|
Chelyabinsk Meteor
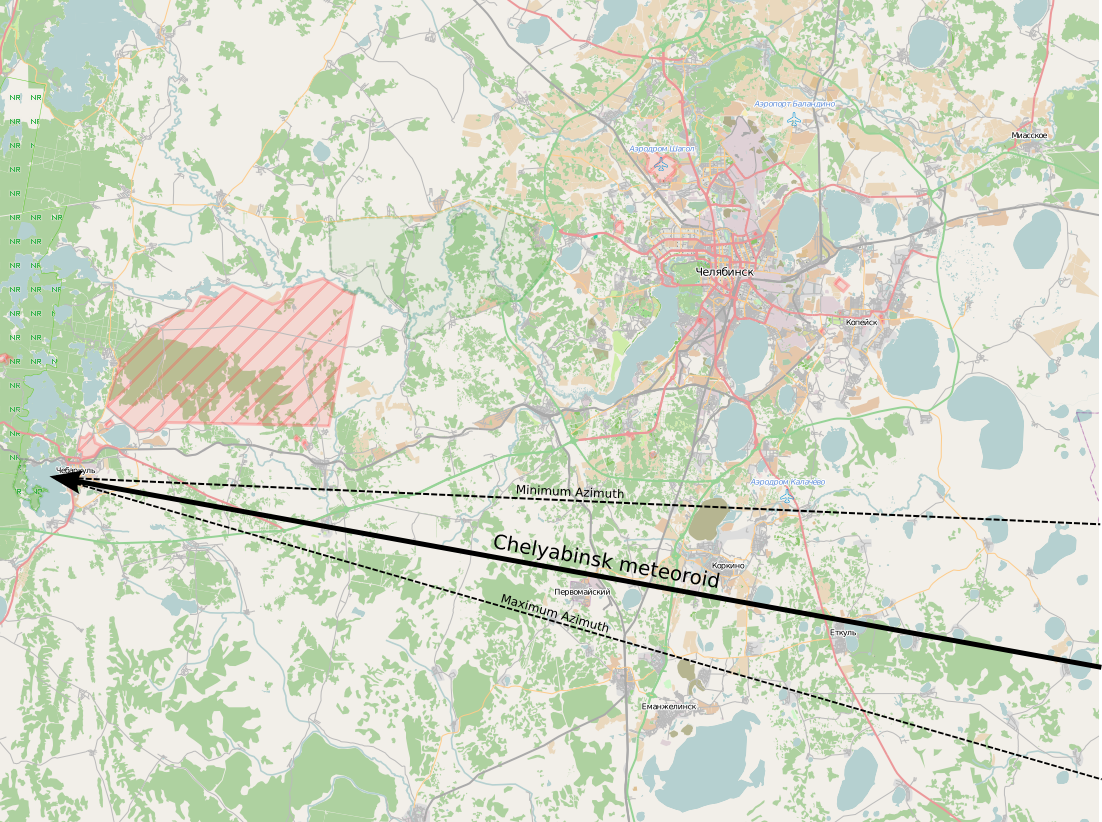
The Chelyabinsk meteor was a superbolide that entered Earth's atmosphere over the southern Ural region in Russia on 15 February 2013 at about 09:20 YEKT (03:20 UTC). It was caused by an approximately near-Earth asteroid that entered the atmosphere at a shallow 18.3 ± 0.4 degree angle with a speed relative to Earth of 19.16 ± 0.15 kilometres per second (69,000 km/h or 42,690 mph). The light from the meteor was briefly brighter than the Sun, visible up to away. It was observed over a wide area of the region and in neighbouring republics. Some eyewitnesses also felt intense heat from the fireball. The object exploded in a meteor air burst over Chelyabinsk Oblast, at a height of around . The explosion generated a bright flash, producing a hot cloud of dust and gas that penetrated to , and many surviving small fragmentary meteorites. The bulk of the object's energy was absorbed by the atmosphere, creating a large shock wave with a total kinetic energy bef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelyabinsk Meteorite
The Chelyabinsk meteorite (Russian: Челябинский метеорит, ''Chelyabinskii meteorit'') is the fragmented remains of the large Chelyabinsk meteor of 15 February 2013 which reached the ground after the meteor's passage through the atmosphere. The descent of the meteor, visible as a brilliant superbolide in the morning sky, caused a series of shock waves that shattered windows, damaged approximately 7,200 buildings and left 1,500 people injured. The resulting fragments were scattered over a wide area. The largest fragment raised from the bottom of Lake Chebarkul on 16 October 2013 had a mass of and the total mass of other 7 meteorite fragments found nearby was . Naming The meteor and meteorite are named after Chelyabinsk Oblast, over which the meteor exploded. An initial proposal was to name the meteorite after Lake Chebarkul, where one of its major fragments impacted and made a 6-metre-wide hole in the frozen lake surface. Composition and classification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
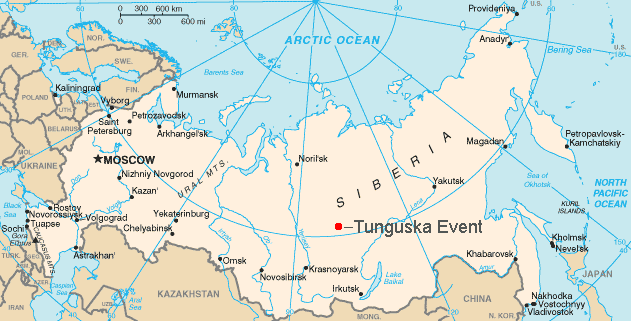
Tunguska Event
The Tunguska event (occasionally also called the Tunguska incident) was an approximately 12- megaton explosion that occurred near the Podkamennaya Tunguska River in Yeniseysk Governorate (now Krasnoyarsk Krai), Russia, on the morning of June 30, 1908. The explosion over the sparsely populated Eastern Siberian Taiga flattened an estimated 80 million trees over an area of of forest, and eyewitness reports suggest that at least three people may have died in the event. The explosion is generally attributed to a meteor air burst: the atmospheric explosion of a stony asteroid about in size. The supposed asteroid approached from the east-southeast, and likely with a relatively high speed of about (~ Ma 80). It is classified as an impact event, even though no impact crater has been found; the object is thought to have disintegrated at an altitude of rather than having hit the surface of the Earth. The Tunguska event is the largest impact event on Earth in recorded histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yekaterinburg Time
Yekaterinburg Time (YEKT) is the time zone five hours ahead of UTC ( UTC+05:00) and 2 hours ahead of Moscow Time (MSK+2). In 2011, Russia moved to year-round daylight saving time. Instead of switching between UTC+05:00 in winter and UTC+06:00 in summer, Yekaterinburg time was set to UTC+06:00 until 2014, when it was reset back to UTC+05:00 year-round. The time zone applies to the Ural Federal District, and Bashkortostan, Orenburg Oblast and Perm Krai Perm Krai (russian: Пе́рмский край, r=Permsky kray, p=ˈpʲɛrmskʲɪj ˈkraj, ''Permsky krai'', , ''Perem lador'') is a federal subject of Russia (a krai) that came into existence on December 1, 2005 as a result of the 2004 re ... in the Volga Federal District.https://www.timeanddate.com/time/zone/russia See also * Time in Russia References Time zones Time in Russia {{Standard-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrasound
Infrasound, sometimes referred to as low status sound, describes sound waves with a frequency below the lower limit of human audibility (generally 20 Hz). Hearing becomes gradually less sensitive as frequency decreases, so for humans to perceive infrasound, the sound pressure must be sufficiently high. The ear is the primary organ for sensing low sound, but at higher intensities it is possible to feel infrasound vibrations in various parts of the body. The study of such sound waves is sometimes referred to as infrasonics, covering sounds beneath 20 Hz down to 0.1 Hz (and rarely to 0.001 Hz). People use this frequency range for monitoring earthquakes and volcanoes, charting rock and petroleum formations below the earth, and also in ballistocardiography and seismocardiography to study the mechanics of the heart. Infrasound is characterized by an ability to get around obstacles with little dissipation. In music, acoustic waveguide methods, such as a large pipe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunguska And Chelyabinsk Meteoroid Size
Tunguska, formerly also written Tungonska, may refer to: * The Tunguska event, a catastrophic explosion over Siberia in 1908. Places * Rivers in Russia: ** Upper Tunguska, an old name of the lower course of the Angara, tributary of the Yenisey ** Podkamennaya Tunguska ("Stony Tunguska", also: "Middle Tunguska"), tributary of the Yenisey; the place of the Tunguska event ** Nizhnyaya Tunguska ("Lower Tunguska"), tributary of the Yenisey ** Tunguska (Amur), tributary of the Amur *Tunguska Plateau In arts and entertainment * ''Tunguska'' (album), a 2006 album by Suns of the Tundra * '' Secret Files: Tunguska'', a 2006 video game * "Tunguska", a song by Cymbals Eat Guitars * "Tunguska", a song by Darkest Hour on their album, '' Deliver Us'' * "Tunguska", a song by Fanfarlo on their album, ''Rooms Filled with Light'' * "Tunguska", a song by Hopesfall on their album, '' Arbiter'' * "Tunguska" (''The X-Files''), a 1996 episode of ''The X-Files'' Other uses * 2K22 Tunguska, a Russian an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trajectory Of Chelyabinsk Meteoroid En
A trajectory or flight path is the path that an object with mass in motion follows through space as a function of time. In classical mechanics, a trajectory is defined by Hamiltonian mechanics via canonical coordinates; hence, a complete trajectory is defined by position and momentum, simultaneously. The mass might be a projectile or a satellite. For example, it can be an orbit — the path of a planet, asteroid, or comet as it travels around a central mass. In control theory, a trajectory is a time-ordered set of states of a dynamical system (see e.g. Poincaré map). In discrete mathematics, a trajectory is a sequence (f^k(x))_ of values calculated by the iterated application of a mapping f to an element x of its source. Physics of trajectories A familiar example of a trajectory is the path of a projectile, such as a thrown ball or rock. In a significantly simplified model, the object moves only under the influence of a uniform gravitational force field. This can be a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
367943 Duende
367943 Duende (provisional designation ) is a micro-asteroid and a near-Earth object of the Aten and Atira group, approximately in diameter. It was discovered by astronomers of the Astronomical Observatory of Mallorca at its robotic La Sagra Observatory in 2012, and named for the duende, a goblin-like creature from Iberian and Filipino mythology and folklore. ''Duende'' is likely an uncommon L-type asteroid and significantly elongated. For an asteroid of its size, it has a relatively long rotation period of 9.485 hours. On 15 February 2013, ''Duende'' passed at a record distance of or 4.3 Earth radii from Earth's surface. Due to its close passage, its orbit was perturbed significantly enough that it changed from an Apollo asteroid to an Aten asteroid. ''Duende'' passage also coincided with the completely unrelated Chelyabinsk meteor, which entered Earth's atmosphere above Russia just 16 hours earlier. Discovery and past risk assessments ''Duende'' was discovered on 23 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of Russia since the latter half of the 16th century, after the Russians conquered lands east of the Ural Mountains. Siberia is vast and sparsely populated, covering an area of over , but home to merely one-fifth of Russia's population. Novosibirsk, Krasnoyarsk and Omsk are the largest cities in the region. Because Siberia is a geographic and historic region and not a political entity, there is no single precise definition of its territorial borders. Traditionally, Siberia extends eastwards from the Ural Mountains to the Pacific Ocean, and includes most of the drainage basin of the Arctic Ocean. The river Yenisey divides Siberia into two parts, Western and Eastern. Siberia stretches southwards from the Arctic Ocean to the hills of nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Ton
The short ton (symbol tn) is a measurement unit equal to . It is commonly used in the United States, where it is known simply as a ton, although the term is ambiguous, the single word being variously used for short, long, and metric ton. The various tons are defined as units of mass.Butcher, Crown and Gentry, NIST Special Publication 1038, The International System of Units (SI) – Conversion Factors for General Use, 2006 They are sometimes used as units of weight, the force exerted by a mass at standard gravity (e.g., short ton-force). One short ton exerts a weight at one standard gravity of 2,000 pound-force (lbf). United States In the United States, a short ton is usually known simply as a "ton", without distinguishing it from the tonne (), known there as the "metric ton", or the long ton also known as the "imperial ton" (). There are, however, some U.S. applications where unspecified ''tons'' normally mean long tons (for example, naval ships) or metric tons (world grain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United States customary units), and the long ton ( British imperial units). It is equivalent to approximately 2204.6 pounds, 1.102 short tons, and 0.984 long tons. The official SI unit is the megagram (symbol: Mg), a less common way to express the same mass. Symbol and abbreviations The BIPM symbol for the tonne is t, adopted at the same time as the unit in 1879.Table 6 . BIPM. Retrieved on 2011-07-10. Its use is also official for the metric ton in the United States, having been adopted by the United States |
Radiant (meteor Shower)
The radiant or apparent radiant of a meteor shower is the celestial point in the sky from which (from the point of view of a terrestrial observer) the paths of meteors appear to originate. The Perseids, for example, are meteors which appear to come from a point within the constellation of Perseus. Meteor paths appear at random locations in the sky, but the apparent paths of two or more meteors from the same shower will converge at the radiant. The radiant is the vanishing point of the meteor paths, which are parallel lines in three-dimensional space, as seen from the perspective of the observer, who views a two-dimensional projection against the sky. The geometric effect is identical to crepuscular rays, where parallel sunbeams appear to converge. A meteor that does not point back to the known radiant for a given shower is known as a ''sporadic'' and is not considered part of that shower. Shower meteors may appear a short time before the radiant has risen in the observer's ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Entry
Atmospheric entry is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. There are two main types of atmospheric entry: ''uncontrolled entry'', such as the entry of astronomical objects, space debris, or bolides; and ''controlled entry'' (or ''reentry'') of a spacecraft capable of being navigated or following a predetermined course. Technologies and procedures allowing the controlled atmospheric ''entry, descent, and landing'' of spacecraft are collectively termed as ''EDL''. Objects entering an atmosphere experience atmospheric drag, which puts mechanical stress on the object, and aerodynamic heating—caused mostly by compression of the air in front of the object, but also by drag. These forces can cause loss of mass ( ablation) or even complete disintegration of smaller objects, and objects with lower compressive strength can explode. Crewed space vehicles must be slowed to subsonic s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |