|
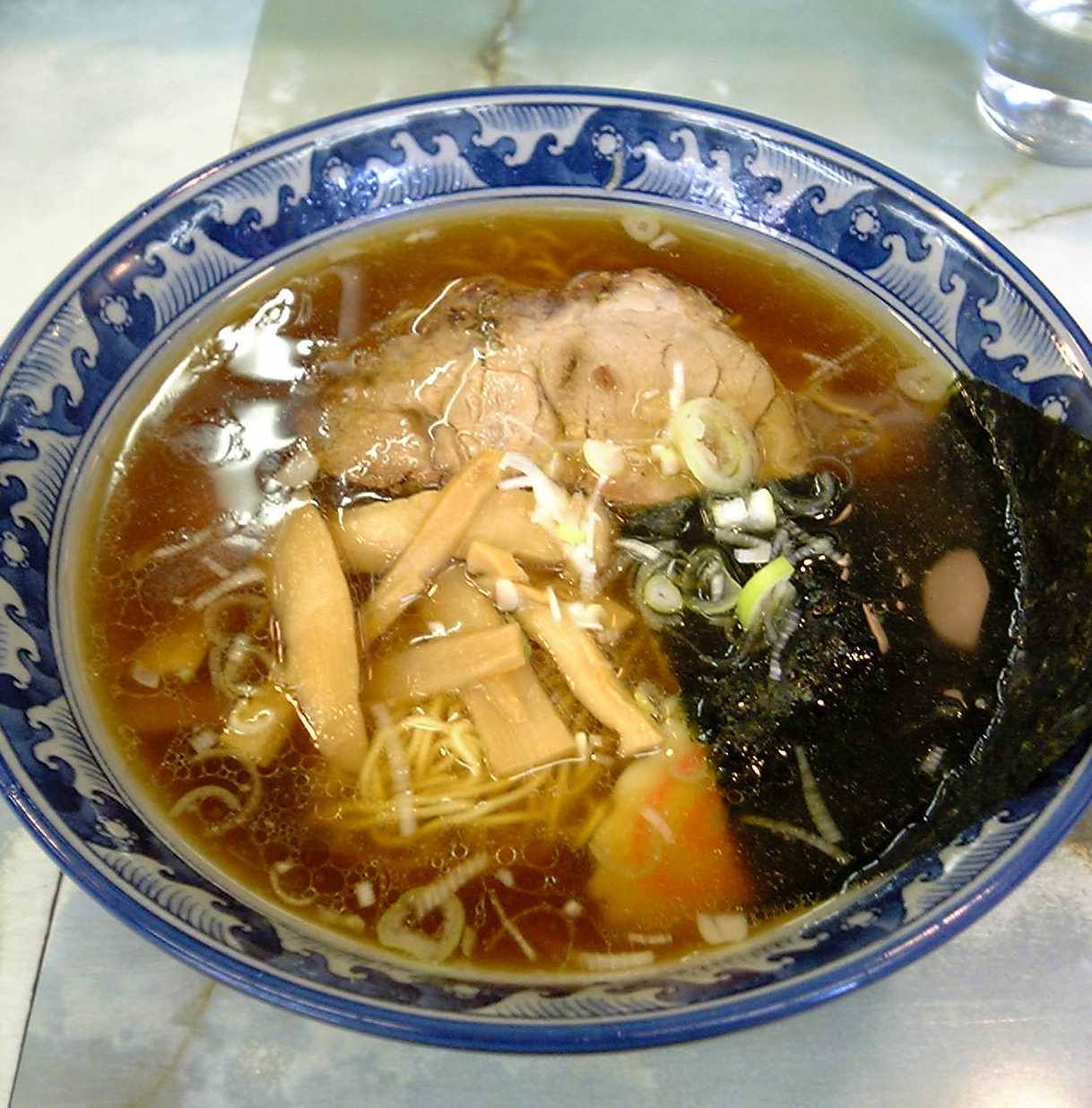
Rāmen
is a Japanese noodle dish. It consists of served in a broth; common flavors are soy sauce and miso, with typical toppings including , nori (dried seaweed), menma (bamboo shoots), and scallions. Ramen has its roots in Chinese noodle dishes. Nearly every region in Japan has its own variation of ramen, such as the ''tonkotsu'' (pork bone broth) ramen of Kyushu and the ''miso'' ramen of Hokkaido. History Etymology The word ''ramen'' is a Japanese borrowing of the Mandarin Chinese '' lāmiàn'' (, "pulled noodles"). However, historian Barak Kushner argues that this borrowing occurred retroactively and that various independent Japanese corruptions of Chinese words had already led to Japanese people calling this Chinese noodle dish "ramen". One theory suggests that the Japanese mistook the Chinese particles "le" (了) or "la" (啦, a contraction of 了啊) for a "ra" sound when Chinese cooks would announce "hăo le" (好了) to communicate that a dish was complete. The Japanese th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shōyu
Soy sauce (also called simply soy in American English and soya sauce in British English) is a liquid condiment of Chinese origin, traditionally made from a fermented paste of soybeans, roasted grain, brine, and '' Aspergillus oryzae'' or ''Aspergillus sojae'' molds. It is considered to contain a strong umami taste. Soy sauce in its current form was created about 2,200 years ago during the Western Han dynasty of ancient China, and it has spread throughout East and Southeast Asia where it is used in cooking and as a condiment. Use and storage Soy sauce can be added directly to food, and is used as a dip or salt flavor in cooking. It is often eaten with rice, noodles, and sushi or sashimi, or can also be mixed with ground wasabi for dipping. Bottles of soy sauce for salty seasoning of various foods are common on restaurant tables in many countries. Soy sauce can be stored at room temperature. History East Asia China Soy sauce (, ) is considered almost as old as soy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menma
is a Japanese condiment made from lacto-fermented bamboo shoots. The bamboo shoots are dried in the sun or through other means before the process of fermentation. Menma is a common topping for noodle soups, notably ramen. Menma is primarily produced in China, with brands imported from southern China and Taiwan being popular. Menma is also known as , "Chinese bamboo". Etymology The trading company that would later become Marumatsu Bussan had been exporting dried bamboo shoots produced in Taiwan as ''shinachiku''. In 1946, responding to a formal objection to the use of the term Shina from the Taiwanese government, the Japanese Foreign Ministry issued a memorandum recommending that the term be avoided.See :wikisource:支那の呼稱を避けることに關する件 Marumatsu Bussan founder Shūsui Matsumura claims that he came up with the new product name menma, a portmanteau of ''ramen'' (拉麺) and ''machiku'' (麻竹), the type of bamboo from which it is made, after seeing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong Kong and north of Macau, Guangzhou has a history of over 2,200 years and was a major terminus of the maritime Silk Road; it continues to serve as a major port and transportation hub as well as being one of China's three largest cities. For a long time, the only Chinese port accessible to most foreign traders, Guangzhou was captured by the British during the First Opium War. No longer enjoying a monopoly after the war, it lost trade to other ports such as Hong Kong and Shanghai, but continued to serve as a major transshipment port. Due to a high urban population and large volumes of port traffic, Guangzhou is classified as a Large-Port Megacity, the largest type of port-city in the world. Due to worldwide travel restrictions at the beginni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sohu
Sohu, Inc. () is a Chinese Internet company headquartered in the Sohu Internet Plaza in Haidian District, Beijing. Sohu and its subsidiaries offer advertising, a search engine (Sogou.com), on-line multiplayer gaming (ChangYou.com) and other services. History Sohu was founded as Internet Technologies China (ITC) in 1996 by Charles Zhang after he completed his PhD from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and received venture capital funding from colleagues he met there. The following year, Zhang changed the name of ITC to Sohoo in homage to Yahoo! after meeting its cofounder, Jerry Yang; the name was soon after changed to Sohu to differentiate it from the American company. Sohu has been listed on NASDAQ since 2000 through a variable interest entity (VIE) based in Delaware. Sohu's Sogou.com search engine was in talks to be sold in July 2013 to Qihoo for around $1.4 billion. On September 17, 2013, it was announced that Tencent has invested $448 million for a minority shar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
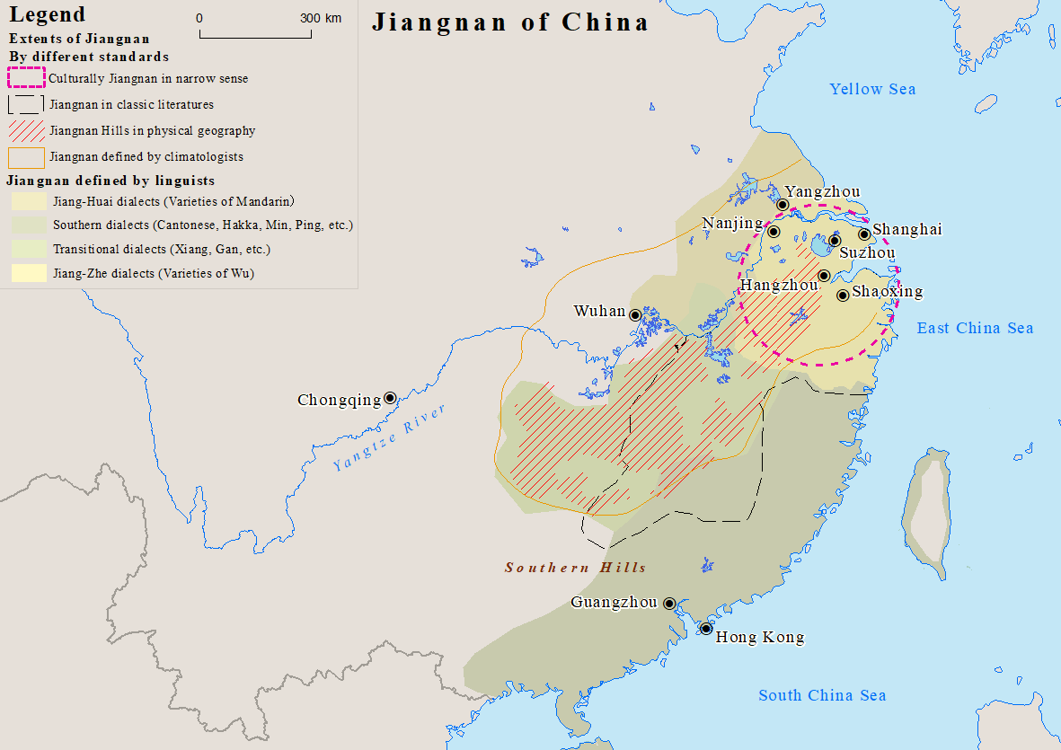
Jiangnan
Jiangnan or Jiang Nan (; formerly romanized Kiang-nan, literally "South of the River" meaning "South of the Yangtze") is a geographic area in China referring to lands immediately to the south of the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, including the southern part of its delta. The region encompasses the city of Shanghai, the southern part of Jiangsu Province, the southeastern part of Anhui Province, the northern part of Jiangxi Province and the northern part of Zhejiang Province. The most important cities in the area include Anqing, Changzhou, Hangzhou, Nanjing, Ningbo, Shaoxing, Suzhou, Wuxi, Wenzhou, and Zhenjiang. Jiangnan has long been regarded as one of the most prosperous regions in China due to its wealth in trade and very high human development. Most people of the region speak Wu Chinese dialects as their native languages. Etymology The word Jiangnan is based on the Chinese name for the Yangtze, ''Cháng Jiāng'', and ''nán'' meaning "south." In the 19th century, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) across a total area of about , Guangdong is the most populous province of China and the 15th-largest by area as well as the second-most populous country subdivision in the world (after Uttar Pradesh in India). Its economy is larger than that of any other province in the nation and the fifth largest sub-national economy in the world with a GDP (nominal) of 1.95 trillion USD (12.4 trillion CNY) in 2021. The Pearl River Delta Economic Zone, a Chinese megalopolis, is a core for high technology, manufacturing and foreign trade. Located in this zone are two of the four top Chinese cities and the top two Chinese prefecture-level cities by GDP; Guangzhou, the capital of the province, and Shenzhen, the first special economic zone in the count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Char Siu
''Char siu'' () is a Chinese, specifically Cantonese–style of barbecued pork. Originating in Guangdong, it is eaten with rice, used as an ingredient for noodle dishes or in stir fries, and as a filling for '' chasiu baau'' or '' pineapple buns.'' Five-spice powder is the primary spice, honey or other sweeteners are used as a glaze, and the characteristic red color comes from the red yeast rice when made traditionally. It is classified as a type of ''siu mei'' (), Cantonese roasted meat. Meat cuts Pork cuts used for ''char siu'' can vary, but a few main cuts are common: * Pork loin * Pork belly – produces juicy and fatter ''char siu'' * Pork butt (shoulder) – produces leaner ''char siu'' * Pork fat * Pork neck end – very marbled (''jyu geng yuk'') Cantonese cuisine ''Char siu'' literally means "fork roasted" (''siu'' being burn/roast and ''cha'' being fork, both noun and verb) after the traditional cooking method for the dish: long strips of seasoned boneless por ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barak Kushner
Barak Kushner (born 7 April 1968) is Professor of East Asian History at the University of Cambridge and Fellow at Corpus Christi College, Cambridge. He has written and edited numerous books and articles and has spoken on a range of East Asian history topics including Japanese imperial propaganda, the Japanese empire in East Asia, Japanese war crimes, and justice in East Asia. He has also written on other subjects, ranging from Godzilla and Japanese humor to ramen and the Chinese influence on early twentieth century notions of modern cuisine in Japan. Kushner is married to Mami Mizutori BrandeisMAGAZINE Assistant Secretary-General and |
Lamian
Lamian (simplified Chinese: 拉面; traditional Chinese: 拉麵; pinyin: ''Lāmiàn'') is a type of soft wheat flour Chinese noodle that is particularly common in northern China. Lamian is made by twisting, stretching and folding the dough into strands, using the weight of the dough. The length and thickness of the strands depends on the number of times the dough is folded. This unique method of making noodles originated in China. The ''Songshi Yangsheng Bu'' (), which was written by Song Xu and dates back to 1504, has the earliest description of the method to make lamian. Description The hand-making process involves taking a lump of dough and repeatedly stretching it to produce many strands of thin, long noodle. Literally, ''lā'', (拉) means to pull or stretch, while ''miàn'' (simplified Chinese: 面; traditional Chinese: 麵) means noodle. There are several styles of twisting the dough but they all employ the same concept: a piece of soft wheat dough is repeatedly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Chinese
Standard Chinese ()—in linguistics Standard Northern Mandarin or Standard Beijing Mandarin, in common speech simply Mandarin, better qualified as Standard Mandarin, Modern Standard Mandarin or Standard Mandarin Chinese—is a modern Standard language, standardized form of Mandarin Chinese that was first developed during the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republican Era (1912‒1949). It is designated as the official language of Languages of China, mainland China and a major language in the United Nations languages, United Nations, Languages of Singapore, Singapore, and Languages of Taiwan, Taiwan. It is largely based on the Beijing dialect. Standard Chinese is a pluricentric language with local standards in mainland China, Taiwan and Singapore that mainly differ in their lexicon. Hong Kong written Chinese, used for formal written communication in Hong Kong and Macau, is a form of Standard Chinese that is read aloud with the Cantonese reading of characters. Like other Sinit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hokkaido
is Japan's second largest island and comprises the largest and northernmost prefecture, making up its own region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu; the two islands are connected by the undersea railway Seikan Tunnel. The largest city on Hokkaidō is its capital, Sapporo, which is also its only ordinance-designated city. Sakhalin lies about 43 kilometers (26 mi) to the north of Hokkaidō, and to the east and northeast are the Kuril Islands, which are administered by Russia, though the four most southerly are claimed by Japan. Hokkaidō was formerly known as ''Ezo'', ''Yezo'', ''Yeso'', or ''Yesso''. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "Hokkaidō" in Although there were Japanese settlers who ruled the southern tip of the island since the 16th century, Hokkaido was considered foreign territory that was inhabited by the indigenous people of the island, known as the Ainu people. While geographers such as Mogami Tokunai and Mamiya Rinzō explored the isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)