|
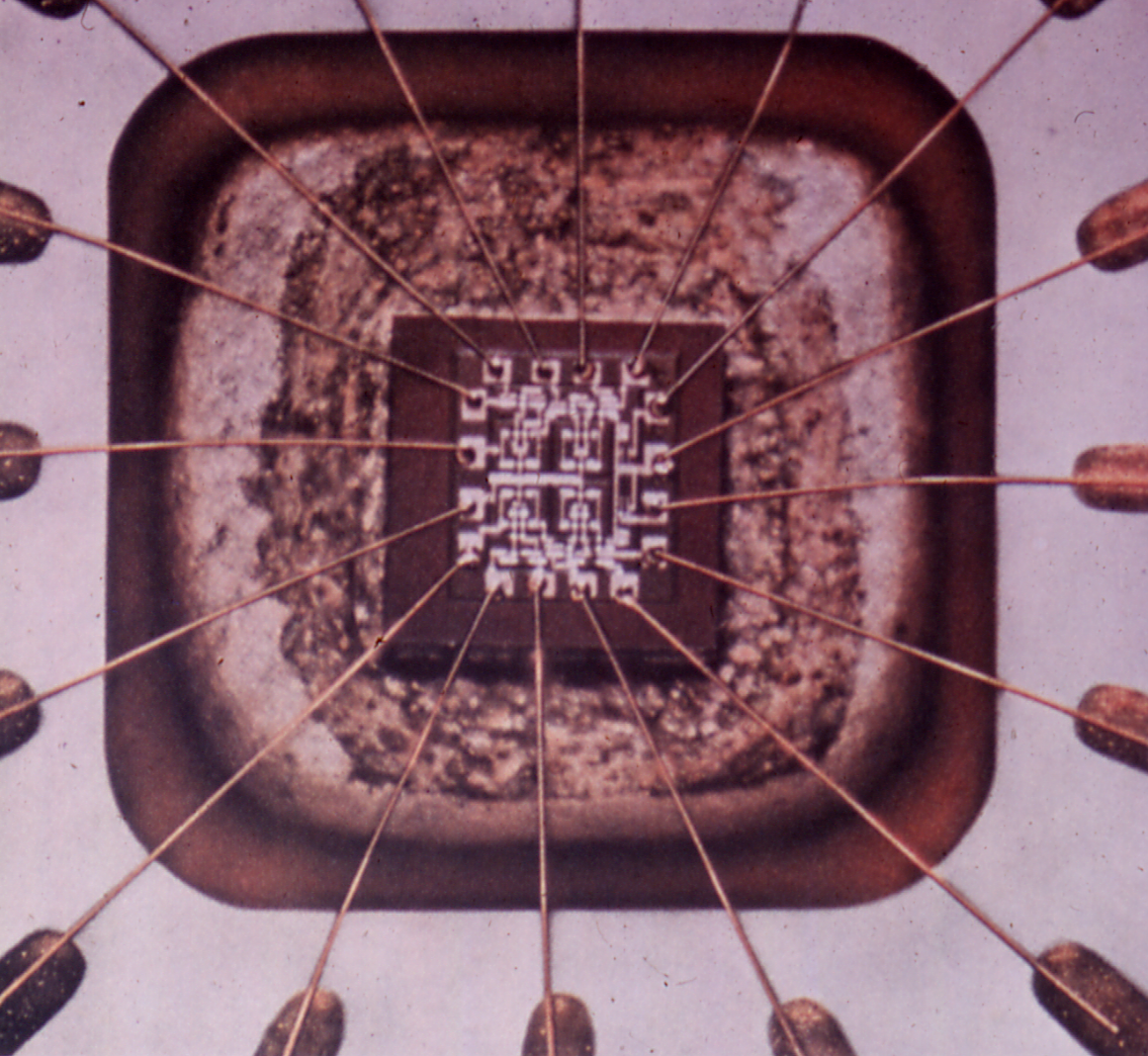
Thermosonic Bonding
Thermosonic bonding is widely used to wire bond silicon integrated circuits into computers. Alexander Coucoulas was named "Father of Thermosonic Bonding" by George Harman, the world's foremost authority on wire bonding, where he referenced Coucoulas's leading edge publications in his book, ''Wire Bonding In Microelectronics''.Coucoulas, A., Trans. Metallurgical Society Of AIME, "Ultrasonic Welding of Aluminum Leads to Tantalum Thin Films", 1966, pp. 587–589. abstract https://sites.google.com/site/coucoulasthermosonicbondaltaCoucoulas, A., "Hot Work Ultrasonic Bonding – A Method Of Facilitating Metal Flow By Restoration Processes", Proc. 20th IEEE Electronic Components Conf. Washington, D.C., May 1970, pp. 549–556.https://sites.google.com/site/hotworkultrasonicbonding Owing to the well proven reliability of thermosonic bonds, it is extensively used to connect the central processing units (CPUs), which are encapsulated silicon integrated circuits that serve as the "brains" of to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Circuits
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) integrate into a small chip. This results in circuits that are orders of magnitude smaller, faster, and less expensive than those constructed of discrete electronic components. The IC's mass production capability, reliability, and building-block approach to integrated circuit design has ensured the rapid adoption of standardized ICs in place of designs using discrete transistors. ICs are now used in virtually all electronic equipment and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones and other home appliances are now inextricable parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the small size and low cost of ICs such as modern compute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flip Chip
Flip chip, also known as controlled collapse chip connection or its abbreviation, C4, is a method for interconnecting dies such as semiconductor devices, IC chips, integrated passive devices and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), to external circuitry with solder bumps that have been deposited onto the chip pads. The technique was developed by General Electric's Light Military Electronics Department, Utica, New York. The solder bumps are deposited on the chip pads on the top side of the wafer during the final wafer processing step. In order to mount the chip to external circuitry (e.g., a circuit board or another chip or wafer), it is flipped over so that its top side faces down, and aligned so that its pads align with matching pads on the external circuit, and then the solder is reflowed to complete the interconnect. This is in contrast to wire bonding, in which the chip is mounted upright and fine wires are welded onto the chip pads and lead frame contacts to interconnect t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light-emitting Diodes
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photons) is determined by the energy required for electrons to cross the band gap of the semiconductor. White light is obtained by using multiple semiconductors or a layer of light-emitting phosphor on the semiconductor device. Appearing as practical electronic components in 1962, the earliest LEDs emitted low-intensity infrared (IR) light. Infrared LEDs are used in remote-control circuits, such as those used with a wide variety of consumer electronics. The first visible-light LEDs were of low intensity and limited to red. Early LEDs were often used as indicator lamps, replacing small incandescent bulbs, and in seven-segment displays. Later developments produced LEDs available in visible, ultraviolet (UV), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink). A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electrical power, power. The transistor is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semiconductor material, usually with at least three terminals for connection to an electronic circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits. Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld proposed the concept of a field-effect transistor in 1926, but it was not possible to actually constru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor Device Fabrication
Semiconductor device fabrication is the process used to manufacture semiconductor devices, typically integrated circuit (IC) chips such as modern computer processors, microcontrollers, and memory chips such as NAND flash and DRAM that are present in everyday electrical and electronics, electronic devices. It is a multiple-step sequence of Photolithography, photolithographic and chemical processing steps (such as surface passivation, thermal oxidation, planar process, planar diffusion and p–n junction isolation, junction isolation) during which electronic circuits are gradually created on a wafer (electronics), wafer made of pure semiconducting material. Silicon is almost always used, but various compound semiconductors are used for specialized applications. The entire manufacturing process takes time, from start to packaged chips ready for shipment, at least six to eight weeks (tape-out only, not including the circuit design) and is performed in highly specialized semiconduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flip Chip
Flip chip, also known as controlled collapse chip connection or its abbreviation, C4, is a method for interconnecting dies such as semiconductor devices, IC chips, integrated passive devices and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), to external circuitry with solder bumps that have been deposited onto the chip pads. The technique was developed by General Electric's Light Military Electronics Department, Utica, New York. The solder bumps are deposited on the chip pads on the top side of the wafer during the final wafer processing step. In order to mount the chip to external circuitry (e.g., a circuit board or another chip or wafer), it is flipped over so that its top side faces down, and aligned so that its pads align with matching pads on the external circuit, and then the solder is reflowed to complete the interconnect. This is in contrast to wire bonding, in which the chip is mounted upright and fine wires are welded onto the chip pads and lead frame contacts to interconnect t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light-emitting Diodes
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photons) is determined by the energy required for electrons to cross the band gap of the semiconductor. White light is obtained by using multiple semiconductors or a layer of light-emitting phosphor on the semiconductor device. Appearing as practical electronic components in 1962, the earliest LEDs emitted low-intensity infrared (IR) light. Infrared LEDs are used in remote-control circuits, such as those used with a wide variety of consumer electronics. The first visible-light LEDs were of low intensity and limited to red. Early LEDs were often used as indicator lamps, replacing small incandescent bulbs, and in seven-segment displays. Later developments produced LEDs available in visible, ultraviolet (UV), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SQUID
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting these criteria. Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, bilateral symmetry, and a mantle. They are mainly soft-bodied, like octopuses, but have a small internal skeleton in the form of a rod-like gladius (cephalopod), gladius or pen, made of chitin. Squid diverged from other cephalopods during the Jurassic and occupy a similar role to teleost fish as open water predators of similar size and behaviour. They play an important role in the open water food web. The two long tentacles are used to grab prey and the eight arms to hold and control it. The beak then cuts the food into suitable size chunks for swallowing. Squid are rapid swimmers, moving by Aquatic locomotion#Jet propulsion, jet propulsion, and largely locate their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josephson Effect
In physics, the Josephson effect is a phenomenon that occurs when two superconductors are placed in proximity, with some barrier or restriction between them. It is an example of a macroscopic quantum phenomenon, where the effects of quantum mechanics are observable at ordinary, rather than atomic, scale. The Josephson effect has many practical applications because it exhibits a precise relationship between different physics quantities, such as voltage and frequency, facilitating highly accurate measurements. The Josephson effect produces a current, known as a supercurrent, that flows continuously without any voltage applied, across a device known as a Josephson junction (JJ). These consist of two or more superconductors coupled by a weak link. The weak link can be a thin insulating barrier (known as a superconductor–insulator–superconductor junction, or S-I-S), a short section of non-superconducting metal (S-N-S), or a physical constriction that weakens the superconductivit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) integrate into a small chip. This results in circuits that are orders of magnitude smaller, faster, and less expensive than those constructed of discrete electronic components. The IC's mass production capability, reliability, and building-block approach to integrated circuit design has ensured the rapid adoption of standardized ICs in place of designs using discrete transistors. ICs are now used in virtually all electronic equipment and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones and other home appliances are now inextricable parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the small size and low cost of ICs such as modern computer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Coucoulas
Alexander Coucoulas is an American inventor, research engineer, and author. He was named "father of thermosonic bonding" by George Harman, the world's foremost authority on wire bonding, where he referenced Coucoulas's leading edge publications in his book, ''Wire Bonding In Microelectronics.Coucoulas, A., Trans. Metallurgical Society of AIME, "Ultrasonic Welding of Aluminum Leads to Tantalum Thin Films", 1966, pp. 587–589. abstract https://sites.google.com/site/coucoulasthermosonicbondaltaCoucoulas, A., "Hot Work Ultrasonic Bonding – A Method Of Facilitating Metal Flow By Restoration Processes", Proc. 20th IEEE Electronic Components Conf. Washington, D.C., May 1970, pp. 549–556.https://sites.google.com/site/hotworkultrasonicbonding A thermosonic bond is formed using a set of parameters which include ultrasonic, thermal and mechanical (force) energies. Thermosonic bonding is widely used to electrically connect silicon integrated circuit microprocessor chipsT.R. Reid, "The Chip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrasonic Welding
Ultrasonic welding is an industrial process whereby high-frequency ultrasonic acoustic vibrations are locally applied to work pieces being held together under pressure to create a solid-state weld. It is commonly used for plastics and metals, and especially for joining dissimilar materials. In ultrasonic welding, there are no connective bolts, nails, soldering materials, or adhesives necessary to bind the materials together. When used to join metals, the temperature stays well below the melting point of the involved materials, preventing any unwanted properties which may arise from high temperature exposure of the metal. History Practical application of ultrasonic welding for rigid plastics was completed in the 1960s. At this point only hard plastics could be welded. The patent for the ultrasonic method for welding rigid thermoplastic parts was awarded to Robert Soloff and Seymour Linsley in 1965. Soloff, the founder of Sonics & Materials Inc., was a lab manager at Branson Instr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

