|
Trimethylsilylmethyl Chloride
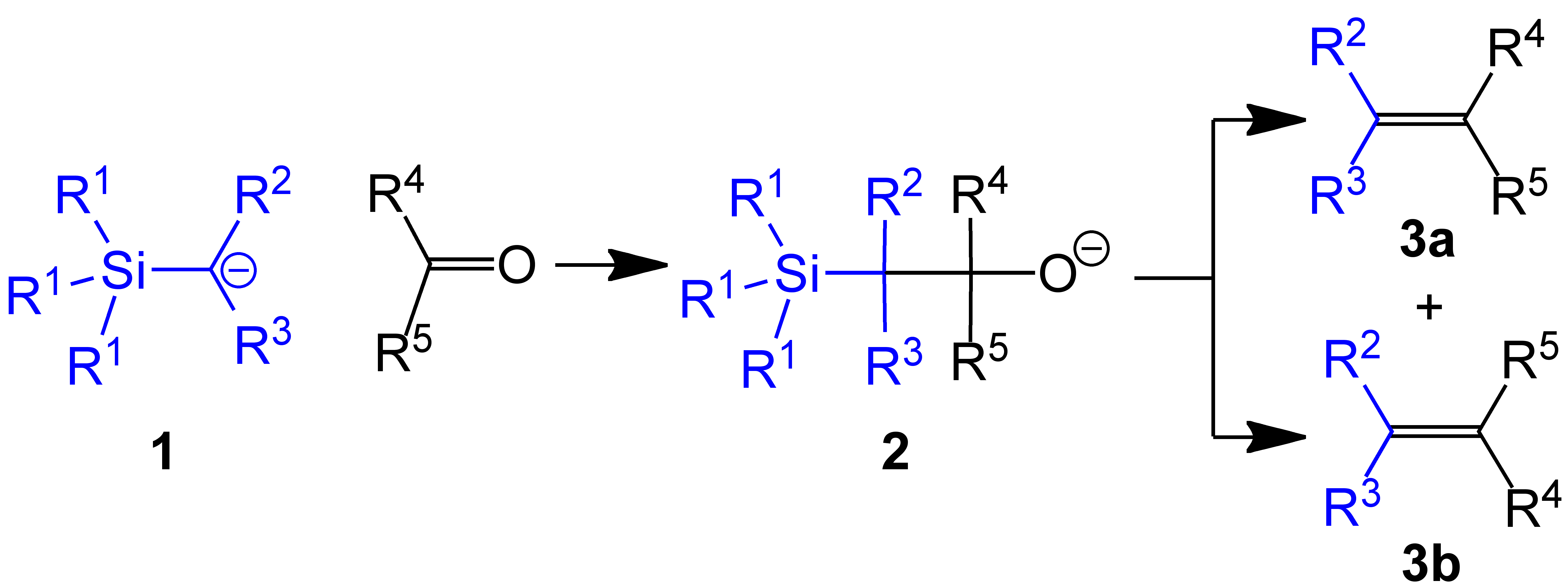
(Trimethylsilyl)methyl chloride is the organosilicon compound with the formula (CH3)3SiCH2Cl. A colorless, volatile liquid, it is an alkylating agent that is employed in organic synthesis Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one o ..., especially as a precursor to (trimethylsilyl)methyllithium. In the presence of triphenylphosphine, it olefinates benzophenones: : See also * Trimethylsilyl chloride, a silyl chloride References {{DEFAULTSORT:Trimethylsilyl methyl chloride Organosilicon compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organosilicon Compound
Organosilicon compounds are organometallic compounds containing carbon–silicon chemical bond, bonds. Organosilicon chemistry is the corresponding science of their preparation and properties. Most organosilicon compounds are similar to the ordinary organic compounds, being colourless, flammable, hydrophobic, and stable to air. Silicon carbide is an ''inorganic chemistry, inorganic'' compound. History In 1846 Von Ebelman's had synthesized Tetraethyl orthosilicate (Si(OC2H5)4). In 1863 Friedel and Crafts managed to make the first organosilieon compound with C-Si bonds which gone byound the syntheses of orthosilicic acid esters. The same year they also described a «polysilicic acid ether» in the preparation of Ethanol, ethyl- and methyl-o-silicic acid. The early extensive research in the field of organosilicon compounds was pioneerd in the beginning of 20th century by Frederic Kipping. He also had coined the term «silicone» (akin to ketones) in relation to these materials ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one of the most important branches of organic chemistry. There are several main areas of research within the general area of organic synthesis: ''total synthesis'', ''semisynthesis'', and ''methodology''. Total synthesis A total synthesis is the complete chemical synthesis of complex organic molecules from simple, commercially available petrochemical or natural precursors. Total synthesis may be accomplished either via a linear or convergent approach. In a ''linear'' synthesis—often adequate for simple structures—several steps are performed one after another until the molecule is complete; the chemical compounds made in each step are called synthetic intermediates. Most often, each step in a synthesis refers to a separate rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
(Trimethylsilyl)methyllithium
(Trimethylsilyl)methyllithium is classified both as an organolithium compound and an organosilicon compound. It has the empirical formula LiCH2Si(CH3)3, often abbreviated LiCH2tms. It crystallizes as the hexagonal prismatic hexamer iCH2tmssub>6, akin to some polymorphs of methyllithium. Many adducts have been characterized including the diethyl ether complexed cubane i4(μ3-CH2tms)4(Et2O)2and tmeda)2]. Preparation (Trimethylsilyl)methyllithium, which is commercially available as a THF solution, is usually prepared by treatment of (Trimethylsilyl)methyl chloride, [(trimethylsilyl)methyl chloride with butyllithium: :(CH3)3SiCH2Cl + BuLi → (CH3)3SiCH2Li + BuCl Trimethylsilylmethyl magnesium chloride is often functionally equivalent to trimethylsilylmethyllithium. It is prepared by the Grignard reaction of trimethylsilylmethyl chloride. Use in methylenations In one example of the Peterson olefination, (trimethylsilyl)methyllithium reacts with aldehydes and keton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triphenylphosphine
Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to P Ph3 or Ph3P. It is widely used in the synthesis of organic and organometallic compounds. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether. Preparation and structure Triphenylphosphine can be prepared in the laboratory by treatment of phosphorus trichloride with phenylmagnesium bromide or phenyllithium. The industrial synthesis involves the reaction between phosphorus trichloride, chlorobenzene, and sodium: :PCl3 + 3 PhCl + 6 Na → PPh3 + 6 NaCl Triphenylphosphine crystallizes in triclinic and monoclinic modification. In both cases, the molecule adopts a pyramidal structure with propeller-like arrangement of the three phenyl groups. Principal reactions with chalcogens, halogens, and acids Oxidation Triphenylphosphine undergoes slow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzophenone
Benzophenone is the organic compound with the formula (C6H5)2CO, generally abbreviated Ph2CO. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. Benzophenone is a widely used building block in organic chemistry, being the parent diarylketone. Uses Benzophenone can be used as a photo initiator in UV(Ultra-violet)-curing applications such as inks, imaging, and clear coatings in the printing industry. Benzophenone prevents ultraviolet ( UV) light from damaging scents and colors in products such as perfumes and soaps. Benzophenone can also be added to plastic packaging as a UV blocker to prevent photo-degradation of the packaging polymers or its contents. Its use allows manufacturers to package the product in clear glass or plastic (such as a PETE water bottle). Without it, opaque or dark packaging would be required. In biological applications, benzophenones have been used extensively as photophysical probes to identify and map peptide–protein interactions. Benzophenone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimethylsilyl Chloride
Trimethylsilyl chloride, also known as chlorotrimethylsilane is an organosilicon compound ( silyl halide), with the formula (CH3)3SiCl, often abbreviated Me3SiCl or TMSCl. It is a colourless volatile liquid that is stable in the absence of water. It is widely used in organic chemistry. Preparation TMSCl is prepared on a large scale by the '' direct process'', the reaction of methyl chloride with a silicon-copper alloy. The principal target of this process is dimethyldichlorosilane, but substantial amounts of the trimethyl and monomethyl products are also obtained. The relevant reactions are (Me = CH3): : x MeCl + Si → Me3SiCl, Me2SiCl2, MeSiCl3, other products Typically about 2–4% of the product stream is the monochloride, which forms an azeotrope with MeSiCl3. Reactions and uses TMSCl is reactive toward nucleophiles, resulting in the replacement of the chloride. In a characteristic reaction of TMSCl, the nucleophile is water, resulting in hydrolysis to give the hexamethy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |