|
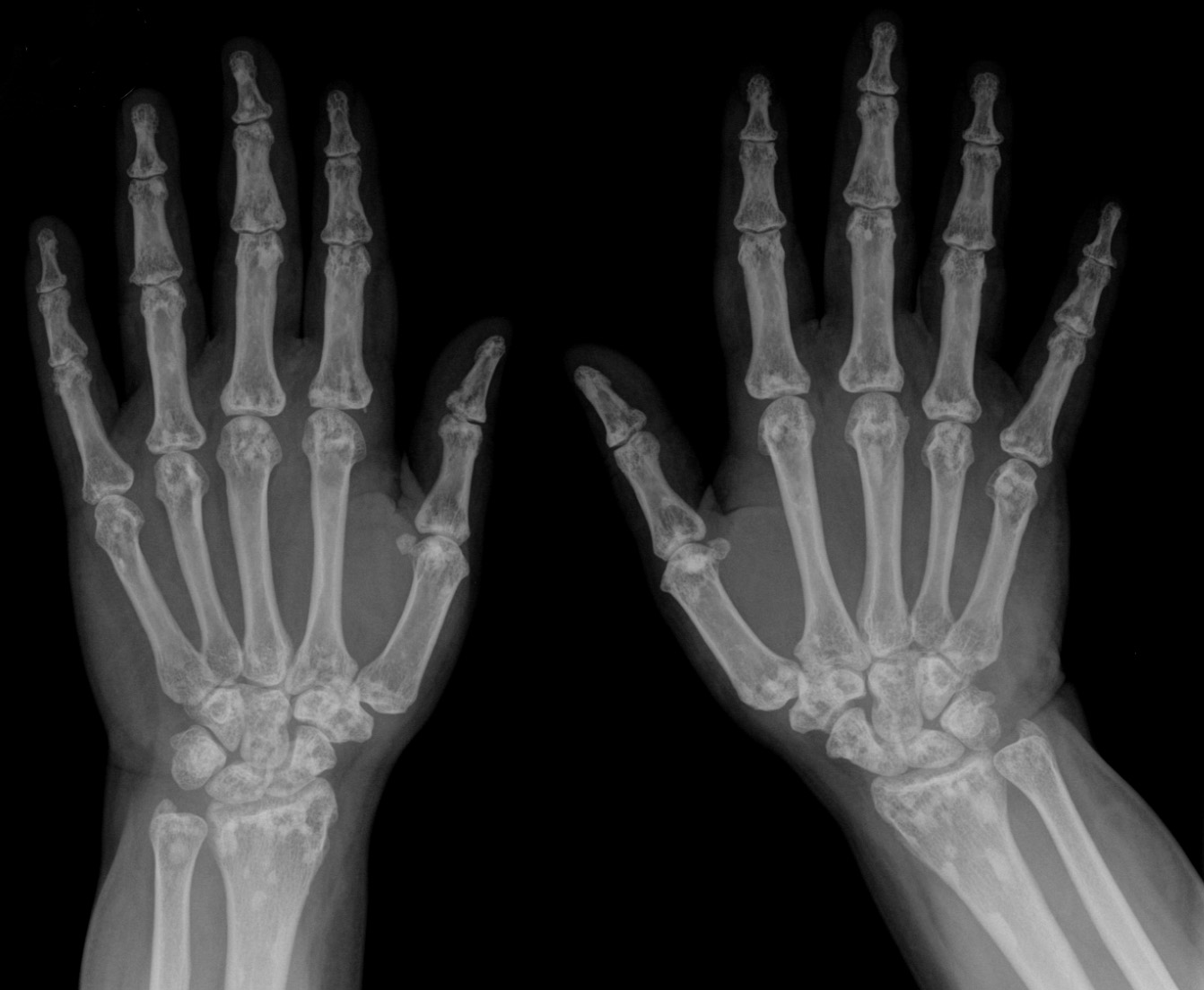
Melorheostosis
Melorheostosis is a medical developmental disorder and mesenchymal dysplasia in which the bony cortex widens and becomes hyperdense in a sclerotomal distribution. The condition begins in childhood and is characterized by thickening of the bones. Pain is a frequent symptom and the bone can have the appearance of dripping candle wax. Cause A randomly occurring somatic mutation of the MAP2K1 gene during fetal development is believed to be the cause. It is not known if LEMD3 mutations can cause isolated melorheostosis in the absence of osteopoikilosis or Buschke–Ollendorff syndrome. Diagnosis Melorheostosis is a mesenchymal dysplasia manifesting as regions of dripping wax appearance or flowing candle wax appearance. The disorder can be detected by radiograph due to thickening of bony cortex resembling "dripping candle wax." It is included on the spectrum of developmental bone dysplasias including pycnodysostosis and osteopoikilosis. The disorder tends to be unilateral and monostot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteopoikilosis
Osteopoikilosis is a benign, autosomal dominant sclerosing dysplasia of bone characterized by the presence of numerous bone islands in the skeleton. Presentation The radiographic appearance of osteopoikilosis on an X-ray is characterized by a pattern of numerous white densities of similar size spread throughout all the bones. This is a systemic condition. It must be differentiated from blastic metastasis, which can also present radiographically as white densities interspersed throughout bone. Blastic metastasis tends to present with larger and more irregular densities in less of a uniform pattern. Another differentiating factor is age, with blastic metastasis mostly affecting older people, and osteopoikilosis being found in people 20 years of age and younger. The distribution is variable, though it does not tend to affect the ribs, spine, or skull. Cause Epidemiology Men and women are affected in equal number, reflecting the fact that osteopoikilosis attacks indiscriminately. Ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LEMD3
LEM domain-containing protein 3 (LEMD3), also known as MAN1, is an integral protein in the inner nuclear membrane (INM) of the nuclear envelope. It is encoded by the ''LEMD3'' gene and was first identified after it was isolated from the serum of a patient with a collagen vascular disease. Structure The protein is 82.3 kDa and has a 40 amino acid long LEM domain located at its amino-terminal region. In its carboxyl end it has a RNA recognition motif (RRM). The LEM domain is also common to two other integral proteins of the INM: lamina-associated polypeptide 2 (LAP2) and emerin. The LEM segment enables LEMD3 to attach to the barrier-to-autointegration factor (BAF), and therefore, indirectly interact with the chromatin. LEMD3 also has several implications in regulating the cytokine family such as the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) and bone morphogenic protein (BMPs). The RRM domain in its carboxylic region attaches to the SMAD (protein) proteins, which is involved in medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesenchyme
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly every organ in the developing embryo. Vertebrates Structure Mesenchyme is characterized morphologically by a prominent ground substance matrix containing a loose aggregate of reticular fibers and unspecialized mesenchymal stem cells. Mesenchymal cells can migrate easily (in contrast to epithelial cells, which lack mobility), are organized into closely adherent sheets, and are polarized in an apical-basal orientation. Development The mesenchyme originates from the mesoderm. From the mesoderm, the mesenchyme appears as an embryologically primitive "soup". This "soup" exists as a combination of the mesenchymal cells plus serous fluid plus the many different tissue proteins. Serous fluid is typically stocked with the many serous elements, such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysplasia
Dysplasia is any of various types of abnormal growth or development of cells (microscopic scale) or organs (macroscopic scale), and the abnormal histology or anatomical structure(s) resulting from such growth. Dysplasias on a mainly microscopic scale include epithelial dysplasia and fibrous dysplasia of bone. Dysplasias on a mainly macroscopic scale include hip dysplasia (human), hip dysplasia, myelodysplastic syndrome, and multicystic dysplastic kidney. In one of the modern histopathology, histopathological senses of the term, dysplasia is sometimes differentiated from other categories of tissue change including hyperplasia, metaplasia, and neoplasia, and dysplasias are thus generally not cancerous. An exception is that the myelodysplasias include a range of benign tumor, benign, precancerous condition, precancerous, and cancerous forms. Various other dysplasias tend to be precancerous. The word's meanings thus cover a spectrum of histopathological variations. Microscopic sca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cortex (anatomy)
In anatomy and zoology, the cortex (plural cortices) is the outermost (or superficial) layer of an organ. Organs with well-defined cortical layers include kidneys, adrenal glands, ovaries, the thymus, and portions of the brain, including the cerebral cortex, the best-known of all cortices. Etymology The word is of Latin origin and means bark, rind, shell or husk. Notable examples * The renal cortex, between the renal capsule and the renal medulla; assists in ultrafiltration * The adrenal cortex, situated along the perimeter of the adrenal gland; mediates the stress response through the production of various hormones * The thymic cortex, mainly composed of lymphocytes; functions as a site for somatic recombination of T cell receptors, and positive selection * The cerebral cortex, the outer layer of the cerebrum, plays a key role in memory, attention, perceptual awareness, thought, language, and consciousness. * Cortical bone is the hard outer layer of bone; distinct from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteosclerosis
Osteosclerosis is a disorder that is characterized by abnormal hardening of bone and an elevation in bone density. It may predominantly affect the medullary portion and/or cortex of bone. Plain radiographs are a valuable tool for detecting and classifying osteosclerotic disorders. It can manifest in localized or generalized osteosclerosis. Localized osteosclerosis can be caused by Legg–Calvé–Perthes disease, sickle-cell disease and osteoarthritis among others. Osteosclerosis can be classified in accordance with the causative factor into acquired and hereditary. Types Acquired osteosclerosis * Osteogenic bone metastasis caused by carcinoma of prostate and breast * Paget's disease of bone * Myelofibrosis (primary disorder or secondary to intoxication or malignancy) * Osteosclerosing types of chronic osteomyelitis * Hypervitaminosis D * hyperparathyroidism * Schnitzler syndrome * Mastocytosis Skeletal fluorosis * Monoclonal IgM Kappa cryoglobulinemia * Hepatitis C. Heredita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAP2K1
Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAP2K1'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the dual-specificity protein kinase family that acts as a mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase kinase. MAP kinases, also known as extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs), act as an integration point for multiple biochemical signals. This protein kinase lies upstream of MAP kinases and stimulates the enzymatic activity of MAP kinases upon activation by a wide variety of extra- and intracellular signals. As an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway, this kinase is involved in many cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, transcription regulation and development. MAP2K1 is altered in 1.05% of all human cancers. Meiosis The genomes of diploid organisms in natural populations are highly polymorphic for insertions and deletions. During meiosis do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buschke–Ollendorff Syndrome
Buschke–Ollendorff syndrome (BOS) is a rare genetic disorder associated with LEMD3. It is believed to be inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. It is named for Abraham Buschke and Helene Ollendorff Curth, who described it in a 45-year-old woman. Its frequency is almost 1 case per every 20,000 people, and it is equally found in both males and females. Signs and symptoms The signs and symptoms of this condition are consistent with the following (possible complications include aortic stenosis and hearing loss): :::::::*Osteopoikilosis :::::::*Bone pain :::::::* Connective tissue nevi :::::::*Metaphysis abnormality Pathogenesis Buschke–Ollendorff syndrome is caused by one important factor: mutations in the LEMD3 gene (12q14), located on chromosome 12. Among the important aspects of Buschke–Ollendorff syndrome condition, genetically speaking are: :::::::::* LEMD3 (protein) referred also as MAN1, is an important protein in inner nuclear membrane. :::::::::* LEMD3 gene g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pycnodysostosis
Pycnodysostosis (from Greek: πυκνός (puknos) meaning "dense", ''dys'' ("defective"), and ''ostosis'' ("condition of the bone")), is a lysosomal storage disease of the bone caused by a mutation in the gene that codes the enzyme cathepsin K. It is also known as PKND and PYCD. History The disease was first described by Maroteaux and Lamy in 1962 at which time it was defined by the following characteristics: dwarfism; osteopetrosis; partial agenesis of the terminal digits of the hands and feet; cranial anomalies, such as persistence of fontanelles and failure of closure of cranial sutures; frontal and occipital bossing; and hypoplasia of the angle of the mandible. The defective gene responsible for the disease was discovered in 1996. The French painter Henri de Toulouse Lautrec (1864-1901) is believed to have had the disease. Signs and symptoms Pycnodysostosis causes the bones to be abnormally dense; the last bones of the fingers (the distal phalanges) to be unusually short; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner Ear
The inner ear (internal ear, auris interna) is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the temporal bone of the skull with a system of passages comprising two main functional parts: * The cochlea, dedicated to hearing; converting sound pressure patterns from the outer ear into electrochemical impulses which are passed on to the brain via the auditory nerve. * The vestibular system, dedicated to balance The inner ear is found in all vertebrates, with substantial variations in form and function. The inner ear is innervated by the eighth cranial nerve in all vertebrates. Structure The labyrinth can be divided by layer or by region. Bony and membranous labyrinths The bony labyrinth, or osseous labyrinth, is the network of passages with bony walls lined with periosteum. The three major parts of the bony labyrinth are the vestib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteosclerosis
Osteosclerosis is a disorder that is characterized by abnormal hardening of bone and an elevation in bone density. It may predominantly affect the medullary portion and/or cortex of bone. Plain radiographs are a valuable tool for detecting and classifying osteosclerotic disorders. It can manifest in localized or generalized osteosclerosis. Localized osteosclerosis can be caused by Legg–Calvé–Perthes disease, sickle-cell disease and osteoarthritis among others. Osteosclerosis can be classified in accordance with the causative factor into acquired and hereditary. Types Acquired osteosclerosis * Osteogenic bone metastasis caused by carcinoma of prostate and breast * Paget's disease of bone * Myelofibrosis (primary disorder or secondary to intoxication or malignancy) * Osteosclerosing types of chronic osteomyelitis * Hypervitaminosis D * hyperparathyroidism * Schnitzler syndrome * Mastocytosis Skeletal fluorosis * Monoclonal IgM Kappa cryoglobulinemia * Hepatitis C. Heredita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, patient education, physical intervention, rehabilitation, disease prevention, and health promotion. Physical therapists are known as physiotherapists in many countries. In addition to clinical practice, other aspects of physical therapist practice include research, education, consultation, and health administration. Physical therapy is provided as a primary care treatment or alongside, or in conjunction with, other medical services. In some jurisdictions, such as the United Kingdom, physical therapists have the authority to prescribe medication. Overview Physical therapy addresses the illnesses or injuries that limit a person's abilities to move and perform functional activities in their daily lives. PTs use an individual's history and physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |