|
Uniformly Smooth Space
Uniform distribution may refer to: * Continuous uniform distribution * Discrete uniform distribution In probability theory and statistics, the discrete uniform distribution is a symmetric probability distribution wherein each of some finite whole number ''n'' of outcome values are equally likely to be observed. Thus every one of the ''n'' out ... * Uniform distribution (ecology) * Equidistributed sequence See also * * Homogeneous distribution {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Uniform Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the continuous uniform distributions or rectangular distributions are a family of symmetric probability distributions. Such a distribution describes an experiment where there is an arbitrary outcome that lies between certain bounds. The bounds are defined by the parameters, a and b, which are the minimum and maximum values. The interval can either be closed (i.e. ,b/math>) or open (i.e. (a,b)). Therefore, the distribution is often abbreviated U(a,b), where U stands for uniform distribution. The difference between the bounds defines the interval length; all intervals of the same length on the distribution's support are equally probable. It is the maximum entropy probability distribution for a random variable X under no constraint other than that it is contained in the distribution's support. Definitions Probability density function The probability density function of the continuous uniform distribution is f(x) = \begin \dfrac & ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discrete Uniform Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the discrete uniform distribution is a symmetric probability distribution wherein each of some finite whole number ''n'' of outcome values are equally likely to be observed. Thus every one of the ''n'' outcome values has equal probability 1/''n''. Intuitively, a discrete uniform distribution is "a known, finite number of outcomes all equally likely to happen." A simple example of the discrete uniform distribution comes from throwing a fair six-sided die. The possible values are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and each time the die is thrown the probability of each given value is 1/6. If two dice were thrown and their values added, the possible sums would not have equal probability and so the distribution of sums of two dice rolls is not uniform. Although it is common to consider discrete uniform distributions over a contiguous range of integers, such as in this six-sided die example, one can define discrete uniform distributions over any finite set. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
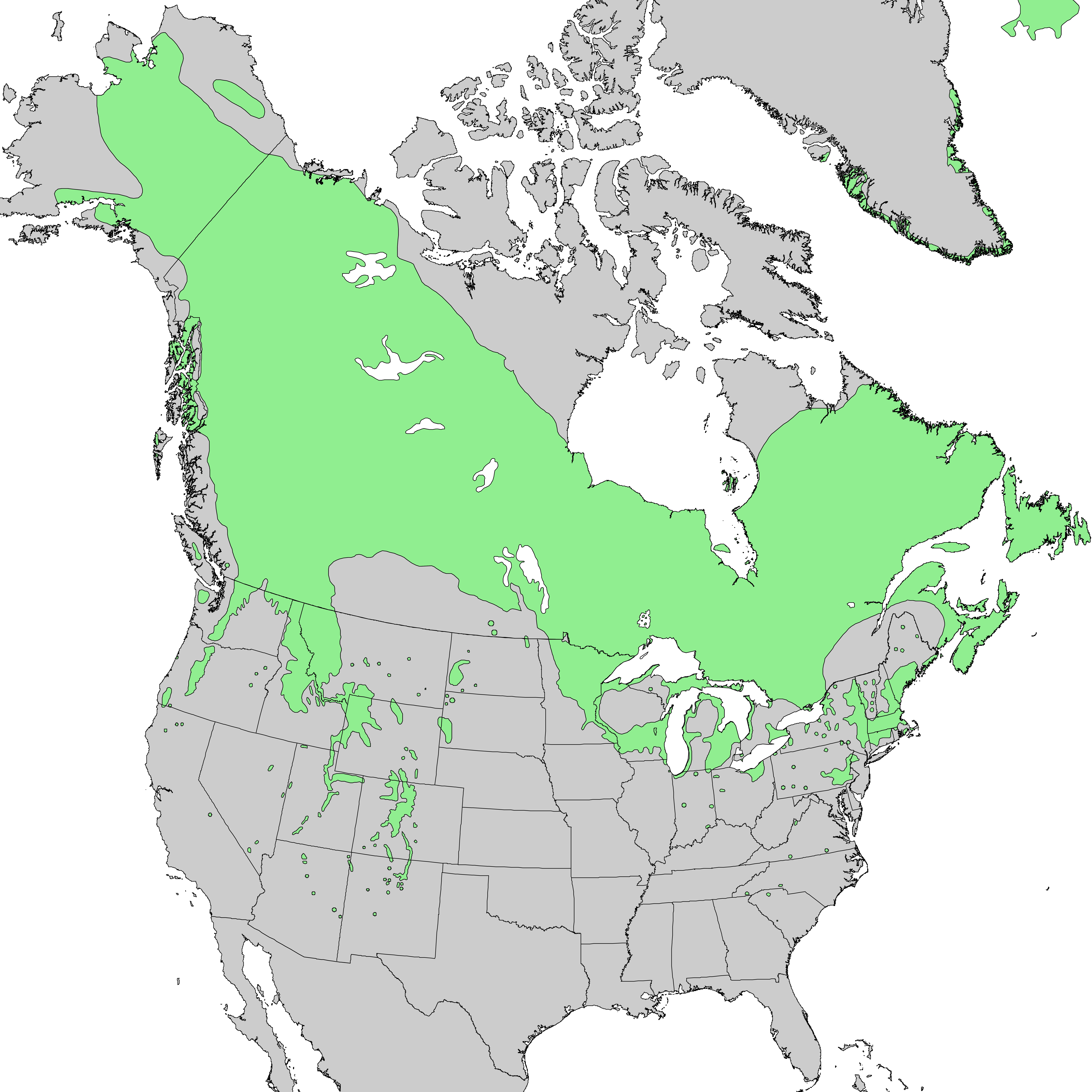
Uniform Distribution (ecology)
Species distribution, or species dispersion, is the manner in which a biological taxon is spatially arranged. The geographic limits of a particular taxon's distribution is its range, often represented as shaded areas on a map. Patterns of distribution change depending on the scale at which they are viewed, from the arrangement of individuals within a small family unit, to patterns within a population, or the distribution of the entire species as a whole (range). Species distribution is not to be confused with dispersal, which is the movement of individuals away from their region of origin or from a population center of high density. Range In biology, the range of a species is the geographical area within which that species can be found. Within that range, distribution is the general structure of the species population, while dispersion is the variation in its population density. Range is often described with the following qualities: * Sometimes a distinction is made between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equidistributed Sequence
In mathematics, a sequence (''s''1, ''s''2, ''s''3, ...) of real numbers is said to be equidistributed, or uniformly distributed, if the proportion of terms falling in a subinterval is proportional to the length of that subinterval. Such sequences are studied in Diophantine approximation theory and have applications to Monte Carlo integration. Definition A sequence (''s''1, ''s''2, ''s''3, ...) of real numbers is said to be ''equidistributed'' on a non-degenerate interval 'a'', ''b''if for every subinterval 'c'', ''d''of 'a'', ''b''we have :\lim_= . (Here, the notation , ∩ 'c'', ''d'' denotes the number of elements, out of the first ''n'' elements of the sequence, that are between ''c'' and ''d''.) For example, if a sequence is equidistributed in , 2 since the interval .5, 0.9occupies 1/5 of the length of the interval , 2 as ''n'' becomes large, the proportion of the first ''n'' members of the sequence which fall between 0.5 and 0.9 must approach 1/5. L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |