Cardiac stress test on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A cardiac stress test (also referred to as a cardiac diagnostic test, cardiopulmonary exercise test, or abbreviated CPX test) is a cardiological test that measures the heart's ability to respond to external stress in a controlled clinical environment. The stress response is induced by exercise or by intravenous pharmacological stimulation.
Cardiac stress tests compare the
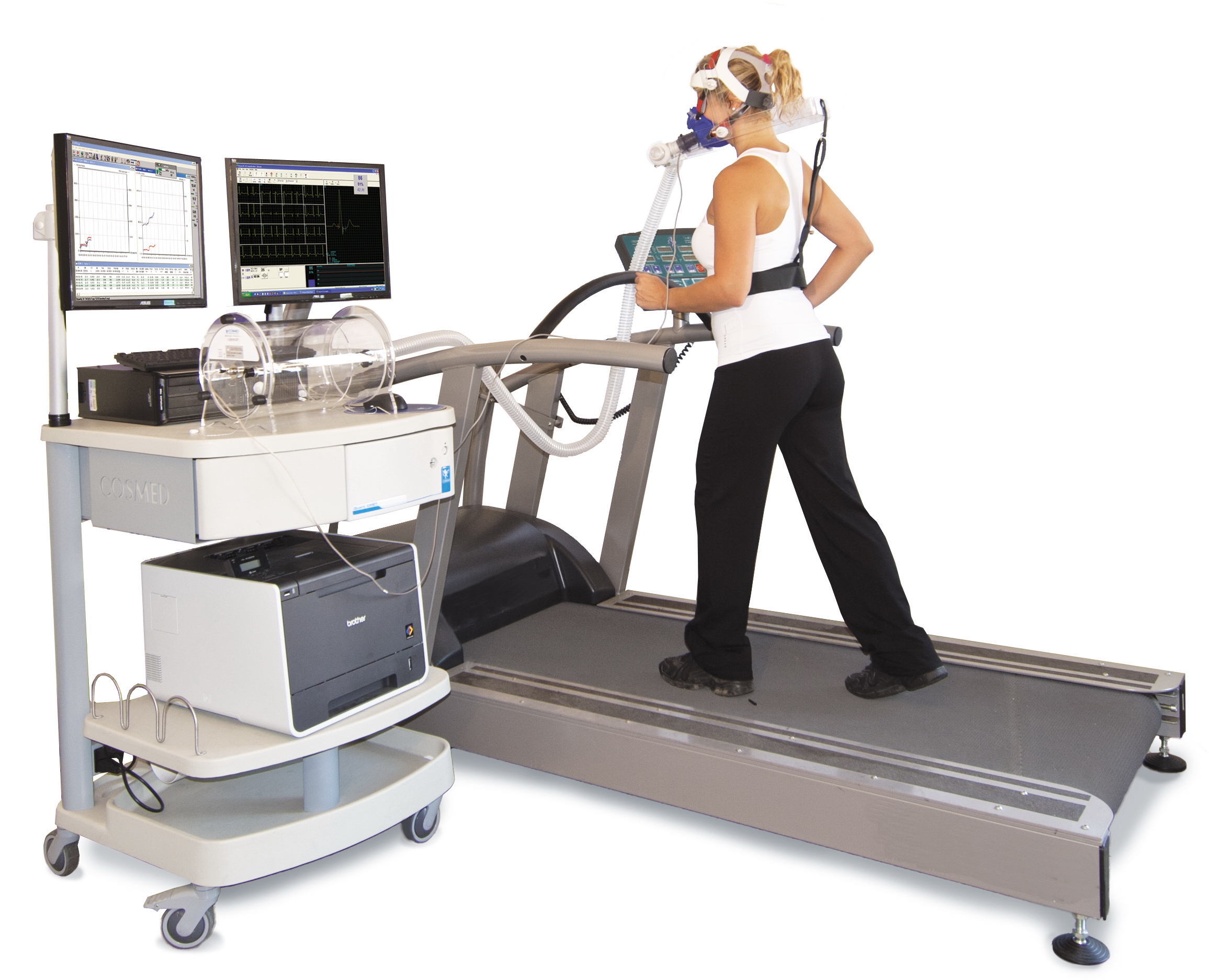 While also measuring breathing gases (e.g. O2, VO2), the test is often referred to as a cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET).
Common indications for a cardiopulmonary exercise test is:
Evaluation of dyspnea.
Work up before heart transplantation.
Prognosis and risk assessment of heart failure patients.
The test is also common in sport science for measuring athlete's VO2 max.
While also measuring breathing gases (e.g. O2, VO2), the test is often referred to as a cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET).
Common indications for a cardiopulmonary exercise test is:
Evaluation of dyspnea.
Work up before heart transplantation.
Prognosis and risk assessment of heart failure patients.
The test is also common in sport science for measuring athlete's VO2 max.
Preparing for the exercise stress test
"A Simple Exercise Tolerance Test for Circulatory Efficiency with Standard Tables for Normal Individuals," ''American Journal of the Medical Sciences''
"Optimal Medical Therapy with or without PCI for Stable Coronary Disease," ''New England Journal of Medicine''
Stress test information from the American Heart Association
at NIH MedLine {{DEFAULTSORT:Cardiac Stress Test Diagnostic cardiology Nuclear medicine
coronary circulation
Coronary circulation is the circulation of blood in the blood vessels that supply the heart muscle (myocardium).
Coronary arteries supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. Cardiac veins then drain away the blood after it has been deoxygenat ...
while the patient is at rest with the same patient's circulation during maximum cardiac exertion, showing any abnormal blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in th ...
flow to the myocardium
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle, myocardium, cardiomyocytes and cardiac myocytes) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that ...
(heart muscle tissue). The results can be interpreted as a reflection on the general physical condition of the test patient. This test can be used to diagnose coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic pla ...
(also known as ischemic heart disease) and assess patient prognosis after a myocardial infarction (heart attack).
Exercise-induced stressors are most commonly either exercise on a treadmill or pedalling a stationary exercise bicycle ergometer. The level of stress is progressively increased by raising the difficulty (steepness of the slope on a treadmill or resistance on an ergometer) and speed. People who cannot use their legs may exercise with a bicycle-like crank that they turn with their arms, or may be given a medication to induce cardiac stress. Once the stress test is completed, the patient generally is advised to not suddenly stop activity but to slowly decrease the intensity of the exercise over the course of several minutes.
The test administrator or attending physician examines the symptoms and blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" r ...
response. To measure the heart's response to the stress the patient may be connected to an electrocardiogram (ECG); in this case the test is most commonly called a cardiac stress test but is known by other names, such as exercise testing, stress testing treadmills, exercise tolerance test, stress test or stress test ECG. Alternatively a stress test may use an echocardiogram for ultrasonic imaging of the heart (in which case the test is called an echocardiography stress test or stress echo), or a gamma camera to image radioisotopes injected into the bloodstream (called a nuclear stress test
A cardiac stress test (also referred to as a cardiac diagnostic test, cardiopulmonary exercise test, or abbreviated CPX test) is a cardiological test that measures the heart's ability to respond to external stress in a controlled clinical environ ...
).
Stress echocardiography
A stress test may be accompanied byechocardiography
An echocardiography, echocardiogram, cardiac echo or simply an echo, is an ultrasound of the heart.
It is a type of medical imaging of the heart, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound.
Echocardiography has become routinely used in t ...
. The echocardiography is performed both before and after the exercise so that structural differences can be compared.
A resting echocardiogram is obtained prior to stress. The images obtained are similar to the ones obtained during a full surface echocardiogram, commonly referred to as transthoracic echocardiogram. The patient is subjected to stress in the form of exercise or chemically (usually dobutamine). After the target heart rate is achieved, 'stress' echocardiogram images are obtained. The two echocardiogram images are then compared to assess for any abnormalities in wall motion of the heart. This is used to detect obstructive coronary artery disease.
Cardiopulmonary exercise test
 While also measuring breathing gases (e.g. O2, VO2), the test is often referred to as a cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET).
Common indications for a cardiopulmonary exercise test is:
Evaluation of dyspnea.
Work up before heart transplantation.
Prognosis and risk assessment of heart failure patients.
The test is also common in sport science for measuring athlete's VO2 max.
While also measuring breathing gases (e.g. O2, VO2), the test is often referred to as a cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET).
Common indications for a cardiopulmonary exercise test is:
Evaluation of dyspnea.
Work up before heart transplantation.
Prognosis and risk assessment of heart failure patients.
The test is also common in sport science for measuring athlete's VO2 max.
Nuclear stress test
A nuclear stress test uses a gamma camera to image radioisotopes injected into the bloodstream. The best known example is myocardial perfusion imaging. Typically, a radiotracer ( Tc-99 sestamibi, Myoview or thallous chloride 201) may be injected during the test. After a suitable waiting period to ensure proper distribution of the radiotracer, scans are acquired with a gamma camera to capture images of the blood flow. Scans acquired before and after exercise are examined to assess the state of the coronary arteries of the patient. Showing the relative amounts of radioisotope within the heart muscle, the nuclear stress tests more accurately identify regional areas of reduced blood flow. Stress and potential cardiac damage from exercise during the test is a problem in patients with ECG abnormalities at rest or in patients with severe motor disability. Pharmacological stimulation from vasodilators such as dipyridamole or adenosine, or positive chronotropic agents such as dobutamine can be used. Testing personnel can include a cardiac radiologist, a nuclear medicine physician, a nuclear medicine technologist, a cardiology technologist, a cardiologist, and/or a nurse. The typical dose of radiation received during this procedure can range from 9.4 to 40.7millisieverts
The sievert (symbol: SvNot be confused with the sverdrup or the svedberg, two non-SI units that sometimes use the same symbol.) is a unit in the International System of Units (SI) intended to represent the stochastic health risk of ionizing ra ...
.
Function
The American Heart Association recommends ECG treadmill testing as the first choice for patients with medium risk of coronary heart disease according to risk factors of smoking, family history of coronary artery stenosis, hypertension, diabetes and high cholesterol. In 2013, in its "Exercise Standards for Testing and Training", the AHA indicated that high frequency QRS analysis during ECG treadmill test have useful test performance for detection of coronary heart disease. *Perfusion
Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the circulatory system or lymphatic system to an organ or a tissue, usually referring to the delivery of blood to a capillary bed in tissue. Perfusion is measured as the rate at which blood is deliver ...
stress test (with 99mTc labelled sestamibi) is appropriate for select patients, especially those with an abnormal resting electrocardiogram.
* Intracoronary ultrasound or angiogram can provide more information at the risk of complications associated with cardiac catheterization
Cardiac catheterization (heart cath) is the insertion of a catheter into a chamber or vessel of the heart. This is done both for diagnostic and interventional purposes.
A common example of cardiac catheterization is coronary catheterization that ...
.
Diagnostic value
The common approach for stress testing by American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association indicates the following: * Treadmill test: sensitivity 73-90%, specificity 50-74% (modifiedBruce protocol
The Bruce protocol is a diagnostic test used in the evaluation of cardiac function, developed by Robert A. Bruce.
It is a standardized multistage treadmill test for assessing cardiovascular health. Developed by Robert A. Bruce in 1963 who was an ...
)
* Nuclear test: sensitivity 81%, specificity 85-95%
(Sensitivity
Sensitivity may refer to:
Science and technology Natural sciences
* Sensitivity (physiology), the ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli
** Sensory processing sensitivity in humans
* Sensitivity and specificity, statisti ...
is the percentage of people with the condition who are correctly identified by the test as having the condition; specificity is the percentage of people without the condition are correctly identified by the test as not having the condition).
To arrive at the patient's posttest likelihood of disease, interpretation of the stress test result requires integration of the patient's pretest likelihood with the test's sensitivity and specificity. This approach, first described by Diamond and Forrester in the 1970s, results in an estimate of the patient's post-test likelihood of disease.
The value of stress tests has always been recognized as limited in assessing heart disease such as atherosclerosis, a condition which mainly produces wall thickening and enlargement of the arteries. This is because the stress test compares the patient's coronary flow status before and after exercise and is suitable to detecting specific areas of ischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems wi ...
and lumen narrowing, not a generalized arterial thickening.
According to American Heart Association data, about 65% of men and 47% of women present with a heart attack or sudden cardiac arrest as their first symptom of cardiovascular disease. Stress tests, carried out shortly before these events, are not relevant to the prediction of infarction in the majority of individuals tested. Over the past two decades, better methods have been developed to identify atherosclerotic disease before it becomes symptomatic. These detection methods include ''anatomical'' and ''physiological'' methods.
; Examples of anatomical methods
* CT coronary calcium score
* Coronary CT angiography
* Intima-media thickness
Intima–media thickness (IMT), also called intimal medial thickness, is a measurement of the thickness of tunica intima and tunica media, the innermost two layers of the wall of an artery. The measurement is usually made by external ultrasound and ...
(IMT)
* Intravascular ultrasound
Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) or intravascular echocardiography is a medical imaging methodology using a specially designed catheter with a miniaturized ultrasound probe attached to the distal end of the catheter. The proximal end of the ca ...
(IVUS)
; Examples of physiological methods
* Lipoprotein analysis
* HbA1c
* Hs-CRP
C-reactive protein (CRP) is an annular (ring-shaped) pentameric protein found in blood plasma, whose circulating concentrations rise in response to inflammation. It is an acute-phase protein of hepatic origin that increases following interleukin- ...
* Homocysteine
The anatomic methods directly measure some aspects of the actual process of atherosclerosis itself and therefore offer the possibility of early diagnosis but are often more expensive and may be invasive (in the case of IVUS, for example). The physiological methods are often less expensive and safer but are not able to quantify the current status of the disease or directly track progression.
Contraindications and termination conditions
Stress cardiac imaging is not recommended for asymptomatic, low-risk patients as part of their routine care. Some estimates show that such screening accounts for 45% of cardiac stress imaging, and evidence does not show that this results in better outcomes for patients. Unless high-risk markers are present, such as diabetes in patients aged over 40, peripheral arterial disease; or a risk of coronary heart disease greater than 2 percent yearly, most health societies do not recommend the test as a routine procedure. Absolute contraindications to cardiac stress test include: * Acute myocardial infarction within 48 hours * Unstableangina
Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by ischemia, insufficient blood flow to the Cardiac muscle, heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease.
Angina is typical ...
not yet stabilized with medical therapy
* Uncontrolled cardiac arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults ...
, which may have significant hemodynamic responses (e.g. ventricular tachycardia)
* Severe symptomatic aortic stenosis, aortic dissection, pulmonary embolism, and pericarditis
Pericarditis is inflammation of the pericardium, the fibrous sac surrounding the heart. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp chest pain, which may also be felt in the shoulders, neck, or back. The pain is typically less severe when sit ...
* Multivessel coronary artery diseases that have a high risk of producing an acute myocardial infarction
* Decompensated or inadequately controlled congestive heart failure
* Uncontrolled hypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
(blood pressure>200/110mm Hg)
* Severe pulmonary hypertension
* Acute aortic dissection
* Acutely ill for any reason
Indications for termination:
A cardiac stress test should be terminated before completion under the following circumstances:
Absolute indications for termination include:
* Systolic blood pressure decreases by more than 10 mmHg with increase in work rate, or drops below baseline in the same position, with other evidence of ischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems wi ...
.
* Increase in nervous system symptoms: Dizziness, ataxia or near syncope
* Moderate to severe anginal pain (above 3 on standard 4-point scale)
* Signs of poor perfusion, e.g. cyanosis
Cyanosis is the change of body tissue color to a bluish-purple hue as a result of having decreased amounts of oxygen bound to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells of the capillary bed. Body tissues that show cyanosis are usually in locations ...
or pallor
* Request of the test subject
* Technical difficulties (e.g. difficulties in measuring blood pressure or EGC)
* ST Segment elevation of more than 1 mm in aVR, V1 or non-Q wave leads
* Sustained ventricular tachycardia
Relative indications for termination include:
* Systolic blood pressure decreases by more than 10 mmHg with increase in work rate, or drops below baseline in the same position, without other evidence of ischemia.
* ST or QRS segment changes, e.g. more than 2 mm horizontal or downsloping ST segment depression in non-Q wave leads, or marked axis shift
* Arrhythmias other than sustained ventricular tachycardia e.g. Premature ventricular contractions, both multifocal or triplet; heart block; supraventricular tachycardia
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is an umbrella term for fast heart rhythms arising from the upper part of the heart. This is in contrast to the other group of fast heart rhythms – ventricular tachycardia, which start within the lower cham ...
or bradyarrhythmias
* Intraventricular conduction delay or bundle branch block or that cannot be distinguished from ventricular tachycardia
* Increasing chest pain
* Fatigue, shortness of breath, wheezing, claudication or leg cramps
* Hypertensive response (systolic blood pressure > 250 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure > 115 mmHg)
Adverse effects
Side effects from cardiac stress testing may include * Palpitations, chest pain, myocardial infarction, shortness of breath, headache, nausea or fatigue. * Adenosine and dipyridamole can cause mild hypotension. * As the tracers used for this test are carcinogenic, frequent use of these tests carries a small risk of cancer.Pharmacological agents
Pharmacologic stress testing relies on coronary steal. Vasodilators are used to dilate coronary vessels, which causes increased blood velocity and flow rate in normal vessels and less of a response in stenotic vessels. This difference in response leads to a steal of flow and perfusion defects appear in cardiac nuclear scans or as ST-segment changes. The choice of pharmacologic stress agents used in the test depends on factors such as potential drug interactions with other treatments and concomitant diseases. Pharmacologic agents such as adenosine, Lexiscan (regadenoson), or dipyridamole is generally used when a patient cannot achieve adequate work level with treadmill exercise, or has poorly controlledhypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
or left bundle branch block. However, an exercise stress test may provide more information about exercise tolerance than a pharmacologic stress test.
Commonly used agents include:
* Vasodilators acting as adenosine receptor agonists, such as adenosine
Adenosine ( symbol A) is an organic compound that occurs widely in nature in the form of diverse derivatives. The molecule consists of an adenine attached to a ribose via a β-N9-glycosidic bond. Adenosine is one of the four nucleoside building ...
itself, and dipyridamole (brand name "Persantine"), which acts indirectly at the receptor.
* Regadenoson (brand name "Lexiscan"), which acts specifically at the adenosine A2A receptor, thus affecting the heart more than the lung.
* Dobutamine. The effects of beta-agonist
Beta adrenergic agonists or beta agonists are medications that relax muscles of the airways, causing widening of the airways and resulting in easier breathing. They are a class of sympathomimetic agents, each acting upon the beta adrenoceptors. I ...
s such as dobutamine can be reversed by administering beta-blockers such as propranolol.
Lexiscan (Regadenoson) or Dobutamine is often used in patients with severe reactive airway disease
Reactive airway disease (RAD) is an informal label that physicians apply to patients with symptoms similar to those of asthma. An exact definition of the condition does not exist. Individuals who are typically labeled as having RAD generally have ...
( asthma or COPD) as adenosine and dipyridamole can cause acute exacerbation of these conditions. If the patient's Asthma is treated with an inhaler then it should be used as a pre-treatment prior to the injection of the pharmacologic stress agent. In addition, if the patient is actively wheezing then the physician should determine the benefits versus the risk to the patient of performing a stress test especially outside of a hospital setting. Caffeine is usually held 24 hours prior to an adenosine stress test, as it is a competitive antagonist of the A2A adenosine receptor and can attenuate the vasodilatory effects of adenosine.
Aminophylline
Aminophylline is a compound of the bronchodilator theophylline with ethylenediamine in 2:1 ratio. The ethylenediamine improves solubility, and the aminophylline is usually found as a dihydrate.
Aminophylline is less potent and shorter-acting tha ...
may be used to attenuate severe and/or persistent adverse reactions to Adenosine and Lexiscan.
Limitations
The stress test does not detect: * Atheroma *Vulnerable plaques
A vulnerable plaque is a kind of atheromatous plaque – a collection of white blood cells (primarily macrophages) and lipids (including cholesterol) in the wall of an artery – that is particularly unstable and prone to produce sudden major prob ...
The test has relatively high rates of false positives and false negatives compared with other clinical tests. Females in particular have a higher rate of false positives, which is theorized to be because on average they have smaller hearts.
Results
* Increased spatial resolution allows a more sensitive detection of ischemia. * Stress testing, even if made in time, is not able to guarantee the prevention of symptoms, fainting, or death. Stress testing, although more effective than a resting ECG at detecting heart function, is only able to detect certain cardiac properties. * The detection of high-grade coronary artery stenosis by a cardiac stress test has been the key to recognizing people who have heart attacks since 1980. From 1960 to 1990, despite the success of stress testing to identify many who were at high risk of heart attack, the inability of this test to correctly identify many others is discussed in medical circles but unexplained. * High degrees of coronary artery stenosis, which are detected by stress testing methods are often, though not always, responsible for recurrent symptoms of angina. * Unstable atheroma produces "vulnerable plaques" hidden within the walls of coronary arteries which go undetected by this test. * Limitation in blood flow to the left ventricle can lead to recurrent angina pectoris.See also
*Cardiac steal syndrome Coronary steal (with its symptoms termed coronary steal syndrome or cardiac steal syndrome) is a phenomenon where an alteration of circulation patterns leads to a reduction in the blood flow directed to the coronary circulation. It is caused when t ...
* Duke Treadmill Score
Duke Treadmill Score is one of the tools for predicting the risk of ischemia or infarction in the heart muscle. The calculation is done based on the information obtained from an exercise test by this formula:
: Bruce_protocol.html" ;"title="xercise ...
* Harvard step test
* Metabolic equivalent
* Robert A. Bruce
* Wasserman 9-Panel Plot
The Wasserman 9-Panel Plot, often called a Nine-Panel Plot, is a standard layout for the graphical representation of data produced by a cardiopulmonary exercise test. The layout was updated in 2012. The graphs give an overview of cardiovascular, v ...
References
External links
Preparing for the exercise stress test
"A Simple Exercise Tolerance Test for Circulatory Efficiency with Standard Tables for Normal Individuals," ''American Journal of the Medical Sciences''
"Optimal Medical Therapy with or without PCI for Stable Coronary Disease," ''New England Journal of Medicine''
Stress test information from the American Heart Association
at NIH MedLine {{DEFAULTSORT:Cardiac Stress Test Diagnostic cardiology Nuclear medicine