|
Strain Rate Imaging
Strain rate imaging is a method in echocardiography (medical ultrasound) for measuring regional or global deformation of the myocardium (heart muscle). The term "deformation" refers to the myocardium changing shape and dimensions during the cardiac cycle. If there is myocardial ischemia, or there has been a myocardial infarction, in part of the heart muscle, this part is weakened and shows reduced and altered systolic function. Also in regional asynchrony, as in bundle branch block, there is regional heterogeneity of systolic function. By strain rate imaging, the simultaneous function of different regions can be displayed and measured. The method was first based on colour tissue Doppler.Heimdal A, Stoylen A, Torp H, Skjaerpe T. Real-time strain rate imaging of the left ventricle by ultrasound. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 1998 Nov;11(11):1013-19 by using the longitudinal myocardial velocity gradient, already in use transmurally. Later, the regional deformation has also been available b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echocardiography
An echocardiography, echocardiogram, cardiac echo or simply an echo, is an ultrasound of the heart. It is a type of medical imaging of the heart, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound. Echocardiography has become routinely used in the diagnosis, management, and follow-up of patients with any suspected or known heart diseases. It is one of the most widely used diagnostic imaging modalities in cardiology. It can provide a wealth of helpful information, including the size and shape of the heart (internal chamber size quantification), pumping capacity, location and extent of any tissue damage, and assessment of valves. An echocardiogram can also give physicians other estimates of heart function, such as a calculation of the cardiac output, ejection fraction, and diastolic function (how well the heart relaxes). Echocardiography is an important tool in assessing wall motion abnormality in patients with suspected cardiac disease. It is a tool which helps in reaching an ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sum Of Absolute Differences
In digital image processing, the sum of absolute differences (SAD) is a measure of the similarity between image blocks. It is calculated by taking the absolute difference between each pixel in the original block and the corresponding pixel in the block being used for comparison. These differences are summed to create a simple metric of block similarity, the ''L''1 norm of the difference image or Manhattan distance between two image blocks. The sum of absolute differences may be used for a variety of purposes, such as object recognition, the generation of disparity maps for stereo images, and motion estimation for video compression. Example This example uses the sum of absolute differences to identify which part of a search image is most similar to a template image. In this example, the template image is 3 by 3 pixels in size, while the search image is 3 by 5 pixels in size. Each pixel is represented by a single integer from 0 to 9. Template Search image 2 5 5 2 7 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Bundle Branch Block
Left bundle branch block (LBBB) is a conduction abnormality in the heart that can be seen on an electrocardiogram (ECG). In this condition, activation of the left ventricle of the heart is delayed, which causes the left ventricle to contract later than the right ventricle. Causes Among the causes of LBBB are: * Aortic stenosis * Dilated cardiomyopathy * Acute myocardial infarction * Extensive coronary artery disease * Primary disease of the cardiac electrical conduction system * Long standing hypertension leading to aortic root dilatation and subsequent aortic regurgitation * Lyme disease Mechanisms Slow or absent conduction through the left bundle branch means that it takes longer than normal for the left ventricle to fully depolarise. This can be due to a damaged bundle branch that is completely unable to conduct, but may represent intact conduction that is slower than normal. LBBB may be fixed, present at all times, but may be intermittent for example occurring only durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricular Dyssynchrony
In cardiology, ventricular dyssynchrony is a difference in the timing, or lack of synchrony, of contractions in different ventricles in the heart. Large differences in timing of contractions can reduce cardiac efficiency and is correlated with heart failure. Types of dyssynchrony Three chief presentations of dyssynchrony can occur: Atrioventricular (AV) dyssynchrony occurs when there is an unfavorable difference in timing between atrial and ventricular contractions. Interventricular dyssynchrony occurs when there is a difference in timing between right ventricular (RV) and left ventricular (LV) Systole. Intraventricular dyssynchrony occurs when the timing in a sequence of activations and contractions of segments of the LV wall becomes abnormal. In all three types, changes in timing lead to changes in the dynamic behavior of the myocardial tissues, leading to ''mechanical dyssynchrony''. All three presentations allow distinct and easily reproducible electrical signatures as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronary Flow Reserve
Coronary flow reserve (CFR) is the maximum increase in blood flow through the coronary arteries above the normal resting volume. Its measurement is often used in medicine to assist in the treatment of conditions affecting the coronary arteries and to determine the efficacy of treatments used. Overview When demand for oxygen in the myocardium is increased, the vascular resistance of the coronary arteries has the ability to reduce, and this can increase the volume of blood passing through the blood vessels. This reduction occurs because the arteries dilate, which causes an increase in the diameter of the lumen. The greatest potential for this change is normally in the branches (arterioles) of the coronary artery that penetrate the myocardium, rather than those on the surface of the heart. Measurement Coronary flow reserve can be measured through a variety of methods, including digital subtraction cineangiography with coronary catheterization, doppler echocardiography, and positro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
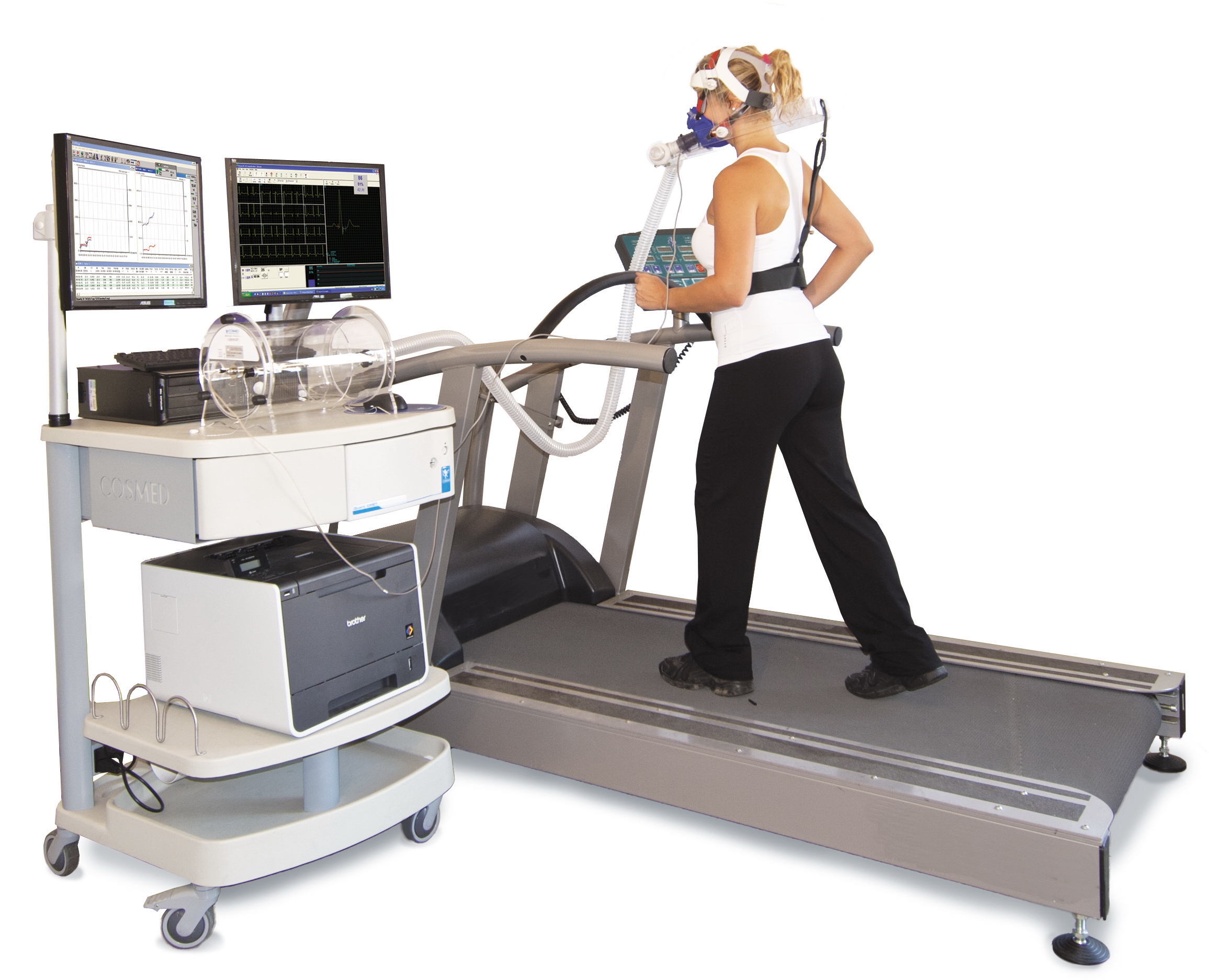
Cardiac Stress Test
A cardiac stress test (also referred to as a cardiac diagnostic test, cardiopulmonary exercise test, or abbreviated CPX test) is a cardiological test that measures the heart's ability to respond to external stress in a controlled clinical environment. The stress response is induced by exercise or by intravenous pharmacological stimulation. Cardiac stress tests compare the coronary circulation while the patient is at rest with the same patient's circulation during maximum cardiac exertion, showing any abnormal blood flow to the myocardium (heart muscle tissue). The results can be interpreted as a reflection on the general physical condition of the test patient. This test can be used to diagnose coronary artery disease (also known as ischemic heart disease) and assess patient prognosis after a myocardial infarction (heart attack). Exercise-induced stressors are most commonly either exercise on a treadmill or pedalling a stationary exercise bicycle ergometer. The level of stress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
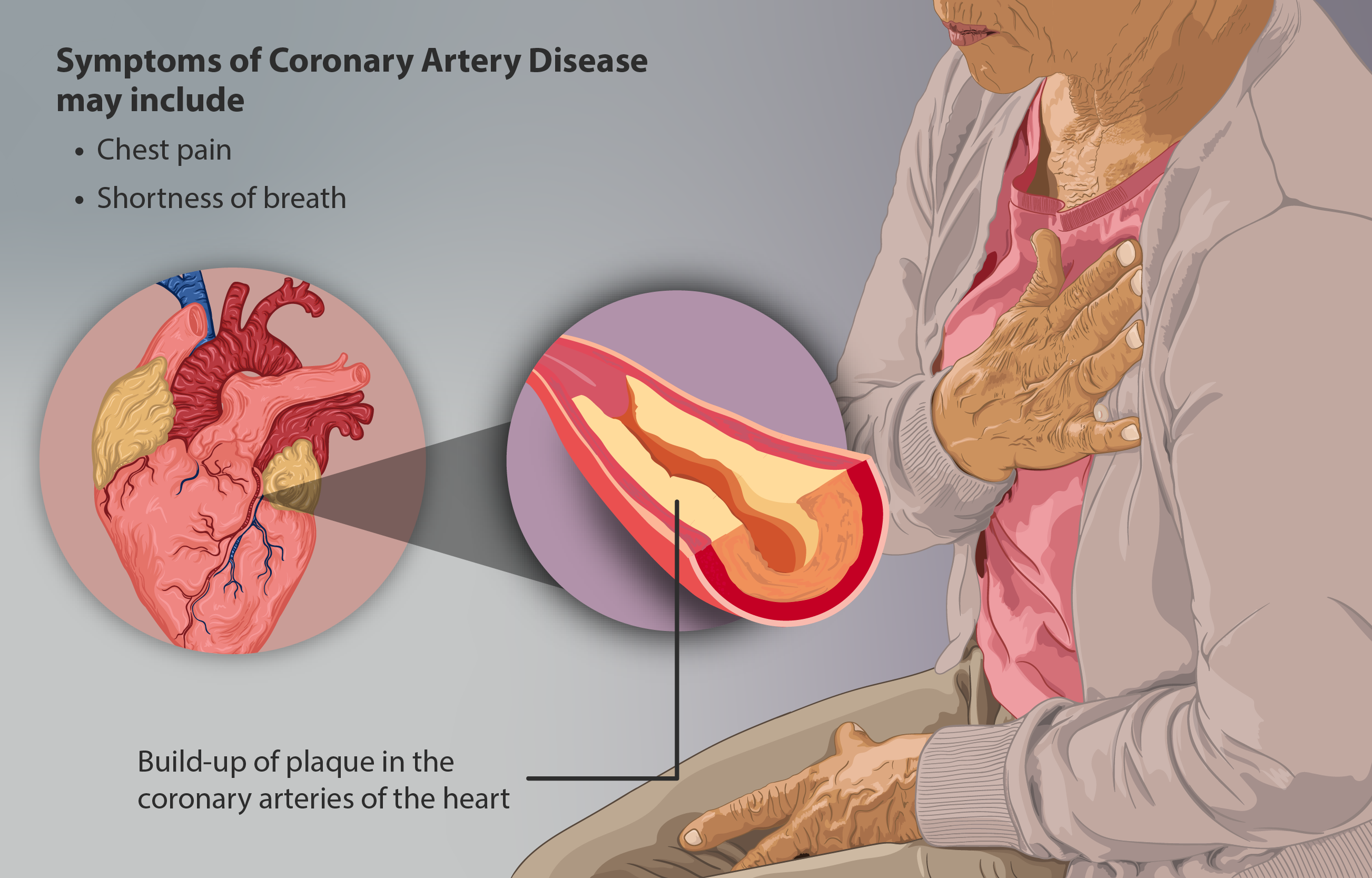
Myocardial Ischemia
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic plaque in the arteries of the heart. It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases. Types include stable angina, unstable angina, myocardial infarction, and sudden cardiac death. A common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Occasionally it may feel like heartburn. Usually symptoms occur with exercise or emotional stress, last less than a few minutes, and improve with rest. Shortness of breath may also occur and sometimes no symptoms are present. In many cases, the first sign is a heart attack. Other complications include heart failure or an abnormal heartbeat. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocardial Stunning
Myocardial stunning or transient post-ischemic myocardial dysfunction is a state of mechanical cardiac dysfunction that can occur in a portion of myocardium without necrosis after a brief interruption in perfusion, despite the timely restoration of normal coronary blood flow. In this situation, even after ischemia has been relieved (by for instance angioplasty or coronary artery bypass surgery) and myocardial blood flow (MBF) returns to normal, myocardial function is still depressed for a variable period of time, usually days to weeks. This reversible reduction of function of heart contraction after reperfusion is not accounted for by tissue damage or reduced blood flow, but rather, its thought to represent a perfusion-contraction "mismatch". Myocardial stunning was first described in laboratory canine experiments in the 1970s where LV wall abnormalities were observed following coronary artery occlusion and subsequent reperfusion. Cause Clinical situations associated with myocard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocardial Infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck or jaw. Often it occurs in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms. Women more often present without chest pain and instead have neck pain, arm pain or feel tired. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, cardiogenic shock or cardiac arrest. Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strain Rate CAMM
Strain may refer to: Science and technology * Strain (biology), variants of plants, viruses or bacteria; or an inbred animal used for experimental purposes * Strain (chemistry), a chemical stress of a molecule * Strain (injury), an injury to a muscle (tear in tendon) in which the muscle fibers tear as a result of over-stretching * Strain (mechanics), a geometrical measure of deformation representing the relative displacement between particles in a material body * Filtration, separating solids from fluids (liquids or gases) by interposing a strainer, a medium through which only the fluid can pass * Percolation, the movement and filtering of fluids through porous materials * Psychological stress Other uses * straining, in cooking, the separation of liquid from solids using a strainer or sieve. * , the process of making a mash or purée by forcing through a sieve, rather than using a power blender. Cf. ricing (cooking) * strain (bridge), the indication of either the trump suit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Traces
Multiple may refer to: Economics * Multiple finance, a method used to analyze stock prices *Multiples of the price-to-earnings ratio *Chain stores, are also referred to as 'Multiples' *Box office multiple, the ratio of a film's total gross to that of its opening weekend Sociology * Multiples (sociology), a theory in sociology of science by Robert K. Merton, see Science *Multiple (mathematics), multiples of numbers *List of multiple discoveries, instances of scientists, working independently of each other, reaching similar findings * Multiple birth, because having twins is sometimes called having "multiples" *Multiple sclerosis, an inflammatory disease *Parlance for people with multiple identities, sometimes called "multiples"; often theorized as having dissociative identity disorder Printing *Printmaking, where ''multiple'' is often used as a term for a print, especially in the US * Artist's multiple, series of identical prints, collages or objects by an artist, subverting the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |