|
Vindoline
Vindoline is a chemical precursor to vinblastine. Vindoline is formed through biosynthesis from Tabersonine Tabersonine is a terpene indole alkaloid found in the medicinal plant ''Catharanthus roseus'' and also in the genus Voacanga (both taxa belonging to the alkaloid-rich family Apocynaceae). Tabersonine is hydroxylated at the 16 position by the enzy .... See also * Lochnericine References Tryptamine alkaloids Indolizidines {{alkaloid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinblastine
Vinblastine (VBL), sold under the brand name Velban among others, is a chemotherapy medication, typically used with other medications, to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes Hodgkin's lymphoma, non-small cell lung cancer, bladder cancer, brain cancer, melanoma, and testicular cancer. It is given by injection into a vein. Most people experience some side effects. Commonly it causes a change in sensation, constipation, weakness, loss of appetite, and headaches. Severe side effects include low blood cell counts and shortness of breath. It should not be given to people who have a current bacterial infection. Use during pregnancy will likely harm the baby. Vinblastine works by blocking cell division. Vinblastine was isolated in 1958. An example of a natural herbal remedy that has since been developed into a conventional medicine, vinblastine was originally obtained from the Madagascar periwinkle. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabersonine
Tabersonine is a terpene indole alkaloid found in the medicinal plant ''Catharanthus roseus'' and also in the genus Voacanga (both taxa belonging to the alkaloid-rich family Apocynaceae). Tabersonine is hydroxylated at the 16 position by the enzyme tabersonine 16-hydroxylase (T16H) to form 16-hydroxytabersonine.St-Pierre and De Luca (1995) A Cytochrome P-450 Monooxygenase Catalyzes the First Step in the Conversion of Tabersonine to Vindoline in Catharanthus roseus. Plant Physiology. 109(1). 131-139 The enzyme leading to its formation is currently unknown. Tabersonine is the first intermediate leading to the formation of vindoline one of the two precursors required for vinblastine biosynthesis. See also *Conopharyngine * Tabernanthine *Vinblastine Vinblastine (VBL), sold under the brand name Velban among others, is a chemotherapy medication, typically used with other medications, to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes Hodgkin's lymphoma, non-small cell lung c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lochnericine
Lochnericine is a major monoterpene indole alkaloid present in the roots of ''Catharanthus roseus''. It is also present in ''Tabernaemontana divaricata''. Chemistry Synthesis Lochnericine is formed from stereoselective epoxidation of carbons 6 and 7 of tabersonine. Derivatives See also * Pericine * Pervine * Tabersonine * Vincamine Vincamine is a monoterpenoid indole alkaloid found in the leaves of ''Vinca minor'' (lesser periwinkle), comprising about 25-65% of its indole alkaloids by weight. It can also be synthesized from related alkaloids. Uses Vincamine is sold in Eur ... References {{Reflist Indole alkaloids Alkaloids found in Apocynaceae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
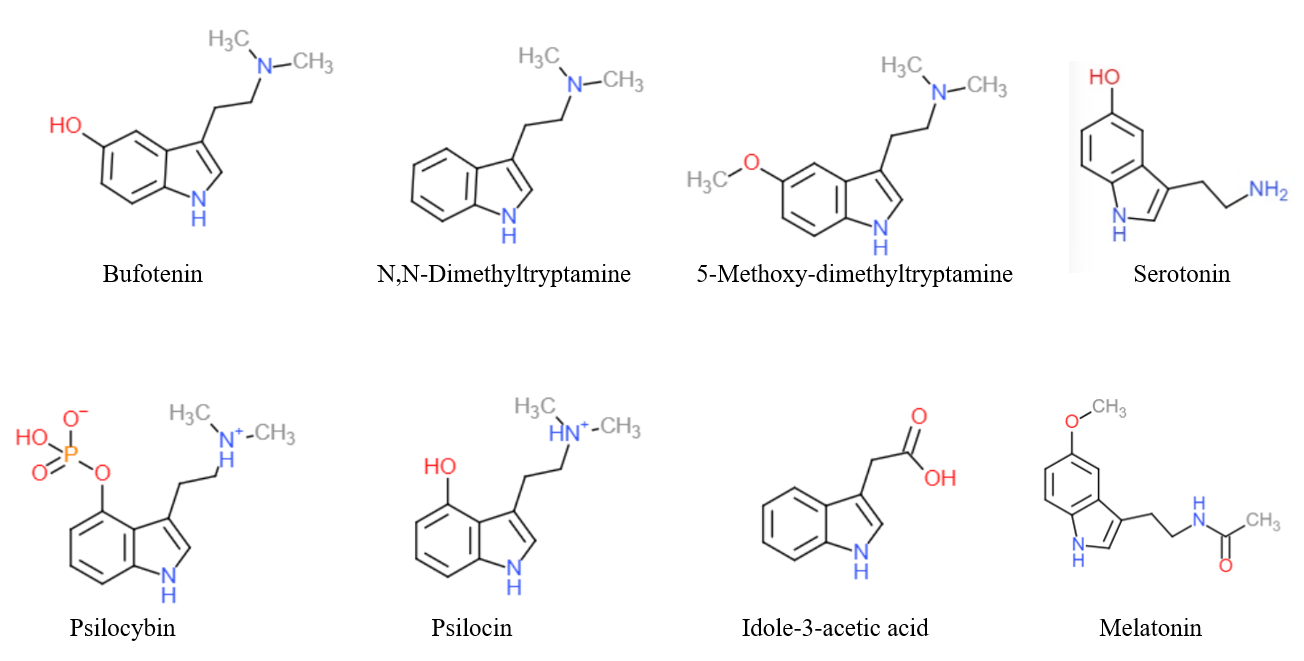
Tryptamine Alkaloids
Tryptamine is an indolamine metabolite of the essential amino acid, tryptophan. The chemical structure is defined by an indole ─ a fused benzene and pyrrole ring, and a 2-aminoethyl group at the second carbon (third aromatic atom, with the first one being the heterocyclic nitrogen). The structure of tryptamine is a shared feature of certain aminergic neuromodulators including melatonin, serotonin, bufotenin and psychedelic derivatives such as dimethyltryptamine (DMT), psilocybin, psilocin and others. Tryptamine has been shown to activate trace amine-associated receptors expressed in the mammalian brain, and regulates the activity of dopaminergic, serotonergic and glutamatergic systems. In the human gut, symbiotic bacteria convert dietary tryptophan to tryptamine, which activates 5-HT4 receptors and regulates gastrointestinal motility. Multiple tryptamine-derived drugs have been developed to treat migraines, while trace amine-associated receptors are being explored as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |