|
Operator Grammar
Operator grammar is a mathematical theory of human language that explains how language carries information. This theory is the culmination of the life work of Zellig Harris, with major publications toward the end of the last century. Operator grammar proposes that each human language is a self-organizing system in which both the syntactic and semantic properties of a word are established purely in relation to other words. Thus, no external system ( metalanguage) is required to define the rules of a language. Instead, these rules are learned through exposure to usage and through participation, as is the case with most social behavior. The theory is consistent with the idea that language evolved gradually, with each successive generation introducing new complexity and variation. Operator grammar posits three universal constraints: dependency (certain words depend on the presence of other words to form an utterance), likelihood (some combinations of words and their dependents a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
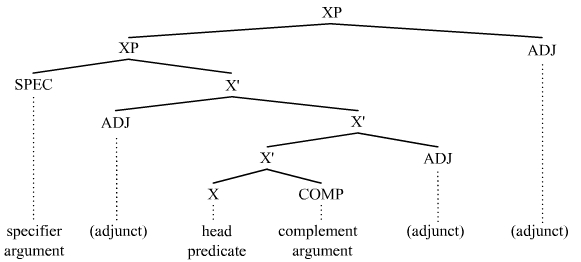
Argument (linguistics)
In linguistics, an argument is an expression that helps complete the meaning of a predicate (grammar), predicate, the latter referring in this context to a main verb and its auxiliaries. In this regard, the ''Complement (linguistics), complement'' is a closely related concept. Most predicates take one, two, or three arguments. A predicate and its arguments form a ''predicate-argument structure''. The discussion of predicates and arguments is associated most with (content) verbs and noun phrases (NPs), although other syntactic category, syntactic categories can also be construed as predicates and as arguments. Arguments must be distinguished from adjunct (grammar), adjuncts. While a predicate needs its arguments to complete its meaning, the adjuncts that appear with a predicate are optional; they are not necessary to complete the meaning of the predicate. Most theories of syntax and semantics acknowledge arguments and adjuncts, although the terminology varies, and the distinction is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphrase
A paraphrase () or rephrase is the rendering of the same text in different words without losing the meaning of the text itself. More often than not, a paraphrased text can convey its meaning better than the original words. In other words, it is a copy of the text in meaning, but which is different from the original. For example, when someone tells a story they heard, in their own words, they paraphrase, with the meaning being the same. The term itself is derived via Latin ', . The act of paraphrasing is also called ''paraphrasis''. History Although paraphrases likely abounded in oral traditions, paraphrasing as a specific educational exercise dates back to at least Roman times, when the author Quintilian recommended it for students to develop dexterity in language. In the Middle Ages, this tradition continued, with authors such as Geoffrey of Vinsauf developing schoolroom exercises that included both rhetorical manipulations and paraphrasing as a way of generating poems and spee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transposition (mathematics)
In mathematics, and in particular in group theory, a cyclic permutation is a permutation consisting of a single cycle. In some cases, cyclic permutations are referred to as cycles; if a cyclic permutation has ''k'' elements, it may be called a ''k''-cycle. Some authors widen this definition to include permutations with fixed points in addition to at most one non-trivial cycle. In Permutation#Cycle notation, cycle notation, cyclic permutations are denoted by the list of their elements enclosed with parentheses, in the order to which they are permuted. For example, the permutation (1 3 2 4) that sends 1 to 3, 3 to 2, 2 to 4 and 4 to 1 is a 4-cycle, and the permutation (1 3 2)(4) that sends 1 to 3, 3 to 2, 2 to 1 and 4 to 4 is considered a 3-cycle by some authors. On the other hand, the permutation (1 3)(2 4) that sends 1 to 3, 3 to 1, 2 to 4 and 4 to 2 is not a cyclic permutation because it separately permutes the pairs and . For the wider definition of a cyclic permutation, allowi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relative Pronoun
A relative pronoun is a pronoun that marks a relative clause. An example is the word ''which'' in the sentence "This is the house which Jack built." Here the relative pronoun ''which'' introduces the relative clause. The relative clause modifies the noun ''house.'' The relative pronoun, "which," plays the role of an object within that clause, "which Jack built." In the English language, the following are the most common relative pronouns: ''which'', '' who'', ''whose'', ''whom'', ''whoever'', ''whomever'', and ''that'', though some linguists analyze ''that'' in relative clauses as a conjunction / complementizer. Antecedents The element in the main clause that the relative pronoun in the relative clause stands for (''house'' in the above example) is the ''antecedent'' of that pronoun. In most cases the antecedent is a nominal (noun or noun phrase), though the pronoun can also refer to a whole proposition, as in "The train was late, which annoyed me greatly", where the antecedent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semicolon
The semicolon (or semi-colon) is a symbol commonly used as orthographic punctuation. In the English language, a semicolon is most commonly used to link (in a single sentence) two independent clauses that are closely related in thought, such as when restating the preceding idea with a different expression. When a semicolon joins two or more ideas in one sentence, those ideas are then given equal rank. Semicolons can also be used in place of commas to separate items in a list, particularly when the elements of the list themselves have embedded commas. The semicolon is one of the least understood of the standard marks, and is not frequently used by many English speakers. In the QWERTY keyboard layout, the semicolon resides in the unshifted homerow beneath the little finger of the right hand and has become widely used in programming languages as a statement separator or terminator. History In 1496, the semicolon is attested in Pietro Bembo's book ' printed by Aldo Manuz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subordinate Clause
A dependent clause, also known as a subordinate clause, subclause or embedded clause, is a certain type of clause that juxtaposes an independent clause within a complex sentence. For instance, in the sentence "I know Bette is a dolphin", the clause "Bette is a dolphin" occurs as the complement of the verb "know" rather than as a freestanding sentence. Subtypes of dependent clauses include content clauses, relative clauses, adverbial clauses, and clauses that complement an independent clause in the subjunctive mood. Content clause A content clause, also known as a "noun clause", provides content implied or commented upon by its main clause. It can be a subject, predicate nominative, direct object, appositive, indirect object, or object of the preposition. Some of the English words that introduce content clauses are ''that, who'' (and formal ''whom''), ''whoever'' (and formal ''whomever''), ''whether, why, what, how, when'', and ''where''. Notice that some of these words also in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prepositional Phrase
An adpositional phrase is a syntactic category that includes ''prepositional phrases'', ''postpositional phrases'', and ''circumpositional phrases''. Adpositional phrases contain an adposition (preposition, postposition, or circumposition) as head (linguistics), head and usually a Complement (linguistics), complement such as a noun phrase. Language syntax treats adpositional phrases as units that act as Argument (linguistics), arguments or Adjunct (grammar), adjuncts. Prepositional and postpositional phrases differ by the order of the words used. Languages that are primarily Head-directionality parameter, head-initial such as English predominantly use prepositional phrases whereas head-final languages predominantly employ postpositional phrases. Many languages have both types, as well as circumpositional phrases. Types There are three types of adpositional phrases: prepositional phrases, postpositional phrases, and circumpositional phrases. Prepositional phrases The underlined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology (linguistics)
In linguistics, morphology is the study of words, including the principles by which they are formed, and how they relate to one another within a language. Most approaches to morphology investigate the structure of words in terms of morphemes, which are the smallest units in a language with some independent meaning. Morphemes include roots that can exist as words by themselves, but also categories such as affixes that can only appear as part of a larger word. For example, in English the root ''catch'' and the suffix ''-ing'' are both morphemes; ''catch'' may appear as its own word, or it may be combined with ''-ing'' to form the new word ''catching''. Morphology also analyzes how words behave as parts of speech, and how they may be inflected to express grammatical categories including number, tense, and aspect. Concepts such as productivity are concerned with how speakers create words in specific contexts, which evolves over the history of a language. The basic fields of ling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Link Grammar
Link grammar (LG) is a theory of syntax by Davy Temperley and Daniel Sleator which builds relations between pairs of words, rather than constructing constituents in a phrase structure hierarchy. Link grammar is similar to dependency grammar, but dependency grammar includes a head-dependent relationship, whereas link grammar makes the head-dependent relationship optional (links need not indicate direction). Colored Multiplanar Link Grammar (CMLG) is an extension of LG allowing crossing relations between pairs of words. The relationship between words is indicated with link types, thus making the Link grammar closely related to certain categorial grammars. For example, in a subject–verb–object language like English, the verb would look left to form a subject link, and right to form an object link. Nouns would look right to complete the subject link, or left to complete the object link. In a subject–object–verb language like Persian, the verb would look left to form a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selection (linguistics)
In linguistics, selection denotes the ability of predicates to determine the semantic content of their arguments. Predicates select their arguments, which means they limit the semantic content of their arguments. A distinction may sometimes be drawn between types of selection; viz., ''s(emantic)-selection'' versus ''c(ategory)-selection''. Selection in general stands in contrast to subcategorization: selection is a semantic concept, whereas subcategorization is a syntactic one; predicates both ''select'' and ''subcategorize'' for their complement arguments, but only ''select'' their subject arguments. Selection is closely related to valency, a term used in grammars other than the Chomskian generative grammar for a similar phenomenon. Examples The following pairs of sentences illustrate the concept of selection; the # indicates semantic deviance: ::a. ''The plant is wilting.'' ::b. ''#The building is wilting.'' – The argument ''the building'' violates the selectional restric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
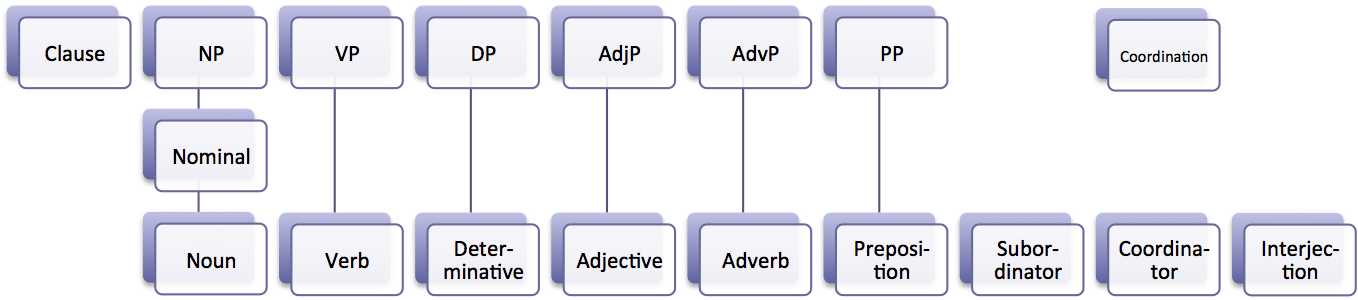
Part Of Speech
In grammar, a part of speech or part-of-speech ( abbreviated as POS or PoS, also known as word class or grammatical category) is a category of words (or, more generally, of lexical items) that have similar grammatical properties. Words that are assigned to the same part of speech generally display similar syntactic behavior (they play similar roles within the grammatical structure of sentences), sometimes similar morphological behavior in that they undergo inflection for similar properties and even similar semantic behavior. Commonly listed English parts of speech are noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, interjection, numeral, article, and determiner. Other terms than ''part of speech''—particularly in modern linguistic classifications, which often make more precise distinctions than the traditional scheme does—include word class, lexical class, and lexical category. Some authors restrict the term ''lexical category'' to refer only to a par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |