Arietis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Aries is one of the

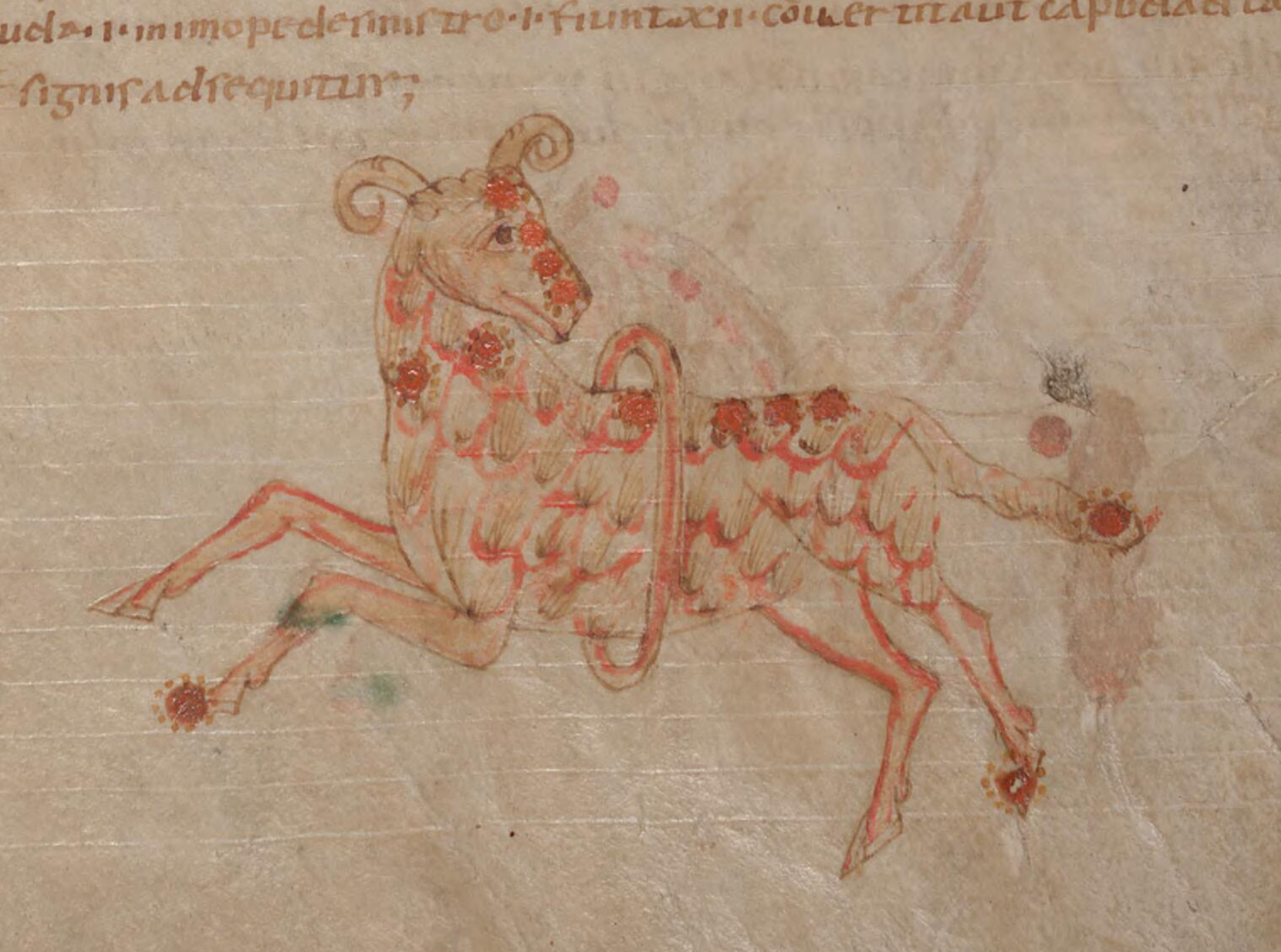 Aries was not fully accepted as a constellation until classical times. In
Aries was not fully accepted as a constellation until classical times. In


The Deep Photographic Guide to the Constellations: Aries
Warburg Institute Iconographic Database (medieval and early modern images of Aries)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Aries (Constellation) Constellations Constellations listed by Ptolemy Northern constellations
constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the e ...
s of the zodiac. It is located in the Northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces
Pisces may refer to:
* Pisces, an obsolete (because of land vertebrates) taxonomic superclass including all fish
*Pisces (astrology), an astrological sign
*Pisces (constellation), a constellation
**Pisces Overdensity, an overdensity of stars in t ...
to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram. Its old astronomical symbol is (♈︎). It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation ranking 39th in overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, ...
).
Aries has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourth magnitude). The few deep-sky objects within the constellation are quite faint and include several pairs of interacting galaxies. Several meteor shower
A meteor shower is a celestial event in which a number of meteors are observed to radiate, or originate, from one point in the night sky. These meteors are caused by streams of cosmic debris called meteoroids entering Earth's atmosphere at extre ...
s appear to radiate from Aries, including the Daytime Arietids and the Epsilon Arietids.
History and mythology
Aries is now recognized as an official constellation, albeit as a specific region of the sky, by the International Astronomical Union. It was originally defined in ancient texts as a specific pattern of stars, and has remained a constellation since ancient times; it now includes the ancient pattern and the surrounding stars. In the description of theBabylonian zodiac
Babylonian astronomy collated earlier observations and divinations into sets of Babylonian star catalogues, during and after the Kassite rule over Babylonia. These star catalogues, written in cuneiform script, contained lists of constellations, i ...
given in the clay tablets known as the MUL.APIN, the constellation, now known as Aries, was the final station along the ecliptic. The MUL.APIN was a comprehensive table of the rising and settings of stars, which likely served as an agricultural calendar. Modern-day Aries was known as , "The Agrarian Worker" or "The Hired Man". Although likely compiled in the 12th or 11th century BC, the MUL.APIN reflects a tradition that marks the Pleiades as the vernal equinox Spring equinox or vernal equinox or variations may refer to:
* March equinox, the spring equinox in the Northern Hemisphere
* September equinox, the spring equinox in the Southern Hemisphere
Other uses
* Nowruz, Persian/Iranian new year which be ...
, which was the case with some precision at the beginning of the Middle Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
. The earliest identifiable reference to Aries as a distinct constellation comes from the boundary stones that date from 1350 to 1000 BC. On several boundary stones, a zodiacal ram figure is distinct from the other characters. The shift in identification from the constellation as the Agrarian Worker to the Ram likely occurred in later Babylonian tradition because of its growing association with Dumuzi the Shepherd
Dumuzid or Tammuz ( sux, , ''Dumuzid''; akk, Duʾūzu, Dûzu; he, תַּמּוּז, Tammûz),; ar, تمّوز ' known to the Sumerians as Dumuzid the Shepherd ( sux, , ''Dumuzid sipad''), is an ancient Mesopotamian god associated with shep ...
. By the time the MUL.APIN was created—in 1000 BC—modern Aries was identified with both Dumuzi's ram and a hired labourer. The exact timing of this shift is difficult to determine due to the lack of images of Aries or other ram figures.
In ancient Egyptian astronomy, Aries was associated with the god Amon-Ra, who was depicted as a man with a ram's head and represented fertility and creativity. Because it was the location of the vernal equinox, it was called the "Indicator of the Reborn Sun". During the times of the year when Aries was prominent, priests would process statues of Amon-Ra to temples, a practice that was modified by Persian astronomers centuries later. Aries acquired the title of "Lord of the Head" in Egypt, referring to its symbolic and mythological importance.

 Aries was not fully accepted as a constellation until classical times. In
Aries was not fully accepted as a constellation until classical times. In Hellenistic astrology
Hellenistic astrology is a tradition of horoscopic astrology that was developed and practiced in the late Hellenistic period in and around the Mediterranean Basin region, especially in Egypt. The texts and technical terminology of this tradition o ...
, the constellation of Aries is associated with the golden ram of Greek mythology that rescued Phrixus and Helle on orders from Hermes, taking Phrixus to the land of Colchis. Phrixus and Helle were the son and daughter of King Athamas and his first wife Nephele. The king's second wife, Ino
Ino or INO may refer to:
Arts and music
*I-No, a character in the ''Guilty Gear'' series of video games
*Ino (Greek mythology), a queen of Thebes in Greek mythology
*INO Records, an American Christian music label
*Ino Yamanaka, a character in th ...
, was jealous and wished to kill his children. To accomplish this, she induced famine in Boeotia, then falsified a message from the Oracle of Delphi that said Phrixos must be sacrificed to end the famine. Athamas was about to sacrifice his son atop Mount Laphystium
Mount is often used as part of the name of specific mountains, e.g. Mount Everest.
Mount or Mounts may also refer to:
Places
* Mount, Cornwall, a village in Warleggan parish, England
* Mount, Perranzabuloe, a hamlet in Perranzabuloe parish, Co ...
when Aries, sent by Nephele, arrived. Helle fell off of Aries's back in flight and drowned in the Dardanelles, also called the Hellespont in her honour.
Historically, Aries has been depicted as a crouched, wingless ram with its head turned towards Taurus. Ptolemy asserted in his ''Almagest
The ''Almagest'' is a 2nd-century Greek-language mathematical and astronomical treatise on the apparent motions of the stars and planetary paths, written by Claudius Ptolemy ( ). One of the most influential scientific texts in history, it canoni ...
'' that Hipparchus depicted Alpha Arietis
Hamal , designation Alpha Arietis (α Arietis, abbreviated Alpha Ari, α Ari), is the brightest star in the northern zodiacal constellation of Aries.
With an apparent visual magnitude of 2.0, it is the mean 50th-brightest star in the n ...
as the ram's muzzle, though Ptolemy did not include it in his constellation figure. Instead, it was listed as an "unformed star", and denoted as "the star over the head". John Flamsteed, in his '' Atlas Coelestis'', followed Ptolemy's description by mapping it above the figure's head. Flamsteed followed the general convention of maps by depicting Aries lying down. Astrologically, Aries has been associated with the head and its humors. It was strongly associated with Mars, both the planet and the god. It was considered to govern Western Europe and Syria and to indicate a strong temper in a person.
The First Point of Aries, the location of the vernal equinox Spring equinox or vernal equinox or variations may refer to:
* March equinox, the spring equinox in the Northern Hemisphere
* September equinox, the spring equinox in the Southern Hemisphere
Other uses
* Nowruz, Persian/Iranian new year which be ...
, is named for the constellation. This is because the Sun crossed the celestial equator from south to north in Aries more than two millennia ago. Hipparchus defined it in 130 BC. as a point south of Gamma Arietis. Because of the precession of the equinoxes, the First Point of Aries has since moved into Pisces
Pisces may refer to:
* Pisces, an obsolete (because of land vertebrates) taxonomic superclass including all fish
*Pisces (astrology), an astrological sign
*Pisces (constellation), a constellation
**Pisces Overdensity, an overdensity of stars in t ...
and will move into Aquarius by around 2600 AD. The Sun now appears in Aries from late April through mid-May, though the constellation is still associated with the beginning of spring.
Medieval Muslim astronomers depicted Aries in various ways. Astronomers like al-Sufi
ʿAbd al-Rahman al-Sufi ( fa, عبدالرحمن صوفی; December 7, 903 – May 25, 986) was an iranianRobert Harry van Gent. Biography of al-Sūfī'. "The Persian astronomer Abū al-Husayn ‘Abd al-Rahmān ibn ‘Umar al-Sūfī was born in ...
saw the constellation as a ram, modelled on the precedent of Ptolemy. However, some Islamic celestial globes depicted Aries as a nondescript four-legged animal with what may be antlers instead of horns. Some early Bedouin
The Bedouin, Beduin, or Bedu (; , singular ) are nomadic Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, the Levant, and Mesopotamia. The Bedouin originated in the Syrian Desert and A ...
observers saw a ram elsewhere in the sky; this constellation featured the Pleiades as the ram's tail. The generally accepted Arabic formation of Aries consisted of thirteen stars in a figure along with five "unformed" stars, four of which were over the animal's hindquarters and one of which was the disputed star over Aries's head. Al-Sufi's depiction differed from both other Arab astronomers' and Flamsteed's, in that his Aries was running and looking behind itself.
The obsolete constellations
Former constellations are old historical Western constellations that for various reasons are no longer widely recognised or are not officially recognised by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Prior to 1930, many of these defunct cons ...
of Aries (Apes
Apes (collectively Hominoidea ) are a clade of Old World simians native to sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia (though they were more widespread in Africa, most of Asia, and as well as Europe in prehistory), which together with its sister g ...
/ Vespa/ Lilium/ Musca (Borealis)) all centred on the same the northern stars. In 1612, Petrus Plancius introduced Apes, a constellation representing a bee. In 1624, the same stars were used by Jakob Bartsch as for Vespa, representing a wasp. In 1679, Augustin Royer used these stars for his constellation Lilium, representing the fleur-de-lis. None of these constellations became widely accepted. Johann Hevelius renamed the constellation "Musca" in 1690 in his '' Firmamentum Sobiescianum''. To differentiate it from Musca, the southern fly, it was later renamed Musca Borealis but it did not gain acceptance and its stars were ultimately officially reabsorbed into Aries. The asterism involved was 33, 35, 39, and 41 Arietis.
In 1922, the International Astronomical Union defined its recommended three-letter abbreviation, "Ari". The official boundaries of Aries were defined in 1930 by Eugène Delporte as a polygon of 12 segments. Its right ascension
Right ascension (abbreviated RA; symbol ) is the angular distance of a particular point measured eastward along the celestial equator from the Sun at the March equinox to the (hour circle of the) point in question above the earth.
When paired w ...
is between 1h 46.4m and 3h 29.4m and its declination
In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol ''δ'') is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. Declination's angle is measured north or south of the ...
is between 10.36° and 31.22° in the equatorial coordinate system.
In non-Western astronomy
In traditional Chinese astronomy, stars from Aries were used in several constellations. The brightest stars—Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Arietis—formed a constellation called ''Lou'' (婁), variously translated as "bond", "lasso", and "sickle", which was associated with the ritual sacrifice of cattle. This name was shared by the 16th lunar mansion, the location of the full moon closest to the autumnal equinox. This constellation has also been associated with harvest-time as it could represent a woman carrying a basket of food on her head. 35, 39, and 41 Arietis were part of a constellation called ''Wei'' (胃), which represented a fat abdomen and was the namesake of the 17th lunar mansion, which represented granaries. Delta andZeta Arietis
Zeta Arietis, Latinized from ζ Arietis, is the Bayer designation for a star in the northern constellation of Aries. It is dimly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +4.89. Based upon an annual parallax shift of ...
were a part of the constellation ''Tianyin'' (天陰), thought to represent the Emperor's hunting partner. ''Zuogeng'' (左更), a constellation depicting a marsh and pond inspector, was composed of Mu, Nu, Omicron, Pi, and Sigma Arietis. He was accompanied by ''Yeou-kang'', a constellation depicting an official in charge of pasture distribution.
In a similar system to the Chinese, the first lunar mansion in Hindu astronomy was called "Aswini", after the traditional names for Beta and Gamma Arietis, the Aswins. Because the Hindu new year began with the vernal equinox, the Rig Veda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts (''śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one Sh ...
contains over 50 new-year's related hymns to the twins, making them some of the most prominent characters in the work. Aries itself was known as "''Aja''" and "''Mesha''". In Hebrew astronomy Aries was named "''Taleh''"; it signified either Simeon or Gad, and generally symbolizes the "Lamb of the World". The neighboring Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
ns named the constellation "Amru", and the bordering Turks named it "Kuzi". Half a world away, in the Marshall Islands, several stars from Aries were incorporated into a constellation depicting a porpoise
Porpoises are a group of fully aquatic marine mammals, all of which are classified under the family Phocoenidae, parvorder Odontoceti (toothed whales). Although similar in appearance to dolphins, they are more closely related to narwhals an ...
, along with stars from Cassiopeia, Andromeda, and Triangulum. Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Arietis formed the head of the porpoise, while stars from Andromeda formed the body and the bright stars of Cassiopeia formed the tail. Other Polynesian peoples recognized Aries as a constellation. The Marquesas islanders called it ''Na-pai-ka''; the Māori constellation ''Pipiri'' may correspond to modern Aries as well. In indigenous Peruvian astronomy, a constellation with most of the same stars as Aries existed. It was called the "Market Moon" and the "Kneeling Terrace", as a reminder of when to hold the annual harvest festival, Ayri Huay.
Features

Stars
Aries has three prominent stars forming an asterism, designated Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Arietis byJohann Bayer
Johann Bayer (1572 – 7 March 1625) was a German lawyer and uranographer (celestial cartographer). He was born in Rain, Lower Bavaria, in 1572. At twenty, in 1592 he began his study of philosophy and law at the University of Ingolstadt, a ...
. Alpha (Hamal) and Beta (Sheratan) are commonly used for navigation. There is also one other star above the fourth magnitude, 41 Arietis (Bharani). α Arietis, called Hamal, is the brightest star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked ...
in Aries. Its traditional name is derived from the Arabic word for "lamb" or "head of the ram" (''ras al-hamal''), which references Aries's mythological background. With a spectral class of K2 and a luminosity class of III, it is an orange giant with an apparent visual magnitude of 2.00, which lies 66 light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 ...
s from Earth. Hamal has a luminosity
Luminosity is an absolute measure of radiated electromagnetic power (light), the radiant power emitted by a light-emitting object over time. In astronomy, luminosity is the total amount of electromagnetic energy emitted per unit of time by a st ...
of and its absolute magnitude is −0.1.
β Arietis, also known as Sheratan, is a blue-white star with an apparent visual magnitude of 2.64. Its traditional name is derived from "''sharatayn''", the Arabic word for "the two signs", referring to both Beta and Gamma Arietis in their position as heralds of the vernal equinox. The two stars were known to the Bedouin
The Bedouin, Beduin, or Bedu (; , singular ) are nomadic Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, the Levant, and Mesopotamia. The Bedouin originated in the Syrian Desert and A ...
as "''qarna al-hamal''", "horns of the ram". It is 59 light-years from Earth. It has a luminosity of and its absolute magnitude is 2.1. It is a spectroscopic binary
A binary star is a system of two star, stars that are gravity, gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separa ...
star, one in which the companion star is only known through analysis of the spectra. The spectral class of the primary is A5. Hermann Carl Vogel determined that Sheratan was a spectroscopic binary in 1903; its orbit was determined by Hans Ludendorff in 1907. It has since been studied for its eccentric orbit.
γ Arietis, with a common name of Mesarthim, is a binary star
A binary star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in wh ...
with two white-hued components, located in a rich field of magnitude 8–12 stars. Its traditional name has conflicting derivations. It may be derived from a corruption of "al-sharatan", the Arabic word meaning "pair" or a word for "fat ram". However, it may also come from the Sanskrit for "first star of Aries" or the Hebrew for "ministerial servants", both of which are unusual languages of origin for star names. Along with Beta Arietis, it was known to the Bedouin as "''qarna al-hamal''". The primary is of magnitude 4.59 and the secondary is of magnitude 4.68. The system is 164 light-years from Earth. The two components are separated by 7.8 arcsecond
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The na ...
s, and the system as a whole has an apparent magnitude of 3.9. The primary has a luminosity of and the secondary has a luminosity of ; the primary is an A-type star with an absolute magnitude of 0.2 and the secondary is a B9-type star with an absolute magnitude of 0.4. The angle between the two components is 1°. Mesarthim was discovered to be a double star by Robert Hooke
Robert Hooke FRS (; 18 July 16353 March 1703) was an English polymath active as a scientist, natural philosopher and architect, who is credited to be one of two scientists to discover microorganisms in 1665 using a compound microscope that ...
in 1664, one of the earliest such telescopic discoveries. The primary, γ1 Arietis, is an Alpha² Canum Venaticorum variable
An Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum variable (or α2 CVn variable) is a type of variable star. These stars are chemically peculiar main sequence stars of spectral class B8p to A7p. They have strong magnetic fields and strong silicon, strontium, or chro ...
star that has a range of 0.02 magnitudes and a period of 2.607 days. It is unusual because of its strong silicon emission lines.
The constellation is home to several double stars, including Epsilon, Lambda, and Pi Arietis. ε Arietis is a binary star with two white components. The primary is of magnitude 5.2 and the secondary is of magnitude 5.5. The system is 290 light-years from Earth. Its overall magnitude is 4.63, and the primary has an absolute magnitude of 1.4. Its spectral class is A2. The two components are separated by 1.5 arcseconds. λ Arietis is a wide double star with a white-hued primary and a yellow-hued secondary. The primary is of magnitude 4.8 and the secondary is of magnitude 7.3. The primary is 129 light-years from Earth. It has an absolute magnitude of 1.7 and a spectral class of F0. The two components are separated by 36 arcseconds at an angle of 50°; the two stars are located 0.5° east of 7 Arietis. π Arietis is a close binary star with a blue-white primary and a white secondary. The primary is of magnitude 5.3 and the secondary is of magnitude 8.5. The primary is 776 light-years from Earth. The primary itself is a wide double star with a separation of 25.2 arcseconds; the tertiary has a magnitude of 10.8. The primary and secondary are separated by 3.2 arcseconds.
Most of the other stars in Aries visible to the naked eye have magnitudes between 3 and 5. δ Ari, called Boteïn, is a star of magnitude 4.35, 170 light-years away. It has an absolute magnitude of −0.1 and a spectral class of K2. ζ Arietis is a star of magnitude 4.89, 263 light-years away. Its spectral class is A0 and its absolute magnitude is 0.0. 14 Arietis
14 Arietis (abbreviated 14 Ari) is a star in the constellation of Aries. ''14 Arietis'' is the Flamsteed designation. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 4.98, which means it is visible to the naked eye. Based upon a measured annual p ...
is a star of magnitude 4.98, 288 light-years away. Its spectral class is F2 and its absolute magnitude is 0.6. 39 Arietis
39 Arietis (abbreviated 39 Ari), officially named Lilii Borea , is a star in the northern constellation of Aries. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +4.5. The distance to this star, as determined from an ...
(Lilii Borea) is a similar star of magnitude 4.51, 172 light-years away. Its spectral class is K1 and its absolute magnitude is 0.0. 35 Arietis
35 Arietis (abbreviated 35 Ari) is a binary star in the northern constellation of Aries. ''35 Arietis'' is the Flamsteed designation. It is approximately distant from the Earth, based upon an annual parallax shift of 9.51 mas. Th ...
is a dim star of magnitude 4.55, 343 light-years away. Its spectral class is B3 and its absolute magnitude is −1.7. 41 Arietis, known both as c Arietis and Nair al Butain, is a brighter star of magnitude 3.63, 165 light-years away. Its spectral class is B8 and it has a luminosity of . Its absolute magnitude is −0.2. 53 Arietis is a runaway star of magnitude 6.09, 815 light-years away. Its spectral class is B2. It was likely ejected from the Orion Nebula
The Orion Nebula (also known as Messier 42, M42, or NGC 1976) is a diffuse nebula situated in the Milky Way, being south of Orion's Belt in the constellation of Orion. It is one of the brightest nebulae and is visible to the naked eye in the nig ...
approximately five million years ago, possibly due to supernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or when ...
e. Finally, Teegarden's Star is the closest star to Earth in Aries. It is a red dwarf
''Red Dwarf'' is a British science fiction comedy franchise created by Rob Grant and Doug Naylor, which primarily consists of a television sitcom that aired on BBC Two between 1988 and 1999, and on Dave since 2009, gaining a cult following. T ...
of magnitude 15.14 and spectral class M6.5V. With a proper motion of 5.1 arcseconds per year, it is the 24th closest star to Earth overall.
Aries has its share of variable stars, including R and U Arietis, Mira-type variable stars, and T Arietis, a semi-regular variable star. R Arietis is a Mira variable star that ranges in magnitude from a minimum of 13.7 to a maximum of 7.4 with a period of 186.8 days. It is 4,080 light-years away. U Arietis is another Mira variable star that ranges in magnitude from a minimum of 15.2 to a maximum of 7.2 with a period of 371.1 days. T Arietis
T, or t, is the twentieth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''tee'' (pronounced ), plural ''tees''. It is de ...
is a semiregular variable star that ranges in magnitude from a minimum of 11.3 to a maximum of 7.5 with a period of 317 days. It is 1,630 light-years away. One particularly interesting variable in Aries is SX Arietis, a rotating variable star considered to be the prototype of its class, helium variable stars. SX Arietis stars have very prominent emission lines of Helium I and Silicon III. They are normally main-sequence B0p—B9p stars, and their variations are not usually visible to the naked eye. Therefore, they are observed photometrically, usually having periods that fit in the course of one night. Similar to Alpha² Canum Venaticorum variable
An Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum variable (or α2 CVn variable) is a type of variable star. These stars are chemically peculiar main sequence stars of spectral class B8p to A7p. They have strong magnetic fields and strong silicon, strontium, or chro ...
s, SX Arietis stars have periodic changes in their light and magnetic field, which correspond to the periodic rotation; they differ from the Alpha² Canum Venaticorum variables in their higher temperature. There are between 39 and 49 SX Arietis variable stars currently known; ten are noted as being "uncertain" in the General Catalog of Variable Stars.
Deep sky objects

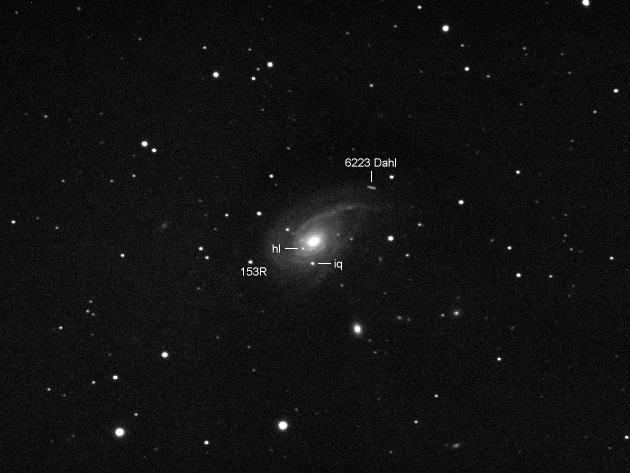
NGC 772
NGC 772 (also known as ''Arp 78'') is an unbarred spiral galaxy approximately 130 million light-years away in the constellation Aries.
Characteristics
At around 200,000 light years in diameter, NGC 772 is somewhat larger than the Milky Way ...
is a spiral galaxy
Spiral galaxies form a class of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work ''The Realm of the Nebulae''integrated magnitude
In astronomy, surface brightness (SB) quantifies the apparent brightness or flux density per unit angular area of a spatially extended object such as a galaxy or nebula, or of the night sky background. An object's surface brightness depends on its ...
of 10.3, located southeast of β Arietis and 15 arcminutes west of 15 Arietis
15 Arietis (abbreviated 15 Ari) is a single variable star in the northern constellation of Aries. ''15 Arietis'' is the Flamsteed designation; it also bears the variable star designation AV Arietis. It has an apparent visual magnitude ...
. It is a relatively bright galaxy and shows obvious nebulosity and ellipticity in an amateur telescope. It is 7.2 by 4.2 arcminutes, meaning that its surface brightness, magnitude 13.6, is significantly lower than its integrated magnitude. NGC 772 is a class SA(s)b galaxy, which means that it is an unbarred spiral galaxy without a ring that possesses a somewhat prominent bulge and spiral arms that are wound somewhat tightly. The main arm, on the northwest side of the galaxy, is home to many star forming regions; this is due to previous gravitational interactions with other galaxies. NGC 772 has a small companion galaxy, NGC 770
NGC 770 is an elliptical galaxy in the constellation Aries. It is around 120 million light years from the Milky Way and has a diameter of around . NGC 770 is gravitationally linked to NGC 772. The galaxy was discovered on November 3, 1855 by R ...
, that is about 113,000 light-years away from the larger galaxy. The two galaxies together are also classified as Arp 78 in the Arp peculiar galaxy catalog. NGC 772 has a diameter of 240,000 light-years and the system is 114 million light-years from Earth. Another spiral galaxy in Aries is NGC 673
NGC commonly refers to:
* New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars, a catalogue of deep sky objects in astronomy
NGC may also refer to:
Companies
* NGC Corporation, name of US electric company Dynegy, Inc. from 1995 to 1998
* Na ...
, a face-on class SAB(s)c galaxy. It is a weakly barred spiral galaxy with loosely wound arms. It has no ring and a faint bulge and is 2.5 by 1.9 arcminutes. It has two primary arms with fragments located farther from the core. 171,000 light-years in diameter, NGC 673 is 235 million light-years from Earth.
NGC 678
NGC commonly refers to:
* New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars, a catalogue of deep sky objects in astronomy
NGC may also refer to:
Companies
* NGC Corporation, name of US electric company Dynegy, Inc. from 1995 to 1998
* Nati ...
and NGC 680
NGC 680 is an elliptical galaxy located in the constellation Aries. It is located at a distance of circa 120 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 680 is about 100,000 light years across. It was disc ...
are a pair of galaxies in Aries that are only about 200,000 light-years apart. Part of the NGC 691
NGC 691 is an unbarred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Aries. It is located at a distance of circa 120 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 691 is about 130,000 light years across. It was ...
group of galaxies, both are at a distance of approximately 130 million light-years. NGC 678 is an edge-on spiral galaxy that is 4.5 by 0.8 arcminutes. NGC 680, an elliptical galaxy with an asymmetrical boundary, is the brighter of the two at magnitude 12.9; NGC 678 has a magnitude of 13.35. Both galaxies have bright cores, but NGC 678 is the larger galaxy at a diameter of 171,000 light-years; NGC 680 has a diameter of 72,000 light-years. NGC 678 is further distinguished by its prominent dust lane. NGC 691 itself is a spiral galaxy slightly inclined to our line of sight. It has multiple spiral arms and a bright core. Because it is so diffuse, it has a low surface brightness. It has a diameter of 126,000 light-years and is 124 million light-years away. NGC 877
NGC 877 is an intermediate spiral galaxy located in the constellation Aries. It is located at a distance of circa 160 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 877 is about 115,000 light years across. I ...
is the brightest member of an 8-galaxy group that also includes NGC 870, NGC 871, and NGC 876, with a magnitude of 12.53. It is 2.4 by 1.8 arcminutes and is 178 million light-years away with a diameter of 124,000 light-years. Its companion is NGC 876, which is about 103,000 light-years from the core of NGC 877. They are interacting gravitationally, as they are connected by a faint stream of gas and dust. Arp 276
NGC 935 and IC 1801 are a pair of interacting galaxies within the Aries constellation. They were discovered on 18 September 1885 by Lewis Swift. NGC 935 is the northern member of the pair, and IC 1801 is the southern. Together, they are liste ...
is a different pair of interacting galaxies in Aries, consisting of NGC 935 and IC 1801.
NGC 821 is an E6 elliptical galaxy. It is unusual because it has hints of an early spiral structure, which is normally only found in lenticular
Lenticular is an adjective often relating to lenses. It may refer to:
* A term used with two meanings in botany: see
* Lenticular cloud, a lens-shaped cloud
* Lenticular galaxy, a lens-shaped galaxy
* Lenticular (geology), adjective describing a ...
and spiral galaxies. NGC 821 is 2.6 by 2.0 arcminutes and has a visual magnitude of 11.3. Its diameter is 61,000 light-years and it is 80 million light-years away. Another unusual galaxy in Aries is Segue 2
Segue 2 is a dwarf spheroidal galaxy situated in the constellation Aries and discovered in 2009 in the data obtained by Sloan Digital Sky Survey. The galaxy is located at the distance of about from the Sun and moves towards the Sun at a speed of . ...
, a dwarf and satellite galaxy of the Milky Way, recently discovered to be a potential relic of the epoch of reionization.
Meteor showers
Aries is home to severalmeteor shower
A meteor shower is a celestial event in which a number of meteors are observed to radiate, or originate, from one point in the night sky. These meteors are caused by streams of cosmic debris called meteoroids entering Earth's atmosphere at extre ...
s. The Daytime Arietid
The Arietids are a strong meteor shower that lasts from May 22 to July 2 each year, and peaks on June 7. The Arietids, along with the Zeta Perseids, are the most intense daylight meteor showers of the year. The source of the shower is unknown, but ...
meteor shower is one of the strongest meteor showers that occurs during the day, lasting from 22 May to 2 July. It is an annual shower associated with the Marsden group of comets that peaks on 7 June with a maximum zenithal hourly rate of 54 meteors. Its parent body may be the asteroid Icarus
In Greek mythology, Icarus (; grc, Ἴκαρος, Íkaros, ) was the son of the master craftsman Daedalus, the architect of the labyrinth of Crete. After Theseus, king of Athens and enemy of Minos, escaped from the labyrinth, King Minos suspe ...
. The meteors are sometimes visible before dawn, because the radiant
Radiant may refer to:
Computers, software, and video games
* Radiant (software), a content management system
* GtkRadiant, a level editor created by id Software for their games
* Radiant AI, a technology developed by Bethesda Softworks for ''The ...
is 32 degrees away from the Sun. They usually appear at a rate of 1–2 per hour as "earthgrazers", meteors that last several seconds and often begin at the horizon. Because most of the Daytime Arietids are not visible to the naked eye, they are observed in the radio spectrum. This is possible because of the ionized gas they leave in their wake. Other meteor showers radiate from Aries during the day; these include the Daytime Epsilon Arietids and the Northern and Southern Daytime May Arietids. The Jodrell Bank Observatory discovered the Daytime Arietids in 1947 when James Hey and G. S. Stewart adapted the World War II-era radar systems for meteor observations.
The Delta Arietids
Delta commonly refers to:
* Delta (letter) (Δ or δ), a letter of the Greek alphabet
* River delta, at a river mouth
* D ( NATO phonetic alphabet: "Delta")
* Delta Air Lines, US
* Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 that causes COVID-19
Delta may als ...
are another meteor shower radiating from Aries. Peaking on 9 December with a low peak rate, the shower lasts from 8 December to 14 January, with the highest rates visible from 8 to 14 December. The average Delta Arietid meteor is very slow, with an average velocity of per second. However, this shower sometimes produces bright fireball
Fireball may refer to:
Science
* Fireball (meteor), a brighter-than-usual meteor
* Ball lightning, an atmospheric electrical phenomenon
* ''Bassia scoparia'', a plant species
Arts and entertainment Films
* ''The Fireball'', a 1950 film starring ...
s. This meteor shower has northern and southern components, both of which are likely associated with 1990 HA
Year 199 ( CXCIX) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was sometimes known as year 952 ''Ab urbe condita''. The denomination 199 for this year has been used since th ...
, a near-Earth asteroid
A near-Earth object (NEO) is any small Solar System body whose orbit brings it into proximity with Earth. By convention, a Solar System body is a NEO if its closest approach to the Sun (perihelion) is less than 1.3 astronomical units (AU). ...
.
The Autumn Arietids
Autumn, also known as fall in American English and Canadian English, is one of the four temperate seasons on Earth. Outside the tropics, autumn marks the transition from summer to winter, in September (Northern Hemisphere) or March (Souther ...
also radiate from Aries. The shower lasts from 7 September to 27 October and peaks on 9 October. Its peak rate is low. The Epsilon Arietids appear from 12 to 23 October. Other meteor showers radiating from Aries include the October Delta Arietids, Daytime Epsilon Arietids
Daytime as observed on Earth is the period of the day during which a given location experiences natural illumination from direct sunlight. Daytime occurs when the Sun appears above the local horizon, that is, anywhere on the globe's hem ...
, Daytime May Arietids
Daytime as observed on Earth is the period of the day during which a given location experiences natural illumination from direct sunlight. Daytime occurs when the Sun appears above the local horizon, that is, anywhere on the globe's hemi ...
, Sigma Arietids
Sigma (; uppercase Σ, lowercase σ, lowercase in word-final position ς; grc-gre, σίγμα) is the eighteenth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 200. In general mathematics, uppercase Σ is used ...
, Nu Arietids
Nu or NU may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music
* Nu metal, a heavy metal fusion genre
* Nu jazz, a jazz fusion genre
* Nu-disco, a genre of dance music
* Nu gaze, a shoegaze fusion genre
* Nu prog, a subgenre of progressive rock
* Nu-fun ...
, and Beta Arietids
Beta (, ; uppercase , lowercase , or cursive ; grc, βῆτα, bē̂ta or ell, βήτα, víta) is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 2. In Modern Greek, it represents the voiced lab ...
. The Sigma Arietids, a class IV meteor shower, are visible from 12 to 19 October, with a maximum zenithal hourly rate of less than two meteors per hour on 19 October.
Planetary systems
Aries contains several stars with extrasolar planets.HIP 14810
HIP 14810 is a star with three exoplanetary companions in the northern constellation of Aries. It positioned about 1.3° to the north of Delta Arietis, but is too faint to be visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 8 ...
, a G5 type star, is orbited by three giant planets (those more than ten times the mass of Earth
An Earth mass (denoted as M_\mathrm or M_\oplus, where ⊕ is the standard astronomical symbol for Earth), is a unit of mass equal to the mass of the planet Earth. The current best estimate for the mass of Earth is , with a relative uncertain ...
). HD 12661
HD 12661 is a G-type main sequence star in the northern constellation of Aries. The star is slightly larger and more massive than the Sun, with an estimated age of seven billion years. It has two known extrasolar planets.
Properties
Th ...
, like HIP 14810, is a G-type main sequence star, slightly larger than the Sun, with two orbiting planets. One planet is 2.3 times the mass of Jupiter, and the other is 1.57 times the mass of Jupiter. HD 20367
HD 20367 is a star in the constellation of Aries, close to the border with the Perseus constellation. It is a yellow-white hued star that is a challenge to view with the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 6.40. Based upon p ...
is a G0 type star, approximately the size of the Sun, with one orbiting planet. The planet, discovered in 2002, has a mass 1.07 times that of Jupiter and orbits every 500 days. In 2019, scientists conducting the CARMENES survey at the Calar Alto Observatory
The Calar Alto Observatory (Centro Astronómico Hispano en Andalucía or "Spanish Astronomical Centre in Andalusia") is an astronomical observatory located in Almería province in Spain on Calar Alto, a mountain in the Sierra de Los Filabres ra ...
announced evidence of two Earth-mass exoplanets orbiting Teegarden's star, located in Aries, within its habitable zone. The star is a small red dwarf
''Red Dwarf'' is a British science fiction comedy franchise created by Rob Grant and Doug Naylor, which primarily consists of a television sitcom that aired on BBC Two between 1988 and 1999, and on Dave since 2009, gaining a cult following. T ...
with only around a tenth of the mass and radius of the Sun. It has a large radial velocity
The radial velocity or line-of-sight velocity, also known as radial speed or range rate, of a target with respect to an observer is the temporal rate of change, rate of change of the distance or Slant range, range between the two points. It is e ...
.
See also
*Aries (Chinese astronomy) According to traditional Chinese uranography, the modern constellation Aries is located within the western quadrant of the sky, which is symbolized as the White Tiger of the West (西方白虎, ''Xī Fāng Bái Hǔ'').
The name of the western con ...
References
Explanatory notes
Citations
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Online sources
* * * * * * * * * * * '' SIMBAD'' * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
The Deep Photographic Guide to the Constellations: Aries
Warburg Institute Iconographic Database (medieval and early modern images of Aries)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Aries (Constellation) Constellations Constellations listed by Ptolemy Northern constellations