|
Rhodamine B
Rhodamine B is a chemical compound and a dye. It is often used as a tracer dye within water to determine the rate and direction of flow and transport. Rhodamine dyes fluoresce and can thus be detected easily and inexpensively with fluorometers. Rhodamine B is used in biology as a staining fluorescent dye, sometimes in combination with auramine O, as the auramine-rhodamine stain to demonstrate acid-fast organisms, notably ''Mycobacterium''. Rhodamine dyes are also used extensively in biotechnology applications such as fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry, fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and ELISA. It is also used in rose milk, a popular Indian beverage. Other uses Rhodamine B is often mixed with herbicides to show where they have been used. It is also being tested for use as a biomarker in oral rabies vaccines for wildlife, such as raccoons, to identify animals that have eaten a vaccine bait. The rhodamine is incorporated into the animal's whiskers and teeth. Rhodam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracer Dye
Dye tracing is a method of tracking and tracing various flows using dye as a flow tracer when added to a liquid. Dye tracing may be used to analyse the flow of the liquid or the transport of objects within the liquid. Dye tracking may be either qualitative, showing the presence of a particular flow, or quantitative, when the amount of the traced dye is measured by special instruments. Fluorescent dyes Fluorescent dyes are often used in situations where there is insufficient lighting (e.g., sewers or cave waters), and where precise quantitative data are required (measured by a fluorometer). In 1871, Fluorescein was among the first fluorescent dyes to be developed. Its disodium salt (under the trademark " Uranine") was developed several years later and still remains among the best tracer dyes.An educational website about karst and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raccoon
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the common raccoon to distinguish it from other species, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest of the procyonid family, having a body length of , and a body weight of . Its grayish coat mostly consists of dense underfur, which insulates it against cold weather. Three of the raccoon's most distinctive features are its extremely dexterous front paws, its facial mask, and its ringed tail, which are themes in the mythologies of the indigenous peoples of the Americas relating to the animal. The raccoon is noted for its intelligence, as studies show that it is able to remember the solution to tasks for at least three years. It is usually nocturnal and omnivorous, eating about 40% invertebrates, 33% plants, and 27% vertebrates. The original habitats of the raccoon are deciduous and mixed forests, but due to their adaptability, they have extended their range to mountainous areas, coastal marshes, and urban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economically Motivated Adulteration
Food defense is the protection of food products from ''intentional'' contamination or adulteration by biological, chemical, physical, or radiological agents introduced for the purpose of causing harm. It addresses additional concerns including physical, personnel and operational security. Food defense is one of the four categories of the food protection risk matrix which include: food safety, which is based on unintentional or environmental contamination that can cause harm; Food fraud, which is based on intentional deception for economic gain; and Food quality, which may also be affected by profit-driven behavior but without intention to cause harm. Overarching these four categories is food security, which deals with individuals having access to enough food for an active, healthy life. Food protection is the umbrella term encompassing both food defense and food safety. These six terms are often conflated. Along with protecting the food system, food defense also deals with pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
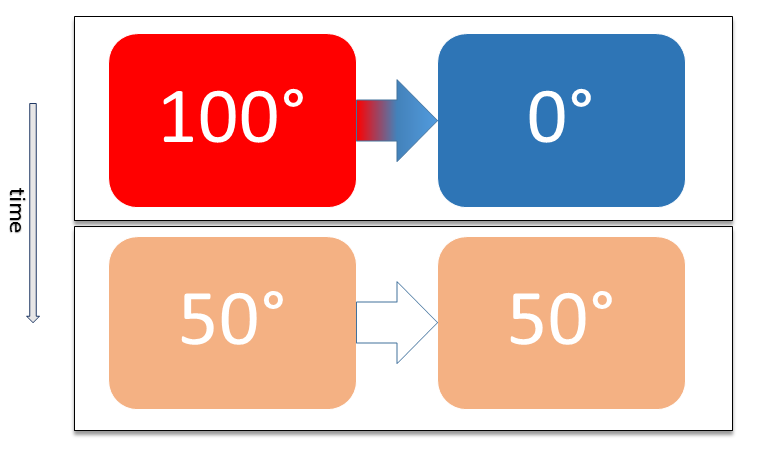
Thermal Equilibrium
Two physical systems are in thermal equilibrium if there is no net flow of thermal energy between them when they are connected by a path permeable to heat. Thermal equilibrium obeys the zeroth law of thermodynamics. A system is said to be in thermal equilibrium with itself if the temperature within the system is spatially uniform and temporally constant. Systems in thermodynamic equilibrium are always in thermal equilibrium, but the converse is not always true. If the connection between the systems allows transfer of energy as 'change in internal energy' but does not allow transfer of matter or transfer of energy as work, the two systems may reach thermal equilibrium without reaching thermodynamic equilibrium. Two varieties of thermal equilibrium Relation of thermal equilibrium between two thermally connected bodies The relation of thermal equilibrium is an instance of equilibrium between two bodies, which means that it refers to transfer through a selectively permeable p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluxional Molecule
In chemistry and molecular physics, fluxional (or non-rigid) molecules are molecules that undergo dynamics such that some or all of their atoms interchange between symmetry-equivalent positions. Because virtually all molecules are fluxional in some respects, e.g. bond rotations in most organic compounds, the term fluxional depends on the context and the method used to assess the dynamics. Often, a molecule is considered fluxional if its spectroscopic signature exhibits line-broadening (beyond that dictated by the Heisenberg uncertainty principle) due to chemical exchange. In some cases, where the rates are slow, fluxionality is not detected spectroscopically, but by isotopic labeling and other methods. Spectroscopic studies Many organometallic compounds exhibit fluxionality. Fluxionality is however pervasive. NMR spectroscopy Temperature dependent changes in the NMR spectra result from dynamics associated with the fluxional molecules when those dynamics proceed at rates comparabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Luminescence
The ''Journal of Luminescence'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Elsevier. The editor-in-chief is Xueyuan Chen. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 4.171, ranking it 26th out of 101 journals in the category "Optics". The journal covers all aspects related to the emission of light (luminescence). Editors The editors-in-chief are: *S. Tanabe (Kyoto University *D. Poelman (Universiteit Gent, Ghent, Belgium. *K.-L. Wong (Hong Kong Baptist University *M.F. Reid (Dodd-Walls Centre for Photonic and Quantum Technologies The Dodd-Walls Centre for Photonic and Quantum Technologies () is a New Zealand Centre of Research Excellence, established in 2015, hosted by the University of Otago, and composed of researchers in six New Zealand universities as well as partn ...) References External links * Elsevier academic journals Optics journals Publications established in 1968 Monthly journals English-language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Yield
The quantum yield (Φ) of a radiation-induced process is the number of times a specific event occurs per photon absorbed by the system. Applications Fluorescence spectroscopy The fluorescence quantum yield is defined as the ratio of the number of photons emitted to the number of photons absorbed.Lakowicz, Joseph R. ''Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy'' (Kluwer Academic / Plenum Publishers 1999) p.10. Fluorescence quantum yield is measured on a scale from 0 to 1.0, but is often represented as a percentage. A quantum yield of 1.0 (100%) describes a process where each photon absorbed results in a photon emitted. Substances with the largest quantum yields, such as rhodamines, display the brightest emissions; however, compounds with quantum yields of 0.10 are still considered quite fluorescent. Quantum yield is defined by the fraction of excited state fluorophores that decay through fluorescence: where \Phi_ is the fluorescence quantum yield, k_ is the rate constant f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dye Laser
A dye laser is a laser that uses an organic dye as the lasing medium, usually as a liquid solution. Compared to gases and most solid state lasing media, a dye can usually be used for a much wider range of wavelengths, often spanning 50 to 100 nanometers or more. The wide bandwidth makes them particularly suitable for tunable lasers and pulsed lasers. The dye rhodamine 6G, for example, can be tuned from 635 nm (orangish-red) to 560 nm (greenish-yellow), and produce pulses as short as 16 femtoseconds. Moreover, the dye can be replaced by another type in order to generate an even broader range of wavelengths with the same laser, from the near-infrared to the near-ultraviolet, although this usually requires replacing other optical components in the laser as well, such as dielectric mirrors or pump lasers. Dye lasers were independently discovered by P. P. Sorokin and F. P. Schäfer (and colleagues) in 1966. In addition to the usual liquid state, dye lasers are also availa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group). Ethanol is a Volatility (chemistry), volatile, Combustibility and flammability, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. It is a psychoactive recreational drug, the active ingredient in alcoholic drinks. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of Carbohydrate, sugars by yeasts or via Petrochemistry, petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. It has medical applications as an antiseptic and disinfectant. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the Chemical synthesis, synthesis of organic compounds, and as a Alcohol fuel, fuel source. Ethanol also can be dehydrated to make ethylene, an important chemical feedstock. As of 2006, world produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthese Von Rhodamin B
''Synthese'' () is a scholarly periodical specializing in papers in epistemology, methodology, and philosophy of science, and related issues. Its subject area is divided into four specialties, with a focus on the first three: (1) "epistemology, methodology, and philosophy of science, all broadly understood"; (2) "foundations of logic and mathematics, where 'logic', 'mathematics', and 'foundations' are all broadly understood"; (3) "formal methods in philosophy, including methods connecting philosophy to other academic fields"; and (4) "issues in ethics and the history and sociology of logic, mathematics, and science that contribute to the contemporary studies". As of 2022, according to Google Scholar's metrics ( h-5 index and h-5 index median), it is the top philosophy journal, but other metrics do not rank the journal as highly. Overview Published articles include specific treatment of methodological issues in science such as induction, probability, causation, statistics, symboli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shades Of Magenta
The color magenta has notable tints and shades. These various colors are shown below. Definition of magenta Magenta is a color made up of equal parts of red and blue light. This would be the precise definition of the color as defined for computer display (the color #FF00FF shown in the color swatch above). It is a pure chroma on the RGB color wheel ( Image of RGB color wheel:) midway between purple and rose. In HSV color space, ''magenta'' has a hue of 300°. In a color proximity sense, a primary color has a color range of 120° (60° on each side of the color's hue) and any color has to be within that range to be considered a variation of that color. Secondary colors have a color range of 60° (30°), tertiary colors have a color range of 30° (15°), quaternary colors have a color range of 15° (7.5°), quinary colors have a color range of 7.5° (3.75°), and so on. Because magenta is located at a hue angle of 300°, it has a tertiary color range of 285° and 315°, and any ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
_2.jpg)