|
Liquid Chromatography–mass Spectrometry
Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS) is an analytical chemistry technique that combines the physical separation capabilities of liquid chromatography (or HPLC) with the mass analysis capabilities of mass spectrometry (MS). Coupled chromatography - MS systems are popular in chemical analysis because the individual capabilities of each technique are enhanced synergistically. While liquid chromatography separates mixtures with multiple components, mass spectrometry provides spectral information that may help to identify (or confirm the suspected identity of) each separated component. MS is not only sensitive, but provides selective detection, relieving the need for complete chromatographic separation. LC-MS is also appropriate for metabolomics because of its good coverage of a wide range of chemicals. This tandem technique can be used to analyze biochemical, organic, and inorganic compounds commonly found in complex samples of environmental and biological origin. Theref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
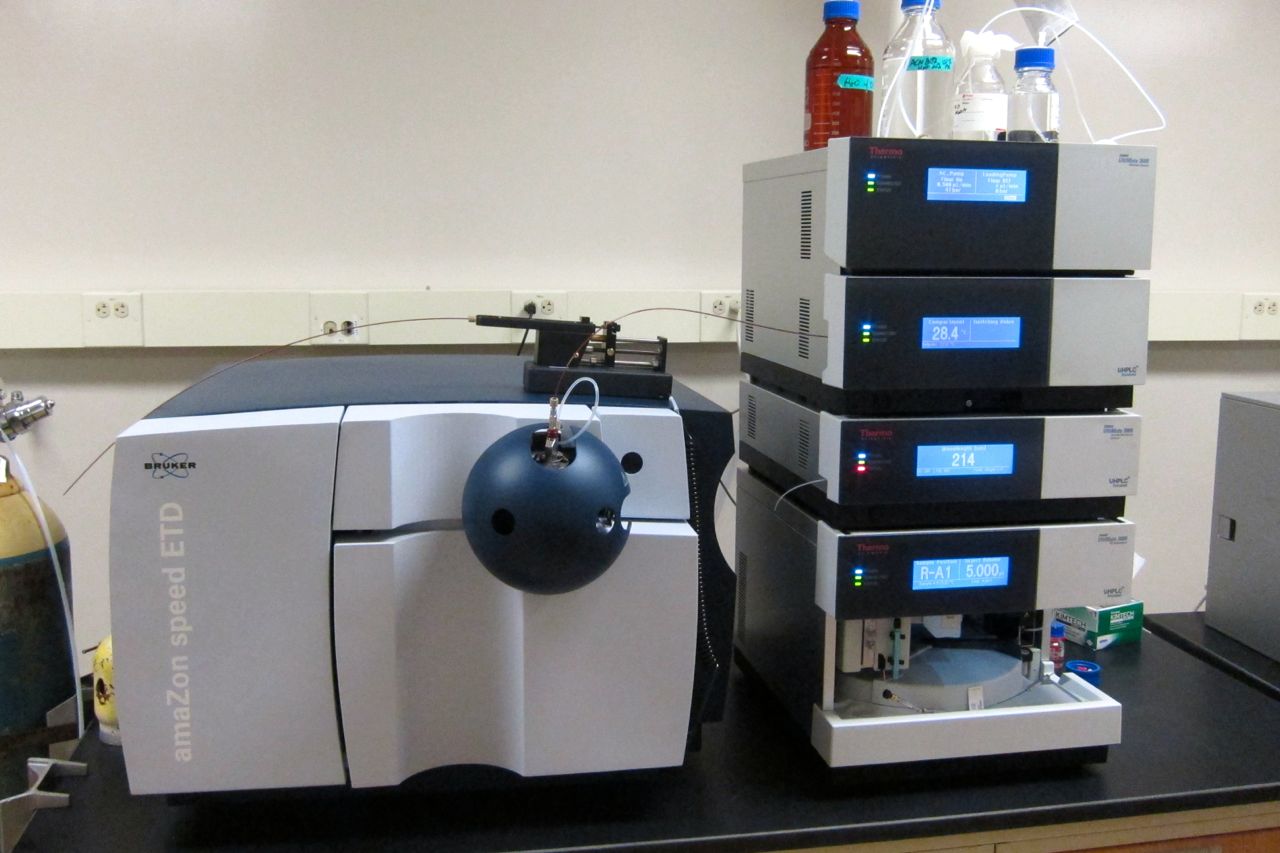
Bruker Amazon Speed ETD
Bruker Corporation is an American manufacturer of scientific instruments for molecular and materials research, as well as for industrial and applied analysis. It is headquartered in Billerica, Massachusetts, and is the publicly traded parent company of Bruker Scientific Instruments (Bruker AXS, Bruker BioSpin, Bruker Daltonics and Bruker Optics) and Bruker Energy & Supercon Technologies (BEST) divisions. In April 2010, Bruker created a Chemical Analysis Division (headquartered in Fremont, CA) under the Bruker Daltonics subsidiary. This division contains three former Varian product lines: ICPMS systems, laboratory gas chromatography (GC), and GC-triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (originally designed by Bear Instruments and acquired by Varian in 2001). In 2012, it sponsored the Fritz Feigl Prize, and since 1999 the company has also sponsored the Günther Laukien Prize. History The company was founded on September 7, 1960, in Karlsruhe, Germany as ''Bruker-Physik AG'' by five pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used by Károly Ereky in 1919, meaning the production of products from raw materials with the aid of living organisms. Definition The concept of biotechnology encompasses a wide range of procedures for modifying living organisms according to human purposes, going back to domestication of animals, cultivation of the plants, and "improvements" to these through breeding programs that employ artificial selection and hybridization. Modern usage also includes genetic engineering as well as cell and tissue culture technologies. The American Chemical Society defines biotechnology as the application of biological organisms, systems, or processes by various industries to learning about the science of life and the improvement of the value of materia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sector Mass Spectrometer
A sector instrument is a general term for a class of mass spectrometer that uses a static electric (E) or magnetic (B) sector or some combination of the two (separately in space) as a mass analyzer. Popular combinations of these sectors have been the EB, BE (of so-called reverse geometry), three-sector BEB and four-sector EBEB (electric-magnetic-electric-magnetic) instruments. Most modern sector instruments are double-focusing instruments (first developed by Francis William Aston, Arthur Jeffrey Dempster, Kenneth Bainbridge and Josef Mattauch in 1936) in that they focus the ion beams both in direction and velocity. Theory The behavior of ions in a homogeneous, linear, static electric or magnetic field (separately) as is found in a sector instrument is simple. The physics are described by a single equation called the Lorentz force law. This equation is the fundamental equation of all mass spectrometric techniques and applies in non-linear, non-homogeneous cases too and is an imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
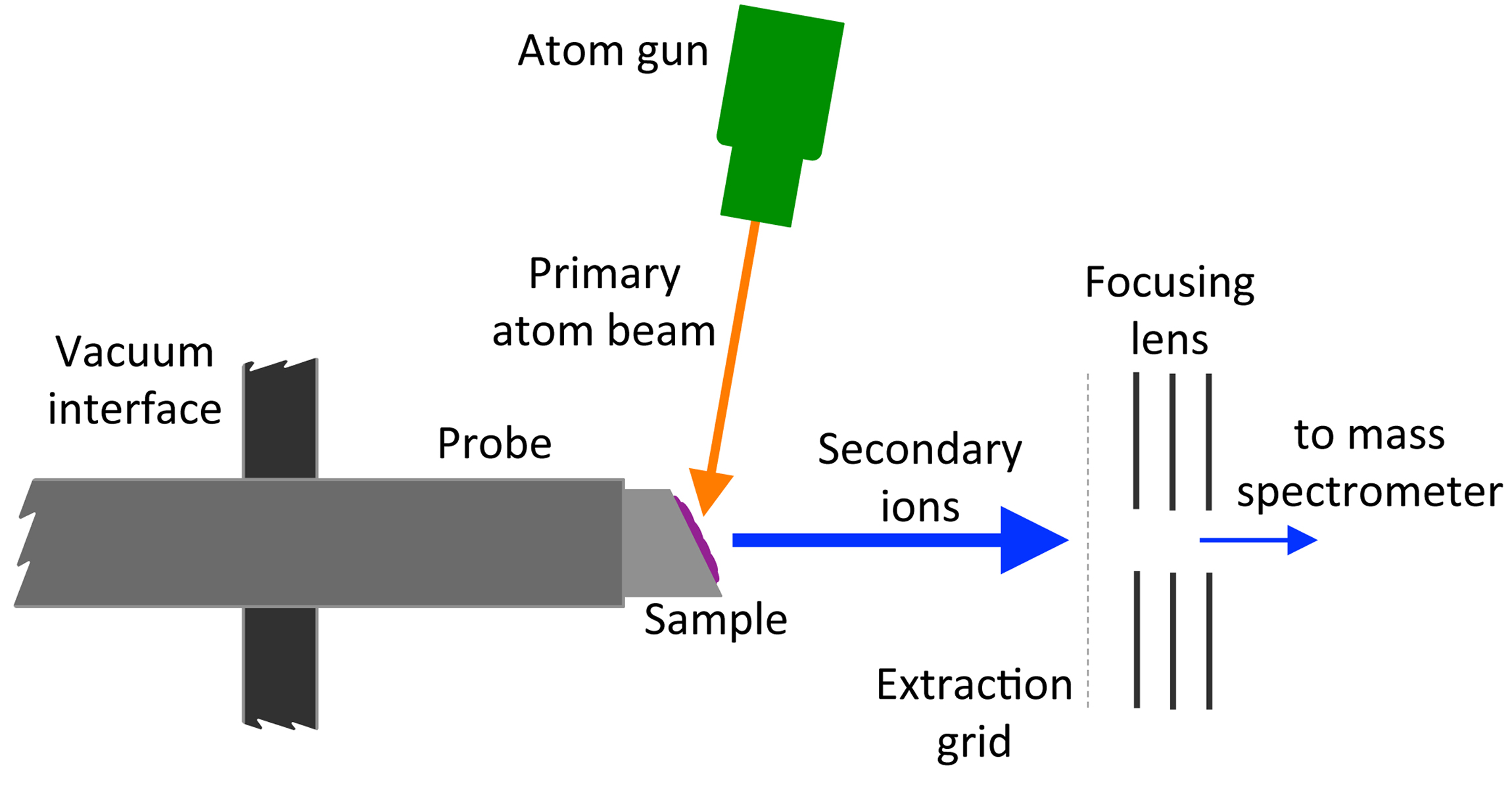
Fast Atom Bombardment
Fast atom bombardment (FAB) is an ionization technique used in mass spectrometry in which a beam of high energy atoms strikes a surface to create ions. It was developed by Michael Barber at the University of Manchester in 1980. When a beam of high energy ions is used instead of atoms (as in secondary ion mass spectrometry), the method is known as liquid secondary ion mass spectrometry (LSIMS). In FAB and LSIMS, the material to be analyzed is mixed with a non-volatile chemical protection environment, called a matrix, and is bombarded under vacuum with a high energy (4000 to 10,000 electron volts) beam of atoms. The atoms are typically from an inert gas such as argon or xenon. Common matrices include glycerol, thioglycerol, 3-nitrobenzyl alcohol (3-NBA), 18-crown-6 ether, 2-nitrophenyloctyl ether, sulfolane, diethanolamine, and triethanolamine. This technique is similar to secondary ion mass spectrometry and plasma desorption mass spectrometry. Ionization mechanism FAB is a rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Ionization
Chemical ionization (CI) is a soft ionization technique used in mass spectrometry. This was first introduced by Burnaby Munson and Frank H. Field in 1966. This technique is a branch of gaseous ion-molecule chemistry. Reagent gas molecules (often methane or ammonia) are ionized by electron ionization to form reagent ions, which subsequently react with analyte molecules in the gas phase to create analyte ions for analysis by mass spectrometry. Negative chemical ionization (NCI), charge-exchange chemical ionization, atmospheric-pressure chemical ionization (APCI) and atmospheric pressure photoionization (APPI) are some of the common variants of the technique. CI mass spectrometry finds general application in the identification, structure elucidation and quantitation of organic compounds as well as some utility in biochemical analysis. Samples to be analyzed must be in vapour form, or else (in the case of liquids or solids), must be vapourized before introduction into the source. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Ionization
Electron ionization (EI, formerly known as electron impact ionization and electron bombardment ionization) is an ionization method in which energetic electrons interact with solid or gas phase atoms or molecules to produce ions. EI was one of the first ionization techniques developed for mass spectrometry. However, this method is still a popular ionization technique. This technique is considered a hard (high fragmentation) ionization method, since it uses highly energetic electrons to produce ions. This leads to extensive fragmentation, which can be helpful for structure determination of unknown compounds. EI is the most useful for organic compounds which have a molecular weight below 600. Also, several other thermally stable and volatile compounds in solid, liquid and gas states can be detected with the use of this technique when coupled with various separation methods. History Electron ionization was first described in 1918 by Canadian-American Physicist Arthur J. Dempster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Chromatography
Gas chromatography (GC) is a common type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry for separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without decomposition. Typical uses of GC include testing the purity of a particular substance, or separating the different components of a mixture. In preparative chromatography, GC can be used to prepare pure compounds from a mixture. Gas chromatography is also sometimes known as vapor-phase chromatography (VPC), or gas–liquid partition chromatography (GLPC). These alternative names, as well as their respective abbreviations, are frequently used in scientific literature. Gas chromatography is the process of separating compounds in a mixture by injecting a gaseous or liquid sample into a mobile phase, typically called the carrier gas, and passing the gas through a stationary phase. The mobile phase is usually an inert gas or an unreactive gas such as helium, argon, nitrogen or hydrogen. The stationary phase is a microscopic lay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Pressure Photoionization
Atmospheric pressure photoionization (APPI) is a soft ionization method used in mass spectrometry (MS) usually coupled to liquid chromatography (LC). Molecules are ionized using a vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) light source operating at atmospheric pressure (105 Pa), either by direct absorption followed by electron ejection or through ionization of a dopant molecule that leads to chemical ionization of target molecules. The sample is usually a solvent spray that is vaporized by nebulization and heat. The benefit of APPI is that it ionizes molecules across a broad range of polarity and is particularly useful for ionization of low polarity molecules for which other popular ionization methods such as electrospray ionization (ESI) and atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) are less suitable. It is also less prone to ion suppression and matrix effects compared to ESI and APCI and typically has a wide linear dynamic range. The application of APPI with LC/MS is commonly used for anal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric-pressure Chemical Ionization
Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) is an ionization method used in mass spectrometry which utilizes gas-phase ion-molecule reactions at atmospheric pressure (105 Pa), commonly coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). APCI is a soft ionization method similar to chemical ionization where primary ions are produced on a solvent spray. The main usage of APCI is for polar and relatively less polar thermally stable compounds with molecular weight less than 1500 Da. The application of APCI with HPLC has gained a large popularity in trace analysis detection such as steroids, pesticides and also in pharmacology for drug metabolites. Instrument structure A typical APCI source usually consists of three main parts: a sample inlet, a corona discharge needle, and an ion transfer region under intermediate pressure. In the case of the heated nebulizer inlet from an LC, as shown in the figure, the eluate flows at 0.2 to 2.0 mL/min into a pneumatic nebulizer which cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrospray Ionization
Electrospray ionization (ESI) is a technique used in mass spectrometry to produce ions using an electrospray in which a high voltage is applied to a liquid to create an aerosol. It is especially useful in producing ions from macromolecules because it overcomes the propensity of these molecules to fragment when ionized. ESI is different from other ionization processes (e.g. matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI)) since it may produce multiple-charged ions, effectively extending the mass range of the analyser to accommodate the kDa-MDa orders of magnitude observed in proteins and their associated polypeptide fragments. Mass spectrometry using ESI is called electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) or, less commonly, electrospray mass spectrometry (ES-MS). ESI is a so-called 'soft ionization' technique, since there is very little fragmentation. This can be advantageous in the sense that the molecular ion (or more accurately a pseudo molecular ion) is almost a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
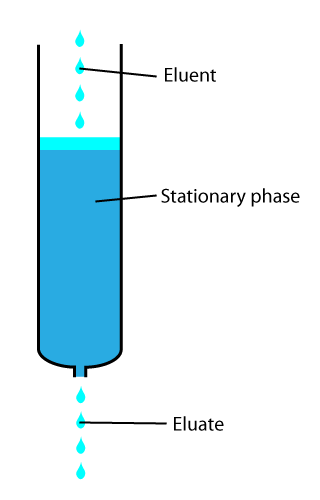
Elution
In analytical and organic chemistry, elution is the process of extracting one material from another by washing with a solvent; as in washing of loaded ion-exchange resins to remove captured ions. In a liquid chromatography experiment, for example, an analyte is generally adsorbed, or "bound to", an adsorbent in a liquid chromatography column. The adsorbent, a solid phase (stationary phase), is a powder which is coated onto a solid support. Based on an adsorbent's composition, it can have varying affinities to "hold" onto other molecules—forming a thin film on the surface of its particles. Elution then is the process of removing analytes from the adsorbent by running a solvent, called an "eluent", past the adsorbent/analyte complex. As the solvent molecules "elute", or travel down through the chromatography column, they can either pass by the adsorbent/analyte complex or they can displace the analyte by binding to the adsorbent in its place. After the solvent molecules displac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmetics
Cosmetics are constituted mixtures of chemical compounds derived from either natural sources, or synthetically created ones. Cosmetics have various purposes. Those designed for personal care and skin care can be used to cleanse or protect the body or skin. Cosmetics designed to enhance or alter one's appearance (makeup) can be used to conceal blemishes, enhance one's natural features (such as the eyebrows and eyelashes), add color to a person's face, or change the appearance of the face entirely to resemble a different person, creature or object. Cosmetics can also be designed to add fragrance to the body. Definition and etymology The word ''cosmetics'' derives from the Greek (), meaning "technique of dress and ornament", from (), "skilled in ordering or arranging" and that from (), meaning "order" and "ornament". Cosmetics are constituted from a mixture of chemical compounds derived from either natural sources, or synthetically created ones. Legal definition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |