|
Process–architecture–optimization Model
Process–architecture–optimization is a development model for central processing units (CPUs) that Intel adopted in 2016. Under this three-phase (three-year) model, every microprocessor die shrink is followed by a microarchitecture In computer engineering, microarchitecture, also called computer organization and sometimes abbreviated as µarch or uarch, is the way a given instruction set architecture (ISA) is implemented in a particular processor. A given ISA may be impl ... change and then by one or more optimizations. It replaced the two-phase (two-year) tick–tock model that Intel adopted in 2006. The tick–tock model was no longer economically sustainable, according to Intel, because production of ever smaller dies becomes ever more costly. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Processing Unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, and input/output (I/O) operations specified by the instructions in the program. This contrasts with external components such as main memory and I/O circuitry, and specialized processors such as graphics processing units (GPUs). The form, design, and implementation of CPUs have changed over time, but their fundamental operation remains almost unchanged. Principal components of a CPU include the arithmetic–logic unit (ALU) that performs arithmetic and logic operations, processor registers that supply operands to the ALU and store the results of ALU operations, and a control unit that orchestrates the fetching (from memory), decoding and execution (of instructions) by directing the coordinated operations of the ALU, registers and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7 Nm Process
In semiconductor manufacturing, the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors defines the 7 nm process as the MOSFET technology node following the 10 nm node. It is based on FinFET (fin field-effect transistor) technology, a type of multi-gate MOSFET technology. Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) began production of 256 Mbit SRAM memory chips using a 7 nm process called N7 in June 2016, before Samsung began mass production of their 7 nm process called 7LPP devices in 2018. The first mainstream 7 nm mobile processor intended for mass market use, the Apple A12 Bionic, was released at Apple's September 2018 event. Although Huawei announced its own 7 nm processor before the Apple A12 Bionic, the Kirin 980 on August 31, 2018, the Apple A12 Bionic was released for public, mass market use to consumers before the Kirin 980. Both chips are manufactured by TSMC. AMD has released their "Rome" (EPYC 2) processors for servers an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
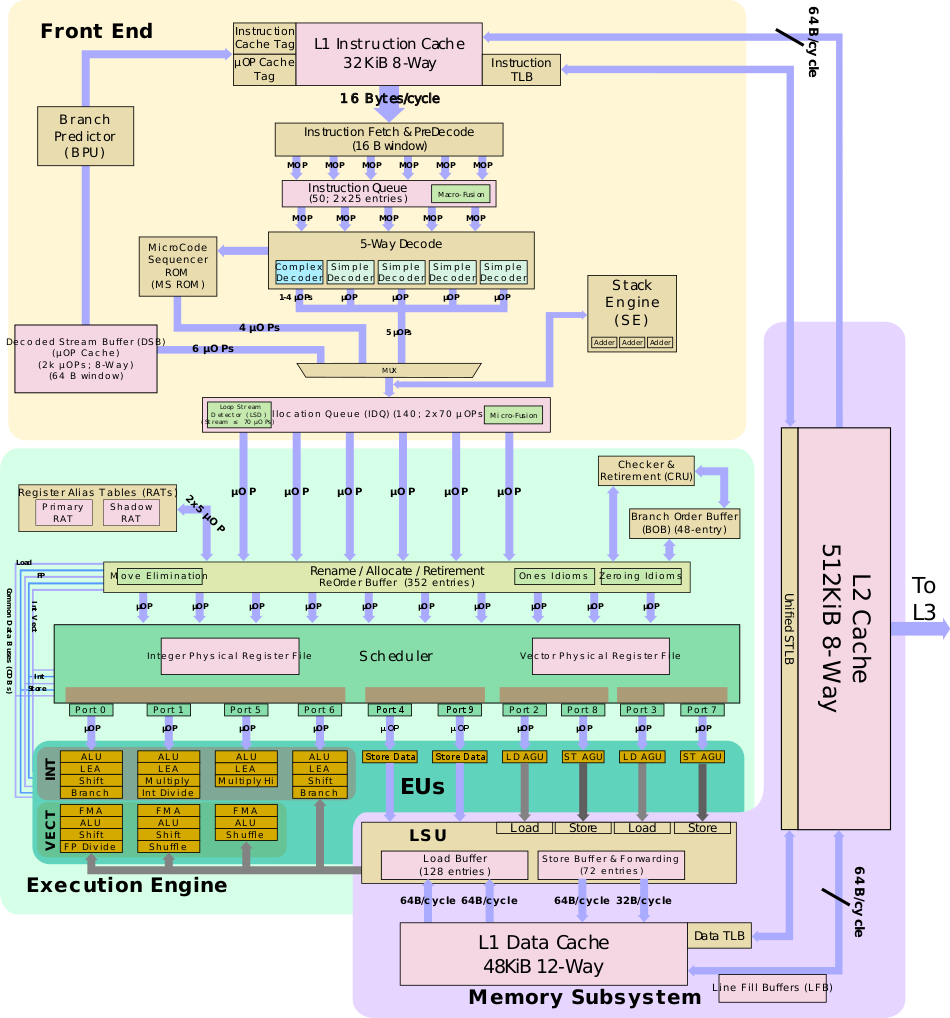
List Of Intel CPU Microarchitectures
The following is a ''partial'' list of Intel CPU microarchitectures. The list is ''incomplete''. Additional details can be found in Intel's Tick–tock model and Process–architecture–optimization model. x86 microarchitectures 16-bit ; 8086: first x86 processor; initially a temporary substitute for the iAPX 432 to compete with Motorola, Zilog, and National Semiconductor and to top the successful Z80. 8088 version, with an 8-bit bus, used in the original IBM Personal Computer. ; 186: included a DMA controller, interrupt controller, timers, and chip select logic. A small number of additional instructions. The 80188 was a version with an 8-bit bus. ; 286: first x86 processor with protected mode including segmentation based virtual memory management. Performance improved by a factor of 3 to 4 over 8086. Included instructions relating to protected mode. 32-bit (IA-32) ; i386: first 32-bit x86 processor. Introduced paging on top of segmentation which is the most commonl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel 20A
In semiconductor manufacturing, the 2 nm process is the next MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor) die shrink after the 3 nm process node. , TSMC is expected to begin production sometime after 2023; Intel also forecasts production by 2024. The term "2 nanometer" or alternatively "20 angstrom" (a term used by Intel) has no relation to any actual physical feature (such as gate length, metal pitch or gate pitch) of the transistors. It is a commercial or marketing term used by the semiconductor chip fabrication industry to refer to a new, improved generation of silicon semiconductor chips in terms of increased transistor density (i.e. a higher degree of miniaturization), increased speed and reduced power consumption. Background In late 2018, TSMC chairman Mark Liu predicted chip scaling would continue to 3 nm and 2 nm nodes; however, as of 2019, other semiconductor specialists were undecided as to whether nodes beyond 3 nm could become viabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5 Nm Process
In semiconductor manufacturing, the International Roadmap for Devices and Systems defines the 5 nm process as the MOSFET technology node following the 7 nm node. In 2020, Samsung and TSMC entered volume production of 5 nm chips, manufactured for companies including Apple, Marvell, Huawei and Qualcomm. The term "5 nanometer" has no relation to any actual physical feature (such as gate length, metal pitch or gate pitch) of the transistors. According to the projections contained in the 2021 update of the International Roadmap for Devices and Systems published by IEEE Standards Association Industry Connection, a 5 nm node is expected to have a contacted gate pitch of 51 nanometers and a tightest metal pitch of 30 nanometers. However, in real world commercial practice, "5 nm" is used primarily as a marketing term by individual microchip manufacturers to refer to a new, improved generation of silicon semiconductor chips in terms of increased transistor density (i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raptor Lake
Raptor Lake is Intel's codename for the 13th-generation of Intel Core processors based on a hybrid architecture, utilizing Raptor Cove performance cores and Gracemont efficient cores. Raptor Lake launched on October 20, 2022. Mobile versions are expected to be released by the end of the year. Like Alder Lake, Raptor Lake is fabricated using Intel's Intel 7 process. At Intel's Investor Meeting 2022, it was confirmed that Raptor Lake would feature up to 24 cores (8 performance cores plus 16 efficient cores) and 32 threads and is socket compatible with Alder Lake systems ( LGA 1700). The company spokesman revealed that Raptor Lake was conjured in the last-minute, to benefit from all the process improvements before Meteor Lake arrives since the next microarchitecture was not ready on time. Raptor Lake competes with the AMD Ryzen 7000 series that was launched about one month earlier on September 27, 2022. Features CPU * Cores ** Raptor Cove performance cores (P-core) ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Cove
Golden Cove is a codename for a CPU microarchitecture developed by Intel and released in November 2021. It succeeds four microarchitectures: Sunny Cove, Skylake, Willow Cove, and Cypress Cove. It is fabricated using Intel's Intel 7 process node, previously referred to as 10nm Enhanced SuperFin (10ESF). The microarchitecture is used in the high-performance cores (P-core) of the 12th-generation Intel Core processors (codenamed " Alder Lake") and will power fourth-generation Xeon Scalable server processors (codenamed " Sapphire Rapids"). History and features Intel first unveiled Golden Cove during their Architecture Day 2020, with further details released at the same event in August 2021. Similar to Skylake, Golden Cove was described by Intel as a major update to the core microarchitecture, with Intel stating that it would "allow performance for the next decade of compute". Intel also described Golden Cove as the largest microarchitectural upgrade to the Core family in a decade, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alder Lake
Alder Lake is Intel's codename for the 12th generation of Intel Core processors based on a hybrid architecture utilizing Golden Cove performance cores and Gracemont efficient cores. It is fabricated using Intel's Intel 7 process, previously referred to as Intel 10 nm Enhanced SuperFin (10ESF). The 10ESF has a 10%-15% boost in performance over the 10SF used in the mobile Tiger Lake processors. Intel officially announced 12th Gen Intel Core CPUs on October 27, 2021. Intel officially announced 12th Gen Intel Core mobile CPUs and non-K series desktop CPUs on January 4, 2022. Intel officially announced the launch of Alder Lake-P and -U series on February 23, 2022, and Alder Lake-HX series on May 10, 2022. History Fabricated using Intel's Intel 7 process, which was previously referred to as Intel 10 nm Enhanced SuperFin (10ESF), Intel officially announced 12th Gen Intel Core CPUs on October 27, 2021. Intel then officially announced 12th Gen Intel Core mobile CPUs and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willow Cove
Willow Cove is a codename for a CPU microarchitecture developed by Intel and released in September 2020. Willow Cove is the successor to the Sunny Cove microarchitecture, and is fabricated using Intel's enhanced 10 nm process node called 10 nm SuperFin (10SF). The microarchitecture powers 11th-generation Intel Core mobile processors (codenamed "Tiger Lake"). The Willow Cove microarchitecture was succeeded by Golden Cove. Features Intel first described Tiger Lake and Willow Cove during their Architecture Day in 2020. Willow Cove is almost identical to the previous microarchitecture but introduces new security features, a redesigned cache subsystem, and higher clock speeds. Intel claims that these changes, in addition to the new 10SF process node, give an additional 10–20% performance increase from Sunny Cove. Improvements * Larger L2 caches (1.25 MB per core from 512 KB per core) * Larger L3 caches (3 MB per core from 2 MB per core) * A new AVX-512 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiger Lake
Tiger Lake is Intel's codename for the 11th generation Intel Core mobile processors based on the new Willow Cove Core microarchitecture, manufactured using Intel's third-generation 10 nm process node known as 10SF ("10 nm SuperFin"). Tiger Lake replaces the Ice Lake family of mobile processors, representing an Optimization step in Intel's process–architecture–optimization model. Tiger Lake processors launched on September 2, 2020, are part of the Tiger Lake-U family and include dual-core and quad-core 9 W (7–15 W) TDP and 15 W (12–28 W) TDP models. They power 2020 "Project Athena" laptops. The quad-core 96 EU die measures 13.6 × 10.7 mm (146.1 mm2), which is 19.2% wider than the 11.4 × 10.7 mm (122.5 mm2) quad-core 64 EU Ice Lake die. The 8-core 32 EU die used in Tiger Lake-H is around 190 mm2. According to Yehuda Nissan and his team, the architecture is named after a lake across Puget Sound, Washington from Seattle. Laptops ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunny Cove (microarchitecture)
Sunny Cove is a codename for a CPU microarchitecture developed by Intel, first released in September 2019. It succeeds the Palm Cove microarchitecture and is fabricated using Intel's 10 nm process node. The microarchitecture is implemented in 10th-generation Intel Core processors for mobile (codenamed '' Ice Lake'') and third generation Xeon scalable server processors (codenamed ''Ice Lake-SP''). 10th-generation Intel Core mobile processors were released in September 2019, while the Xeon server processors were released in April 6, 2021. There are no desktop products featuring Sunny Cove. However, a variant named Cypress Cove is used for the 11th-generation Intel Core desktop processors (codenamed ''Rocket Lake''). Cypress Cove is a version of the Sunny Cove microarchitecture backported to Intel's 14 nm process node. The direct successor to the Sunny Cove microarchitecture is the Willow Cove microarchitecture, which powers the 11th-generation Intel Core mobile processo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Lake (microprocessor)
Ice Lake is Intel's codename for the 10th generation Intel Core mobile and 3rd generation Xeon Scalable server processors based on the Sunny Cove microarchitecture. Ice Lake represents an Architecture step in Intel's Process-Architecture-Optimization model. Produced on the second generation of Intel's 10 nm process, 10 nm+, Ice Lake is Intel's second microarchitecture to be manufactured on the 10 nm process, following the limited launch of Cannon Lake in 2018. However, Intel altered their naming scheme in 2020 for the 10 nm process. In this new naming scheme, Ice Lake's manufacturing process is called simply 10 nm, without any appended pluses. Ice Lake CPUs are sold together with the 14 nm Comet Lake CPUs as Intel's "10th Generation Core" product family. There are no Ice Lake desktop or high-power mobile processors; Comet Lake fulfills this role. Sunny Cove-based Xeon Scalable CPUs (codenamed "Ice Lake-SP") officially launched on April 6, 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |