|
Gibraltar Arc
The Gibraltar Arc is a geological region corresponding to an arcuate orogen surrounding the Alboran Sea, between the Iberian Peninsula and Africa. It consists of the Betic Cordillera (south Spain), and the Rif (North Morocco). The Gibraltar Arc is located at the western end of the Mediterranean Alpine belt and formed during the Neogene due to convergence of the Eurasian and African plates. Maximum altitudes of the region are reached at the Mulhacén peak at the Cordillera Betica. Precipitation is collected mainly by the Guadalquivir (Betics) and Sebou (Rif) rivers, which have delivered most sedimentary infill of the homonym sedimentary foreland basins.. Tectonic evolution North–south convergence of the Eurasian and African plates occurred during the middle Oligocene to the late Miocene, followed by northwest–southeast convergence from the late Tortonian to present. The Gibraltar Arc was formed during the Neogene due to a combination of western migration of the orogenic mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arco De Gibraltar
ARCO ( ) is a brand of gasoline stations currently owned by Marathon Petroleum after BP sold its rights. BP commercializes the brand in Northern California, Oregon and Washington, while Marathon has rights for the rest of the United States and in Mexico. ARCO had been established in 1966 as the "Atlantic Richfield Company", an independent oil and gas company formed after the merger of Atlantic Petroleum and the Richfield Oil Corporation. History From 1966 to 2000, the 'Atlantic Richfield Company', doing business as ARCO, was an independent American oil company with operations in the United States, Indonesia, the North Sea, the South China Sea, and Mexico. After its acquisition of Anaconda Copper Mining Company in 1977, ARCO had owned hard rock mines in several western states, which has created environmental clean-up liabilities to the company to this day even after the mines were closed in the early 1980s. In 2000, BP acquired ARCO for $26.8 billion. ARCO's retail and mark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accretion (geology)
Accretion, in geology, is a process by which material is added to a tectonic plate at a subduction zone, frequently on the edge of existing continental landmasses. The added material may be sediment, volcanic arcs, seamounts, oceanic crust or other igneous features. Description Accretion involves the addition of material to a tectonic plate via subduction, the process by which one plate is forced under the other when two plates collide. The plate which is being forced down, the subducted plate, is pushed against the upper, over-riding plate. Sediment on the ocean floor of the subducting plate is often scraped off as the plate descends. This accumulated material is called an accretionary wedge (or accretionary prism), which is pushed against and attaches to the upper plate. In addition to accumulated ocean sediments, volcanic island arcs or seamounts present on the subducting plate may be amalgamated onto existing continental crust on the upper plate, increasing the continental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrust Fault
A thrust fault is a break in the Earth's crust, across which older rocks are pushed above younger rocks. Thrust geometry and nomenclature Reverse faults A thrust fault is a type of reverse fault that has a dip of 45 degrees or less. If the angle of the fault plane is lower (often less than 15 degrees from the horizontal) and the displacement of the overlying block is large (often in the kilometer range) the fault is called an ''overthrust'' or ''overthrust fault''. Erosion can remove part of the overlying block, creating a ''fenster'' (or ''window'') – when the underlying block is exposed only in a relatively small area. When erosion removes most of the overlying block, leaving island-like remnants resting on the lower block, the remnants are called ''klippen'' (singular ''klippe''). Blind thrust faults If the fault plane terminates before it reaches the Earth's surface, it is referred to as a ''blind thrust'' fault. Because of the lack of surface evidence, blind thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folding (geology)
In structural geology, a fold is a stack of originally planar surfaces, such as sedimentary strata, that are bent or curved during permanent deformation. Folds in rocks vary in size from microscopic crinkles to mountain-sized folds. They occur as single isolated folds or in periodic sets (known as ''fold trains''). Synsedimentary folds are those formed during sedimentary deposition. Folds form under varied conditions of stress, pore pressure, and temperature gradient, as evidenced by their presence in soft sediments, the full spectrum of metamorphic rocks, and even as primary flow structures in some igneous rocks. A set of folds distributed on a regional scale constitutes a fold belt, a common feature of orogenic zones. Folds are commonly formed by shortening of existing layers, but may also be formed as a result of displacement on a non-planar fault (''fault bend fold''), at the tip of a propagating fault (''fault propagation fold''), by differential compaction or due to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin ''creta'', "chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation ''Kreide''. The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now- extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was ice free, and forests extended to the poles. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds appeared. During the Early Cretaceous, flowering plants appeared and began to rapidly diversify, becoming the dominant group of plants across the Earth b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flysch
Flysch () is a sequence of sedimentary rock layers that progress from deep-water and turbidity flow deposits to shallow-water shales and sandstones. It is deposited when a deep basin forms rapidly on the continental side of a mountain building episode. Examples are found near the North American Cordillera, the Alps, the Pyrenees and the Carpathians. Sedimentological properties Flysch consists of repeated sedimentary cycles with upwards fining of the sediments. There are sometimes coarse conglomerates or breccias at the bottom of each cycle, which gradually evolve upwards into sandstone and shale/mudstone. Flysch typically consists of a sequence of shales rhythmically interbedded with thin, hard, graywacke-like sandstones. Typically the shales do not contain many fossils, while the coarser sandstones often have fractions of micas and glauconite. Tectonics In a continental collision, a subducting tectonic plate pushes on the plate above it, making the rock fold, often to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
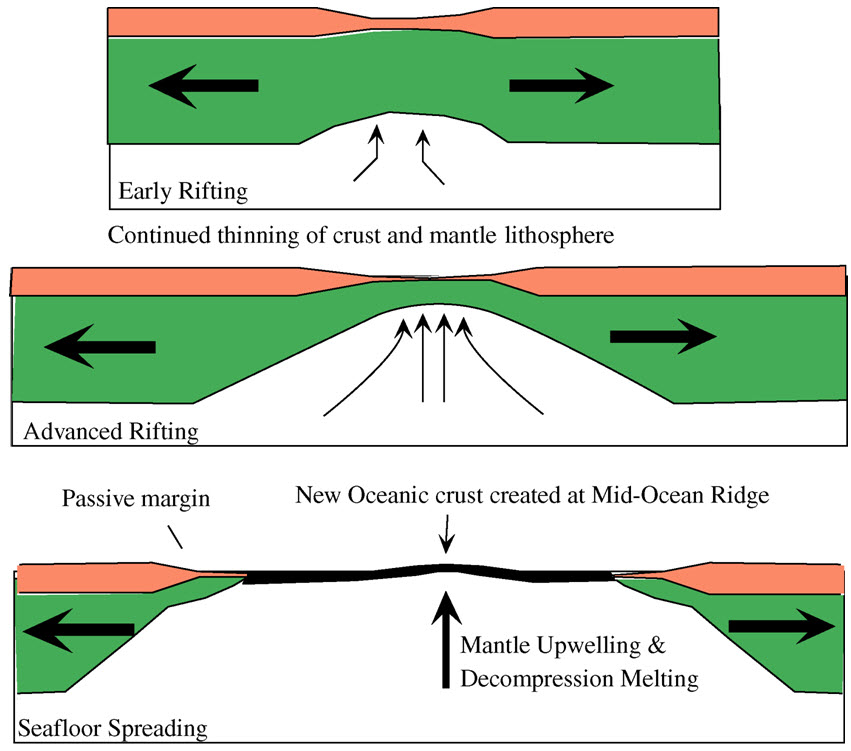
Passive Margin
A passive margin is the transition between oceanic and continental lithosphere that is not an active plate margin. A passive margin forms by sedimentation above an ancient rift, now marked by transitional lithosphere. Continental rifting creates new ocean basins. Eventually the continental rift forms a mid-ocean ridge and the locus of extension moves away from the continent-ocean boundary. The transition between the continental and oceanic lithosphere that was originally created by rifting is known as a passive margin. Global distribution Passive margins are found at every ocean and continent boundary that is not marked by a strike-slip fault or a subduction zone. Passive margins define the region around the Arctic Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, and western Indian Ocean, and define the entire coasts of Africa, Australia, Greenland, and the Indian Subcontinent. They are also found on the east coast of North America and South America, in Western Europe and most of Antarctica. Northeas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphic Rocks
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causing profound physical or chemical changes. During this process, the rock remains mostly in the solid state, but gradually recrystallizes to a new texture or mineral composition. The protolith may be an igneous, sedimentary, or existing metamorphic rock. Metamorphic rocks make up a large part of the Earth's crust and form 12% of the Earth's land surface. They are classified by their protolith, their chemical and mineral makeup, and their texture. They may be formed simply by being deeply buried beneath the Earth's surface, where they are subject to high temperatures and the great pressure of the rock layers above. They can also form from tectonic processes such as continental collisions, which cause horizontal pressure, friction, and distort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transtension
Transtension is the state in which a rock mass or area of the Earth's crust experiences both ''extensive'' and ''transtensive'' shear. As such, transtensional regions are characterised by both extensional structures ( normal faults, grabens) and wrench structures (strike-slip faults). In general, many tectonic regimes that were previously defined as simple strike-slip shear zones are actually transtensional. It is unlikely that a deforming body will experience 'pure' extension or 'pure' strike-slip. Transtensional shear zones are characterized by the co-existence of different structures, related to both strike-slip shear and extension. End member structures include pure strike-slip faults and purely extensional ("normal") dip-slip faults. Faults which have components of both (termed 'oblique' slip faults) are abundant. Releasing bend ''Releasing bends'' are transtensional structures that form where the orientation of a strike-slip fault becomes oblique to the regional slip vector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transpression
In geology, transpression is a type of strike-slip deformation that deviates from simple shear because of a simultaneous component of shortening perpendicular to the fault plane. This movement ends up resulting in oblique shear. It is generally very unlikely that a deforming body will experience "pure" shortening or "pure" strike-slip. The relative amounts of shortening and strike-slip can be expressed in the convergence angle alpha which ranges from zero (ideal strike-slip) to 90 degrees (ideal convergence). During shortening, unless material is lost, transpression produces vertical thickening in the crust. Transpression that occurs on a regional scale along plate boundaries is characterized by oblique convergence. More locally, transpression occurs within restraining bends in strike-slip fault zones. Transpressional structures Transpressional shear zones are characterized by an association of structures that suggest zone-normal shortening and zone-parallel shearing. Commonly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault (geology)
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A ''fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can blur the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |