|
Venomics
Venomics is the large-scale study of proteins associated with venom. Venom is a toxic substance secreted by animals, which is typically injected either offensively or defensively into prey or aggressors, respectively. Venom is produced in a specialised gland (or glands) and is delivered through hollow fangs or a stinger. The main function of venom is to disrupt the physiological processes of the wounded animal through either neurotoxic or haemotoxic mechanisms. This can then help in certain processes such as procuring prey or deterring/escaping predators. Venom has evolved many times in multiple phyla, each having developed their own unique types of venom and methods of delivery independently. However, due to the excessive amounts of venomous animals in the world, they are the major cause of animal-related deaths (~ 57,000 in 2013) than non-venomous animals (~22,000). For example, snakes are responsible for more than 1-5 million biting-injuries, 421,000 (to 1.8 million) envenoming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venomics Workflow
Venomics is the large-scale study of proteins associated with venom. Venom is a toxic substance secreted by animals, which is typically injected either offensively or defensively into prey or aggressors, respectively. Venom is produced in a specialised gland (or glands) and is delivered through hollow fangs or a stinger. The main function of venom is to disrupt the physiological processes of the wounded animal through either Neurotoxin, neurotoxic or Hemotoxin, haemotoxic mechanisms. This can then help in certain processes such as procuring prey or deterring/escaping predators. Venom has evolved many times in multiple phyla, each having developed their own unique types of venom and methods of delivery independently. However, due to the excessive amounts of venomous animals in the world, they are the major cause of animal-related deaths (~ 57,000 in 2013) than non-venomous animals (~22,000). For example, snakes are responsible for more than 1-5 million biting-injuries, 421,000 (to 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcriptomics Technologies
Transcriptomics technologies are the techniques used to study an organism's transcriptome, the sum of all of its RNA transcripts. The information content of an organism is recorded in the DNA of its genome and expressed through transcription. Here, mRNA serves as a transient intermediary molecule in the information network, whilst non-coding RNAs perform additional diverse functions. A transcriptome captures a snapshot in time of the total transcripts present in a cell. Transcriptomics technologies provide a broad account of which cellular processes are active and which are dormant. A major challenge in molecular biology is to understand how a single genome gives rise to a variety of cells. Another is how gene expression is regulated. The first attempts to study whole transcriptomes began in the early 1990s. Subsequent technological advances since the late 1990s have repeatedly transformed the field and made transcriptomics a widespread discipline in biological sciences. There ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three-finger Protein
Three-finger proteins or three-finger protein domains (3FP or TFPD) are a protein superfamily consisting of small, roughly 60-80 amino acid residue protein domains with a common tertiary structure: three beta strand loops extended from a hydrophobic core stabilized by disulfide bonds. The family is named for the outstretched "fingers" of the three loops. Members of the family have no enzymatic activity, but are capable of forming protein-protein interactions with high specificity and affinity. The founding members of the family, also the best characterized by structure, are the three-finger toxins found in snake venom, which have a variety of pharmacological effects, most typically by disruption of cholinergic signaling. The family is also represented in non-toxic proteins, which have a wide taxonomic distribution; 3FP domains occur in the extracellular domains of some cell-surface receptors as well as in GPI-anchored and secreted globular proteins, usually involved in signaling. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venom Amino Acid Structure
Venom or zootoxin is a type of toxin produced by an animal that is actively delivered through a wound by means of a bite, sting, or similar action. The toxin is delivered through a specially evolved ''venom apparatus'', such as fangs or a stinger, in a process called envenomation. Venom is often distinguished from poison, which is a toxin that is passively delivered by being ingested, inhaled, or absorbed through the skin, and toxungen, which is actively transferred to the external surface of another animal via a physical delivery mechanism. Venom has evolved in terrestrial and marine environments and in a wide variety of animals: both predators and prey, and both vertebrates and invertebrates. Venoms kill through the action of at least four major classes of toxin, namely necrotoxins and cytotoxins, which kill cells; neurotoxins, which affect nervous systems; myotoxins, which damage muscles; and haemotoxins, which disrupt blood clotting. Venomous animals cause tens of thousan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venom
Venom or zootoxin is a type of toxin produced by an animal that is actively delivered through a wound by means of a bite, sting, or similar action. The toxin is delivered through a specially evolved ''venom apparatus'', such as fangs or a stinger, in a process called envenomation. Venom is often distinguished from poison, which is a toxin that is passively delivered by being ingested, inhaled, or absorbed through the skin, and toxungen, which is actively transferred to the external surface of another animal via a physical delivery mechanism. Venom has evolved in terrestrial and marine environments and in a wide variety of animals: both predators and prey, and both vertebrates and invertebrates. Venoms kill through the action of at least four major classes of toxin, namely necrotoxins and cytotoxins, which kill cells; neurotoxins, which affect nervous systems; myotoxins, which damage muscles; and haemotoxins, which disrupt blood clotting. Venomous animals cause tens of thousa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genomics
Genomics is an interdisciplinary field of biology focusing on the structure, function, evolution, mapping, and editing of genomes. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes as well as its hierarchical, three-dimensional structural configuration. In contrast to genetics, which refers to the study of ''individual'' genes and their roles in inheritance, genomics aims at the collective characterization and quantification of ''all'' of an organism's genes, their interrelations and influence on the organism. Genes may direct the production of proteins with the assistance of enzymes and messenger molecules. In turn, proteins make up body structures such as organs and tissues as well as control chemical reactions and carry signals between cells. Genomics also involves the sequencing and analysis of genomes through uses of high throughput DNA sequencing and bioinformatics to assemble and analyze the function and structure of entire genomes. Advances in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natriuretic Peptide Precursor C
Natriuretic peptide precursor C, also known as NPPC, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NPPC'' gene. The precursor NPPC protein is cleaved to the 22 amino acid peptide C-type natriuretic peptide (''CNP''). Function Natriuretic peptides comprise a family of 3 structurally related molecules: atrial natriuretic peptide ( ANP), brain natriuretic peptide ( BNP), and C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP), encoded by a gene symbolized ''NPPC''. These peptides possess potent natriuretic, diuretic, and vasodilating activities and are implicated in body fluid homeostasis and blood pressure control. Unlike ANP and BNP, CNP does not have direct natriuretic activity. This is because CNP is a selective agonist An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the ago ... for the B-type natriure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phospholipase A2
The enzyme phospholipase A2 (EC 3.1.1.4, PLA2, systematic name phosphatidylcholine 2-acylhydrolase) catalyse the cleavage of fatty acids in position 2 of phospholipids, hydrolyzing the bond between the second fatty acid “tail” and the glycerol molecule: :phosphatidylcholine + H2O = 1-acylglycerophosphocholine + a carboxylate This particular phospholipase specifically recognizes the ''sn''2 acyl bond of phospholipids and catalytically hydrolyzes the bond, releasing arachidonic acid and lysophosphatidic acid. Upon downstream modification by cyclooxygenases or lipoxygenases, arachidonic acid is modified into active compounds called eicosanoids. Eicosanoids include prostaglandins and leukotrienes, which are categorized as anti-inflammatory and inflammatory mediators. PLA2 enzymes are commonly found in mammalian tissues as well as arachnid, insect, and snake venom. Venom from bees is largely composed of melittin, which is a stimulant of PLA2. Due to the increased presenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metalloproteinase
A metalloproteinase, or metalloprotease, is any protease enzyme whose catalytic mechanism involves a metal. An example is ADAM12 which plays a significant role in the fusion of muscle cells during embryo development, in a process known as myogenesis. Most metalloproteases require zinc, but some use cobalt. The metal ion is coordinated to the protein via three ligands. The ligands coordinating the metal ion can vary with histidine, glutamate, aspartate, lysine, and arginine. The fourth coordination position is taken up by a labile water molecule. Treatment with chelating agents such as EDTA leads to complete inactivation. EDTA is a metal chelator that removes zinc, which is essential for activity. They are also inhibited by the chelator orthophenanthroline. Classification There are two subgroups of metalloproteinases: * Exopeptidases, metalloexopeptidases ( EC number: 3.4.17). * Endopeptidases, metalloendopeptidases (3.4.24). Well known metalloendopeptidases include ADAM pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
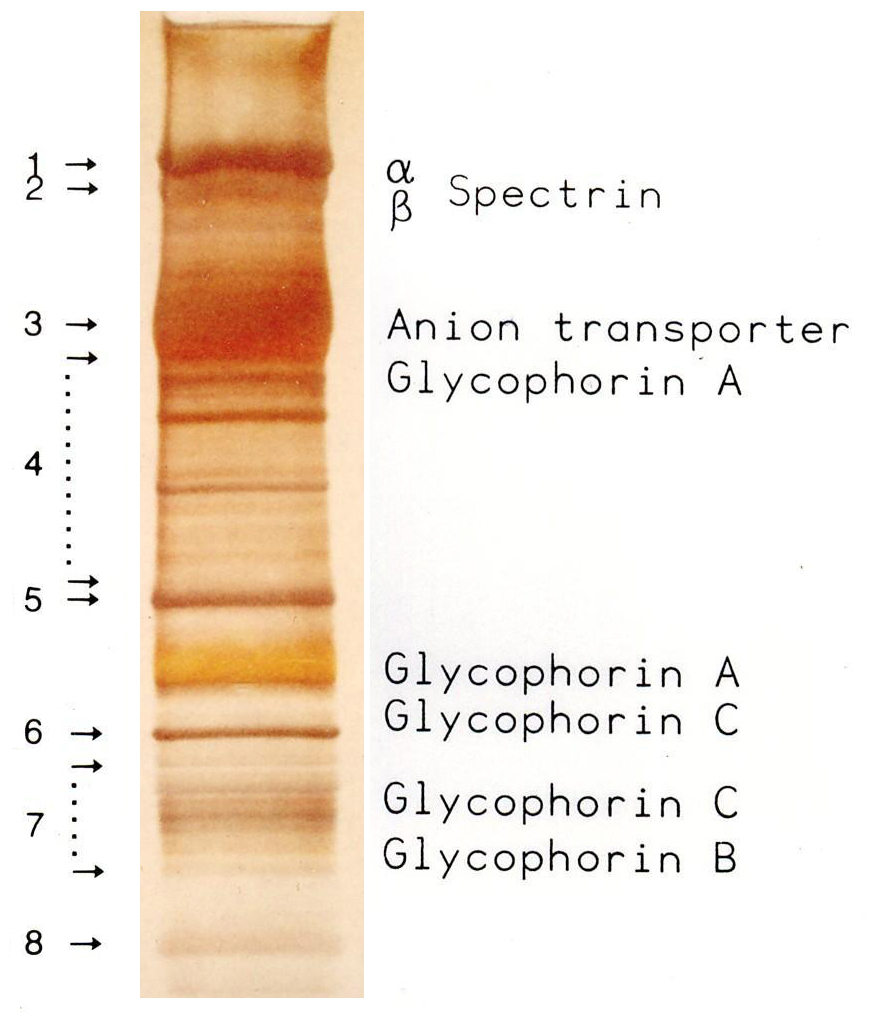
SDS-PAGE
SDS-PAGE (sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) is a discontinuous electrophoretic system developed by Ulrich K. Laemmli which is commonly used as a method to separate proteins with molecular masses between 5 and 250 kDa. The combined use of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS, also known as sodium lauryl sulfate) and polyacrylamide gel allows to eliminate the influence of structure and charge, and proteins are separated solely on the basis of differences in their molecular weight. Properties SDS-PAGE is an electrophoresis method that allows protein separation by mass. The medium (also referred to as ′matrix′) is a polyacrylamide-based discontinuous gel. The polyacrylamide-gel is typically sandwiched between two glass plates in a slab gel. Although tube gels (in glass cylinders) were used historically, they were rapidly made obsolete with the invention of the more convenient slab gels. In addition, SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate) is used. About 1.4 grams of S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
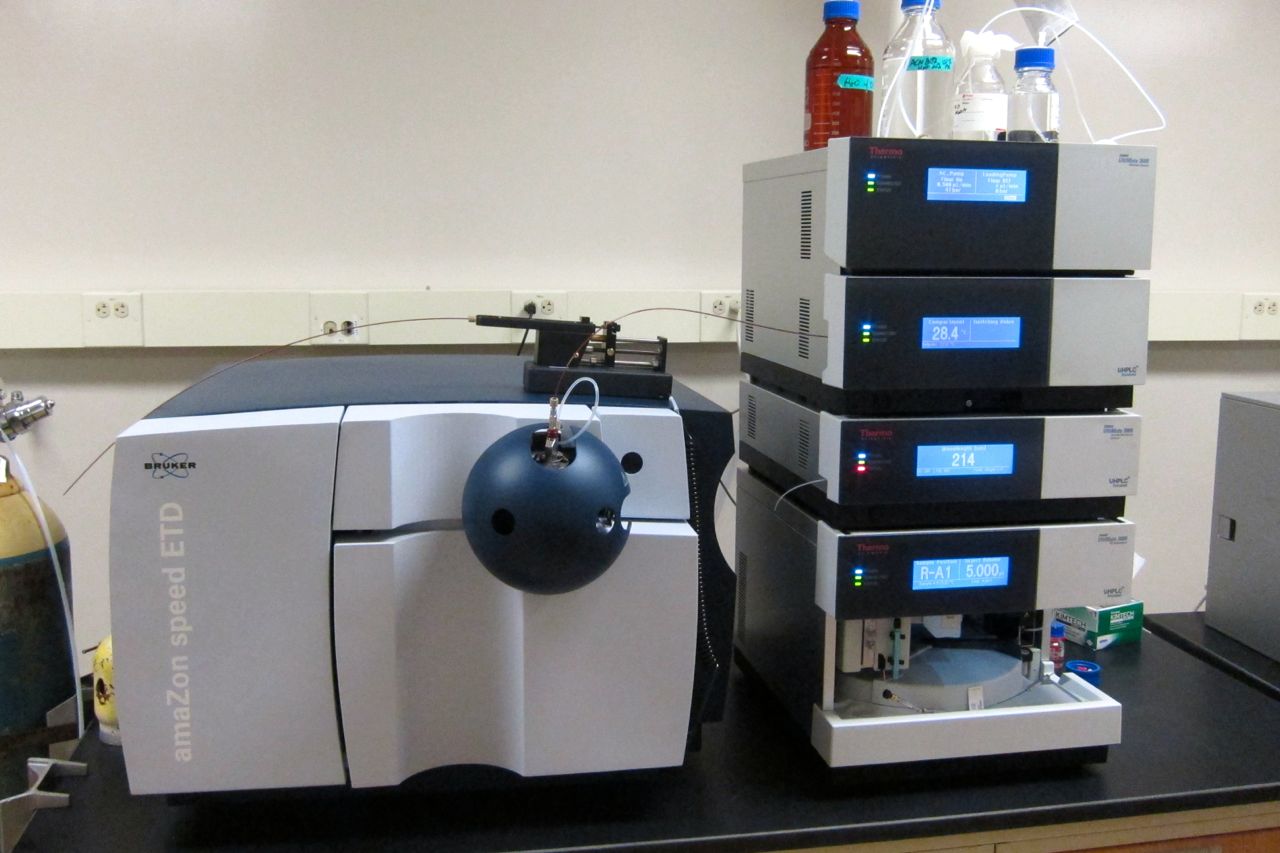
Liquid Chromatography–mass Spectrometry
Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS) is an analytical chemistry technique that combines the physical separation capabilities of liquid chromatography (or HPLC) with the mass analysis capabilities of mass spectrometry (MS). Coupled chromatography - MS systems are popular in chemical analysis because the individual capabilities of each technique are enhanced synergistically. While liquid chromatography separates mixtures with multiple components, mass spectrometry provides spectral information that may help to identify (or confirm the suspected identity of) each separated component. MS is not only sensitive, but provides selective detection, relieving the need for complete chromatographic separation. LC-MS is also appropriate for metabolomics because of its good coverage of a wide range of chemicals. This tandem technique can be used to analyze biochemical, organic, and inorganic compounds commonly found in complex samples of environmental and biological origin. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |