(Trimethylsilyl)methyllithium on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
(Trimethylsilyl)methyllithium is classified both as an
 Trimethylsilylmethyllithium is widely used in organotransition metal chemistry to affix trimethylsilylmethyl ligands. Such complexes are usually produced by salt metathesis involving metal chlorides. These compounds are often highly soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. These complexes enjoy stability because trimethylsilylmethyl ligands are bulky and they resist
Trimethylsilylmethyllithium is widely used in organotransition metal chemistry to affix trimethylsilylmethyl ligands. Such complexes are usually produced by salt metathesis involving metal chlorides. These compounds are often highly soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. These complexes enjoy stability because trimethylsilylmethyl ligands are bulky and they resist
organolithium compound
In organometallic chemistry, organolithium reagents are chemical compounds that contain carbon–lithium (C–Li) bonds. These reagents are important in organic synthesis, and are frequently used to transfer the organic group or the lithium atom ...
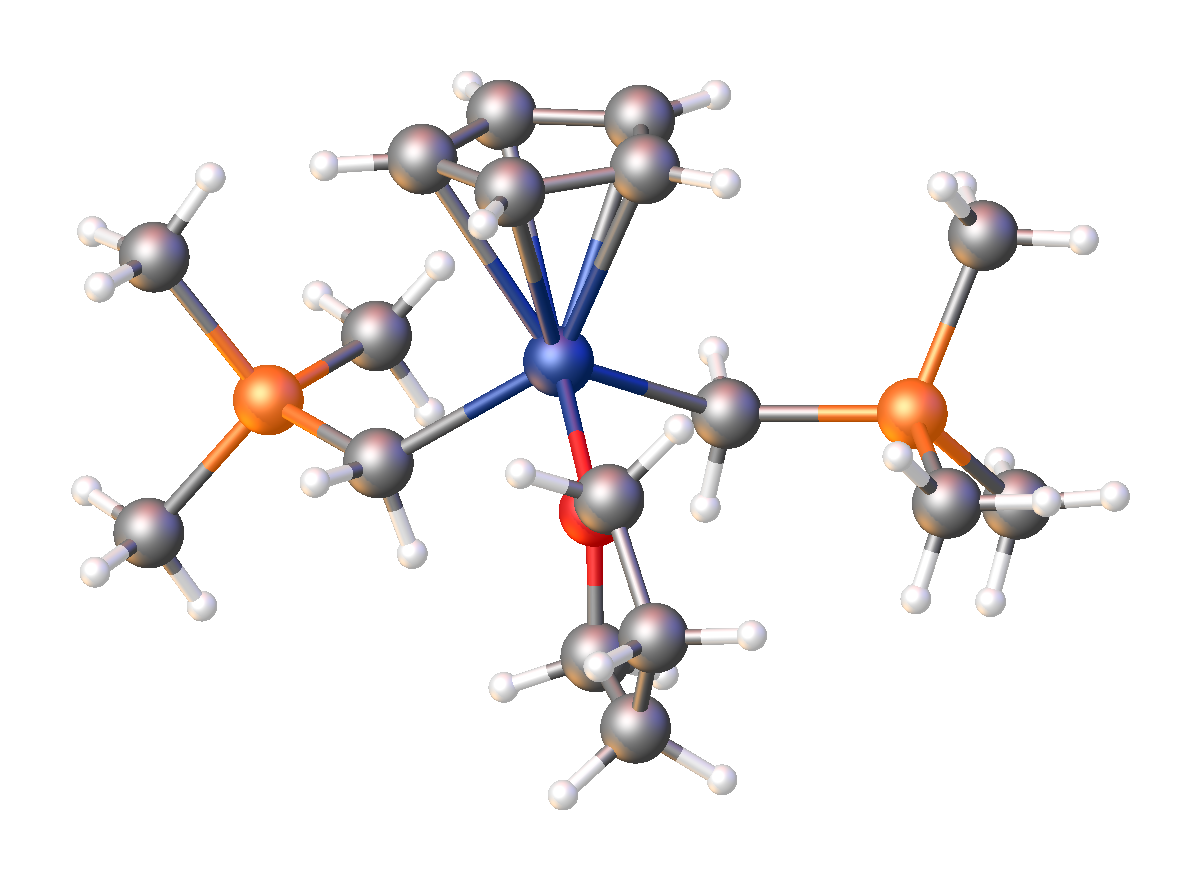
and an organosilicon compound. It has the empirical formula LiCH2Si(CH3)3, often abbreviated LiCH2tms. It crystallizes as the hexagonal prismatic hexamer iCH2tmssub>6, akin to some polymorph
Polymorphism, polymorphic, polymorph, polymorphous, or polymorphy may refer to:
Computing
* Polymorphism (computer science), the ability in programming to present the same programming interface for differing underlying forms
* Ad hoc polymorphi ...
s of methyllithium. Many adducts have been characterized including the diethyl ether complexed cubane i4(μ3-CH2tms)4(Et2O)2and tmeda
Tetramethylethylenediamine (TMEDA or TEMED) is a chemical compound with the formula (CH3)2NCH2CH2N(CH3)2. This species is derived from ethylenediamine by replacement of the four amine hydrogens with four methyl groups. It is a colorless liquid, ...
)2].
Preparation
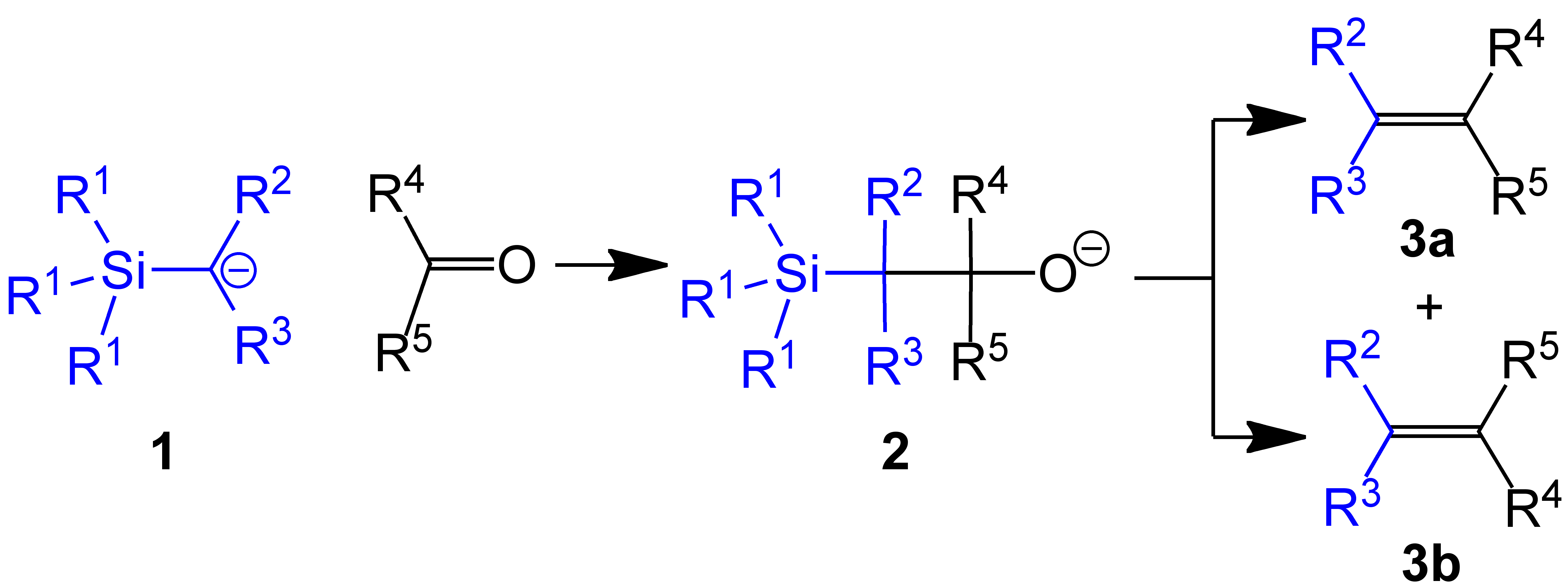
(Trimethylsilyl)methyllithium, which is commercially available as a THF solution, is usually prepared by treatment of (Trimethylsilyl)methyl chloride, [(trimethylsilyl)methyl chloride with butyllithium: :(CH3)3SiCH2Cl + BuLi → (CH3)3SiCH2Li + BuCl Trimethylsilylmethyl magnesium chloride is often functionally equivalent to trimethylsilylmethyllithium. It is prepared by the Grignard reaction of trimethylsilylmethyl chloride.Use in methylenations
In one example of the Peterson olefination, (trimethylsilyl)methyllithium reacts with aldehydes andketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)– (which contains a carbon-oxygen double bo ...
s to give the terminal alkene (R1 = Me, R2 & R3 = H):
:
Metal derivatives
 Trimethylsilylmethyllithium is widely used in organotransition metal chemistry to affix trimethylsilylmethyl ligands. Such complexes are usually produced by salt metathesis involving metal chlorides. These compounds are often highly soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. These complexes enjoy stability because trimethylsilylmethyl ligands are bulky and they resist
Trimethylsilylmethyllithium is widely used in organotransition metal chemistry to affix trimethylsilylmethyl ligands. Such complexes are usually produced by salt metathesis involving metal chlorides. These compounds are often highly soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. These complexes enjoy stability because trimethylsilylmethyl ligands are bulky and they resist beta-hydride elimination
β-Hydride elimination is a reaction in which an alkyl group bonded to a metal centre is converted into the corresponding metal-bonded hydride and an alkene. The alkyl must have hydrogens on the β-carbon. For instance butyl groups can undergo th ...
. In these regards, trimethylsilylmethyl is akin to neopentyl.
Bis(trimethylsilylmethyl)magnesium is used as an alternative to (trimethylsilyl)methyllithium.
Related compounds
* bis(trimethylsilyl)methyllithium * tris(trimethylsilyl)methyllithiumReferences
{{DEFAULTSORT:Trimethylsilyl methyllithium Organolithium compounds Organosilicon compounds