|
World's Littlest Skyscraper
The Newby–McMahon Building, commonly referred to as the World's littlest skyscraper, is located at 511 7th Street (on the corner of Seventh and La Salle streets) in downtown Wichita Falls, Texas. It is a late Neoclassical style red brick and cast stone structure. It stands tall, and its exterior dimensions are deep and wide. Its interior dimensions are approximately by , or approximately . Steep, narrow, internal stairways leading to the upper floors occupy roughly 25% of the interior area. Reportedly the result of a fraudulent investment scheme by a confidence man, the Newby–McMahon Building was a source of great embarrassment to the city and its residents after its completion in 1919. During the 1920s, the Newby–McMahon Building was featured in Robert Ripley's '' Ripley's Believe It or Not!'' syndicated column as "the world's littlest skyscraper," a nickname that has stuck with it ever since. The Newby–McMahon Building is now part of the Depot Square Historic Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wichita Falls, Texas
Wichita Falls ( ) is a city in and the seat of government of Wichita County, Texas, United States. It is the principal city of the Wichita Falls Metropolitan Statistical Area, which encompasses all of Archer, Clay, and Wichita counties. According to the 2010 census, it had a population of 104,553, making it the 38th-most populous city in Texas. In addition, its central business district is 5 miles (8 km) from Sheppard Air Force Base, which is home to the Air Force's largest technical training wing and the Euro-NATO Joint Jet Pilot Training program, the world's only multinationally staffed and managed flying training program chartered to produce combat pilots for both USAF and NATO. The city is home to the Newby-McMahon Building (otherwise known as the "world's littlest skyscraper"), constructed downtown in 1919 and featured in Robert Ripley's '' Ripley's Believe It or Not!''. History The Choctaw Native Americans settled the area in the early 1800s from their native Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Since 1854, the city has been coextensive with Philadelphia County, the most populous county in Pennsylvania and the urban core of the Delaware Valley, the nation's seventh-largest and one of world's largest metropolitan regions, with 6.245 million residents . The city's population at the 2020 census was 1,603,797, and over 56 million people live within of Philadelphia. Philadelphia was founded in 1682 by William Penn, an English Quaker. The city served as capital of the Pennsylvania Colony during the British colonial era and went on to play a historic and vital role as the central meeting place for the nation's founding fathers whose plans and actions in Philadelphia ultimately inspired the American Revolution and the nation's inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
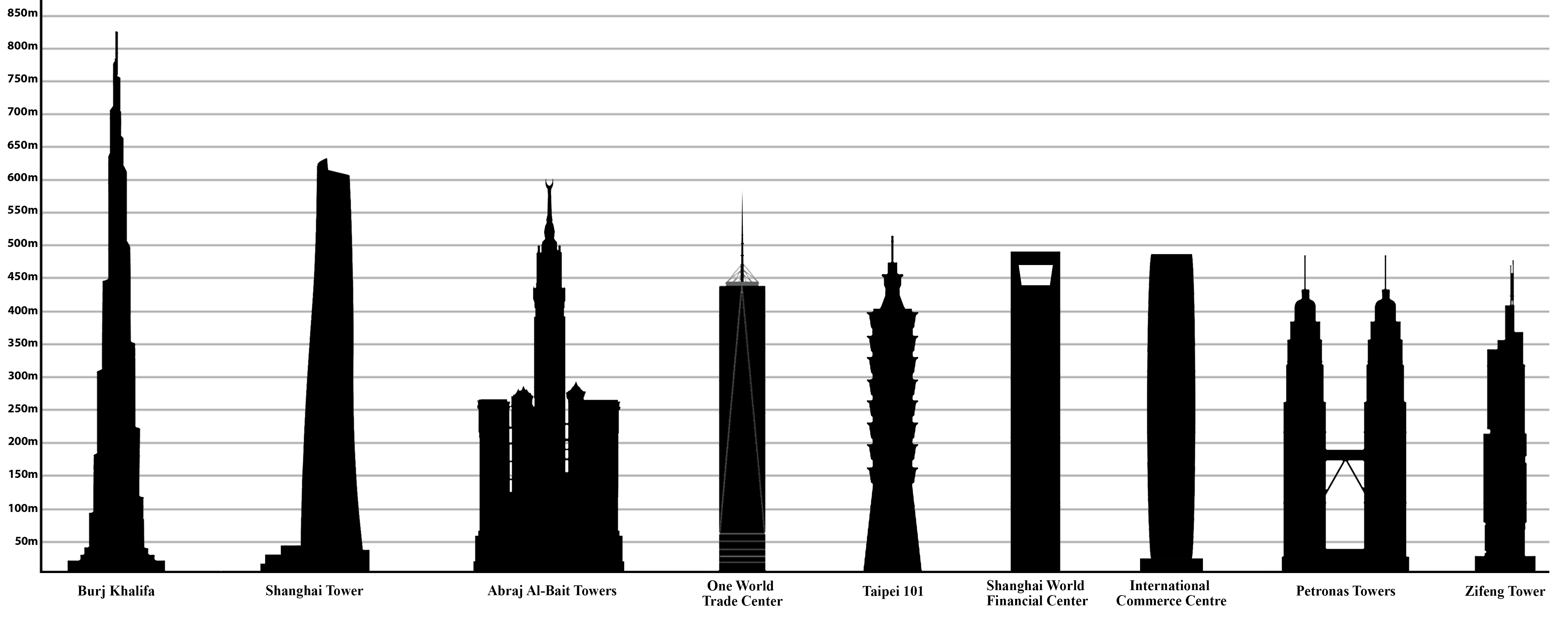
History Of The Tallest Buildings In The World
The tallest building in the world, as of , is the Burj Khalifa. The title of " world's tallest building" has been borne by various buildings, such as the Lincoln Cathedral, the Empire State Building and the original World Trade Center. Before the modern skyscraper era, between 1311 and 1884, the tallest buildings and structures were mostly Christian churches and cathedrals. Before the 13th century, the tallest buildings in the world cannot be conclusively determined. For instance, the Lighthouse of Alexandria (completed about 280 BC) has been estimated to have been tall, but its true height is not known. For thousands of years, the Great Pyramid in Egypt was the tallest ''structure'' in the world until Lincoln Cathedral of 1311, but the Great Pyramid is not considered a building since it is not habitable. Similarly, the Eiffel Tower was the world's tallest structure from 1889, when it was built, but not the tallest building. The skyscraper was invented in Chicago in 1884 when th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Register Of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic value". A property listed in the National Register, or located within a National Register Historic District, may qualify for tax incentives derived from the total value of expenses incurred in preserving the property. The passage of the National Historic Preservation Act (NHPA) in 1966 established the National Register and the process for adding properties to it. Of the more than one and a half million properties on the National Register, 95,000 are listed individually. The remainder are contributing resources within historic districts. For most of its history, the National Register has been administered by the National Park Service (NPS), an agency within the U.S. Department of the Interior. Its goals are to help property owners and inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tower Block
A tower block, high-rise, apartment tower, residential tower, apartment block, block of flats, or office tower is a tall building A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and fun ..., as opposed to a low-rise building and is defined differently in terms of height depending on the jurisdiction. It is used as a apartment building, residential, office building, or other functions including hotel, retail, or with multiple purposes combined. Residential high-rise buildings are also known in some varieties of English, such as British English, as tower blocks and may be referred to as MDUs, standing for multi-dwelling units. A very tall high-rise building is referred to as a skyscraper. High-rise buildings became possible to construct with the invention of the elevator (lift) and wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skyscraper
A skyscraper is a tall continuously habitable building having multiple floors. Modern sources currently define skyscrapers as being at least or in height, though there is no universally accepted definition. Skyscrapers are very tall high-rise buildings. Historically, the term first referred to buildings with between 10 and 20 stories when these types of buildings began to be constructed in the 1880s. Skyscrapers may host offices, hotels, residential spaces, and retail spaces. One common feature of skyscrapers is having a steel frame that supports curtain walls. These curtain walls either bear on the framework below or are suspended from the framework above, rather than resting on load-bearing walls of conventional construction. Some early skyscrapers have a steel frame that enables the construction of load-bearing walls taller than of those made of reinforced concrete. Modern skyscrapers' walls are not load-bearing, and most skyscrapers are characterised by large surface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax Increment Financing
Tax increment financing (TIF) is a public financing method that is used as a subsidy for redevelopment, infrastructure, and other community-improvement projects in many countries, including the United States. The original intent of a TIF program is to stimulate private investment in a blighted area that has been designated to be in need of economic revitalization. Similar or related value capture strategies are used around the world. Through the use of TIF, municipalities typically divert future property tax revenue increases from a defined area or district toward an economic development project or public improvement project in the community. TIF subsidies are not appropriated directly from a city's budget, but the city incurs loss through forgone tax revenue. The first TIF was used in California in 1952. By 2004, all U.S. states excepting Arizona had authorized the use of TIF. The first TIF in Canada was used in 2007. This model has been heavily criticized by Libertarian-Conservat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wichita Falls October 2015 18 (Hello Again! And "world's Littlest Skyscraper")
Wichita ( ) may refer to: People *Wichita people, a Native American tribe *Wichita language, the language of the tribe Places in the United States * Wichita, Kansas, a city * Wichita County, Kansas, a county in western Kansas (city of Wichita is located in Sedgwick County) * Wichita Falls, Texas, a city * Wichita County, Texas * Wichita Mountains In the military *, a heavy cruiser class of the US Navy **, the only ship of the class; active in World War II *, a class of US Navy oilers from the late 1960s to the mid-1990s **, the lead ship of the class; in service from 1969 to 1993 *Beechcraft AT-10 Wichita, a World War II trainer airplane for the United States Army Air Forces In entertainment * ''Wichita'' (1955 film), a 1955 American Western movie directed by Jacques Tourneur *''Wichita'', early title of a proposed movie, eventually made as ''Knight and Day'' starring Cameron Diaz and Tom Cruise *Wichita Recordings, a London-based independent record label See also *Ouachita ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagion began around September and led to the Wall Street stock market crash of October 24 (Black Thursday). It was the longest, deepest, and most widespread depression of the 20th century. Between 1929 and 1932, worldwide gross domestic product (GDP) fell by an estimated 15%. By comparison, worldwide GDP fell by less than 1% from 2008 to 2009 during the Great Recession. Some economies started to recover by the mid-1930s. However, in many countries, the negative effects of the Great Depression lasted until the beginning of World War II. Devastating effects were seen in both rich and poor countries with falling personal income, prices, tax revenues, and profits. International trade fell by more than 50%, unemployment in the U.S. rose to 23% and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas Oil Boom
The Texas oil boom, sometimes called the gusher age, was a period of dramatic change and economic growth in the U.S. state of Texas during the early 20th century that began with the discovery of a large petroleum reserve near Beaumont, Texas. The find was unprecedented in its size (worldwide) and ushered in an age of rapid regional development and industrialization that has few parallels in U.S. history. Texas quickly became one of the leading oil-producing states in the U.S., along with Oklahoma and California; soon the nation overtook the Russian Empire as the top producer of petroleum. By 1940 Texas had come to dominate U.S. production. Some historians even define the beginning of the world's Oil Age as the beginning of this era in Texas. The major petroleum strikes that began the rapid growth in petroleum exploration and speculation occurred in Southeast Texas, but soon reserves were found across Texas and wells were constructed in North Texas, East Texas, and the Permia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resource Curse
The resource curse, also known as the paradox of plenty or the poverty paradox, is the phenomenon of countries with an abundance of natural resources (such as fossil fuels and certain minerals) having less economic growth, less democracy, or worse economic development, development outcomes than countries with fewer natural resources. There are many theories and much academic debate about the reasons for, and exceptions to, these adverse outcomes. Most experts believe the resource curse is not universal or inevitable, but affects certain types of countries or regions under certain conditions. Thesis As far back as 1711 ''The Spectator (1711), The Spectator'' wrote "It is generally observed, that in countries of the greatest plenty there is the poorest living". The idea that resources might be more of an economic curse than a blessing emerged in debates in the 1950s and 1960s about the economic problems of low and middle-income countries. In 1993 Richard Auty first used the term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)