|
Neo-Lamarckism
Lamarckism, also known as Lamarckian inheritance or neo-Lamarckism, is the notion that an organism can pass on to its offspring physical characteristics that the parent organism acquired through use or disuse during its lifetime. It is also called the inheritance of acquired characteristics or more recently soft inheritance. The idea is named after the French zoologist Jean-Baptiste Lamarck (1744–1829), who incorporated the classical era theory of soft inheritance into his theory of evolution as a supplement to his concept of orthogenesis, a drive towards Evolution of biological complexity, complexity. Introductory textbooks contrast Lamarckism with Charles Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection. However, Darwin's book ''On the Origin of Species'' gave credence to the idea of heritable effects of use and disuse, as Lamarck had done, and his own concept of pangenesis similarly implied soft inheritance. Many researchers from the 1860s onwards attempted to find evidence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
On The Origin Of Species
''On the Origin of Species'' (or, more completely, ''On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life''),The book's full original title was ''On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life''. In the 1872 sixth edition, "On" was omitted, so the full title is ''The origin of species by means of natural selection, or the preservation of favoured races in the struggle for life.'' This edition is usually known as ''The Origin of Species.'' The 6th is Darwin's final edition; there were minor modifications in the text of certain subsequent issues. See Freeman, R. B. In Van Wyhe, John, ed. ''Darwin Online: On the Origin of Species'', 2002. published on 24 November 1859, is a work of scientific literature by Charles Darwin that is considered to be the foundation of evolutionary biology. Darwin's book introduced the scientific theory that populatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthogenesis
Orthogenesis, also known as orthogenetic evolution, progressive evolution, evolutionary progress, or progressionism, is an obsolete biological hypothesis that organisms have an innate tendency to evolve in a definite direction towards some goal (teleology) due to some internal mechanism or "driving force". According to the theory, the largest-scale trends in evolution have an absolute goal such as increasing biological complexity. Prominent historical figures who have championed some form of evolutionary progress include Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, Pierre Teilhard de Chardin, and Henri Bergson. The term ''orthogenesis'' was introduced by Wilhelm Haacke in 1893 and popularized by Theodor Eimer five years later. Proponents of orthogenesis had rejected the theory of natural selection as the organizing mechanism in evolution for a rectilinear model of directed evolution. With the emergence of the modern synthesis, in which genetics was integrated with evolution, orthogenesis and othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pangenesis
Pangenesis was Charles Darwin's hypothetical mechanism for heredity, in which he proposed that each part of the body continually emitted its own type of small organic particles called gemmules that aggregated in the gonads, contributing heritable information to the gametes. He presented this 'provisional hypothesis' in his 1868 work ''The Variation of Animals and Plants Under Domestication'', intending it to fill what he perceived as a major gap in evolutionary theory at the time. The etymology of the word comes from the Greek words ''pan'' (a prefix meaning "whole", "encompassing") and ''genesis'' ("birth") or ''genos'' ("origin"). Pangenesis mirrored ideas originally formulated by Hippocrates and other pre-Darwinian scientists, but using new concepts such as cell theory, explaining cell development as beginning with gemmules which were specified to be necessary for the occurrence of new growths in an organism, both in initial development and regeneration. It also accounted for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Synthesis (20th Century)
The modern synthesis was the early 20th-century synthesis of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution and Gregor Mendel's ideas on heredity into a joint mathematical framework. Julian Huxley coined the term in his 1942 book, ''Evolution: The Modern Synthesis''. The synthesis combined the ideas of natural selection, Mendelian inheritance, Mendelian genetics, and population genetics. It also related the broad-scale macroevolution seen by paleontology, palaeontologists to the small-scale microevolution of local population, populations. The synthesis was defined differently by its founders, with Ernst Mayr in 1959, G. Ledyard Stebbins in 1966, and Theodosius Dobzhansky in 1974 offering differing basic postulates, though they all include natural selection, working on heritable variation supplied by mutation. Other major figures in the synthesis included E. B. Ford, Bernhard Rensch, Ivan Schmalhausen, and George Gaylord Simpson. An early event in the modern synthesis was R. A. Fisher's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conway Zirkle
Conway Zirkle (October 28, 1895 – March 28, 1972) was an American botanist and historian of science. Zirkle was professor emeritus at the University of Pennsylvania. He was highly critical of Lamarckism, Lysenkoism and Marxian biology.Joravsky, David. (1960). ''Evolution, Marxian Biology and the Social Scene by Conway Zirkle''. ''Isis''. Vol. 51, No. 3. pp. 348-353. Selected publications Books *''The Beginnings of Plant Hybridization'' (1935) *''Death of a Science in Russia, the Fate of Genetics as Described in "Pravda" and Elsewhere'' (1949) *''Evolution, Marxian Biology, and the Social Scene'' (1959) *''The Evolution of Biology'' (1964) Papers *Zirkle, Conway. (1935). ''The Inheritance of Acquired Characters and the Provisional Hypothesis of Pangenesis''. ''American Naturalist'' 69: 417-445. *Zirkle, Conway. (1936). ''Further Notes on Pangenesis and the Inheritance of Acquired Characters''. ''American Naturalist'' 70: 529-546. *Zirkle, Conway. (1941). ''Natural Selection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
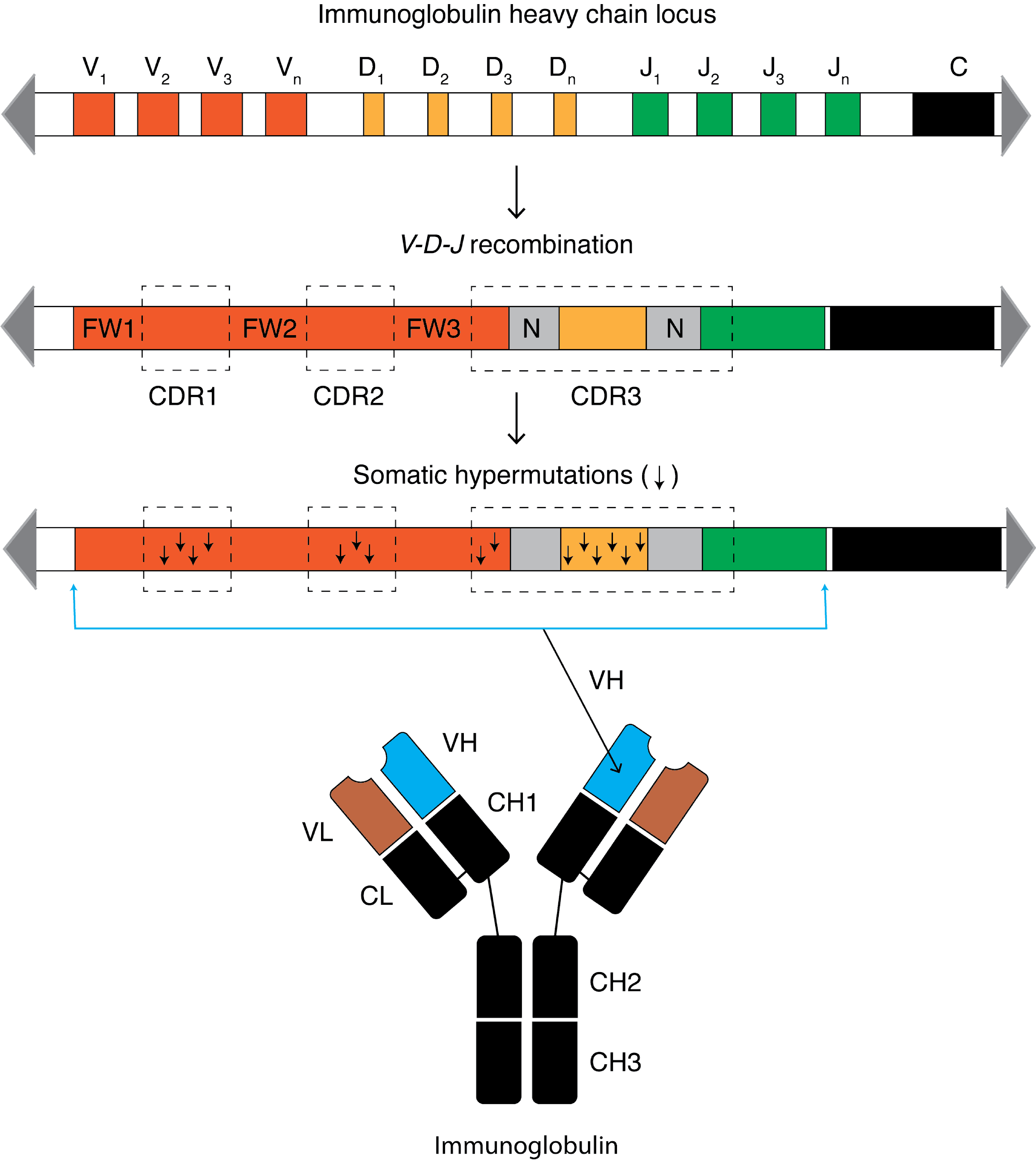
Somatic Hypermutation
Somatic hypermutation (or SHM) is a cellular mechanism by which the immune system adapts to the new foreign elements that confront it (e.g. microbes), as seen during class switching. A major component of the process of affinity maturation, SHM diversifies B cell receptors used to recognize foreign elements (antigens) and allows the immune system to adapt its response to new threats during the lifetime of an organism. Somatic hypermutation involves a programmed process of mutation affecting the variable regions of immunoglobulin genes. Unlike germline mutation, SHM affects only an organism's individual immune cells, and the mutations are not transmitted to the organism's offspring.Oprea, M. (1999''Antibody Repertoires and Pathogen Recognition:'' The Role of Germline Diversity and Somatic Hypermutation'' (Thesis) University of Leeds.'' Because this mechanism is merely selective and not precisely targeted, somatic hypermutation has been strongly implicated in the development of B-cell l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hologenome
The hologenome theory of evolution recasts the individual animal or plant (and other multicellular organisms) as a community or a "holobiont" – the host plus all of its symbiotic microbes. Consequently, the collective genomes of the holobiont form a "hologenome". Holobionts and hologenomes are structural entities that replace misnomers in the context of host-microbiota symbioses such as superorganism (i.e., an integrated social unit composed of conspecifics), organ, and metagenome. Variation in the hologenome may encode phenotypic plasticity of the holobiont and can be subject to evolutionary changes caused by selection and drift, if portions of the hologenome are transmitted between generations with reasonable fidelity. One of the important outcomes of recasting the individual as a holobiont subject to evolutionary forces is that genetic variation in the hologenome can be brought about by changes in the host genome and also by changes in the microbiome, including new acquisitions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-baptiste Lamarck2
Jean-Baptiste is a male French name, originating with Saint John the Baptist, and sometimes shortened to Baptiste. The name may refer to any of the following: Persons * Charles XIV John of Sweden, born Jean-Baptiste Jules Bernadotte, was King of Sweden and King of Norway * Charles-Jean-Baptiste Bouc, businessman and political figure in Lower Canada * Felix-Jean-Baptiste-Joseph Nève, orientalist and philologist * Gui-Jean-Baptiste Target, French lawyer and politician * Hippolyte Jean-Baptiste Garneray, French painter * Jean-Baptiste (songwriter), American music record producer, singer-songwriter * Jean-Baptiste Alphonse Karr, French critic, journalist, and novelist * Jean-Baptiste Bagaza, chairman of Supreme Revolutionary Council in Burundi until 1976 and president of Burundi (1976-1987) * Jean-Baptiste Baudry, son of Guillaume Baudry, Canadian gunsmith bevear goldsmith * Jean-Baptiste Benoît Eyriès, French geographer, author and translator * Jean-Baptiste Bessières, duke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of philosophy within the Lyceum and the wider Aristotelian tradition. His writings cover many subjects including physics, biology, zoology, metaphysics, logic, ethics, aesthetics, poetry, theatre, music, rhetoric, psychology, linguistics, economics, politics, meteorology, geology, and government. Aristotle provided a complex synthesis of the various philosophies existing prior to him. It was above all from his teachings that the West inherited its intellectual lexicon, as well as problems and methods of inquiry. As a result, his philosophy has exerted a unique influence on almost every form of knowledge in the West and it continues to be a subject of contemporary philosophical discussion. Little is known about his life. Aristotle was born in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine. He is traditionally referred to as the "Father of Medicine" in recognition of his lasting contributions to the field, such as the use of prognosis and clinical observation, the systematic categorization of diseases, or the formulation of humoral theory. The Hippocratic school of medicine revolutionized ancient Greek medicine, establishing it as a discipline distinct from other fields with which it had traditionally been associated (theurgy and philosophy), thus establishing medicine as a profession. However, the achievements of the writers of the Hippocratic Corpus, the practitioners of Hippocratic medicine, and the actions of Hippocrates himself were often conflated; thus very little is known about what Hippocrates actually t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epigenetics
In biology, epigenetics is the study of stable phenotypic changes (known as ''marks'') that do not involve alterations in the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix '' epi-'' ( "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are "on top of" or "in addition to" the traditional genetic basis for inheritance. Epigenetics most often involves changes that affect the regulation of gene expression, but the term can also be used to describe any heritable phenotypic change. Such effects on cellular and physiological phenotypic traits may result from external or environmental factors, or be part of normal development. The term also refers to the mechanism of changes: functionally relevant alterations to the genome that do not involve mutation of the nucleotide sequence. Examples of mechanisms that produce such changes are DNA methylation and histone modification, each of which alters how genes are expressed without altering the underlying DNA sequence. Gene expression c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be one of the most accomplished of all medical researchers of antiquity, Galen influenced the development of various scientific disciplines, including anatomy, physiology, pathology, pharmacology, and neurology, as well as philosophy and logic. The son of Aelius Nicon, a wealthy Greek architect with scholarly interests, Galen received a comprehensive education that prepared him for a successful career as a physician and philosopher. Born in the ancient city of Pergamon (present-day Bergama, Turkey), Galen traveled extensively, exposing himself to a wide variety of medical theories and discoveries before settling in Rome, where he served prominent members of Roman society and eventually was given the position of personal physician to several emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_-_Veloso_Salgado.png)