|
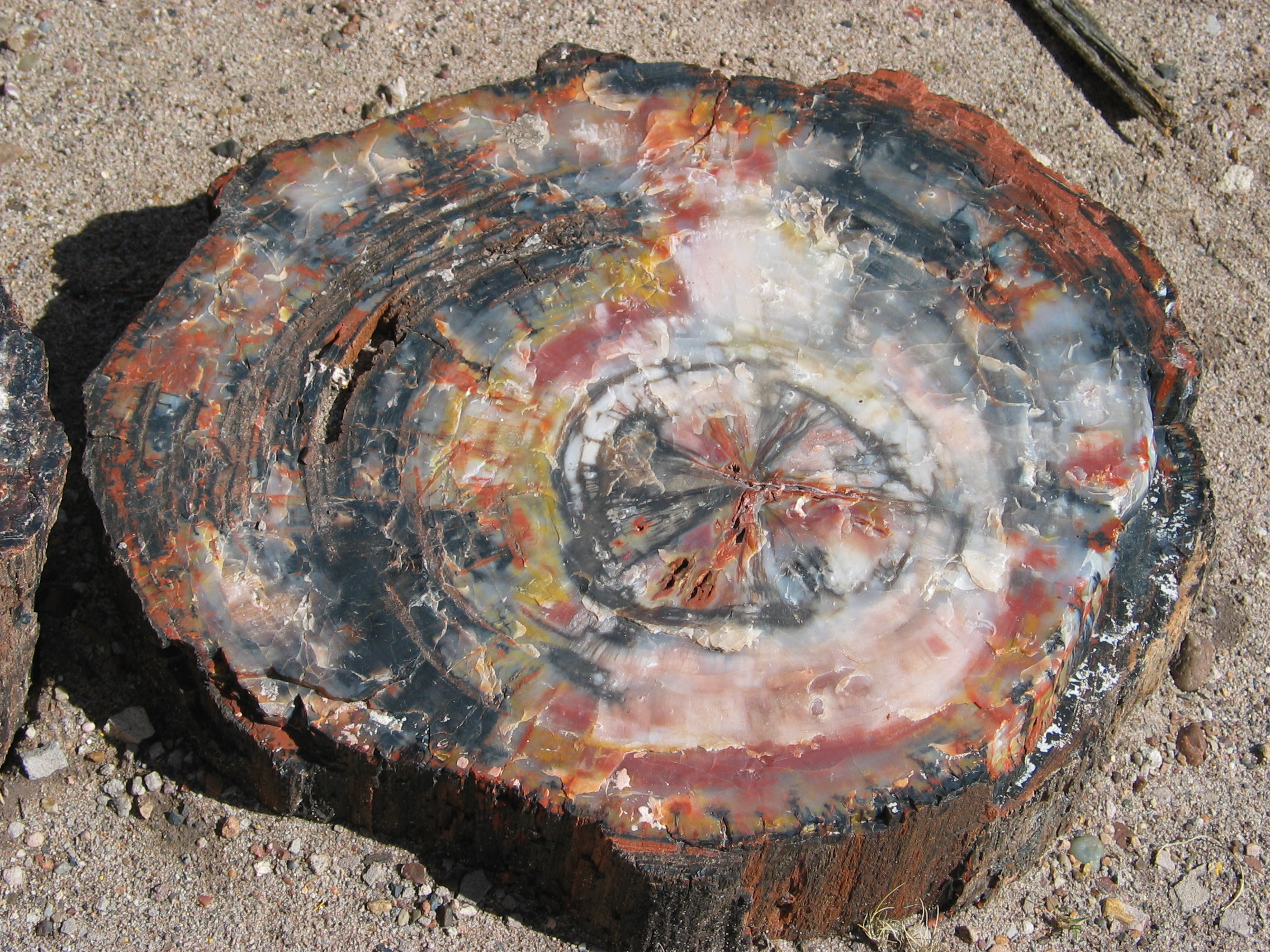
Silicified
In geology, petrifaction or petrification () is the process by which organic material becomes a fossil through the replacement of the original material and the filling of the original pore spaces with minerals. Petrified wood typifies this process, but all organisms, from bacteria to vertebrates, can become petrified (although harder, more durable matter such as bone, beaks, and shells survive the process better than softer remains such as muscle tissue, feathers, or skin). Petrifaction takes place through a combination of two similar processes: permineralization and replacement. These processes create replicas of the original specimen that are similar down to the microscopic level. Processes Permineralization One of the processes involved in petrifaction is permineralization. The fossils created through this process tend to contain a large amount of the original material of the specimen. This process occurs when groundwater containing dissolved minerals (most commonly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
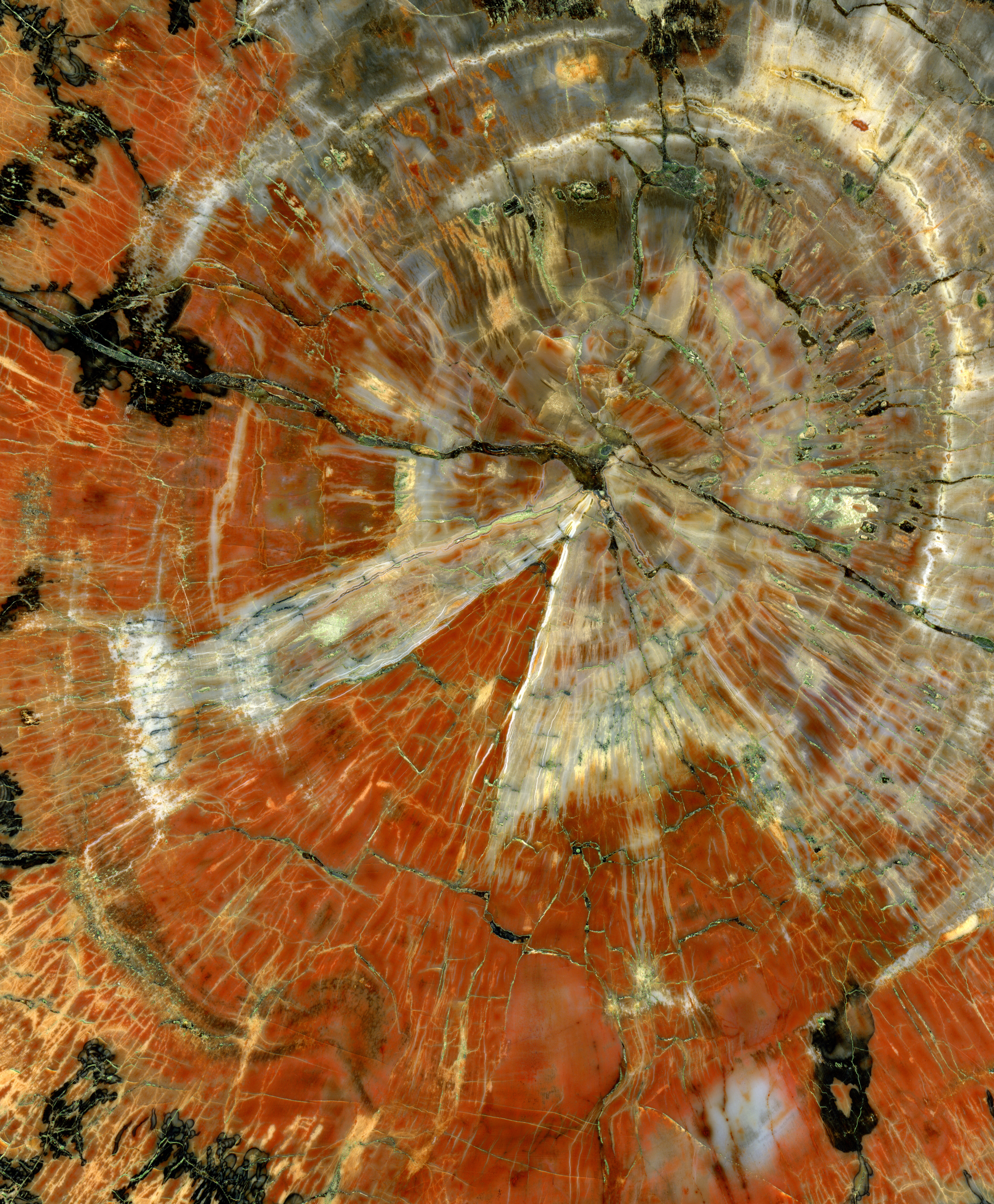
Petrified Wood Closeup 2
In geology, petrifaction or petrification () is the process by which organic material becomes a fossil through the replacement of the original material and the filling of the original pore spaces with minerals. Petrified wood typifies this process, but all organisms, from bacteria to vertebrates, can become petrified (although harder, more durable matter such as bone, beaks, and shells survive the process better than softer remains such as muscle tissue, feathers, or skin). Petrifaction takes place through a combination of two similar processes: permineralization and replacement. These processes create replicas of the original specimen that are similar down to the microscopic level. Processes Permineralization One of the processes involved in petrifaction is permineralization. The fossils created through this process tend to contain a large amount of the original material of the specimen. This process occurs when groundwater containing dissolved minerals (most commonly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrified Wood
Petrified wood, also known as petrified tree (from Ancient Greek meaning 'rock' or 'stone'; literally 'wood turned into stone'), is the name given to a special type of '' fossilized wood'', the fossilized remains of terrestrial vegetation. '' Petrifaction'' is the result of a tree or tree-like plants having been replaced by stone via a mineralization process that often includes permineralization and replacement. The organic materials making up cell walls have been replicated with minerals (mostly silica in the form of opal, chalcedony, or quartz). In some instances, the original structure of the stem tissue may be partially retained. Unlike other plant fossils, which are typically impressions or compressions, petrified wood is a three-dimensional representation of the original organic material. The petrifaction process occurs underground, when wood becomes buried in water-saturated sediment or volcanic ash. The presence of water reduces the availability of oxygen which inhi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permineralization
Permineralization is a process of fossilization of bones and tissues in which mineral deposits form internal casts of organisms. Carried by water, these minerals fill the spaces within organic tissue. Because of the nature of the casts, permineralization is particularly useful in studies of the internal structures of organisms, usually of plants. Process Permineralization, a type of fossilization, involves deposits of minerals within the cells of organisms. Water from the ground, lakes, or oceans seeps into the pores of organic tissue and forms a crystal cast with deposited minerals. Crystals begin to form in the porous cell walls. This process continues on the inner surface of the walls until the central cavity of the cell, the lumen, is completely filled. The cell walls themselves remain intact surrounding the crystals. Silicification In silicification, the weathering of rocks releases silicate minerals and the silica makes its way into a body of still water. Eventually, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur Valley State Park
Dinosaur Valley State Park is a state park near Glen Rose, Texas, United States. History Dinosaur Valley State Park, located just northwest of Glen Rose in Somervell County, Texas, is a scenic park set astride the Paluxy River. The land for the park was acquired from private owners under the State Parks Bonds Program during 1968 and opened to the public in 1972. In addition to being a state park, it is also a National Natural Landmark. Eastward-dipping limestones, sandstones, and mudstones of the Glen Rose Formation were deposited during the early Cretaceous Period approximately 113 million years ago along the shorelines of an ancient sea, and form the geological setting for the park area. Over the last million years or so, these layered formations have been eroded, dissected and sculpted by the Paluxy River which, in many places, has cut down to resistant beds and planed off sizable exposures of rock in the river bottom. Controversy Near Dinosaur Valley State Park, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Journal Of Anatomy And Embryology
The ''Italian Journal of Anatomy and Embryology'' (sometimes abbreviated as the ''IJAE'') is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal of anatomy and embryology. It was established in 1901 by Giulio Chiarugi and is published by Firenze University Press. It is the official journal of the Italian Society of Anatomy and Histology. All articles are submitted in English. Content The journal publishes original papers, invited review articles, historical article, commentaries, obituaries, and book reviews. Its main focus is to understand anatomy through an analysis of structure, function, development and evolution. Focal areas include: * experimental studies * molecular and cell biology * application of modern imaging techniques * comparative functional morphology Morphology, from the Greek and meaning "study of shape", may refer to: Disciplines * Morphology (archaeology), study of the shapes or forms of artifacts * Morphology (astronomy), study of the shape of astronomical objec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany Regions of Italy, region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico anno 2013, datISTAT/ref> Florence was a centre of Middle Ages, medieval European trade and finance and one of the wealthiest cities of that era. It is considered by many academics to have been the birthplace of the Renaissance, becoming a major artistic, cultural, commercial, political, economic and financial center. During this time, Florence rose to a position of enormous influence in Italy, Europe, and beyond. Its turbulent political history includes periods of rule by the powerful House of Medici, Medici family and numerous religious and republican revolutions. From 1865 to 1871 the city served as the capital of the Kingdom of Italy (established in 1861). The Florentine dialect forms the base of Italian language, Stan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Girolamo Segato
Girolamo Segato (13 June 1792 – 3 February 1836) was an Italian naturalist, cartographer, Egyptologist, and anatomist. He is perhaps best known for his work in the artificial petrifaction of human cadavers. Segato was born in the Carthusian monastery of Vedana. As a child, Segato learned basic sciences from Antonio Bagini, a Sospirolo priest. After studying under Bagini, Segato spent a short time as an accountant in Treviso before returning to secondary schooling in Belluno, where his teacher was Tomaso Antonio Catullo. From 1818 onwards Segato participated in several archaeological expeditions to Egypt, where he became an expert in the techniques of mummification; however, most of his studies undertaken during these trips were lost. Upon his return to Florence in 1823, Segato developed a technique similar to mummification, but unique: rather than simply removing water from cadavers, Segato's method consisted of what appears to be mineralization or "petrification". His pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Carbide
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been mass-produced as a powder and crystal since 1893 for use as an abrasive. Grains of silicon carbide can be bonded together by sintering to form very hard ceramics that are widely used in applications requiring high endurance, such as car brakes, car clutches and ceramic plates in bulletproof vests. Large single crystals of silicon carbide can be grown by the Lely method and they can be cut into gems known as synthetic moissanite. Electronic applications of silicon carbide such as light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and detectors in early radios were first demonstrated around 1907. SiC is used in semiconductor electronics devices that operate at high temperatures or high voltages, or both. Natural occurrence Naturally occurring moissanite is found in only minute quantities in cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium Carbide
Titanium carbide, Ti C, is an extremely hard ( Mohs 9–9.5) refractory ceramic material, similar to tungsten carbide. It has the appearance of black powder with the sodium chloride ( face-centered cubic) crystal structure. It occurs in nature as a form of the very rare mineral khamrabaevite () - (Ti,V,Fe)C. It was discovered in 1984 on Mount Arashan in the Chatkal District, USSR (modern Kyrgyzstan), near the Uzbek border. The mineral was named after Ibragim Khamrabaevich Khamrabaev, director of Geology and Geophysics of Tashkent, Uzbekistan. Its crystals as found in nature range in size from 0.1 to 0.3 mm. Physical properties Titanium carbide has an elastic modulus of approximately 400 GPa and a shear modulus of 188 GPa. Manufacturing and machining Tool bits without tungsten content can be made of titanium carbide in nickel-cobalt matrix cermet, enhancing the cutting speed, precision, and smoothness of the workpiece. The resistance to wear, corrosion, and oxidation of a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up only about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. Three isotopes occur naturally, C and C being stable, while C is a radionuclide, decaying with a half-life of about 5,730 years. Carbon is one of the few elements known since antiquity. Carbon is the 15th most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the fourth most abundant element in the universe by mass after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen. Carbon's abundance, its unique diversity of organic compounds, and its unusual ability to form polymers at the temperatures commonly encountered on Earth, enables this element to serve as a common element of all known life. It is the second most abundant element in the human body by mass (about 18.5%) after oxygen. The atoms of carbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in sea water, aqua regia, and chlorine. Titanium was discovered in Cornwall, Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, by William Gregor in 1791 and was named by Martin Heinrich Klaproth after the Titan (mythology), Titans of Greek mythology. The element occurs within a number of minerals, principally rutile and ilmenite, which are widely distributed in the Earth's crust and lithosphere; it is found in almost all living things, as well as bodies of water, rocks, and soils. The metal is extracted from its principal mineral ores by the Kroll process, Kroll and Hunter process, Hunter processes. The most common compound, titanium dioxide, is a popular photocatalysis, photocatalyst and is used in the manufacture of white pigments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) is one of the United States Department of Energy national laboratories, managed by the Department of Energy's (DOE) Office of Science. The main campus of the laboratory is in Richland, Washington. Originally named the Pacific Northwest Laboratory, PNL was established in 1965 when research and development at the Hanford Site was separated from other Hanford operations. In 1995, the laboratory was renamed the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory also known as PNNL. Facilities PNNL houses several scientific user facilities and research facilities. Scientific user facilities The Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory (EMSL) is a U.S. Department of Energy national scientific user facility. EMSL provides researchers around the world with integrated capabilities in oxide and mineral interface chemistry, high-performance computing and computational chemistry software, mass spectrometry, high-field magnetic resonance, and sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |