|
Beta Arietis
Beta Arietis (β Arietis, abbreviated Beta Ari, β Ari), officially named Sheratan , is a star system and the second-brightest star in the constellation of Aries, marking the ram's second horn. Nomenclature ''Beta Arietis'' is the star's Bayer designation. It also bears the Flamsteed designation ''6 Arietis''. The traditional name, ''Sheratan'' (or ''Sharatan, Sheratim),'' in full ''Al Sharatan,'' is from the Arabic الشرطان ''aš-šaraţān'' "the two signs", a reference to the star having marked the northern vernal equinox together with Gamma Arietis several thousand years ago. In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalogue and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN approved the name ''Sheratan'' for this star on 21 August 2016 and it is now so entered in the IAU Catalog of Star Names. In Chinese, (), meaning ''Bond (asterism)'', refers to an asterism consisting of β Arietis, γ Arietis and α ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the Northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram. Its old astronomical symbol is (♈︎). It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation ranking 39th in overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere). Aries has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamal
Hamal , designation Alpha Arietis (α Arietis, abbreviated Alpha Ari, α Ari), is the brightest star in the northern zodiacal constellation of Aries. With an apparent visual magnitude of 2.0, it is the mean 50th-brightest star in the night sky. Based upon parallax measurements made with the ''Hipparcos'' astrometry satellite, Hamal is about from Earth. It is a giant star that may host an orbiting planet with a mass greater than Jupiter. Nomenclature ''Alpha Arietis'' is the star's Bayer designation. It also bears the Flamsteed designation of 13 Arietis. The traditional name ''Hamal'' (also written ''Hemal'', ''Hamul'', ''Ras Hammel'') derives from the Arabic ''rās al-ħamal'' "head of the ram", in turn from the name for the constellation as a whole, ''Al Ħamal'' "the ram". In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN's first bulletin of July 2016 included a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MK Spectral Classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the rainbow of colors interspersed with spectral lines. Each line indicates a particular chemical element or molecule, with the line strength indicating the abundance of that element. The strengths of the different spectral lines vary mainly due to the temperature of the photosphere, although in some cases there are true abundance differences. The ''spectral class'' of a star is a short code primarily summarizing the ionization state, giving an objective measure of the photosphere's temperature. Most stars are currently classified under the Morgan–Keenan (MK) system using the letters ''O'', ''B'', ''A'', ''F'', ''G'', ''K'', and ''M'', a sequence from the hottest (''O'' type) to the coolest (''M'' type). Each letter class is then subdivided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NStars
The ''Nearby Stars Database'' (NStars) began as a NASA project in 1998, then was based at Northern Arizona University. It is now defunct. The stated mission of NStars was "to be a complete and accurate source of scientific data about all stellar systems within 25 parsecs." The website (see below) included search tools and links to an interactive forum. Status As of 1 January 2002, there were 2,633 stars in 2,029 systems in the database. As of 29 January 2008, the site is closed, displaying the message ''"This site is currently undergoing a major redesign and will be returned to service at a later date."'' References External links Nearby Stars Database on the Wayback MachineThe Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia* [https://web.archive.org/web/20071112173559/http://www.chara.gsu.edu/RECONS/TOP100.posted.htm Old Table from Wayback Machine Web Archive] List as of 1 January 2009 Astronomical catalogues of stars Databases in the United States {{Astronomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermonuclear Fusion
Thermonuclear fusion is the process of atomic nuclei combining or “fusing” using high temperatures to drive them close enough together for this to become possible. There are two forms of thermonuclear fusion: ''uncontrolled'', in which the resulting energy is released in an uncontrolled manner, as it is in thermonuclear weapons ("hydrogen bombs") and in most stars; and ''controlled'', where the fusion reactions take place in an environment allowing some or all of the energy released to be harnessed for constructive purposes. Temperature requirements Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of particles, so by heating the material it will gain energy. After reaching sufficient temperature, given by the Lawson criterion, the energy of accidental collisions within the plasma is high enough to overcome the Coulomb barrier and the particles may fuse together. In a deuterium–tritium fusion reaction, for example, the energy necessary to overcome the Coulomb barrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A-type Main-sequence Star
An A-type main-sequence star (A V) or A dwarf star is a main-sequence (hydrogen-burning) star of spectral type A and luminosity class V (five). These stars have spectra defined by strong hydrogen Balmer absorption lines. They measure between 1.4 and 2.1 solar masses () and have surface temperatures between 7,600 and 10,000 K. Bright and nearby examples are Altair (A7 V), Sirius A (A1 V), and Vega (A0 V). A-type stars do not have convective zones and thus are not expected to harbor magnetic dynamos. As a consequence, because they do not have strong stellar winds, they lack a means to generate X-ray emissions. In July 2019, astronomers reported finding an A-type star, S5-HVS1, traveling , faster than any other star detected so far. The star is in the Grus (or Crane) constellation in the southern sky, about 29,000 light-years from Earth, and may have been ejected out of the Milky Way after interacting with Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black hole at the center o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their stellar spectrum, spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a Prism (optics), prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the Continuum (spectrum), rainbow of colors interspersed with spectral lines. Each line indicates a particular chemical element or molecule, with the line strength indicating the abundance of that element. The strengths of the different spectral lines vary mainly due to the temperature of the photosphere, although in some cases there are true abundance differences. The ''spectral class'' of a star is a short code primarily summarizing the ionization state, giving an objective measure of the photosphere's temperature. Most stars are currently classified under the Morgan–Keenan (MK) system using the letters ''O'', ''B'', ''A'', ''F'', ''G'', ''K'', and ''M'', a sequence from the hottest (''O'' type) to the coo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
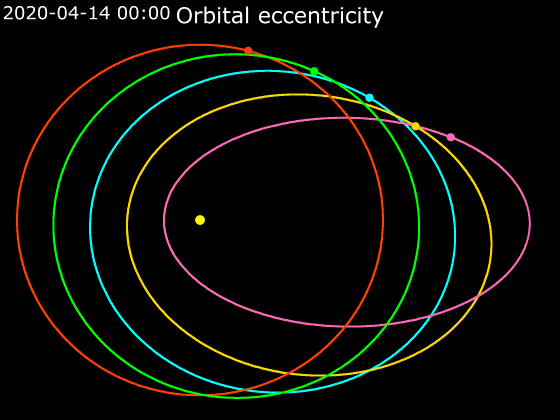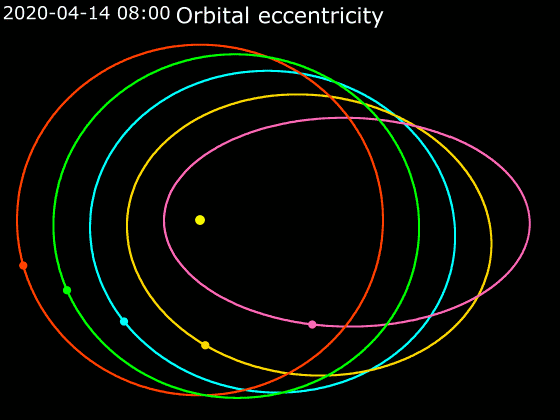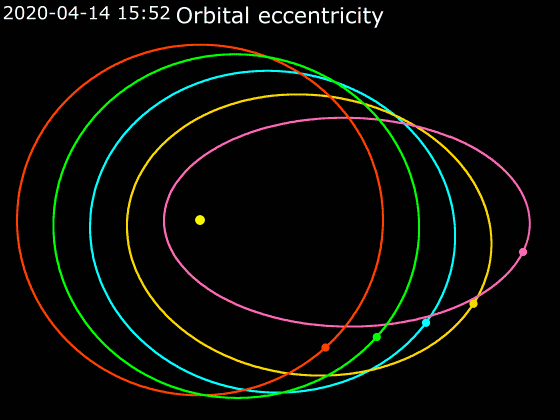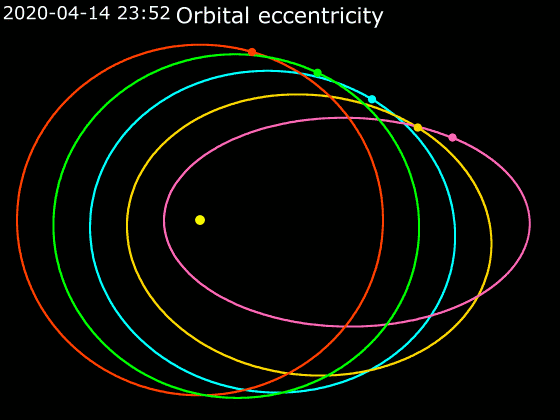
Elliptic Orbit
In astrodynamics or celestial mechanics, an elliptic orbit or elliptical orbit is a Kepler orbit with an eccentricity of less than 1; this includes the special case of a circular orbit, with eccentricity equal to 0. In a stricter sense, it is a Kepler orbit with the eccentricity greater than 0 and less than 1 (thus excluding the circular orbit). In a wider sense, it is a Kepler's orbit with negative energy. This includes the radial elliptic orbit, with eccentricity equal to 1. In a gravitational two-body problem with negative energy, both bodies follow similar elliptic orbits with the same orbital period around their common barycenter. Also the relative position of one body with respect to the other follows an elliptic orbit. Examples of elliptic orbits include: Hohmann transfer orbit, Molniya orbit, and tundra orbit. Velocity Under standard assumptions, no other forces acting except two spherically symmetrical bodies m1 and m2, the orbital speed (v\,) of one body trave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Elements
Orbital elements are the parameters required to uniquely identify a specific orbit. In celestial mechanics these elements are considered in two-body systems using a Kepler orbit. There are many different ways to mathematically describe the same orbit, but certain schemes, each consisting of a set of six parameters, are commonly used in astronomy and orbital mechanics. A real orbit and its elements change over time due to gravitational perturbations by other objects and the effects of general relativity. A Kepler orbit is an idealized, mathematical approximation of the orbit at a particular time. Keplerian elements The traditional orbital elements are the six Keplerian elements, after Johannes Kepler and his laws of planetary motion. When viewed from an inertial frame, two orbiting bodies trace out distinct trajectories. Each of these trajectories has its focus at the common center of mass. When viewed from a non-inertial frame centered on one of the bodies, only the traj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Wilson Observatory
The Mount Wilson Observatory (MWO) is an astronomical observatory in Los Angeles County, California, United States. The MWO is located on Mount Wilson, a peak in the San Gabriel Mountains near Pasadena, northeast of Los Angeles. The observatory contains two historically important telescopes: the Hooker telescope, which was the largest aperture telescope in the world from its completion in 1917 to 1949, and the 60-inch telescope which was the largest operational telescope in the world when it was completed in 1908. It also contains the Snow solar telescope completed in 1905, the 60 foot (18 m) solar tower completed in 1908, the 150 foot (46 m) solar tower completed in 1912, and the CHARA array, built by Georgia State University, which became fully operational in 2004 and was the largest optical interferometer in the world at its completion. Due to the inversion layer that traps warm air and smog over Los Angeles, Mount Wilson has steadier air than any other location in Nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark III Stellar Interferometer
The Mark III Stellar Interferometer was a long-baseline optical astronomical interferometer, located at the Mount Wilson Observatory, California, United States.The Mark III stellar interferometer, M. Shao et al., ''Astronomy and Astrophysics'' 193, #1-2 (March 1988), pp. 357–371, . It had a maximum baseline of 32 meters and operated in wavelengths between 450 and 800 nm. A joint venture between the United States Naval Observatory, the Naval Research Laboratory, the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, it began operation in 1987 and was closed in 1992. The Naval Observatory later constructed a larger interferometer, the Navy Prototype Optical Interferometer.pp. 37–39, Overview of Multiple-Aperture Interferometry Binary Star Results from the Northern Hemisphere, Harold A. McAlister, pp. 35–44 in ''Binary Stars as Critical Tools and Tests in Contemporary Astrophysics, Proceedings of the 240th Symposium of the International Ast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Star
A binary star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in which case they are called ''visual binaries''. Many visual binaries have long orbital periods of several centuries or millennia and therefore have orbits which are uncertain or poorly known. They may also be detected by indirect techniques, such as spectroscopy (''spectroscopic binaries'') or astrometry (''astrometric binaries''). If a binary star happens to orbit in a plane along our line of sight, its components will eclipse and transit each other; these pairs are called ''eclipsing binaries'', or, together with other binaries that change brightness as they orbit, ''photometric binaries''. If components in binary star systems are close enough they can gravitationally distort their mutual outer stellar atmospheres. In some cases, thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |