|
Selection (linguistics)
In linguistics, selection denotes the ability of predicates to determine the semantic content of their arguments. Predicates select their arguments, which means they limit the semantic content of their arguments. A distinction may sometimes be drawn between types of selection; viz., ''s(emantic)-selection'' versus ''c(ategory)-selection''. Selection in general stands in contrast to subcategorization: selection is a semantic concept, whereas subcategorization is a syntactic one; predicates both ''select'' and ''subcategorize'' for their complement arguments, but only ''select'' their subject arguments. Selection is closely related to valency, a term used in grammars other than the Chomskian generative grammar for a similar phenomenon. Examples The following pairs of sentences illustrate the concept of selection; the # indicates semantic deviance: ::a. ''The plant is wilting.'' ::b. ''#The building is wilting.'' – The argument ''the building'' violates the selectional restric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predicate (grammar)
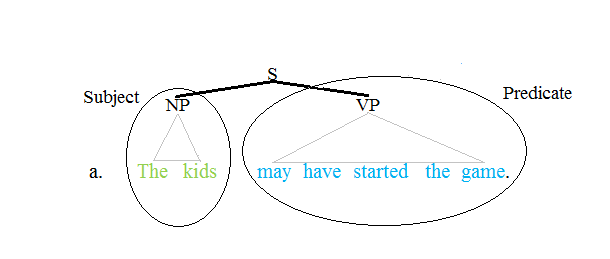
The term predicate is used in two ways in linguistics and its subfields. The first defines a predicate as everything in a standard declarative sentence except the subject (grammar), subject, and the other defines it as only the main content verb or associated predicative expression of a clause. Thus, by the first definition, the predicate of the sentence ''Frank likes cake'' is ''likes cake'', while by the second definition, it is only the content verb ''likes'', and ''Frank'' and ''cake'' are the argument (linguistics), arguments of this predicate. The conflict between these two definitions can lead to confusion. Syntax Traditional grammar The notion of a predicate in traditional grammar traces back to Aristotelian logic. A predicate is seen as a property that a subject has or is characterized by. A predicate is therefore an expression that can be ''true of'' something. Thus, the expression "is moving" is true of anything that is moving. This classical understanding of pred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argument (linguistics)
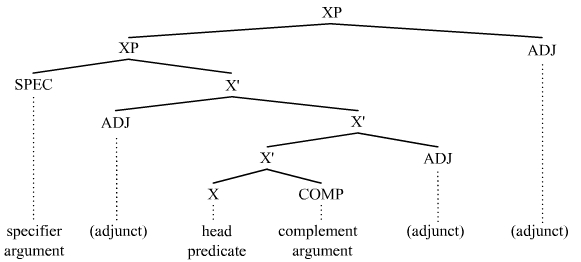
In linguistics, an argument is an expression that helps complete the meaning of a predicate (grammar), predicate, the latter referring in this context to a main verb and its auxiliaries. In this regard, the ''Complement (linguistics), complement'' is a closely related concept. Most predicates take one, two, or three arguments. A predicate and its arguments form a ''predicate-argument structure''. The discussion of predicates and arguments is associated most with (content) verbs and noun phrases (NPs), although other syntactic category, syntactic categories can also be construed as predicates and as arguments. Arguments must be distinguished from adjunct (grammar), adjuncts. While a predicate needs its arguments to complete its meaning, the adjuncts that appear with a predicate are optional; they are not necessary to complete the meaning of the predicate. Most theories of syntax and semantics acknowledge arguments and adjuncts, although the terminology varies, and the distinction is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcategorization
In linguistics, subcategorization denotes the ability/necessity for lexical items (usually verbs) to require/allow the presence and types of the syntactic arguments with which they co-occur. For example, the word "walk" as in "X walks home" requires the noun-phrase X to be animate. The notion of subcategorization is similar to the notion of valency, although the two concepts (subcategorization and valency) stem from different traditions in the study of syntax and grammar. Argument structure Argument structure is the list of selected arguments associated with a lexical category, such as a verb (SKS, 2015). When every predicate, otherwise known as a verb, is used, it selects a specific set of arguments that need to be fulfilled to create a well-formed sentence (Kroger, 2005). These are arguments such as AGENT, PATIENT, EXPERIENCER, THEME, RECIPIENT, and STIMULUS. To illustrate this, the sentence ''The adults asked if the cats would pee on the sofa'', has been broken down into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complement (linguistics)
In grammar, a complement is a word, phrase, or clause that is necessary to complete the meaning of a given expression. Complements are often also arguments (expressions that help complete the meaning of a predicate). Predicative, subject and object complements In many non-theoretical grammars, the terms '' subject complement'' (also called a predicative of the subject) and '' object complement'' are employed to denote the predicative expressions (predicative complements), such as predicative adjectives and nominals (also called a predicative nominative or predicate nominative), that serve to assign a property to a subject or an object: ::Ryan is upset. – Predicative adjective as subject complement ::Rachelle is the boss. – Predicative nominal as subject complement ::That made Michael lazy. – Predicative adjective as object complement ::We call Rachelle the boss. – Predicative nominal as object complement This terminology is used in grammar books: However, this use o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valency (linguistics)
In linguistics, valency or valence is the number and type of arguments and complements controlled by a predicate, content verbs being typical predicates. Valency is related, though not identical, to subcategorization and transitivity, which count only object arguments – valency counts all arguments, including the subject. The linguistic meaning of valency derives from the definition of valency in chemistry. Like valency found in chemistry, there is the binding of specific elements. In the grammatical theory of valency, the verbs organize sentences by binding the specific elements. Examples of elements that would be bound would be the complement and the actant. Although the term originates from valence in chemistry, linguistic valency has a close analogy in mathematics under the term arity. The valency metaphor appeared first in linguistics in Charles Sanders Peirce's essay "The Logic of Relatives" in 1897, and it then surfaced in the works of a number of linguists decade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coercion (linguistics)
In linguistics, coercion is a term applied to a process of reinterpretation triggered by a mismatch between the semantic properties of a selector and the semantic properties of the selected element. As Catalina Ramírez explains it, this phenomenon is called ''coercion'' because the process forces meaning into a lexical phrase where there is otherwise a discrepancy of the semantic aspects of the phrase. The term was first used in the semantic literature in 1988 by Marc Moens and Mark Steedman, who adopted it due to its "loose analogy with type-coercion in programming languages.” In his written framework of the generative lexicon (a formal compositional approach to lexical semantics), Pustejovsky (1995:111) defines coercion as "a semantic operation that converts an argument to the type which is expected by a function, where it would otherwise result in a type error." Coercion in the Pustejovsky framework refers to both ''complement coercion'' and ''aspectual coercion''. ''Comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntactic Category
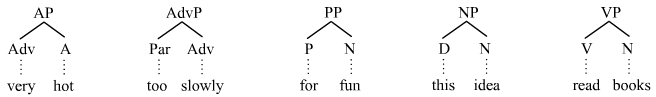
A syntactic category is a syntactic unit that theories of syntax assume. Word classes, largely corresponding to traditional parts of speech (e.g. noun, verb, preposition, etc.), are syntactic categories. In phrase structure grammars, the ''phrasal categories'' (e.g. noun phrase, verb phrase, prepositional phrase, etc.) are also syntactic categories. Dependency grammars, however, do not acknowledge phrasal categories (at least not in the traditional sense). Word classes considered as syntactic categories may be called ''lexical categories'', as distinct from phrasal categories. The terminology is somewhat inconsistent between the theoretical models of different linguists. However, many grammars also draw a distinction between ''lexical categories'' (which tend to consist of content words, or phrases headed by them) and ''functional categories'' (which tend to consist of function words or abstract functional elements, or phrases headed by them). The term ''lexical category'' the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of computer science and especially artificial intelligence. It is primarily concerned with providing computers with the ability to process data encoded in natural language and is thus closely related to information retrieval, knowledge representation and computational linguistics, a subfield of linguistics. Major tasks in natural language processing are speech recognition, text classification, natural-language understanding, natural language understanding, and natural language generation. History Natural language processing has its roots in the 1950s. Already in 1950, Alan Turing published an article titled "Computing Machinery and Intelligence" which proposed what is now called the Turing test as a criterion of intelligence, though at the time that was not articulated as a problem separate from artificial intelligence. The proposed test includes a task that involves the automated interpretation and generation of natural language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vera Demberg
Vera Demberg (born 1981) is a German computational linguist and professor of computer science and computational linguistics at Saarland University. Her research interests include cognitive models of human language comprehension, natural language generation, experimental psycholinguistics, multimodal language processing in a dual-task setting, and experimental and computational discourse research and pragmatics. Career and research Vera Demberg studied computational linguistics at the Institute for Machine Language Processing at the University of Stuttgart from 2001 to 2006. She then completed a Master's degree in Artificial Intelligence at the University of Edinburgh from 2004 to 2005. She received her Ph.D. from the Department of Computer Science there from 2006 to 2010. Her dissertation paper, titled “Broad-Coverage Model of Prediction in Human Sentence Processing”, was awarded the Cognitive Science Society's “Glushko Dissertation Prize in Cognitive Science” in 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thematic Relation
In certain theories of linguistics, thematic relations, also known as semantic roles or thematic roles, are the various roles that a noun phrase may play with respect to the action or state described by a governing verb, commonly the sentence's main verb. For example, in the sentence "Susan ate an apple", ''Susan'' is the doer of the eating, so she is an Agent (grammar), agent; ''an apple'' is the item that is eaten, so it is a Patient (grammar), patient. Since their introduction in the mid-1960s by Jeffrey Gruber and Charles J. Fillmore, Charles Fillmore, semantic roles have been a core linguistic concept and ground of debate between linguist approaches, because of their potential in explaining the relationship between syntax and semantics (also known as the syntax-semantics interface), that is how meaning affects the surface syntactic codification of language. The notion of semantic roles play a central role especially in functionalist linguistics, functionalist and language-com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operator Grammar
Operator grammar is a mathematical theory of human language that explains how language carries information. This theory is the culmination of the life work of Zellig Harris, with major publications toward the end of the last century. Operator grammar proposes that each human language is a self-organizing system in which both the syntactic and semantic properties of a word are established purely in relation to other words. Thus, no external system ( metalanguage) is required to define the rules of a language. Instead, these rules are learned through exposure to usage and through participation, as is the case with most social behavior. The theory is consistent with the idea that language evolved gradually, with each successive generation introducing new complexity and variation. Operator grammar posits three universal constraints: dependency (certain words depend on the presence of other words to form an utterance), likelihood (some combinations of words and their dependents a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Link Grammar
Link grammar (LG) is a theory of syntax by Davy Temperley and Daniel Sleator which builds relations between pairs of words, rather than constructing constituents in a phrase structure hierarchy. Link grammar is similar to dependency grammar, but dependency grammar includes a head-dependent relationship, whereas link grammar makes the head-dependent relationship optional (links need not indicate direction). Colored Multiplanar Link Grammar (CMLG) is an extension of LG allowing crossing relations between pairs of words. The relationship between words is indicated with link types, thus making the Link grammar closely related to certain categorial grammars. For example, in a subject–verb–object language like English, the verb would look left to form a subject link, and right to form an object link. Nouns would look right to complete the subject link, or left to complete the object link. In a subject–object–verb language like Persian, the verb would look left to form a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |