland, with ash falls in Western Europe acting as a stratigraphic marker. The opening of the North Atlantic caused significant uplift of continental crust along the coast. For instance, in spite of 7 km thick basalt, Gunnbjorn Field in East Greenland is the highest point on the island, elevated enough that it exposes older Mesozoic sedimentary rocks at its base, similar to old lava fields above sedimentary rocks in the uplifted Hebrides of western Scotland.
The North Atlantic Ocean contains about 810 seamount
A seamount is a large geologic landform that rises from the ocean floor that does not reach to the water's surface (sea level), and thus is not an island, islet or cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abru ...
s, most of them situated along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. The OSPAR
The Convention for the Protection of the Marine Environment of the North-East Atlantic or OSPAR Convention is the current legislative instrument regulating international cooperation on environmental protection in the North-East Atlantic. Work ...
database (Convention for the Protection of the Marine Environment of the North-East Atlantic) mentions 104 seamounts: 74 within the national Exclusive economic zone. Of these seamounts, 46 are located close to the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
.
South Atlantic
West Gondwana (South America and Africa) broke up in the Early Cretaceous to form the South Atlantic. The apparent fit between the coastlines of the two continents was noted on the first maps that included the South Atlantic and it was also the subject of the first computer-assisted plate tectonic reconstructions in 1965. This magnificent fit, however, has since then proven problematic and later reconstructions have introduced various deformation zones along the shorelines to accommodate the northward-propagating break-up. Intra-continental rifts and deformations have also been introduced to subdivide both continental plates into sub-plates. Geologically the South Atlantic can be divided into four segments: Equatorial segment, from 10°N to the Romanche Fracture Zone (RFZ); Central segment, from RFZ to Florianopolis Fracture Zone (FFZ, north of Walvis Ridge and Rio Grande Rise); Southern segment, from FFZ to the Agulhas-Falkland Fracture Zone (AFFZ); and Falkland segment, south of AFFZ. In the southern segment the Early Cretaceous (133–130 Ma) intensive magmatism of the Paraná–Etendeka Large Igneous Province produced by theTristan hotspot
The Tristan hotspot is a volcanic hotspot which is responsible for the volcanic activity which forms the volcanoes in the southern Atlantic Ocean. It is thought to have formed the island of Tristan da Cunha and the Walvis Ridge on the African Plat ...
resulted in an estimated volume of . It covered an area of in Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay and in Africa. Dyke swarms in Brazil, Angola, eastern Paraguay, and Namibia, however, suggest the LIP originally covered a much larger area and also indicate failed rifts in all these areas. Associated offshore basaltic flows reach as far south as the Falkland Islands and South Africa. Traces of magmatism in both offshore and onshore basins in the central and southern segments have been dated to 147–49 Ma with two peaks between 143 and 121 Ma and 90–60 Ma.
In the Falkland segment rifting began with dextral movements between the Patagonia and Colorado sub-plates between the Early Jurassic (190 Ma) and the Early Cretaceous (126.7 Ma). Around 150 Ma sea-floor spreading propagated northward into the southern segment. No later than 130 Ma rifting had reached the Walvis Ridge–Rio Grande Rise.
In the central segment rifting started to break Africa in two by opening the Benue Trough around 118 Ma. Rifting in the central segment, however, coincided with the Cretaceous Normal Superchron
A geomagnetic reversal is a change in a planet's magnetic field such that the positions of magnetic north and magnetic south are interchanged (not to be confused with geographic north and geographic south). The Earth's field has alternated b ...
(also known as the Cretaceous quiet period), a 40 Ma period without magnetic reversals, which makes it difficult to date sea-floor spreading in this segment.
The equatorial segment is the last phase of the break-up, but, because it is located on the Equator, magnetic anomalies cannot be used for dating. Various estimates date the propagation of sea-floor spreading in this segment and consequent opening of the Equatorial Atlantic Gateway (EAG) to the period 120–96 Ma. This final stage, nevertheless, coincided with or resulted in the end of continental extension in Africa.
About 50 Ma the opening of the Drake Passage resulted from a change in the motions and separation rate of the South American and Antarctic plates. First small ocean basins opened and a shallow gateway appeared during the Middle Eocene. 34–30 Ma a deeper seaway developed, followed by an Eocene–Oligocene climatic deterioration and the growth of the Antarctic ice sheet
The Antarctic ice sheet is one of the two polar ice caps of Earth. It covers about 98% of the Antarctic continent and is the largest single mass of ice on Earth, with an average thickness of over 2 kilometers. It covers an area of almost and ...
.
Closure of the Atlantic
An embryonic subduction margin is potentially developing west of Gibraltar. TheGibraltar Arc
The Gibraltar Arc is a geological region corresponding to an arcuate orogen surrounding the Alboran Sea, between the Iberian Peninsula and Africa. It consists of the Betic Cordillera (south Spain), and the Rif (North Morocco). The Gibraltar Arc is ...
in the western Mediterranean is migrating westward into the Central Atlantic where it joins the converging African and Eurasian plates. Together these three tectonic forces are slowly developing into a new subduction system in the eastern Atlantic Basin. Meanwhile, the Scotia Arc and Caribbean Plate
The Caribbean Plate is a mostly oceanic tectonic plate underlying Central America and the Caribbean Sea off the north coast of South America.
Roughly 3.2 million square kilometers (1.2 million square miles) in area, the Caribbean Plate borders ...
in the western Atlantic Basin are eastward-propagating subduction systems that might, together with the Gibraltar system, represent the beginning of the closure of the Atlantic Ocean and the final stage of the Atlantic Wilson cycle
The Wilson Cycle is a model that describes the opening and closing of ocean basins and the subduction and divergence of tectonic plates during the assembly and disassembly of supercontinents. A classic example of the Wilson Cycle is the opening an ...
.
History
Human origin
Humans evolved in Africa; first by diverging from other apes around 7 mya; then developing stone tools around 2.6 mya; to finally evolve asmodern humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, an ...
around 200 kya. The earliest evidence for the complex behavior associated with this behavioral modernity has been found in the Greater Cape Floristic Region (GCFR) along the coast of South Africa. During the latest glacial stages, the now-submerged plains of the Agulhas Bank were exposed above sea level, extending the South African coastline farther south by hundreds of kilometers. A small population of modern humans — probably fewer than a thousand reproducing individuals — survived glacial maxima by exploring the high diversity offered by these Palaeo-Agulhas plains. The GCFR is delimited to the north by the Cape Fold Belt
The Cape Fold Belt is a fold and thrust belt of late Paleozoic age, which affected the sequence of sedimentary rock layers of the Cape Supergroup in the southwestern corner of South Africa. It was originally continuous with the Ventana Mount ...
and the limited space south of it resulted in the development of social networks out of which complex Stone Age technologies emerged. Human history thus begins on the coasts of South Africa where the Atlantic Benguela Upwelling and Indian Ocean Agulhas Current
The Agulhas Current () is the western boundary current of the southwest Indian Ocean. It flows south along the east coast of Africa from 27°S to 40°S. It is narrow, swift and strong. It is suggested that it is the largest western boundary curren ...
meet to produce an intertidal zone on which shellfish, fur seal, fish and sea birds provided the necessary protein sources.
The African origin of this modern behaviour is evidenced by 70,000 years-old engravings from Blombos Cave, South Africa.
Old World
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial D ...
(mtDNA) studies indicate that 80–60,000 years ago a major demographic expansion within Africa, derived from a single, small population, coincided with the emergence of behavioral complexity and the rapid MIS
MIS or mis may refer to:
Science and technology
* Management information system
* Marine isotope stage, stages of the Earth's climate
* Maximal independent set, in graph theory
* Metal-insulator-semiconductor, e.g., in MIS capacitor
* Minimally in ...
5–4 environmental changes. This group of people not only expanded over the whole of Africa, but also started to disperse out of Africa into Asia, Europe, and Australasia around 65,000 years ago and quickly replaced the archaic humans in these regions. During the Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets were at their greatest extent.
Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Eur ...
(LGM) 20,000 years ago humans had to abandon their initial settlements along the European North Atlantic coast and retreat to the Mediterranean. Following rapid climate changes at the end of the LGM this region was repopulated by Magdalenian
The Magdalenian cultures (also Madelenian; French: ''Magdalénien'') are later cultures of the Upper Paleolithic and Mesolithic in western Europe. They date from around 17,000 to 12,000 years ago. It is named after the type site of La Madele ...
culture. Other hunter-gatherers followed in waves interrupted by large-scale hazards such as the Laacher See
Laacher See (), also known as Lake Laach or Laach Lake, is a volcanic caldera lake with a diameter of in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, about northwest of Koblenz, south of Bonn, and west of Andernach. It is in the Eifel mountain range, and ...
volcanic eruption, the inundation of Doggerland (now the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
), and the formation of the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
. The European coasts of the North Atlantic were permanently populated about 9–8.5 thousand years ago.
This human dispersal left abundant traces along the coasts of the Atlantic Ocean. 50 kya-old, deeply stratified shell middens found in Ysterfontein
Yzerfontein, or Ysterfontein, is a small harbour town with about 1200 inhabitants on the west coast of South Africa about 90 km north of Cape Town. The name in Afrikaans means "Iron Fountain".The town started out when the farm 'Yzerfontein' ...
on the western coast of South Africa are associated with the Middle Stone Age (MSA). The MSA population was small and dispersed and the rate of their reproduction and exploitation was less intense than those of later generations. While their middens resemble 12–11 kya-old Late Stone Age (LSA) middens found on every inhabited continent, the 50–45 kya-old Enkapune Ya Muto
Enkapune Ya Muto, also known as Twilight Cave, is a Late Stone Age site on the Mau Escarpment of Kenya. Beads made of perforated ostrich egg shells found at the site have been dated to 40,000 years ago. The beads found at the site represent the ...
in Kenya probably represents the oldest traces of the first modern humans to disperse out of Africa.
 The same development can be seen in Europe. In
The same development can be seen in Europe. In La Riera Cave
LA most frequently refers to Los Angeles, the second largest city in the United States.
La, LA, or L.A. may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music
* La (musical note), or A, the sixth note
* "L.A.", a song by Elliott Smith on Figure 8 ( ...
(23–13 kya) in Asturias, Spain, only some 26,600 molluscs were deposited over 10 kya. In contrast, 8–7 kya-old shell middens in Portugal, Denmark, and Brazil generated thousands of tons of debris and artefacts. The Ertebølle middens in Denmark, for example, accumulated of shell deposits representing some 50 million molluscs over only a thousand years. This intensification in the exploitation of marine resources has been described as accompanied by new technologies — such as boats, harpoons, and fish-hooks — because many caves found in the Mediterranean and on the European Atlantic coast have increased quantities of marine shells in their upper levels and reduced quantities in their lower. The earliest exploitation, however, took place on the now submerged shelves, and most settlements now excavated were then located several kilometers from these shelves. The reduced quantities of shells in the lower levels can represent the few shells that were exported inland.
New World
During the LGM theLaurentide Ice Sheet
The Laurentide Ice Sheet was a massive sheet of ice that covered millions of square miles, including most of Canada and a large portion of the Northern United States, multiple times during the Quaternary glacial epochs, from 2.58 million years a ...
covered most of northern North America while Beringia
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip ...
connected Siberia to Alaska. In 1973, late American geoscientist Paul S. Martin proposed a "blitzkrieg" colonization of the Americas by which Clovis hunters migrated into North America around 13,000 years ago in a single wave through an ice-free corridor in the ice sheet and "spread southward explosively, briefly attaining a density sufficiently large to overkill much of their prey." Others later proposed a "three-wave" migration over the Bering Land Bridge. These hypotheses remained the long-held view regarding the settlement of the Americas, a view challenged by more recent archaeological discoveries: the oldest archaeological sites in the Americas have been found in South America; sites in north-east Siberia report virtually no human presence there during the LGM; and most Clovis artefacts have been found in eastern North America along the Atlantic coast. Furthermore, colonisation models based on mtDNA, yDNA
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in therian mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is normally the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or abs ...
, and atDNA
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes ...
data respectively support neither the "blitzkrieg" nor the "three-wave" hypotheses but they also deliver mutually ambiguous results. Contradictory data from archaeology and genetics will most likely deliver future hypotheses that will, eventually, confirm each other. A proposed route across the Pacific to South America could explain early South American finds and another hypothesis proposes a northern path, through the Canadian Arctic and down the North American Atlantic coast.
Early settlements across the Atlantic have been suggested by alternative theories, ranging from purely hypothetical to mostly disputed, including the Solutrean hypothesis and some of the Pre-Columbian trans-oceanic contact theories.
 The Norse settlement of the
The Norse settlement of the Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands ( ), or simply the Faroes ( fo, Føroyar ; da, Færøerne ), are a North Atlantic island group and an autonomous territory of the Kingdom of Denmark.
They are located north-northwest of Scotland, and about halfway bet ...
and Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its s ...
began during the 9th and 10th centuries. A settlement on Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is t ...
was established before 1000 CE, but contact with it was lost in 1409 and it was finally abandoned during the early Little Ice Age
The Little Ice Age (LIA) was a period of regional cooling, particularly pronounced in the North Atlantic region. It was not a true ice age of global extent. The term was introduced into scientific literature by François E. Matthes in 1939. Ma ...
. This setback was caused by a range of factors: an unsustainable economy resulted in erosion and denudation, while conflicts with the local Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories ...
resulted in the failure to adapt their Arctic technologies; a colder climate resulted in starvation, and the colony got economically marginalized as the Great Plague
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
and Barbary pirates harvested its victims on Iceland in the 15th century.
Iceland was initially settled 865–930 CE following a warm period when winter temperatures hovered around which made farming favorable at high latitudes. This did not last, however, and temperatures quickly dropped; at 1080 CE summer temperatures had reached a maximum of . The ''Landnámabók'' (''Book of Settlement'') records disastrous famines during the first century of settlement — "men ate foxes and ravens" and "the old and helpless were killed and thrown over cliffs" — and by the early 1200s hay had to be abandoned for short-season crops such as barley.
Atlantic World
 Christopher Columbus Voyages of Christopher Columbus, reached the Americas in 1492 under Spanish flag. Six years later Vasco da Gama reached India under the Portuguese flag, by navigating south around the Cape of Good Hope, thus proving that the Atlantic and Indian Oceans are connected. In 1500, in his voyage to India following Vasco da Gama, Pedro Alvares Cabral reached Brazil, taken by the currents of the South Atlantic Gyre. Following these explorations, Spain and Portugal quickly Colonization of the Americas, conquered and colonized large territories in the New World and forced the Amerindian population into slavery in order to exploit the vast quantities of silver and gold they found. Spain and Portugal monopolized this trade in order to keep other European nations out, but conflicting interests nevertheless led to a series of Spanish-Portuguese wars. A peace treaty mediated by the Pope divided the conquered territories into Spanish and Portuguese sectors while keeping other colonial powers away. England, France, and the Dutch Republic enviously watched the Spanish and Portuguese wealth grow and allied themselves with Piracy in the Atlantic World, pirates such as Henry Mainwaring and Alexandre Exquemelin. They could explore the convoys leaving the Americas because prevailing winds and currents made the transport of heavy metals slow and predictable.
Christopher Columbus Voyages of Christopher Columbus, reached the Americas in 1492 under Spanish flag. Six years later Vasco da Gama reached India under the Portuguese flag, by navigating south around the Cape of Good Hope, thus proving that the Atlantic and Indian Oceans are connected. In 1500, in his voyage to India following Vasco da Gama, Pedro Alvares Cabral reached Brazil, taken by the currents of the South Atlantic Gyre. Following these explorations, Spain and Portugal quickly Colonization of the Americas, conquered and colonized large territories in the New World and forced the Amerindian population into slavery in order to exploit the vast quantities of silver and gold they found. Spain and Portugal monopolized this trade in order to keep other European nations out, but conflicting interests nevertheless led to a series of Spanish-Portuguese wars. A peace treaty mediated by the Pope divided the conquered territories into Spanish and Portuguese sectors while keeping other colonial powers away. England, France, and the Dutch Republic enviously watched the Spanish and Portuguese wealth grow and allied themselves with Piracy in the Atlantic World, pirates such as Henry Mainwaring and Alexandre Exquemelin. They could explore the convoys leaving the Americas because prevailing winds and currents made the transport of heavy metals slow and predictable.
 In the colonies of the Americas, depredation, smallpox and others diseases, and slavery quickly reduced the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous population of the Americas to the extent that the Atlantic slave trade had to be introduced to replace them — a trade that became the norm and an integral part of the colonization. Between the 15th century and 1888, when Slavery in Brazil, Brazil became the last part of the Americas to end the slave trade, an estimated ten million Africans were exported as slaves, most of them destined for agricultural labour. The slave trade was officially abolished in the Slavery in the British Isles, British Empire and the Slavery in the United States, United States in 1808, and slavery itself was abolished in the British Empire in 1838 and in the United States in 1865 after the American Civil War, Civil War.
From Columbus to the Industrial Revolution Trans-Atlantic trade, including colonialism and slavery, became crucial for Western Europe. For European countries with direct access to the Atlantic (including Britain, France, the Netherlands, Portugal, and Spain) 1500–1800 was a period of sustained growth during which these countries grew richer than those in Eastern Europe and Asia. Colonialism evolved as part of the Trans-Atlantic trade, but this trade also strengthened the position of merchant groups at the expense of monarchs. Growth was more rapid in non-absolutist countries, such as Britain and the Netherlands, and more limited in Absolute monarchy, absolutist monarchies, such as Portugal, Spain, and France, where profit mostly or exclusively benefited the monarchy and its allies.
Trans-Atlantic trade also resulted in increasing urbanization: in European countries facing the Atlantic, urbanization grew from 8% in 1300, 10.1% in 1500, to 24.5% in 1850; in other European countries from 10% in 1300, 11.4% in 1500, to 17% in 1850. Likewise, GDP doubled in Atlantic countries but rose by only 30% in the rest of Europe. By end of the 17th century, the volume of the Trans-Atlantic trade had surpassed that of the Mediterranean trade.
The Atlantic Ocean became the scene of one of the longest continuous naval military camapaigns throughout World War II, from 1939 to 1945.
In the colonies of the Americas, depredation, smallpox and others diseases, and slavery quickly reduced the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous population of the Americas to the extent that the Atlantic slave trade had to be introduced to replace them — a trade that became the norm and an integral part of the colonization. Between the 15th century and 1888, when Slavery in Brazil, Brazil became the last part of the Americas to end the slave trade, an estimated ten million Africans were exported as slaves, most of them destined for agricultural labour. The slave trade was officially abolished in the Slavery in the British Isles, British Empire and the Slavery in the United States, United States in 1808, and slavery itself was abolished in the British Empire in 1838 and in the United States in 1865 after the American Civil War, Civil War.
From Columbus to the Industrial Revolution Trans-Atlantic trade, including colonialism and slavery, became crucial for Western Europe. For European countries with direct access to the Atlantic (including Britain, France, the Netherlands, Portugal, and Spain) 1500–1800 was a period of sustained growth during which these countries grew richer than those in Eastern Europe and Asia. Colonialism evolved as part of the Trans-Atlantic trade, but this trade also strengthened the position of merchant groups at the expense of monarchs. Growth was more rapid in non-absolutist countries, such as Britain and the Netherlands, and more limited in Absolute monarchy, absolutist monarchies, such as Portugal, Spain, and France, where profit mostly or exclusively benefited the monarchy and its allies.
Trans-Atlantic trade also resulted in increasing urbanization: in European countries facing the Atlantic, urbanization grew from 8% in 1300, 10.1% in 1500, to 24.5% in 1850; in other European countries from 10% in 1300, 11.4% in 1500, to 17% in 1850. Likewise, GDP doubled in Atlantic countries but rose by only 30% in the rest of Europe. By end of the 17th century, the volume of the Trans-Atlantic trade had surpassed that of the Mediterranean trade.
The Atlantic Ocean became the scene of one of the longest continuous naval military camapaigns throughout World War II, from 1939 to 1945.
Economy
The Atlantic has contributed significantly to the development and economy of surrounding countries. Besides major transatlantic transportation and communication routes, the Atlantic offers abundant petroleum deposits in the sedimentary rocks of the continental shelves. The Atlantic harbors petroleum and gas fields, fish, marine mammals (Pinniped, seals and whales), sand and gravel aggregates, placer deposits, polymetallic nodules, and precious stones.
Gold deposits are a mile or two under water on the ocean floor, however, the deposits are also encased in rock that must be mined through. Currently, there is no cost-effective way to mine or extract gold from the ocean to make a profit.
Various international treaties attempt to reduce pollution caused by environmental threats such as oil spills, marine debris, and the incineration of toxic wastes at sea.
The Atlantic harbors petroleum and gas fields, fish, marine mammals (Pinniped, seals and whales), sand and gravel aggregates, placer deposits, polymetallic nodules, and precious stones.
Gold deposits are a mile or two under water on the ocean floor, however, the deposits are also encased in rock that must be mined through. Currently, there is no cost-effective way to mine or extract gold from the ocean to make a profit.
Various international treaties attempt to reduce pollution caused by environmental threats such as oil spills, marine debris, and the incineration of toxic wastes at sea.
Fisheries
The Continental shelf, shelves of the Atlantic hosts one of the world's richest Wild fisheries, fishing resources. The most productive areas include theGrand Banks of Newfoundland
The Grand Banks of Newfoundland are a series of underwater plateaus south-east of the island of Newfoundland on the North American continental shelf. The Grand Banks are one of the world's richest fishing grounds, supporting Atlantic cod, swordf ...
, the Scotian Shelf, Georges Bank
Georges Bank (formerly known as St. Georges Bank) is a large elevated area of the sea floor between Cape Cod, Massachusetts (United States), and Cape Sable Island, Nova Scotia (Canada). It separates the Gulf of Maine from the Atlantic Ocean.
Th ...
off Cape Cod, the Bahama Banks, the waters around Iceland, the Irish Sea
The Irish Sea or , gv, Y Keayn Yernagh, sco, Erse Sie, gd, Muir Èireann , Ulster-Scots: ''Airish Sea'', cy, Môr Iwerddon . is an extensive body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the Ce ...
, the Bay of Fundy, the Dogger Bank of the North Sea, and the Falkland Banks.
Fisheries have, however, undergone significant changes since the 1950s and global catches can now be divided into three groups of which only two are observed in the Atlantic: fisheries in the Eastern Central and South-West Atlantic oscillate around a globally stable value, the rest of the Atlantic is in overall decline following historical peaks. The third group, "continuously increasing trend since 1950", is only found in the Indian Ocean and Western Pacific.
UN FAO partitioned Atlantic in major fishing areas:
 ;North-East Atlantic:
North-East Atlantic is schematically limited to the 42°00' west longitude except around Greenland and at south to 36°00' north latitude; and 68°30' east longitude at the east, according to FAO fisheries definition and include various seas and/or subareas:
;North-East Atlantic:
North-East Atlantic is schematically limited to the 42°00' west longitude except around Greenland and at south to 36°00' north latitude; and 68°30' east longitude at the east, according to FAO fisheries definition and include various seas and/or subareas: Barents Sea
The Barents Sea ( , also ; no, Barentshavet, ; russian: Баренцево море, Barentsevo More) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located off the northern coasts of Norway and Russia and divided between Norwegian and Russian territo ...
, Norwegian Sea
The Norwegian Sea ( no, Norskehavet; is, Noregshaf; fo, Norskahavið) is a marginal sea, grouped with either the Atlantic Ocean or the Arctic Ocean, northwest of Norway between the North Sea and the Greenland Sea, adjoining the Barents Sea to ...
, Spitzbergen, Bear Island (Norway), Bear Island, Skagerrak, Kattegat, Sound, Belt Sea, Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
, North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
, Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its s ...
, Faroes Grounds, Rockall, Northwest Coast of Scotland, North Ireland, Irish Sea
The Irish Sea or , gv, Y Keayn Yernagh, sco, Erse Sie, gd, Muir Èireann , Ulster-Scots: ''Airish Sea'', cy, Môr Iwerddon . is an extensive body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the Ce ...
, West of Ireland, Porcupine Bank, Eastern and Western English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
, Bay of Biscay
The Bay of Biscay (), known in Spain as the Gulf of Biscay ( es, Golfo de Vizcaya, eu, Bizkaiko Golkoa), and in France and some border regions as the Gulf of Gascony (french: Golfe de Gascogne, oc, Golf de Gasconha, br, Pleg-mor Gwaskogn), ...
, Portuguese Waters, Azores Grounds and Northeast Atlantic South.
: In the North-East Atlantic total catches decreased between the mid-1970s and the 1990s and reached 8.7 million tons in 2013. Blue whiting reached a 2.4 million tons peak in 2004 but was down to 628,000 tons in 2013. Recovery plans for cod, sole, and plaice have reduced mortality in these species. Arctic cod reached its lowest levels in the 1960s–1980s but is now recovered. Pollachius virens, Arctic saithe and haddock are considered fully fished; Sand eel is overfished as was capelin which has now recovered to fully fished. Limited data makes the state of redfishes and deep-water species difficult to assess but most likely they remain vulnerable to overfishing. Stocks of northern shrimp and Norwegian lobster are in good condition. In the North-East Atlantic 21% of stocks are considered overfished.
: This zone makes almost three quarters (72.8 %) of European Union fishing catches in 2020. Main fishing EU countries are Denmark, France, the Netherlands and Spain. Most common species include herring, mackerel and sprats.
 ;North-West Atlantic : In the North-West Atlantic landings have decreased from 4.2 million tons in the early 1970s to 1.9 million tons in 2013. During the 21st century some species have shown weak signs of recovery, including Greenland halibut, yellowtail flounder, Atlantic halibut, haddock, spiny dogfish, while other stocks shown no such signs, including cod, Witch (righteye flounder), witch flounder, and redfish. Stocks of invertebrates, in contrast, remain at record levels of abundance. 31% of stocks are overfished in the North-west Atlantic.
;North-West Atlantic : In the North-West Atlantic landings have decreased from 4.2 million tons in the early 1970s to 1.9 million tons in 2013. During the 21st century some species have shown weak signs of recovery, including Greenland halibut, yellowtail flounder, Atlantic halibut, haddock, spiny dogfish, while other stocks shown no such signs, including cod, Witch (righteye flounder), witch flounder, and redfish. Stocks of invertebrates, in contrast, remain at record levels of abundance. 31% of stocks are overfished in the North-west Atlantic.
 In 1497, John Cabot became the first Western European since the Vikings to explore mainland North America and one of his major discoveries was the abundant resources of Atlantic cod off Newfoundland. Referred to as "Newfoundland Currency" this discovery yielded some 200 million tons of fish over five centuries. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries new fisheries started to exploit haddock, mackerel, and lobster. From the 1950s to the 1970s the introduction of European and Asian distant-water fleets in the area dramatically increased the fishing capacity and the number of exploited species. It also expanded the exploited areas from near-shore to the open sea and to great depths to include deep-water species such as Sebastes, redfish, Greenland halibut, witch flounder, and Grenadiers (fish), grenadiers. Overfishing in the area was recognised as early as the 1960s but, because this was occurring on international waters, it took until the late 1970s before any attempts to regulate was made. In the early 1990s, this finally resulted in the collapse of the Atlantic northwest cod fishery. The population of a number of deep-sea fishes also collapsed in the process, including American plaice, redfish, and Greenland halibut, together with flounder and grenadier.
;Eastern Central Atlantic : In the Eastern Central Atlantic small pelagic fishes constitute about 50% of landings with sardine reaching 0.6–1.0 million tons per year. Pelagic fish stocks are considered fully fished or overfished, with sardines south of Cape Bojador the notable exception. Almost half of the stocks are fished at biologically unsustainable levels. Total catches have been fluctuating since the 1970s; reaching 3.9 million tons in 2013 or slightly less than the peak production in 2010.
In 1497, John Cabot became the first Western European since the Vikings to explore mainland North America and one of his major discoveries was the abundant resources of Atlantic cod off Newfoundland. Referred to as "Newfoundland Currency" this discovery yielded some 200 million tons of fish over five centuries. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries new fisheries started to exploit haddock, mackerel, and lobster. From the 1950s to the 1970s the introduction of European and Asian distant-water fleets in the area dramatically increased the fishing capacity and the number of exploited species. It also expanded the exploited areas from near-shore to the open sea and to great depths to include deep-water species such as Sebastes, redfish, Greenland halibut, witch flounder, and Grenadiers (fish), grenadiers. Overfishing in the area was recognised as early as the 1960s but, because this was occurring on international waters, it took until the late 1970s before any attempts to regulate was made. In the early 1990s, this finally resulted in the collapse of the Atlantic northwest cod fishery. The population of a number of deep-sea fishes also collapsed in the process, including American plaice, redfish, and Greenland halibut, together with flounder and grenadier.
;Eastern Central Atlantic : In the Eastern Central Atlantic small pelagic fishes constitute about 50% of landings with sardine reaching 0.6–1.0 million tons per year. Pelagic fish stocks are considered fully fished or overfished, with sardines south of Cape Bojador the notable exception. Almost half of the stocks are fished at biologically unsustainable levels. Total catches have been fluctuating since the 1970s; reaching 3.9 million tons in 2013 or slightly less than the peak production in 2010.
 ;Western Central Atlantic: In the Western Central Atlantic, catches have been decreasing since 2000 and reached 1.3 million tons in 2013. The most important species in the area, Gulf menhaden, reached a million tons in the mid-1980s but only half a million tons in 2013 and is now considered fully fished. Round sardinella was an important species in the 1990s but is now considered overfished. Groupers and Lutjanidae, snappers are overfished and northern brown shrimp and Eastern oyster, American cupped oyster are considered fully fished approaching overfished. 44% of stocks are being fished at unsustainable levels.
;Western Central Atlantic: In the Western Central Atlantic, catches have been decreasing since 2000 and reached 1.3 million tons in 2013. The most important species in the area, Gulf menhaden, reached a million tons in the mid-1980s but only half a million tons in 2013 and is now considered fully fished. Round sardinella was an important species in the 1990s but is now considered overfished. Groupers and Lutjanidae, snappers are overfished and northern brown shrimp and Eastern oyster, American cupped oyster are considered fully fished approaching overfished. 44% of stocks are being fished at unsustainable levels.
 ;South-East Atlantic: In the South-East Atlantic catches have decreased from 3.3 million tons in the early 1970s to 1.3 million tons in 2013. Horse mackerel and hake are the most important species, together representing almost half of the landings. Off South Africa and Namibia Merluccius paradoxus, deep-water hake and Merluccius capensis, shallow-water Cape hake have recovered to sustainable levels since regulations were introduced in 2006 and the states of Southern African pilchard and Southern African anchovy, anchovy have improved to fully fished in 2013.
;South-West Atlantic: In the South-West Atlantic, a peak was reached in the mid-1980s and catches now fluctuate between 1.7 and 2.6 million tons. The most important species, the Illex argentinus, Argentine shortfin squid, which reached half a million tons in 2013 or half the peak value, is considered fully fished to overfished. Another important species was the Brazilian sardinella, with a production of 100,000 tons in 2013 it is now considered overfished. Half the stocks in this area are being fished at unsustainable levels: Whitehead's round herring has not yet reached fully fished but Cunene horse mackerel is overfished. The sea snail Haliotis midae, perlemoen abalone is targeted by illegal fishing and remain overfished.
;South-East Atlantic: In the South-East Atlantic catches have decreased from 3.3 million tons in the early 1970s to 1.3 million tons in 2013. Horse mackerel and hake are the most important species, together representing almost half of the landings. Off South Africa and Namibia Merluccius paradoxus, deep-water hake and Merluccius capensis, shallow-water Cape hake have recovered to sustainable levels since regulations were introduced in 2006 and the states of Southern African pilchard and Southern African anchovy, anchovy have improved to fully fished in 2013.
;South-West Atlantic: In the South-West Atlantic, a peak was reached in the mid-1980s and catches now fluctuate between 1.7 and 2.6 million tons. The most important species, the Illex argentinus, Argentine shortfin squid, which reached half a million tons in 2013 or half the peak value, is considered fully fished to overfished. Another important species was the Brazilian sardinella, with a production of 100,000 tons in 2013 it is now considered overfished. Half the stocks in this area are being fished at unsustainable levels: Whitehead's round herring has not yet reached fully fished but Cunene horse mackerel is overfished. The sea snail Haliotis midae, perlemoen abalone is targeted by illegal fishing and remain overfished.
Environmental issues
Endangered species
Endangered marine species include the manatee, Pinniped, seals, sea lions, turtles, and whales. Drift net fishing can kill dolphins, albatrosses and other seabirds (petrels, auks), hastening the fish stock decline and contributing to international disputes.Waste and pollution
Marine pollution is a generic term for the entry into the ocean of potentially hazardous chemicals or particles. The biggest culprits are rivers and with them many agriculture fertilizer chemicals as well as livestock and human waste. The excess of oxygen-depleting chemicals leads to Hypoxia (environmental), hypoxia and the creation of a dead zone (ecology), dead zone. Marine debris, which is also known as marine litter, describes human-created waste floating in a body of water. Oceanic debris tends to accumulate at the center of Oceanic gyres, gyres and coastlines, frequently washing aground where it is known as beach litter. The North Atlantic garbage patch is estimated to be hundreds of kilometers across in size. Other pollution concerns include agricultural and municipal waste. Municipal pollution comes from the eastern United States, southern Brazil, and eastern Argentina; oil pollution in theCaribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico ...
, Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of ...
, Lake Maracaibo, Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
, and North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
; and industrial waste and municipal sewage pollution in the Baltic Sea, North Sea, and Mediterranean Sea.
A USAF C-124 Globemaster II, C-124 aircraft from Dover Air Force Base, Delaware was carrying three nuclear bombs over the Atlantic Ocean when it experienced a loss of power. For their own safety, the crew jettisoned two nuclear bombs, which were never recovered.
Climate change
North Atlantic hurricane activity has increased over past decades because of increased sea surface temperature (SST) at tropical latitudes, changes that can be attributed to either the natural Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation (AMO) or to anthropogenic climate change. A 2005 report indicated that the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) slowed down by 30% between 1957 and 2004. If the AMO were responsible for SST variability, the AMOC would have increased in strength, which is apparently not the case. Furthermore, it is clear from statistical analyses of annual tropical cyclones that these changes do not display multidecadal cyclicity. Therefore, these changes in SST must be caused by human activities. The ocean mixed layer plays an important role in heat storage over seasonal and decadal time-scales, whereas deeper layers are affected over millennia and have a heat capacity about 50 times that of the mixed layer. This heat uptake provides a time-lag for climate change but it also results in thermal expansion of the oceans which contributes to sea level rise. 21st-century global warming will probably result in an equilibrium level, equilibrium sea-level rise five times greater than today, whilst melting of glaciers, including that of the Greenland ice-sheet, expected to have virtually no effect during the 21st century, will probably result in a sea-level rise of 3–6 m over a millennium.See also
* List of countries and territories bordering the Atlantic Ocean * List of rivers of the Americas by coastline#Atlantic Ocean coast * Seven Seas * Shutdown of thermohaline circulation, Gulf Stream shutdown * :Shipwrecks in the Atlantic Ocean, Shipwrecks in the Atlantic Ocean * :Atlantic hurricanes, Atlantic hurricanes * Atlantic history * Piracy in the Atlantic World * Transatlantic crossing * Atlantic Revolutions * Natural delimitation between the Pacific and South Atlantic oceans by the Scotia ArcReferences
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *map
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
Further reading
*External links
Cartage.org.lb (archived)
"Map of Atlantic Coast of North America from the Chesapeake Bay to Florida"
from 1639 via the Library of Congress {{Authority control Atlantic Ocean, Oceans History of the Atlantic Ocean, Landforms of the Atlantic Ocean, Articles containing video clips Oceans surrounding Antarctica