|
Strong Consistency
Strong consistency is one of the consistency models used in the domain of concurrent programming (e.g., in distributed shared memory, distributed transactions). The protocol is said to support strong consistency if: # All accesses are seen by all parallel processes (or nodes, processors, etc.) in the same order (sequentially) Therefore, only one consistent state can be observed, as opposed to weak consistency, where different parallel processes (or nodes, etc.) can perceive variables in different states. See also * CAP theorem In database theory, the CAP theorem, also named Brewer's theorem after computer scientist Eric Brewer (scientist), Eric Brewer, states that any distributed data store can provide at most Inconsistent triad, two of the following three guarantees: ; ... References Consistency models {{Tech-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Consistency Model
In computer science, a consistency model specifies a contract between the programmer and a system, wherein the system guarantees that if the programmer follows the rules for operations on memory, memory will be data consistency, consistent and the results of reading, writing, or updating memory will be predictable. Consistency models are used in Distributed computing, distributed systems like distributed shared memory systems or distributed data stores (such as filesystems, databases, optimistic replication systems or web caching). Consistency is different from coherence, which occurs in systems that are cache coherence, cached or cache-less, and is consistency of data with respect to all processors. Coherence deals with maintaining a global order in which writes to a single location or single variable are seen by all processors. Consistency deals with the ordering of operations to multiple locations with respect to all processors. High level languages, such as C++ and Java (progr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Concurrent Programming
Concurrent means happening at the same time. Concurrency, concurrent, or concurrence may refer to: Law * Concurrence, in jurisprudence, the need to prove both ''actus reus'' and ''mens rea'' * Concurring opinion (also called a "concurrence"), a legal opinion which supports the conclusion, though not always the reasoning, of the majority. * Concurrent estate, a concept in property law * Concurrent resolution, a legislative measure passed by both chambers of the United States Congress * Concurrent sentences, in criminal law, periods of imprisonment that are served simultaneously Computing * Concurrency (computer science), the property of program, algorithm, or problem decomposition into order-independent or partially-ordered units * Concurrent computing, the overlapping execution of multiple interacting computational tasks * Concurrence (quantum computing), a measure used in quantum information theory * Concurrent Computer Corporation, an American computer systems manufactur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
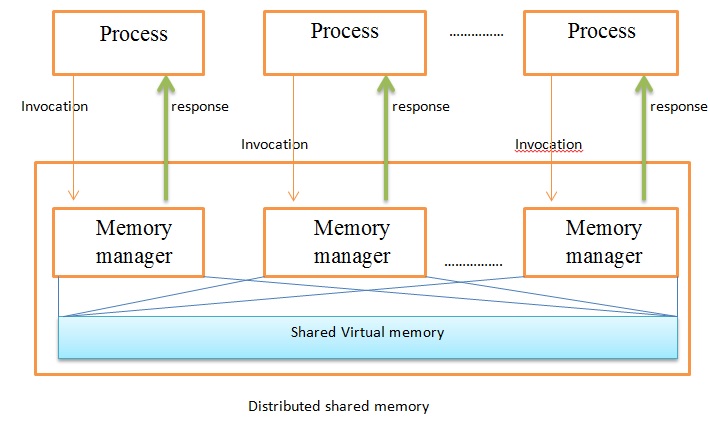
Distributed Shared Memory
In computer science, distributed shared memory (DSM) is a form of memory architecture where physically separated memories can be addressed as a single shared address space. The term "shared" does not mean that there is a single centralized memory, but that the address space is shared—i.e., the same physical address on two Processor (computing), processors refers to the same location in memory. Distributed global address space (DGAS), is a similar term for a wide class of software and hardware implementations, in which each node (networking), node of a computer cluster, cluster has access to shared memory architecture, shared memory in addition to each node's private (i.e., not shared) Random-access memory, memory. Overview DSM can be achieved via software as well as hardware. Hardware examples include cache coherence circuits and network interface controllers. There are three ways of implementing DSM: * Page (computer memory), Page-based approach using virtual memory * Sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Distributed Transactions
A distributed transaction operates within a Distributed computing, distributed environment, typically involving multiple nodes across a network depending on the location of the data. A key aspect of distributed transactions is Atomicity (programming), atomicity, which ensures that the transaction is completed in its entirety or not executed at all. It's essential to note that distributed transactions are not limited to databases. The Open Group, a vendor consortium, proposed the X/Open XA, X/Open Distributed Transaction Processing Model (X/Open XA), which became a de facto standard for the behavior of transaction model components. Databases are common transactional resources and, often, transactions span a couple of such databases. In this case, a distributed transaction can be seen as a database transaction that must be Synchronization, synchronized (or provide ACID properties) among multiple participating databases which are distributed computing, distributed among different phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Weak Consistency
The name weak consistency can be used in two senses. In the first sense, strict and more popular, weak consistency is one of the consistency models used in the domain of concurrent programming (e.g. in distributed shared memory, distributed transactions etc.). A protocol is said to support weak consistency if: #All accesses to synchronization variables are seen by all processes (or nodes, processors) in the same order (sequentially) - these are synchronization operations. Accesses to critical sections are seen sequentially. #All other accesses may be seen in different order on different processes (or nodes, processors). #The set of both read and write operations in between different synchronization operations is the same in each process. Therefore, there can be no access to a synchronization variable if there are pending write operations. And there can not be any new read/write operation started if the system is performing any synchronization operation. In the second, more genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
CAP Theorem
In database theory, the CAP theorem, also named Brewer's theorem after computer scientist Eric Brewer (scientist), Eric Brewer, states that any distributed data store can provide at most Inconsistent triad, two of the following three guarantees: ; Consistency model, Consistency: Every read receives the most recent write or an error. Note that consistency as defined in the CAP theorem is quite different from the consistency guaranteed in ACID database transactions. ; Availability: Every request received by a non-failing node in the system must result in a response. This is the definition of availability in CAP theorem as defined by Gilbert and Lynch. Note that availability as defined in CAP theorem is different from high availability in software architecture. ; Network partitioning, Partition tolerance: The system continues to operate despite an arbitrary number of messages being dropped (or delayed) by the network between nodes. When a network partition failure happens, it must be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |