|
Marginal Propensity To Save
The marginal propensity to save (MPS) is the fraction of an increase in income that is not spent and instead used for saving. It is the slope of the line plotting saving against income. For example, if a household earns one extra dollar, and the marginal propensity to save is 0.35, then of that dollar, the household will spend 65 cents and save 35 cents. Likewise, it is the fractional decrease in saving that results from a decrease in income. The MPS plays a central role in Keynesian economics Keynesian economics ( ; sometimes Keynesianism, named after British economist John Maynard Keynes) are the various macroeconomics, macroeconomic theories and Economic model, models of how aggregate demand (total spending in the economy) strongl ... as it quantifies the saving-income relation, which is the flip side of the consumption-income relation, and according to Keynes it reflects the fundamental psychological law. The marginal propensity to save is also a key variable in determ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Income
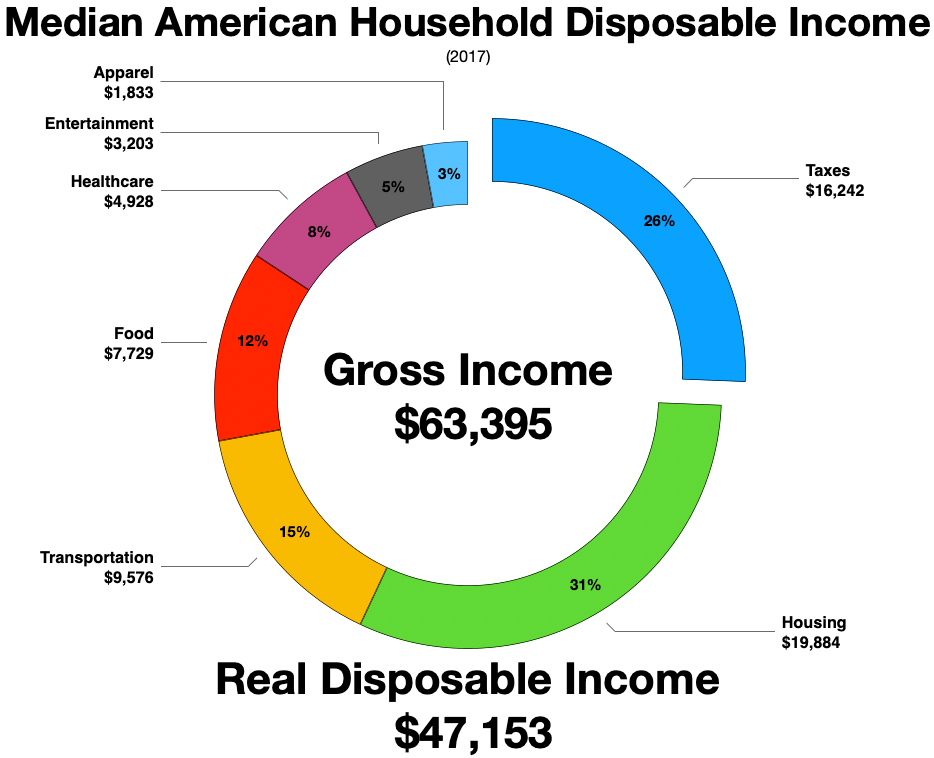
Income is the consumption and saving opportunity gained by an entity within a specified timeframe, which is generally expressed in monetary terms. Income is difficult to define conceptually and the definition may be different across fields. For example, a person's income in an economic sense may be different from their income as defined by law. An extremely important definition of income is Haig–Simons income, which defines income as ''Consumption + Change in net worth'' and is widely used in economics. For households and individuals in the United States, income is defined by tax law as a sum that includes any wage, salary, profit, interest payment, rent, or other form of earnings received in a calendar year.Case, K. & Fair, R. (2007). ''Principles of Economics''. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. p. 54. Discretionary income is often defined as gross income minus taxes and other deductions (such as mandatory pension contributions), and is widely used as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saving
Saving is income not spent, or deferred Consumption (economics), consumption. In economics, a broader definition is any income not used for immediate consumption. Saving also involves reducing expenditures, such as recurring Cost, costs. Methods of saving include putting money in, for example, a savings account, a pension, pension account, an investment fund, or kept as cash. In terms of personal finance, saving generally specifies low-risk preservation of money, as in a deposit account, versus investment, wherein risk is a lot higher. Saving does not automatically include interest. ''Saving'' differs from ''savings''. The former refers to the act of not consuming one's assets, whereas the latter refers to either multiple opportunities to reduce costs; or one's assets in the form of cash. Saving refers to an activity occurring over time, a stock and flow, flow variable, whereas savings refers to something that exists at any one time, a stock and flow, stock variable. This disti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keynesian Economics
Keynesian economics ( ; sometimes Keynesianism, named after British economist John Maynard Keynes) are the various macroeconomics, macroeconomic theories and Economic model, models of how aggregate demand (total spending in the economy) strongly influences Output (economics), economic output and inflation. In the Keynesian view, aggregate demand does not necessarily equal the aggregate supply, productive capacity of the economy. It is influenced by a host of factors that sometimes behave erratically and impact production, employment, and inflation. Keynesian economists generally argue that aggregate demand is volatile and unstable and that, consequently, a market economy often experiences inefficient macroeconomic outcomes, including economic recession, recessions when demand is too low and inflation when demand is too high. Further, they argue that these economic fluctuations can be mitigated by economic policy responses coordinated between a government and their central bank. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keynes
John Maynard Keynes, 1st Baron Keynes ( ; 5 June 1883 – 21 April 1946), was an English economist and philosopher whose ideas fundamentally changed the theory and practice of macroeconomics and the economic policies of governments. Originally trained in mathematics, he built on and greatly refined earlier work on the causes of business cycles. One of the most influential economists of the 20th century, he produced writings that are the basis for the school of thought known as Keynesian economics, and its various offshoots. His ideas, reformulated as New Keynesianism, are fundamental to mainstream macroeconomics. He is known as the "father of macroeconomics". During the Great Depression of the 1930s, Keynes spearheaded a revolution in economic thinking, challenging the ideas of neoclassical economics that held that free markets would, in the short to medium term, automatically provide full employment, as long as workers were flexible in their wage demands. He argued that agg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fundamental Psychological Law
In Keynesian macroeconomics, the Fundamental Psychological Law underlying the consumption function states that marginal propensity to consume (MPC) and marginal propensity to save The marginal propensity to save (MPS) is the fraction of an increase in income that is not spent and instead used for saving. It is the slope of the line plotting saving against income. For example, if a household earns one extra dollar, and the ... (MPS) are greater than zero(0) but less than one(1) MPC+MPS = 1 e.g. Whenever national income rises by $1 part of this will be consumed and part of this will be saved References *. * * * {{macroeconomics-stub Keynesian economics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiplier (economics)
In macroeconomics, a multiplier is a factor of proportionality that measures how much an endogenous variable changes in response to a change in some exogenous variable. For example, suppose variable ''x'' changes by ''k'' units, which causes another variable ''y'' to change by ''M'' × ''k'' units. Then the multiplier is ''M''. Common uses Two multipliers are commonly discussed in introductory macroeconomics. Commercial banks create money, especially under the fractional-reserve banking system used throughout the world. In this system, money is created whenever a bank gives out a new loan. This is because the loan, when drawn on and spent, mostly finishes up as a deposit back in the banking system and is counted as part of money supply. After putting aside a part of these deposits as mandated bank reserves, the balance is available for the making of further loans by the bank. This process continues multiple times, and is called the multiplier effect. The multiplier m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
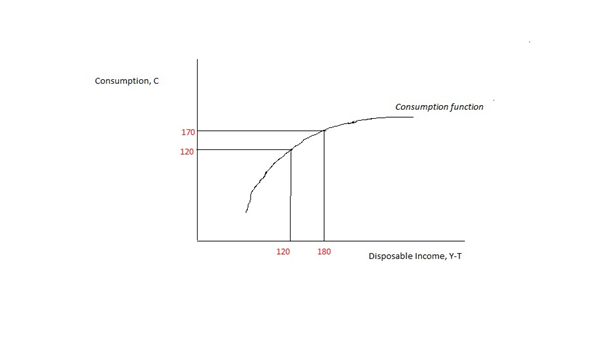
The Savings Function
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disposable Income
Disposable income is total personal income minus current taxes on income. In national accounting, personal income minus personal current taxes equals disposable personal income or household disposable income. Subtracting personal outlays (which includes the major category of personal r privateconsumption expenditure) yields personal (or, private) savings, hence the income left after paying away all the taxes is referred to as disposable income. Restated, consumption expenditure plus savings equals disposable income after accounting for transfers such as payments to children in school or elderly parents' living and care arrangements. The marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is the fraction of a change in disposable income that is consumed. For example, if disposable income rises by $100, and $65 of that $100 is consumed, the MPC is 65%. Restated, the marginal propensity to save is 35%. For the purposes of calculating the amount of income subject to garnishments, United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal Propensity To Consume
In economics, the marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is a metric that quantifies induced consumption, the concept that the increase in personal consumer spending ( consumption) occurs with an increase in disposable income (income after taxes and transfers). The proportion of disposable income which individuals spend on consumption is known as propensity to consume. MPC is the proportion of additional income that an individual consumes. For example, if a household earns one extra dollar of disposable income, and the marginal propensity to consume is 0.65, then of that dollar, the household will spend 65 cents and save 35 cents. Obviously, the household cannot spend ''more'' than the extra dollar (without borrowing or using savings). If the extra money accessed by the individual gives more economic confidence, then the MPC of the individual may well exceed 1, as they may borrow or utilise savings. According to John Maynard Keynes, marginal propensity to consume is less than one. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal Propensity To Import
The marginal propensity to import (MPM) is the fractional change in import expenditure that occurs with a change in disposable income (income after taxes and transfers). For example, if a household earns one extra dollar of disposable income, and the marginal propensity to import is 0.2, then the household will spend 20 cents of that dollar on imported goods and services. Mathematically, the marginal propensity to import (MPM) function is expressed as the derivative of the import (M) function with respect to disposable income (Y).\mathrm=\fracIn other words, the marginal propensity to import is measured as the ratio of the change in imports to the change in income, thus giving us a figure between 0 and 1. Imports are also considered to be automatic stabilisers that work to lessen fluctuations in real GDP. The UK government assumes that UK citizens have a high marginal propensity to import and thus will use a decrease in disposable income as a tool to control the current accou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Average Propensity To Consume
In ordinary language, an average is a single number or value that best represents a set of data. The type of average taken as most typically representative of a list of numbers is the arithmetic mean the sum of the numbers divided by how many numbers are in the list. For example, the mean or average of the numbers 2, 3, 4, 7, and 9 (summing to 25) is 5. Depending on the context, the most representative statistic to be taken as the average might be another measure of central tendency, such as the mid-range, median, mode or geometric mean. For example, the average personal income is often given as the median the number below which are 50% of personal incomes and above which are 50% of personal incomes because the mean would be higher by including personal incomes from a few billionaires. General properties If all numbers in a list are the same number, then their average is also equal to this number. This property is shared by each of the many types of average. Another universal p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Average Propensity To Save
In Keynesian economics, the average propensity to save (APS), also known as the savings ratio, is the proportion of income which is saved, usually expressed for household savings as a fraction of total household disposable income (taxed income). APS=\frac The ratio differs considerably over time and between countries. The savings ratio for an entire economy can be affected by (for example) the proportion of older people (as they have less motivation and capability to save), and the rate of inflation (as expectations of rising prices can encourage people to spend now rather than later) or current interest rates. APS can express the social preference for investing in the future over consuming in the present. The complement (1 minus the APS) is the average propensity to consume (APC). Low average propensity to save might be the indicator of a large percentage of old people or high percentage of irresponsible young people in the population. With income level changes, APS becomes an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |