|
Norleucine
Norleucine (abbreviated as Nle) is an amino acid with the formula CH3(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. A systematic name for this compound is 2-aminohexanoic acid. The compound is an isomer of the more common amino acid leucine. Like most other α-amino acids, norleucine is chiral. It is a white, water-soluble solid. Occurrence Together with norvaline, norleucine is found in small amounts in some bacterial strains where its concentration can approach millimolar. Its biosynthesis has been examined. It arises via the action of 2-isopropylmalate synthase on α-ketobutyrate. The incorporation of Nle into peptides reflects the imperfect selectivity of the associated aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. In Miller–Urey experiments probing prebiotic synthesis of amino acids, norleucine and especially norvaline are formed. Uses It is nearly isosteric with methionine, even though it does not contain sulfur. For this reason, norleucine has been used to probe the role of methionine in Amyloid-β peptide (AΠ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leucines
The leucines are primarily the four isomeric amino acids: leucine, isoleucine, ''tert''-leucine ( terleucine, pseudoleucine) and norleucine. Being compared with the four butanols, they could be classified as butyl-substituted glycines; they represent all four possible variations. Leucine and isoleucine belong to the proteinogenic amino acids; the others are non-natural. Isomers Including the stereoisomers, six further isomers could be added: D-leucine, D-isoleucine, L-alloisoleucine, D-alloisoleucine, D-''tert''-leucine and D-norleucine. Derivatives Cycloleucine could be classified as a cyclic derivative of norleucine. With a cyclopentane-ring, it has two hydrogen atoms fewer and thus is not an isomer. The α-carbon atom is not a stereocenter. See also * L-Photo-Leucine Amino acids Literature * Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Lubert Stryer: ''Biochemie.'' 6 Auflage, Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg 2007. . * Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet: ''Biochemistry.'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminoacid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides. Biosynthesis is usually synonymous with anabolism. The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via pepti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems with language, disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the typical life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years. The cause of Alzheimer's disease is poorly understood. There are many environmental and genetic risk factors associated with its development. The strongest genetic risk factor is from an allele of APOE. Other risk factors include a history of head injury, clinical depression, and high blood pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Amyloid
Beta (, ; uppercase , lowercase , or cursive ; grc, βῆτα, bÄ“Ì‚ta or ell, βήτα, vÃta) is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 2. In Modern Greek, it represents the voiced labiodental fricative while in borrowed words is instead commonly transcribed as μπ. Letters that arose from beta include the Roman letter and the Cyrillic letters and . Name Like the names of most other Greek letters, the name of beta was adopted from the acrophonic name of the corresponding letter in Phoenician, which was the common Semitic word ''*bait'' ('house'). In Greek, the name was ''bêta'', pronounced in Ancient Greek. It is spelled βήτα in modern monotonic orthography and pronounced . History The letter beta was derived from the Phoenician letter beth . Uses Algebraic numerals In the system of Greek numerals, beta has a value of 2. Such use is denoted by a number mark: Β′. Computing Finance Beta is used i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature. Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means "burning stone". Today, almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum.. Downloahere The greatest commercial use of the element is the production ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans. As the precursor of other amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine plays a critical role in the metabolism and health of many species, including humans. It is encoded by the codon AUG. Methionine is also an important part of angiogenesis, the growth of new blood vessels. Supplementation may benefit those suffering from copper poisoning. Overconsumption of methionine, the methyl group donor in DNA methylation, is related to cancer growth in a number of studies. Methionine was first isolated in 1921 by John Howard Mueller. Biochemical details Methionine (abbreviated as Met or M; encoded by the codon AUG) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological pH conditions), an amino group (which is in the protonat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
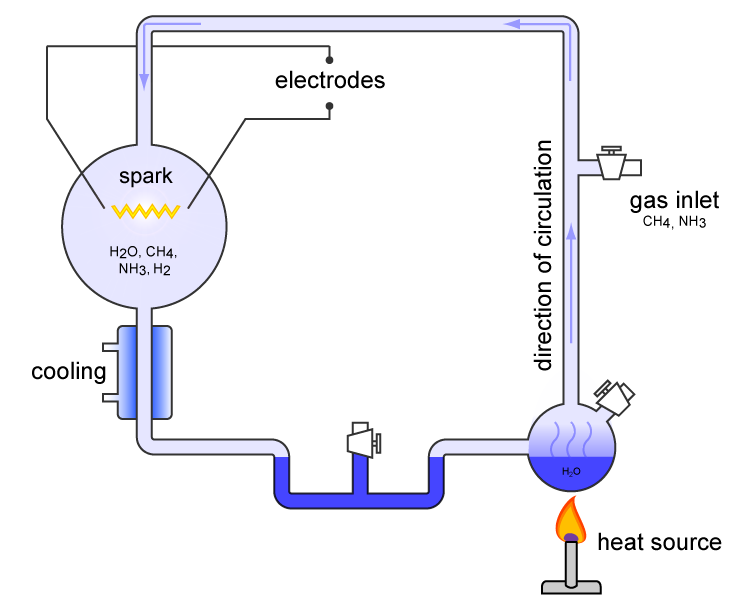
Miller–Urey Experiment
The Miller–Urey experiment (or Miller experiment) is a famous chemistry experiment that simulated the conditions thought at the time (1952) to be present in the atmosphere of the early, prebiotic Earth, in order to test the hypothesis of the chemical origin of life under those conditions. The experiment used water (H2O), methane (CH4), ammonia (NH3), hydrogen (H2), and an electric arc (the latter simulating hypothesized lightning). At the time, it supported Alexander Oparin's and J. B. S. Haldane's hypothesis that the hypothesized conditions on the primitive Earth favored chemical reactions that synthesized more complex organic compounds from simpler inorganic precursors. One of the most famous experiments of all time, it is considered to be groundbreaking, and to be the classic experiment investigating abiogenesis. It was performed in 1952 by Stanley Miller, supervised by Harold Urey at the University of Chicago, and published the following year. After Miller's death in 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
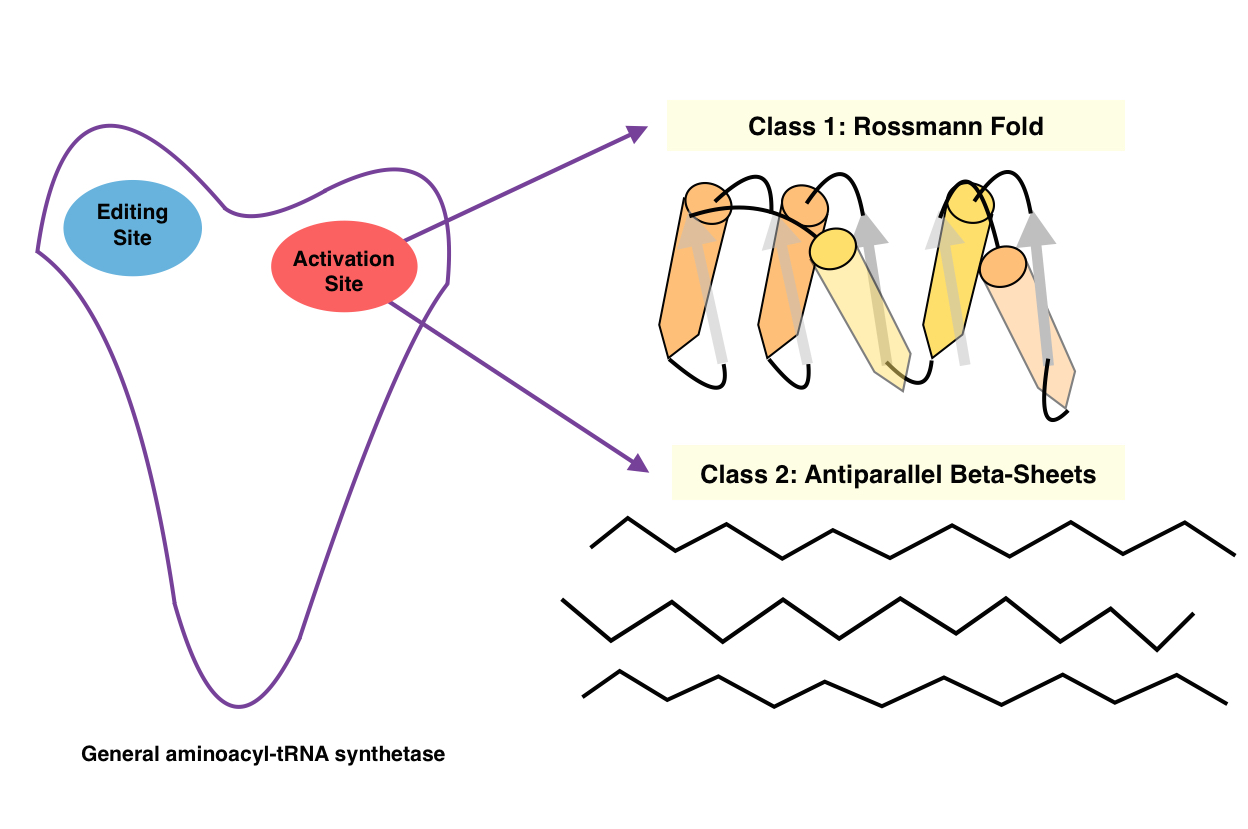
Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetase
An aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS or ARS), also called tRNA-ligase, is an enzyme that attaches the appropriate amino acid onto its corresponding tRNA. It does so by catalyzing the transesterification of a specific cognate amino acid or its precursor to one of all its compatible cognate tRNAs to form an aminoacyl-tRNA. In humans, the 20 different types of aa-tRNA are made by the 20 different aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, one for each amino acid of the genetic code. This is sometimes called "charging" or "loading" the tRNA with an amino acid. Once the tRNA is charged, a ribosome can transfer the amino acid from the tRNA onto a growing peptide, according to the genetic code. Aminoacyl tRNA therefore plays an important role in RNA translation, the expression of genes to create proteins. Mechanism The synthetase first binds ATP and the corresponding amino acid (or its precursor) to form an aminoacyl-adenylate, releasing inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi). The adenylate-aaRS comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-isopropylmalate Synthase
In enzymology, a 2-isopropylmalate synthase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :acetyl-CoA + 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate + H2O \rightleftharpoons (2S)-2-isopropylmalate + CoA The three substrates of this enzyme are acetyl-CoA, 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate, and H2O, and its products are (2S)-2-isopropylmalate and CoA. The enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, specifically those acyltransferases that convert acyl groups into alkyl groups on transfer. The systematic name of this enzyme class is ''acetyl-CoA:3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate C-acetyltransferase (thioester-hydrolysing, carboxymethyl-forming)''. Other names in common use include ''3-carboxy-3-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoate 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate-lyase'', ''(CoA-acetylating)'', ''alpha-isopropylmalate synthetase'', ''alpha-isopropylmalate synthase'', ''alpha-isopropylmalic synthetase'', ''isopropylmalate synthase'', and ''isopropylmalate synthetase''. This enzyme participates in biosynthesis of L-leucine a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norvaline
Norvaline (abbreviated as Nva) is an amino acid with the formula CH3(CH2)2CH(NH2)CO2H. The compound is a structural analog of valeric acid and also an isomer of the more common amino acid valine. Like most other α-amino acids, norvaline is chiral. It is a white, water-soluble solid. Occurrence Norvaline is a non-proteinogenic unbranched-chain amino acid. It has previously been reported to be a natural component of an antifungal peptide of ''Bacillus subtilis''. Norvaline and other modified unbranched chain amino acids have received attention because they appear to be incorporated in some recombinant proteins found in '' E. coli''. Its biosynthesis has been examined. The incorporation of Nva into peptides reflects the imperfect selectivity of the associated aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. In Miller–Urey experiments probing prebiotic synthesis of amino acids, norvaline, but also norleucine, are produced. Nomenclature Norvaline and norleucine Norleucine (abbreviated as Nle) is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |