|
Nycteroleterid
Nycteroleteridae is a family of procolophonian parareptilians (extinct early reptiles) from the Middle to Late Permian of Russia and North America. They are sometimes classified as a sister group to pareiasaurids (but see ''Classification)''. The group includes the genera '' Macroleter'', '' Bashkyroleter'', ''"Bashkyroleter" mesensis'', ''Nycteroleter'', '' Emeroleter'', and probably '' Rhipaeosaurus''. They were carnivorous, and occasionally ate insects. The group was most common in European Russia, with only a few fossils in North America. One fossil has also been found in Africa, but this is the only one from Gondwana. Classification Nycteroleteridae is sometimes considered a sister group to the Pareiasauridae, but Bayesian inference suggests that it was in fact paraphyletic, with '' Rhipaeosaurus'' a basal member of the Pareiasauridae and other members of the Nycteroleteridae as outgroups. This is supported by the appearance of ''Rhipaeosaurus skull and teeth - it had tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhipaeosaurus
''Rhipaeosaurus'' is an extinct genus of nycteroleterid parareptile known from an articulated skeleton from the mid Middle Permian of European Russia. It contained a single species, ''Rhipaeosaurus tricuspidens''. A bayesian analysis suggests that it is more closely related to pareiasaurs than to the other nycteroleterids, due to skull and tooth features. For this reason, "Nycteroleteridae" may be a grade rather than a clade, unless redefined to exclude ''Rhipaeosaurus''. Description ''Rhipaeosaurus'' is around a meter long, larger than any other "nycteroleterids" and closer in size to later pareiasaurs. Postcranial remains were similar to '' Macroleter'', though the limbs were more robust and the ankle bones were unfused. The teeth were flattened and tricuspid (possessing three cusps), seemingly intermediate in form between the one- or two-cusped teeth of earlier nycteroleterids and the multi-cusped teeth of pareiasaurs. Many components of the partial skull and skelet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
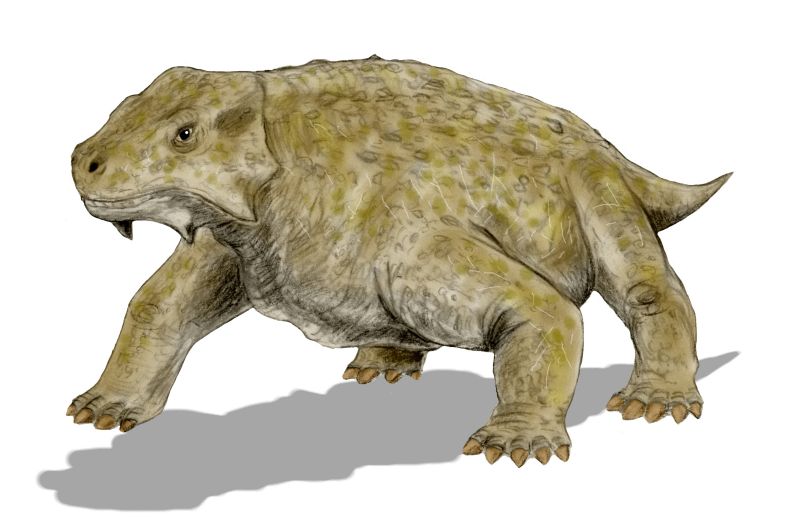
Nycteroleter
''Nycteroleter'' is an extinct genus of nycteroleterid parareptile known from the Middle Permian of European Russia. Fossils were first found in the Mezen River, near to Arkhangelsk. Within the Nycteroleteridae, it is considered most closely related to '' Emeroleter.'' However, its legs were shorter than those of ''Emeroleter'' and its skull was flatter. ''Nycteroleter'' was insectivorous, and may have been nocturnal. It was a small animal, less than a metre long. Classification ''Nycteroleter'' is classified as a primitive procolophonian, related to the Pareisauridae. It is not certain whether the nycteroleterids formed a monophyletic or polyphyletic group, as '' Rhipaeosaurus'' seems to be more similar to pareisaurids than to other nycteroleterids. Previously, it was uncertain whether nycteroleterids were parareptiles Parareptilia ("at the side of reptiles") is a subclass or clade of basal sauropsids (reptiles), typically considered the sister taxon to Eureptilia (t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokosaurus
''Macroleter'' is an extinct genus of nycteroleterid parareptile which existed in Oklahoma and Russia during the upper Permian period. It was a quite generalized primitive reptile, in many ways resembling their amphibian ancestors. It was first named by paleontologists Tverdochlebova and Ivachnenko in 1984. According to classification by Michel Laurin and Robert R. Reisz, the genus is a parareptile, belonging to the same branch as Millerettidae, Procolophonidae and other generalized anapsid reptiles. The type species is ''Macroleter poezicus'' from Upper Permian of Russia. ''Macroleter'' had an 8 cm skull, and an overall length of 75 cm. It was generally lizard-like in build with a rather flat and broad skull. The teeth were small and pointy, indication it predominantly hunted insects and other small invertebrates. ''Seymouria agilis'' (Olson, 1980) that is known from only one specimen (holotype UCMP 143 277) was originally thought to be a reptile-like amphibian an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emeroleter
''Emeroleter'' is an extinct genus of nycteroleterid parareptile known from the early Late Permian of European Russia. It was a long-legged lizard Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbaenia al ...-like small animal with a length about 30 cm. References Permian reptiles of Europe Pareiasauromorphs Fossil taxa described in 1997 Prehistoric reptile genera {{paleo-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pareiasaur
Pareiasaurs (meaning "cheek lizards") are an extinct clade of large, herbivorous parareptiles. Members of the group were armoured with scutes which covered large areas of the body. They first appeared in southern Pangea during the Middle Permian, before becoming globally distributed during the Late Permian. Pareiasaurs were the largest reptiles of the Permian, reaching sizes equivalent to those of contemporary therapsids. Pareiasaurs became extinct at the end of the Permian during the Permian-Triassic extinction event. Description Pareiasaurs ranged in size from long, and may have weighed up to . They were stocky, with short tails, small heads, robust limbs, and broad feet. The cow-sized species '' Bunostegos'', which lived 260 million years ago, is the earliest known example of a tetrapod with a fully erect posture as its legs were positioned directly under its body. Pareiasaurs were protected by bony scutes called osteoderms that were set into the skin. Their heavy skulls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bashkyroleter
''Bashkyroleter'' is an extinct genus of nycteroleterid parareptile which existed in European Russia during the middle Permian The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Pale ... period. References Pareiasauromorphs Permian reptiles of Europe Extinct animals of Russia Prehistoric reptile genera {{paleo-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pareiasaur
Pareiasaurs (meaning "cheek lizards") are an extinct clade of large, herbivorous parareptiles. Members of the group were armoured with scutes which covered large areas of the body. They first appeared in southern Pangea during the Middle Permian, before becoming globally distributed during the Late Permian. Pareiasaurs were the largest reptiles of the Permian, reaching sizes equivalent to those of contemporary therapsids. Pareiasaurs became extinct at the end of the Permian during the Permian-Triassic extinction event. Description Pareiasaurs ranged in size from long, and may have weighed up to . They were stocky, with short tails, small heads, robust limbs, and broad feet. The cow-sized species '' Bunostegos'', which lived 260 million years ago, is the earliest known example of a tetrapod with a fully erect posture as its legs were positioned directly under its body. Pareiasaurs were protected by bony scutes called osteoderms that were set into the skin. Their heavy skulls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians ( tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parareptilia
Parareptilia ("at the side of reptiles") is a subclass or clade of basal sauropsids ( reptiles), typically considered the sister taxon to Eureptilia (the group that likely contains all living reptiles and birds). Parareptiles first arose near the end of the Carboniferous period and achieved their highest diversity during the Permian period. Several ecological innovations were first accomplished by parareptiles among reptiles. These include the first reptiles to return to marine ecosystems (mesosaurs), the first bipedal reptiles (bolosaurids such as ''Eudibamus''), the first reptiles with advanced hearing systems ( nycteroleterids and others), and the first large herbivorous reptiles (the pareiasaurs). The only parareptiles to survive into the Triassic period were the procolophonoids, a group of small generalists, omnivores, and herbivores. The largest family of procolophonoids, the procolophonids, rediversified in the Triassic, but subsequently declined and became extinct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otic Notch
Otic notches are invaginations in the posterior margin of the skull roof, one behind each orbit. Otic notches are one of the features lost in the evolution of amniotes from their tetrapod ancestors. The notches have been interpreted as part of an auditory structure and are often reconstructed as holding a tympanum similar to those seen in modern anurans. Analysis of the ''columella'' (the stapes in amphibians and reptiles) of labyrinthodonts however indicates that it did not function in transmitting low-energy vibrations, thus rendering these animals effectively deaf to airborne sound. The otic notch instead functioned as a spiracle, at least in the early forms.Laurin, M. (1996)Hearing in Stegocephalians from the Tree of Life Web Project The Tree of Life Web Project is an Internet project providing information about the diversity and phylogeny of life on Earth. This collaborative peer reviewed project began in 1995, and is written by biologists from around the world. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutting
Cutting is the separation or opening of a physical object, into two or more portions, through the application of an acutely directed force. Implements commonly used for cutting are the knife and saw, or in medicine and science the scalpel and microtome. However, any sufficiently sharp object is capable of cutting if it has a hardness sufficiently larger than the object being cut, and if it is applied with sufficient force. Even liquids can be used to cut things when applied with sufficient force (see water jet cutter). Cutting is a compressive and shearing phenomenon, and occurs only when the total stress generated by the cutting implement exceeds the ultimate strength of the material of the object being cut. The simplest applicable equation is: \text = or \tau=\frac The stress generated by a cutting implement is directly proportional to the force with which it is applied, and inversely proportional to the area of contact. Hence, the smaller the area (i.e., the sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |