|
Pressure–volume Loop Analysis In Cardiology
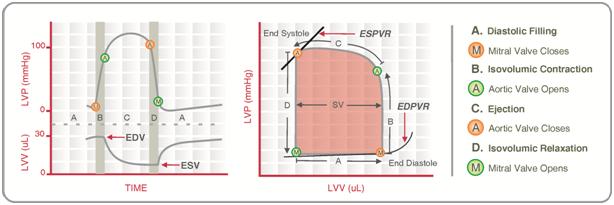
A plot of a system's Pressure-volume curves, pressure versus volume has long been used to measure the work done by the system and its efficiency. This analysis can be applied to heat engines and pumps, including the heart. A considerable amount of information on cardiac performance can be determined from the ''pressure vs. volume'' plot (pressure–volume diagram). A number of pressure–volume loop experiments, methods have been determined for measuring PV-loop values experimentally. Cardiac pressure–volume loops Real-time Ventricle (heart), left ventricular (LV) pressure–volume loops provide a framework for understanding cardiac mechanics in experimental animals and humans. Such loops can be generated by real-time measurement of pressure and volume within the left ventricle. Several physiologically relevant Hemodynamics, hemodynamic parameters such as stroke volume, cardiac output, ejection fraction, myocardial contractility, etc. can be determined from these loops. To gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure-volume Curves
In ecology, pressure-volume curves describe the relationship between total water potential (Ψt) and relative water content (R) of living organisms. These values are widely used in research on plant-water relations, and provide valuable information on the turgor, osmosis, osmotic and Elastic deformation, elastic properties of plant tissues. According to the Boyle–v'ant Hoff Relation, the product of osmotic potential and volume of solution should be a constant for any given amount of osmotically active solutes in an ideal osmotic system. \psi_0\mathit(V)\! = A constant \psi_0\! is osmotic potential and \mathit(V)\! is volume of solution. This can then be manipulated to a linear relation which describes the ideal situation: \psi_0\! = \dfrac{1}V\! \times A constant (mathematics), constant Membrane biology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aortic Stenosis
Aortic stenosis (AS or AoS) is the narrowing of the exit of the left ventricle of the heart (where the aorta begins), such that problems result. It may occur at the aortic valve as well as above and below this level. It typically gets worse over time. Symptoms often come on gradually with a decreased ability to exercise often occurring first. If heart failure, loss of consciousness, or heart related chest pain occur due to AS the outcomes are worse. Loss of consciousness typically occurs with standing or exercising. Signs of heart failure include shortness of breath especially when lying down, at night, or with exercise, and swelling of the legs. Thickening of the valve without narrowing is known as aortic sclerosis. Causes include being born with a bicuspid aortic valve, and rheumatic fever; a normal valve may also harden over the decades. A bicuspid aortic valve affects about one to two percent of the population. As of 2014 rheumatic heart disease mostly occurs in the dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high blood pressure, however, is a major risk factor for stroke, coronary artery disease, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, peripheral arterial disease, vision loss, chronic kidney disease, and dementia. Hypertension is a major cause of premature death worldwide. High blood pressure is classified as primary (essential) hypertension or secondary hypertension. About 90–95% of cases are primary, defined as high blood pressure due to nonspecific lifestyle and genetic factors. Lifestyle factors that increase the risk include excess salt in the diet, excess body weight, smoking, and alcohol use. The remaining 5–10% of cases are categorized as secondary high blood pressure, defined as high blood pressure due to an identifiable cause, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Output
In cardiac physiology, cardiac output (CO), also known as heart output and often denoted by the symbols Q, \dot Q, or \dot Q_ , edited by Catherine E. Williamson, Phillip Bennett is the volumetric flow rate of the heart's pumping output: that is, the volume of blood being pumped by both ventricles of the heart, per unit time (usually measured per minute). Cardiac output (CO) is the product of the heart rate (HR), i.e. the number of heartbeats per minute (bpm), and the stroke volume (SV), which is the volume of blood pumped from the left ventricle per beat; thus giving the formula: :CO = HR \times SV Values for cardiac output are usually denoted as L/min. For a healthy individual weighing 70 kg, the cardiac output at rest averages about 5 L/min; assuming a heart rate of 70 beats/min, the stroke volume would be approximately 70 mL. Because cardiac output is related to the quantity of blood delivered to various parts of the body, it is an important component of how effi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
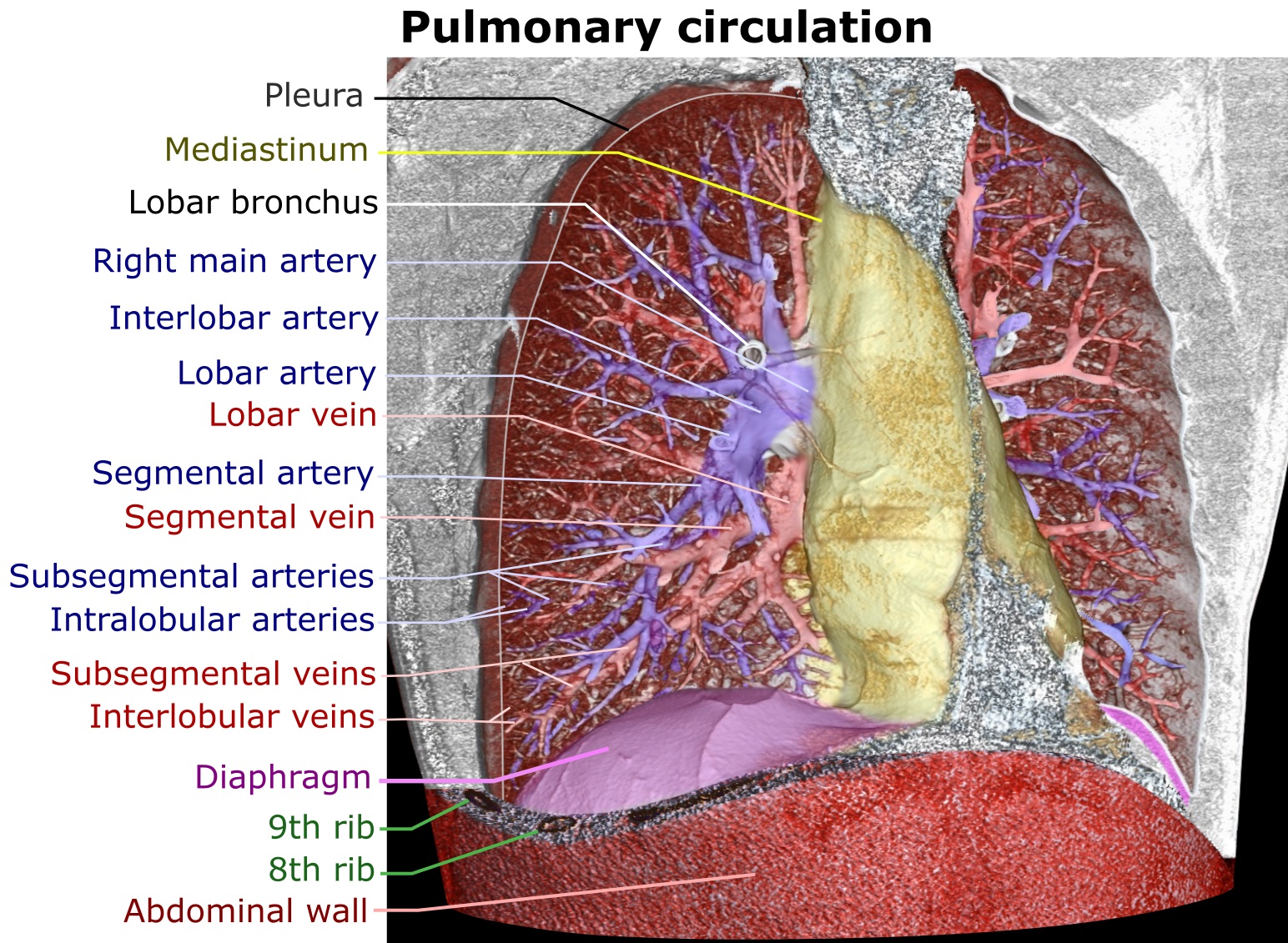
Pulmonary Artery
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and the smallest ones are the arterioles, which lead to the capillaries that surround the pulmonary alveoli. Structure The pulmonary arteries are blood vessels that carry systemic venous blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the microcirculation of the lungs. Unlike in other organs where arteries supply oxygenated blood, the blood carried by the pulmonary arteries is deoxygenated, as it is venous blood returning to the heart. The main pulmonary arteries emerge from the right side of the heart, and then split into smaller arteries that progressively divide and become arterioles, eventually narrowing into the capillary microcirculation of the lungs where gas exchange occurs. Pulmonary trunk In order of blood flow, the pulmonary art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through the systemic circulation. Structure Sections In anatomical sources, the aorta is usually divided into sections. One way of classifying a part of the aorta is by anatomical compartment, where the thoracic aorta (or thoracic portion of the aorta) runs from the heart to the diaphragm. The aorta then continues downward as the abdominal aorta (or abdominal portion of the aorta) from the diaphragm to the aortic bifurcation. Another system divides the aorta with respect to its course and the direction of blood flow. In this system, the aorta starts as the ascending aorta, travels superiorly from the heart, and then makes a hairpin turn known as the aortic arch. Following the aortic arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ejection Fraction
An ejection fraction (EF) is the volumetric fraction (or portion of the total) of fluid (usually blood) ejected from a chamber (usually the heart) with each contraction (or heartbeat). It can refer to the cardiac atrium, ventricle, gall bladder, or leg veins, although if unspecified it usually refers to the left ventricle of the heart. EF is widely used as a measure of the pumping efficiency of the heart and is used to classify heart failure types. It is also used as an indicator of the severity of heart failure, although it has recognized limitations. The EF of the left heart, known as the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), is calculated by dividing the volume of blood pumped from the left ventricle per beat (stroke volume) by the volume of blood collected in the left ventricle at the end of diastolic filling (end-diastolic volume). LVEF is an indicator of the effectiveness of pumping into the systemic circulation. The EF of the right heart, or right ventricular ejection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
End-systolic Volume
End-systolic volume (ESV) is the volume of blood in a ventricle at the end of contraction, or systole, and the beginning of filling, or diastole. ESV is the lowest volume of blood in the ventricle at any point in the cardiac cycle. The main factors that affect the end-systolic volume are afterload and the contractility of the heart. __TOC__ Uses End systolic volume can be used clinically as a measurement of the adequacy of cardiac emptying, related to systolic function. On an electrocardiogram, or ECG, the end-systolic volume will be seen at the end of the T wave. Clinically, ESV can be measured using two-dimensional echocardiography, MRI ( magnetic resonance tomography) or cardiac CT ( computed tomography) or SPECT (single photon emission computed tomography). Sample values Along with end-diastolic volume, ESV determines the stroke volume, or output of blood by the heart during a single phase of the cardiac cycle. The stroke volume is the difference between the end-diastolic vol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroke Volume
In cardiovascular physiology, stroke volume (SV) is the volume of blood pumped from the left ventricle per beat. Stroke volume is calculated using measurements of ventricle volumes from an echocardiogram and subtracting the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of a beat (called end-systolic volume) from the volume of blood just prior to the beat (called end-diastolic volume). The term ''stroke volume'' can apply to each of the two ventricles of the heart, although it usually refers to the left ventricle. The stroke volumes for each ventricle are generally equal, both being approximately 70 mL in a healthy 70-kg man. Stroke volume is an important determinant of cardiac output, which is the product of stroke volume and heart rate, and is also used to calculate ejection fraction, which is stroke volume divided by end-diastolic volume. Because stroke volume decreases in certain conditions and disease states, stroke volume itself correlates with cardiac function. Calculati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
End-diastolic Volume
In cardiovascular physiology, end-diastolic volume (EDV) is the volume of blood in the right or left ventricle at end of filling in diastole which is ammount of blood present in ventricle at the end of diastole systole. Because greater EDVs cause greater distention of the ventricle, ''EDV'' is often used synonymously with ''preload'', which refers to the length of the sarcomeres in cardiac muscle prior to contraction (systole). An increase in EDV increases the preload on the heart and, through the Frank-Starling mechanism of the heart, increases the amount of blood ejected from the ventricle during systole (stroke volume). __TOC__ Sample values The right ventricular end-diastolic volume (RVEDV) ranges between 100 and 160 mL. The right ventricular end-diastolic volume index (RVEDVI) is calculated by RVEDV/ BSA and ranges between 60 and 100 mL/m2. See also * End-systolic volume * Stroke volume In cardiovascular physiology, stroke volume (SV) is the volume of blood pumped from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcomere
A sarcomere (Greek σάρξ ''sarx'' "flesh", μέρος ''meros'' "part") is the smallest functional unit of striated muscle tissue. It is the repeating unit between two Z-lines. Skeletal muscles are composed of tubular muscle cells (called muscle fibers or myofibers) which are formed during embryonic myogenesis. Muscle fibers contain numerous tubular myofibrils. Myofibrils are composed of repeating sections of sarcomeres, which appear under the microscope as alternating dark and light bands. Sarcomeres are composed of long, fibrous proteins as filaments that slide past each other when a muscle contracts or relaxes. The costamere is a different component that connects the sarcomere to the sarcolemma. Two of the important proteins are myosin, which forms the thick filament, and actin, which forms the thin filament. Myosin has a long, fibrous tail and a globular head, which binds to actin. The myosin head also binds to ATP, which is the source of energy for muscle movement. Myos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Myocyte
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle, myocardium, cardiomyocytes and cardiac myocytes) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall of the heart. The cardiac muscle (myocardium) forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the heart wall (the pericardium) and the inner layer (the endocardium), with blood supplied via the coronary circulation. It is composed of individual cardiac muscle cells joined by intercalated discs, and encased by collagen fibers and other substances that form the extracellular matrix. Cardiac muscle contracts in a similar manner to skeletal muscle, although with some important differences. Electrical stimulation in the form of a cardiac action potential triggers the release of calcium from the cell's internal calcium store, the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The rise in calcium causes the cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |