|
Noctilucent Clouds
Noctilucent clouds, or night shining clouds, are tenuous cloud-like phenomena in the upper atmosphere of Earth. When viewed from space, they are called polar mesospheric clouds (PMCs), detectable as a diffuse scattering layer of water ice crystals near the summer polar mesopause. They consist of ice crystals and from the ground are only visible during astronomical twilight. ''Noctilucent'' roughly means "night shining" in Latin. They are most often observed during the summer months from latitudes between ±50° and ±70°. Too faint to be seen in daylight, they are visible only when the observer and the lower layers of the atmosphere are in Earth's shadow, but while these very high clouds are still in sunlight. Recent studies suggest that increased atmospheric methane emissions produce additional water vapor once the methane molecules reach the mesosphere – creating, or reinforcing existing noctilucent clouds. They are the highest clouds in Earth's atmosphere, located in the me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karjasoo
Karjasoo is a village in Põhja-Sakala Parish, Viljandi County in central Estonia, located about west of the town of Suure-Jaani, the administrative centre of the municipality. (retrieved 28 July 2021) Most of the village's territory is covered by the northern part of Kuresoo Bog which is part of the Soomaa National Park. In 2009 Karjasoo had a population of 7. Composer, organist and folk songs collector Mart Saar (1882–1963) was born in Hüpassaare which is now part of Karjasoo village. Gallery File:Mart Saare sünnikodu.jpg, Birthplace of composer Mart Saar Mart Saar ( in Hüpassaare – 28 October 1963) was an Estonian composer, organist and collector of folk songs. Childhood Saar was born at the small borough of Hüpassaare (now in Karjasoo, Suure-Jaani Parish), Kreis Fellin in the Livonian ... in Hüpassaare. File:Laugas Kuresoos Hüppassaare kohal.JPG, Bog in Hüpassaare References Villages in Viljandi County Kreis Fellin {{Viljandi-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeronomy Of Ice In The Mesosphere
The Aeronomy of Ice in the Mesosphere (AIM or Explorer 90) is a NASA satellite originally launched to conduct a 26-month study of noctilucent clouds (NLCs). Its mission was extended, and as of 2022 is still operational. It is the ninetieth Explorer program mission and is part of the NASA-funded Small Explorer program (SMEX). Mission The scientific purpose of the Aeronomy of Ice in the Mesosphere (AIM) mission is focused on the study of polar mesospheric clouds (PMCs) that form about above the surface of Earth in summer and mostly in the polar regions of Earth. The overall goal is to resolve why PMCs form and why they vary. AIM expected lifetime was at least two years. AIM measures PMCs and the thermal, chemical and dynamical environment in which they form. This will allow the connection to be made between these clouds and the meteorology of the polar mesospheric summer echoes. This connection is important because a significant variability in the yearly number of noctilu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Altitude
Altitude or height (also sometimes known as depth) is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context (e.g., aviation, geometry, geographical survey, sport, or atmospheric pressure). Although the term ''altitude'' is commonly used to mean the height above sea level of a location, in geography the term elevation is often preferred for this usage. Vertical distance measurements in the "down" direction are commonly referred to as depth. In aviation In aviation, the term altitude can have several meanings, and is always qualified by explicitly adding a modifier (e.g. "true altitude"), or implicitly through the context of the communication. Parties exchanging altitude information must be clear which definition is being used. Aviation altitude is measured using either mean sea level (MSL) or local ground level (above ground level, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as '' The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national " newspaper of record". For print it is ranked 18th in the world by circulation and 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 1896, through a dual-class share structure after its shares became publicly traded. A. G. Sulzberger, the paper's publisher and the company's chairman, is the fifth generation of the family to head the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Atmospheric And Solar-Terrestrial Physics
The ''Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering the atmospheric and solar-terrestrial physics. It was established in 1950 as the ''Journal of Atmospheric and Terrestrial Physics'', obtaining its current name in 1997. It is published by Elsevier and sponsored by the International Union of Radio Science. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 2.119. Its founding editor was Edward Victor Appleton Sir Edward Victor Appleton (6 September 1892 – 21 April 1965) was an English physicist, Nobel Prize winner (1947) and pioneer in radiophysics. He studied, and was also employed as a lab technician, at Bradford College from 1909 to 1911. He ..., and the current editors are Mark Lester and D. Pancheva. References External links * Geophysics journals Atmospheric sciences journals Publications established in 1950 Elsevier academic journals Monthly journals Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesosphere
The mesosphere (; ) is the third layer of the atmosphere, directly above the stratosphere and directly below the thermosphere. In the mesosphere, temperature decreases as altitude increases. This characteristic is used to define its limits: it begins at the top of the stratosphere (sometimes called the stratopause), and ends at the mesopause, which is the coldest part of Earth's atmosphere, with temperatures below . The exact upper and lower boundaries of the mesosphere vary with latitude and with season (higher in winter and at the tropics, lower in summer and at the poles), but the lower boundary is usually located at altitudes from above sea level, and the upper boundary (the mesopause) is usually from . The stratosphere and mesosphere are sometimes collectively referred to as the "middle atmosphere", which spans altitudes approximately between above Earth's surface. The mesopause, at an altitude of , separates the mesosphere from the thermosphere—the second-outermost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research, and outer space, space research. NASA was National Aeronautics and Space Act, established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo program, Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew Program, Commercial Crew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanometer
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the molecular scale. The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm) or nanometer (American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, American spelling) is a units of measurement, unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), equal to one billionth (short scale) of a metre () and to 1000 picometres. One nanometre can be expressed in scientific notation as , and as metres. History The nanometre was formerly known as the millimicrometre – or, more commonly, the millimicron for short – since it is of a micron (micrometre), and was often denoted by the symbol mμ or (more rarely and confusingly, since it logically should refer to a ''millionth'' of a micron) as μμ. Etymology The name combines the SI prefix ''nano-'' (from the Ancient Greek , ', "dwarf") with the parent unit name ''metre'' (from Greek , ', "unit of measurement"). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolide
A bolide is normally taken to mean an exceptionally bright meteor, but the term is subject to more than one definition, according to context. It may refer to any large crater-forming body, or to one that explodes in the atmosphere. It can be a synonym for a fireball, sometimes specific to those with an apparent magnitude of −14 or brighter. Definitions The word ''bolide'' (; from Italian via Latin, ) may refer to somewhat different phenomena depending on the context in which the word appears, and readers may need to make inferences to determine which meaning is intended in a particular publication. One sense refers to an extremely bright meteor, especially one that explodes in the atmosphere. In astronomy, it refers to a fireball about as bright as the full moon, and it is generally considered a synonym for a fireball. In geology, a bolide is a very large impactor. One definition describes a bolide as a fireball reaching an apparent magnitude of −14 or brightermore th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
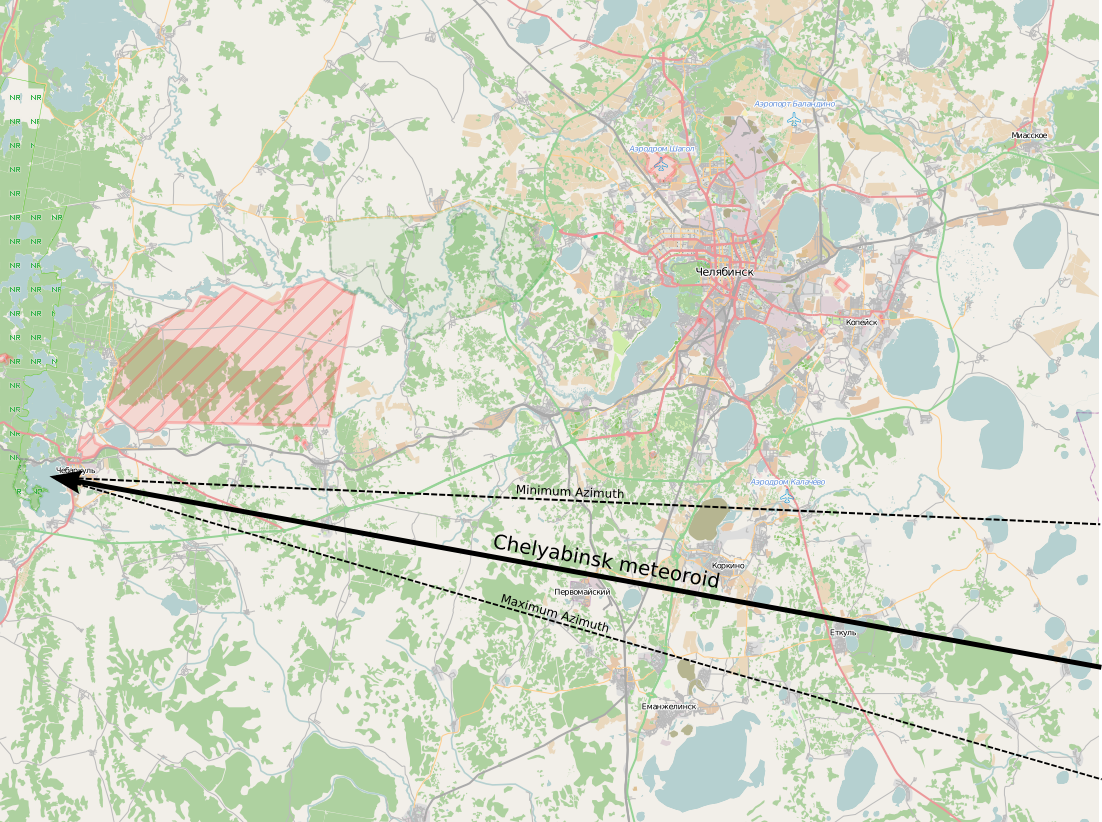
Chelyabinsk Meteor
The Chelyabinsk meteor was a superbolide that entered Earth's atmosphere over the southern Ural region in Russia on 15 February 2013 at about 09:20 YEKT (03:20 UTC). It was caused by an approximately near-Earth asteroid that entered the atmosphere at a shallow 18.3 ± 0.4 degree angle with a speed relative to Earth of 19.16 ± 0.15 kilometres per second (69,000 km/h or 42,690 mph). The light from the meteor was briefly brighter than the Sun, visible up to away. It was observed over a wide area of the region and in neighbouring republics. Some eyewitnesses also felt intense heat from the fireball. The object exploded in a meteor air burst over Chelyabinsk Oblast, at a height of around . The explosion generated a bright flash, producing a hot cloud of dust and gas that penetrated to , and many surviving small fragmentary meteorites. The bulk of the object's energy was absorbed by the atmosphere, creating a large shock wave with a total kinetic energy before at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armagh
Armagh ( ; ga, Ard Mhacha, , "Macha's height") is the county town of County Armagh and a city in Northern Ireland, as well as a civil parish. It is the ecclesiastical capital of Ireland – the seat of the Archbishops of Armagh, the Primates of All Ireland for both the Roman Catholic Church and the Church of Ireland. In ancient times, nearby Navan Fort (''Eamhain Mhacha'') was a pagan ceremonial site and one of the great royal capitals of Gaelic Ireland. Today, Armagh is home to two cathedrals (both named after Saint Patrick) and the Armagh Observatory, and is known for its Georgian architecture. Although classed as a medium-sized town, Armagh was given city status in 1994 and Lord Mayoralty status in 2012, both by Queen Elizabeth II. It had a population of 14,777 people in the 2011 Census. History Foundation ''Eamhain Mhacha'' (or Navan Fort), at the western edge of Armagh, was an ancient pagan ritual or ceremonial site. According to Irish mytholog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)
_-_Meteorite.gif)