|
Two-tail
In statistical significance testing, a one-tailed test and a two-tailed test are alternative ways of computing the statistical significance of a parameter inferred from a data set, in terms of a test statistic. A two-tailed test is appropriate if the estimated value is greater or less than a certain range of values, for example, whether a test taker may score above or below a specific range of scores. This method is used for null hypothesis testing and if the estimated value exists in the critical areas, the alternative hypothesis is accepted over the null hypothesis. A one-tailed test is appropriate if the estimated value may depart from the reference value in only one direction, left or right, but not both. An example can be whether a machine produces more than one-percent defective products. In this situation, if the estimated value exists in one of the one-sided critical areas, depending on the direction of interest (greater than or less than), the alternative hypothesis is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis (often denoted ''H''0) is the claim in scientific research that the effect being studied does not exist. The null hypothesis can also be described as the hypothesis in which no relationship exists between two sets of data or variables being analyzed. If the null hypothesis is true, any experimentally observed effect is due to chance alone, hence the term "null". In contrast with the null hypothesis, an alternative hypothesis (often denoted ''H''A or ''H''1) is developed, which claims that a relationship does exist between two variables. Basic definitions The null hypothesis and the ''alternative hypothesis'' are types of conjectures used in statistical tests to make statistical inferences, which are formal methods of reaching conclusions and separating scientific claims from statistical noise. The statement being tested in a test of statistical significance is called the null hypothesis. The test of significance is designed to assess the strength of the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Significance
In statistical hypothesis testing, a result has statistical significance when a result at least as "extreme" would be very infrequent if the null hypothesis were true. More precisely, a study's defined significance level, denoted by \alpha, is the probability of the study rejecting the null hypothesis, given that the null hypothesis is true; and the p-value, ''p''-value of a result, ''p'', is the probability of obtaining a result at least as extreme, given that the null hypothesis is true. The result is said to be ''statistically significant'', by the standards of the study, when p \le \alpha. The significance level for a study is chosen before data collection, and is typically set to 5% or much lower—depending on the field of study. In any experiment or Observational study, observation that involves drawing a Sampling (statistics), sample from a Statistical population, population, there is always the possibility that an observed effect would have occurred due to sampling error al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-value Graph
In null-hypothesis significance testing, the ''p''-value is the probability of obtaining test results at least as extreme as the result actually observed, under the assumption that the null hypothesis is correct. A very small ''p''-value means that such an extreme observed outcome would be very unlikely ''under the null hypothesis''. Even though reporting ''p''-values of statistical tests is common practice in academic publications of many quantitative fields, misinterpretation and misuse of p-values is widespread and has been a major topic in mathematics and metascience. In 2016, the American Statistical Association (ASA) made a formal statement that "''p''-values do not measure the probability that the studied hypothesis is true, or the probability that the data were produced by random chance alone" and that "a ''p''-value, or statistical significance, does not measure the size of an effect or the importance of a result" or "evidence regarding a model or hypothesis". That sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Z-test
A ''Z''-test is any statistical test for which the distribution of the test statistic under the null hypothesis can be approximated by a normal distribution. ''Z''-test tests the mean of a distribution. For each statistical significance, significance level in the Confidence intervals, confidence interval, the ''Z''-test has a single critical value (for example, 1.96 for 5% two-tailed), which makes it more convenient than the Student's t-test, Student's ''t''-test whose critical values are defined by the sample size (through the corresponding degrees of freedom (statistics), degrees of freedom). Both the ''Z''-test and Student's ''t''-test have similarities in that they both help determine the significance of a set of data. However, the ''Z''-test is rarely used in practice because the population deviation is difficult to determine. Applicability Because of the central limit theorem, many test statistics are approximately normally distributed for large samples. Therefore, many s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-value
In null-hypothesis significance testing, the ''p''-value is the probability of obtaining test results at least as extreme as the result actually observed, under the assumption that the null hypothesis is correct. A very small ''p''-value means that such an extreme observed outcome would be very unlikely ''under the null hypothesis''. Even though reporting ''p''-values of statistical tests is common practice in academic publications of many quantitative fields, misinterpretation and misuse of p-values is widespread and has been a major topic in mathematics and metascience. In 2016, the American Statistical Association (ASA) made a formal statement that "''p''-values do not measure the probability that the studied hypothesis is true, or the probability that the data were produced by random chance alone" and that "a ''p''-value, or statistical significance, does not measure the size of an effect or the importance of a result" or "evidence regarding a model or hypothesis". That ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Student's T-test
Student's ''t''-test is a statistical test used to test whether the difference between the response of two groups is statistically significant or not. It is any statistical hypothesis test in which the test statistic follows a Student's ''t''-distribution under the null hypothesis. It is most commonly applied when the test statistic would follow a normal distribution if the value of a scaling term in the test statistic were known (typically, the scaling term is unknown and is therefore a nuisance parameter). When the scaling term is estimated based on the data, the test statistic—under certain conditions—follows a Student's ''t'' distribution. The ''t''-test's most common application is to test whether the means of two populations are significantly different. In many cases, a ''Z''-test will yield very similar results to a ''t''-test because the latter converges to the former as the size of the dataset increases. History The term "''t''-statistic" is abbreviated from " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
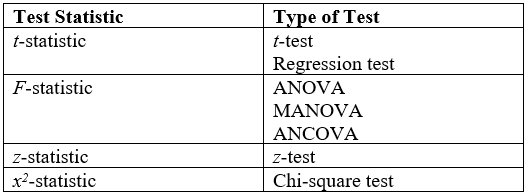
Test Statistic
Test statistic is a quantity derived from the sample for statistical hypothesis testing.Berger, R. L.; Casella, G. (2001). ''Statistical Inference'', Duxbury Press, Second Edition (p.374) A hypothesis test is typically specified in terms of a test statistic, considered as a numerical summary of a data-set that reduces the data to one value that can be used to perform the hypothesis test. In general, a test statistic is selected or defined in such a way as to quantify, within observed data, behaviours that would distinguish the null from the alternative hypothesis, where such an alternative is prescribed, or that would characterize the null hypothesis if there is no explicitly stated alternative hypothesis. An important property of a test statistic is that its sampling distribution under the null hypothesis must be calculable, either exactly or approximately, which allows ''p''-values to be calculated. A ''test statistic'' shares some of the same qualities of a descriptive stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paired Difference Test
A paired difference test, better known as a paired comparison, is a type of location test that is used when comparing two sets of paired sample, paired measurements to assess whether their expected value, population means differ. A paired difference test is designed for situations where there is dependence between pairs of measurements (in which case a test designed for comparing two independent samples would not be appropriate). That applies in a within-subjects study design, i.e., in a study where the same set of subjects undergo both of the conditions being compared. Specific methods for carrying out paired difference tests include the paired-samples t-test, the paired Z-test, the Wilcoxon signed-rank test and others. Use in reducing variance Paired difference tests for reducing variance are a specific type of blocking (statistics), blocking. To illustrate the idea, suppose we are assessing the performance of a drug for treating high cholesterol. Under the design of our stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ronald Fisher
Sir Ronald Aylmer Fisher (17 February 1890 – 29 July 1962) was a British polymath who was active as a mathematician, statistician, biologist, geneticist, and academic. For his work in statistics, he has been described as "a genius who almost single-handedly created the foundations for modern statistical science" and "the single most important figure in 20th century statistics". In genetics, Fisher was the one to most comprehensively combine the ideas of Gregor Mendel and Charles Darwin, as his work used mathematics to combine Mendelian genetics and natural selection; this contributed to the revival of Darwinism in the early 20th-century revision of the theory of evolution known as the Modern synthesis (20th century), modern synthesis. For his contributions to biology, Richard Dawkins declared Fisher to be the greatest of Darwin's successors. He is also considered one of the founding fathers of Neo-Darwinism. According to statistician Jeffrey T. Leek, Fisher is the most in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Methods For Research Workers
''Statistical Methods for Research Workers'' is a classic book on statistics, written by the statistician R. A. Fisher. It is considered by some to be one of the 20th century's most influential books on statistical methods, together with his '' The Design of Experiments'' (1935). It was originally published in 1925, by Oliver & Boyd (Edinburgh); the final and posthumous 14th edition was published in 1970. The impulse to write a book on the statistical methodology he had developed came not from Fisher himself but from D. Ward Cutler, one of the two editors of a series of "Biological Monographs and Manuals" being published by Oliver and Boyd. Reviews According to Denis Conniffe: Ronald A. Fisher was "interested in application and in the popularization of statistical methods and his early book ''Statistical Methods for Research Workers'', published in 1925, went through many editions and motivated and influenced the practical use of statistics in many fields of study. His ''Design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goodness Of Fit
The goodness of fit of a statistical model describes how well it fits a set of observations. Measures of goodness of fit typically summarize the discrepancy between observed values and the values expected under the model in question. Such measures can be used in statistical hypothesis testing, e.g. to test for normality of residuals, to test whether two samples are drawn from identical distributions (see Kolmogorov–Smirnov test), or whether outcome frequencies follow a specified distribution (see Pearson's chi-square test). In the analysis of variance, one of the components into which the variance is partitioned may be a lack-of-fit sum of squares. Fit of distributions In assessing whether a given distribution is suited to a data-set, the following tests and their underlying measures of fit can be used: * Bayesian information criterion * Kolmogorov–Smirnov test * Cramér–von Mises criterion * Anderson–Darling test * Berk-Jones tests * Shapiro–Wilk test * Chi-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Deviation Diagram
Standard may refer to: Symbols * Colours, standards and guidons, kinds of military signs * Heraldic flag, Standard (emblem), a type of a large symbol or emblem used for identification Norms, conventions or requirements * Standard (metrology), an object that bears a defined relationship to a unit of measure used for calibration of measuring devices * Standard (timber unit), an obsolete measure of timber used in trade * Breed standard (also called bench standard), in animal fancy and animal husbandry * BioCompute Object, BioCompute Standard, a standard for next generation sequencing * De facto standard, ''De facto'' standard, product or system with market dominance * Gold standard, a monetary system based on gold; also used metaphorically for the best of several options, against which the others are measured * Internet Standard, a specification ratified as an open standard by the Internet Engineering Task Force * Learning standards, standards applied to education content * Stand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |