|
Vicuña
The vicuña (''Lama vicugna'') or vicuna (both , very rarely spelled ''vicugna'', its former genus name) is one of the two wild South American camelids, which live in the high alpine areas of the Andes, the other being the guanaco, which lives at lower elevations. Vicuñas are relatives of the llama, and are now believed to be the wild ancestor of domesticated alpacas, which are raised for their coats. Vicuñas produce small amounts of extremely fine wool, which is very expensive because the animal can only be shorn every three years and has to be caught from the wild. When knitted together, the product of the vicuña's wool is very soft and warm. The Inca valued vicuñas highly for their wool, and it was against the law for anyone but royalty to wear vicuña garments; today, the vicuña is the national animal of Peru and appears on the Peruvian coat of arms. Both under the rule of the Inca and today, vicuñas have been protected by law, but they were heavily hunted in the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Llama
The llama (; ) (''Lama glama'') is a domesticated South American camelid, widely used as a List of meat animals, meat and pack animal by Inca empire, Andean cultures since the Pre-Columbian era. Llamas are social animals and live with others as a herd. Their wool is soft and contains only a small amount of lanolin. Llamas can learn simple tasks after a few repetitions. When using a pack, they can carry about 25 to 30% of their body weight for 8 to 13 kilometre, km (5–8 miles). The name ''llama'' (in the past also spelled "lama" or "glama") was adopted by European colonization of the Americas, European settlers from Indigenous people in Peru, native Peruvians. The ancestors of llamas are thought to have originated from the Great Plains of North America about 40 million years ago, and subsequently migrated to South America about three million years ago during the Great American Interchange. By the end of the last Quaternary glaciation, ice age (10,000–12,000 years ago), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpaca
The alpaca (''Lama pacos'') is a species of South American camelid mammal. It is similar to, and often confused with, the llama. However, alpacas are often noticeably smaller than llamas. The two animals are closely related and can successfully crossbreed. Both species are believed to have been domesticated from their wild relatives, the vicuña and guanaco. There are two breeds of alpaca: the Suri alpaca and the Huacaya alpaca. Alpacas are kept in herds that graze on the level heights of the Andes of Southern Peru, Western Bolivia, Ecuador, and Northern Chile at an altitude of above sea level. Alpacas are considerably smaller than llamas, and unlike llamas, they were not bred to be working animals, but were bred specifically for their fiber. Alpaca fiber is used for making knitted and woven items, similar to sheep's wool. These items include blankets, sweaters, hats, gloves, scarves, a wide variety of textiles, and ponchos, in South America, as well as sweaters, socks, coat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vicugna
'''' is a genus containing four South American camelids, the wild guanaco and vicuña, and the domesticated llama and alpaca. Before the Spanish conquest of the Americas, llamas and alpacas were the only domesticated ungulates of the continent. They were kept not only for their value as beasts of burden, but also for their flesh, hides, and wool. Classification Although they were often compared to sheep by early writers, their affinity to the camel was soon perceived. They were included in the genus ''Camelus'' in the ''Systema Naturae'' of Linnaeus. In 1800, Cuvier moved the llama, alpaca, and guanaco to the genus ''Lama'', and the vicuña to the genus ''Vicugna''. Later, the alpaca was transferred to ''Vicugna''; both were eventually returned to ''Lama'' by the American Society of Mammalogists in 2021. These camelids are, with the two species of true camels, the sole extant representatives of a distinct section of Artiodactyla (even-toed ungulates) called Tylopoda, or "hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
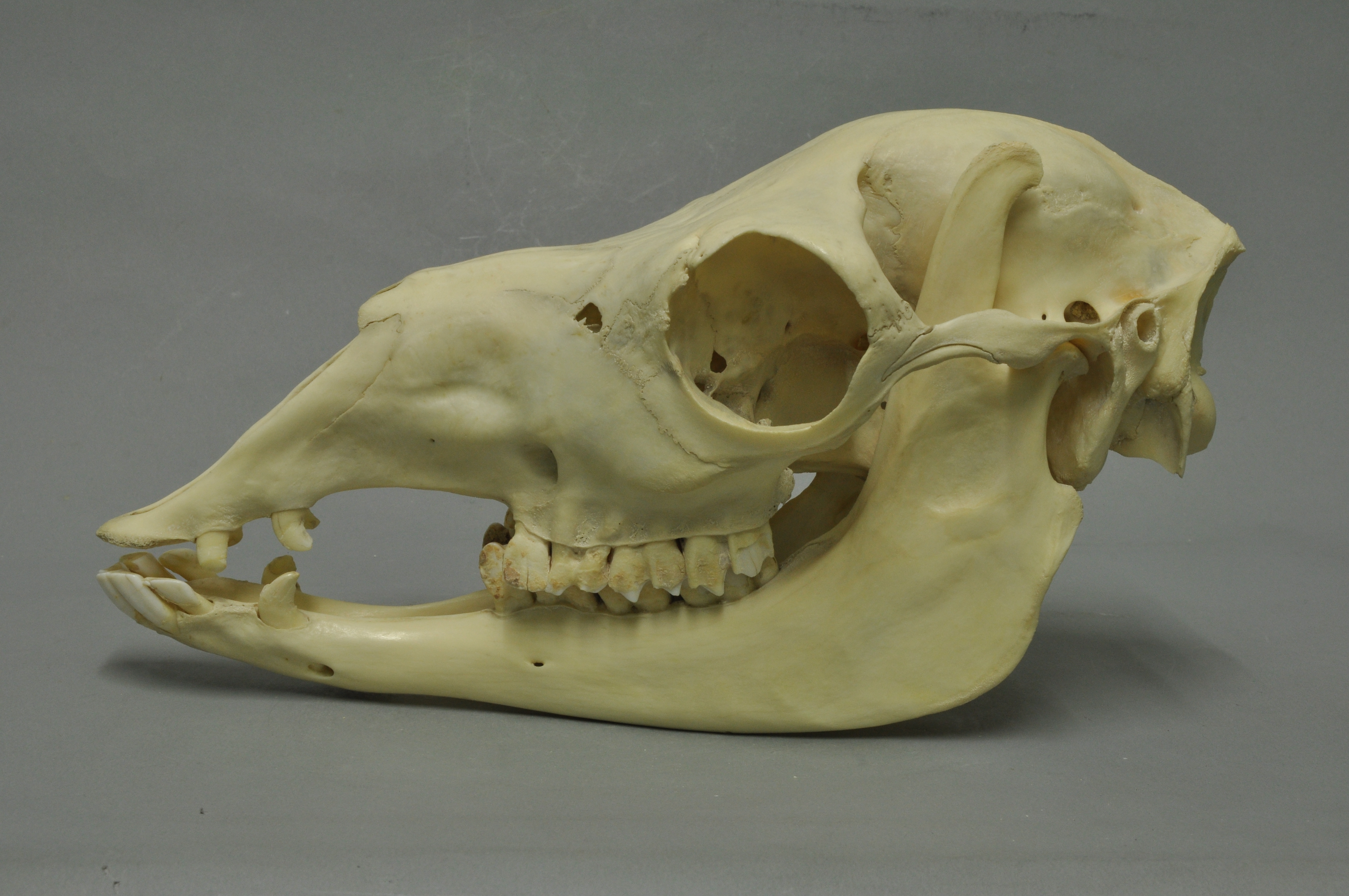
Camelid
Camelids are members of the biological family Camelidae, the only currently living family in the suborder Tylopoda. The seven extant members of this group are: dromedary camels, Bactrian camels, wild Bactrian camels, llamas, alpacas, vicuñas, and guanacos. Camelids are even-toed ungulates classified in the order Cetartiodactyla, along with species like whales, pigs, deer, cattle, and antelopes. Characteristics Camelids are large, strictly herbivorous animals with slender necks and long legs. They differ from ruminants in a number of ways.Fowler, M.E. (2010). ''Medicine and Surgery of Camelids'', Ames, Iowa: Wiley-Blackwell. Chapter 1 "General Biology and Evolution" addresses the fact that camelids (including camels and llamas) are not ruminants, pseudo-ruminants, or modified ruminants. Their dentition show traces of vestigial central incisors in the incisive bone, and the third incisors have developed into canine-like tusks. Camelids also have true canine teeth and tusk-lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
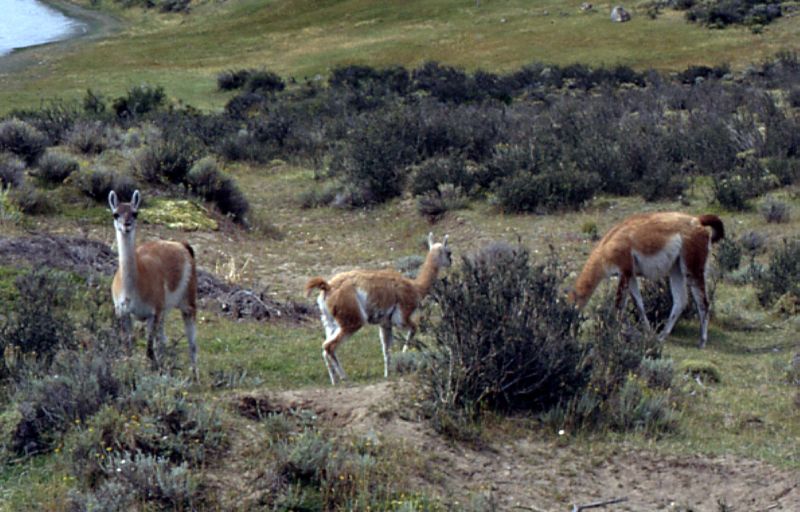
Guanaco
The guanaco (; ''Lama guanicoe'') is a camelid native to South America, closely related to the llama. Guanacos are one of two wild South American camelids, the other being the vicuña, which lives at higher elevations. Etymology The guanaco gets its name from the Quechua word ''huanaco'' (modern spelling ''wanaku''). Young guanacos are called ''chulengos''. Characteristics Guanacos stand between at the shoulder, body length of , and weigh . Their color varies very little (unlike the domestic llama), ranging from a light brown to dark cinnamon and shading to white underneath. Guanacos have grey faces and small, straight ears. The lifespan of a guanaco can be as long as 28 years. Guanacos are one of the largest terrestrial mammals native to South America today.San Diego Zoo's Animal Bytes Other terrestrial mammali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat Of Arms Of Peru
The Coat of arms of Peru is the national symbolic emblem of Peru. Four variants are used: the Coat of arms ''per se'' ('); the National Coat of arms, or National Shield ('); the Great Seal of the State ('); and the Naval Coat of arms ('). Official description Peruvian law describes the coat of arms as follows: :''"The arms of the Peruvian Nation shall consist of a shield divided into three fields: one azure (heraldry), celestial blue to the right, with a vicuna looking inside; other argent, white to the left, with a Cinchona officinalis placed within, and another, gules, red, in the bottom and smaller, with a cornucopia pouring coins, signifying with these symbols the treasures of Peru in the three realms of nature. The coat of arms shall be surmounted by a civic crown in flat view; and accompanied on each side by a flag and a standard of national colors, further described below."'' Variants The Coat of arms The coat of arms (') has a palm branch on its left and a Bay Laurel, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South American
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southern subregion of a single continent called America. South America is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east by the Atlantic Ocean; North America and the Caribbean Sea lie to the northwest. The continent generally includes twelve sovereign states: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, and Venezuela; two dependent territories: the Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and one internal territory: French Guiana. In addition, the ABC islands of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Ascension Island (dependency of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha, a British Overseas Territory), Bouvet Island ( dependency of Norway), Panama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culpeo
The culpeo (''Lycalopex culpaeus''), also known as culpeo zorro, Andean zorro, Andean fox, Paramo wolf, Andean wolf,Comparative ecology of two South American foxes, 'Dusicvon ariseus' and 'culpaeus' by Warren E. Johnson. Doctoral dissertation. Iowa State University; 1992. p2. Accessed July 10, 2021 at https://lib.dr.iastate.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=11006&context=rtd and colpeo fox, is a species of South American fox. Regardless of the name, it is not a true fox, but more closely related to wolves and jackals. Its appearance resembles that of foxes due to convergent evolution. It is the second-largest native canid on the continent after the maned wolf. In appearance, it bears many similarities to the widely recognized red fox. It has grey and reddish fur, a white chin, reddish legs and a stripe on its back that may be barely visible. The culpeo's diet consists largely of rodents, rabbits, birds and lizards, and to a lesser extent, plant material and carrion. The culpeo doe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atacama Desert
The Atacama Desert ( es, Desierto de Atacama) is a desert plateau in South America covering a 1,600 km (990 mi) strip of land on the Pacific coast, west of the Andes Mountains. The Atacama Desert is the driest nonpolar desert in the world, and the second driest overall, just behind some very specific spots within the McMurdo Dry Valleys as well as the only hot true desert to receive less precipitation than the polar deserts, and the largest fog desert in the world. Both regions have been used as experimentation sites on Earth for Mars expedition simulations. The Atacama Desert occupies , or if the barren lower slopes of the Andes are included. Most of the desert is composed of stony terrain, salt lakes (''salares''), sand, and felsic lava that flows towards the Andes. The desert owes its extreme aridity to a constant temperature inversion due to the cool north-flowing Humboldt ocean current and to the presence of the strong Pacific anticyclone. The most arid re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andes
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S latitude), and has an average height of about . The Andes extend from north to south through seven South American countries: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina. Along their length, the Andes are split into several ranges, separated by intermediate depressions. The Andes are the location of several high plateaus—some of which host major cities such as Quito, Bogotá, Cali, Arequipa, Medellín, Bucaramanga, Sucre, Mérida, El Alto and La Paz. The Altiplano plateau is the world's second-highest after the Tibetan plateau. These ranges are in turn grouped into three major divisions based on climate: the Tropical Andes, the Dry Andes, and the Wet Andes. The Andes Mountains are the highest m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inca
The Inca Empire (also known as the Incan Empire and the Inka Empire), called ''Tawantinsuyu'' by its subjects, (Quechua for the "Realm of the Four Parts", "four parts together" ) was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The administrative, political and military center of the empire was in the city of Cusco. The Inca civilization arose from the Peruvian highlands sometime in the early 13th century. The Spanish began the conquest of the Inca Empire in 1532 and by 1572, the last Inca state was fully conquered. From 1438 to 1533, the Incas incorporated a large portion of western South America, centered on the Andean Mountains, using conquest and peaceful assimilation, among other methods. At its largest, the empire joined modern-day Peru, what are now western Ecuador, western and south central Bolivia, northwest Argentina, the southwesternmost tip of Colombia and a large portion of modern-day Chile, and into a state comparable to the historical empires of Eurasia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Holocene
In the geologic time scale, the Greenlandian is the earliest age or lowest stage of the Holocene Epoch or Series, part of the Quaternary. Beginning in 11,650 BP (9701 BCE or 300 HE) and ending 8,276 BP (6237 BCE or 3764 HE), it is the earliest of three sub-divisions of the Holocene. It was officially ratified by the International Commission on Stratigraphy in June 2018 with the later Northgrippian and Meghalayan Ages/Stages. The lower boundary of the Greenlandian Age is the GSSP sample from the North Greenland Ice Core Project in central Greenland (75.1000°N 42.3200°W). The Greenlandian GSSP has been correlated with the end of Younger Dryas The Younger Dryas (c. 12,900 to 11,700 years BP) was a return to glacial conditions which temporarily reversed the gradual climatic warming after the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM, c. 27,000 to 20,000 years BP). The Younger Dryas was the last stage ... (from near-glacial to interglacial) and a "shift in deuterium excess values". Referenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)
