|
Lanthanum Cuprate
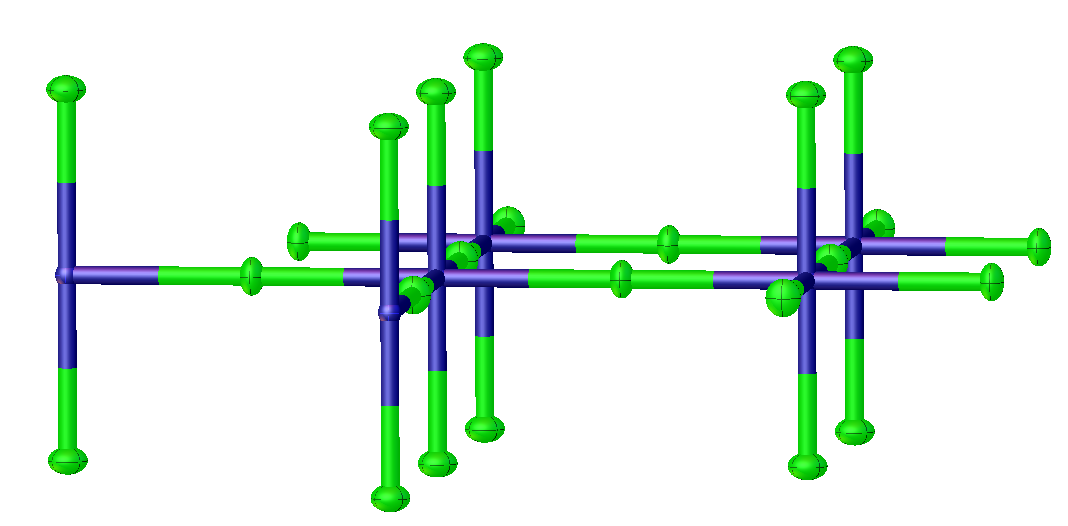
Lanthanum cuprate usually refers to the inorganic compound with the formula CuLa2O4. The name implies that the compound consists of a cuprate (CuOn]2n-) salt of lanthanum (La3+). In fact it is a highly covalent solid. It is prepared by high temperature reaction of lanthanum oxide and copper(II) oxide follow by annealing under oxygen. The material adopts a tetragonal structure related to potassium tetrafluoronickelate (K2NiF4), which is orthorhombic. Replacement of some lanthanum by barium gives the quaternary phase CuLa1.85Ba0.15O4, called lanthanum barium copper oxide. That doped material displays superconductivity at −243 K, which at the time of its discovery was a high temperature. This discovery initiated research on cuprate superconductors and was the basis of a Nobel Prize in Physics to Georg Bednorz Johannes Georg Bednorz (; born 16 May 1950) is a German physicist who, together with K. Alex Müller, discovered high-temperature superconductivity in ceramics, for w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Compound
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep mantle remain active areas of investigation. Some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon (graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, etc.), carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbides, and the following salts of inorganic anions: carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, and thiocyanates. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it does not occur within living things. History Friedrich Wöhler's conversion of ammonium cyanate into urea in 1828 is often cited as the starting point of modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuprate
Cuprate loosely refers to a material that can be viewed as containing anionic copper complexes. Examples include tetrachloridocuprate ( uCl4sup>2−), the superconductor YBa2Cu3O7, and the organocuprates (e.g., dimethylcuprate u(CH3)2sup>−). The term cuprates derives from the Latin word for copper, ''cuprum''. The term is mainly used in three contexts: oxide materials, anionic coordination complexes, and anionic organocopper compounds. Oxides One of the simplest oxide-based cuprates is the copper(III) oxide KCuO2, also known as "potassium cuprate(III)". This species can be viewed as the K+ salt of the polyanion []''n''. As such the material is classified as a cuprate. This dark blue diamagnetic solid is produced by heating potassium peroxide and copper(II) oxide in an atmosphere of oxygen: :K2O2 + 2 CuO → 2 KCuO2 Sodium cuprate(III) NaCuO2 and potassium cuprate(III) KCuO2 can also be produced by using hypochlorites or hypobromites to oxidize copper hydroxide unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanthanum Oxide
Lanthanum(III) oxide, also known as lanthana, chemical formula , is an inorganic compound containing the rare earth element lanthanum and oxygen. It is used in some ferroelectric materials, as a component of optical materials, and is a feedstock for certain catalysts, among other uses. Properties Lanthanum oxide is a white solid that is insoluble in water, but dissolves in acidic solutions. absorbs moisture from air, converts to lanthanum hydroxide. Lanthanum oxide has p-type semiconducting properties and a band gap of approximately 5.8 eV. Its average room temperature resistivity is 10 kΩ·cm, which decreases with an increase in temperature. has the lowest lattice energy of the rare earth oxides, with very high dielectric constant, ε = 27. Structure At low temperatures, has an A- hexagonal crystal structure. The metal atoms are surrounded by a 7 coordinate group of atoms, the oxygen ions are in an octahedral shape around the metal atom and there is one oxygen ion above ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper(II) Oxide
Copper(II) oxide or cupric oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula CuO. A black solid, it is one of the two stable oxides of copper, the other being Cu2O or copper(I) oxide (cuprous oxide). As a mineral, it is known as tenorite. It is a product of copper mining and the precursor to many other copper-containing products and chemical compounds. Production It is produced on a large scale by pyrometallurgy, as one stage in extracting copper from its ores. The ores are treated with an aqueous mixture of ammonium carbonate, ammonia, and oxygen to give copper(I) and copper(II) ammine complexes, which are extracted from the solids. These complexes are decomposed with steam to give CuO. It can be formed by heating copper in air at around 300–800°C: : 2 Cu + O2 → 2 CuO For laboratory uses, pure copper(II) oxide is better prepared by heating copper(II) nitrate, copper(II) hydroxide, or basic copper(II) carbonate: : 2 Cu(NO3)2(s) → 2 CuO(s) + 4 NO2(g) + O2(g) (180° ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Tetrafluoronickelate
Potassium tetrafluoronickelate is the inorganic compound with the formula K2NiF4. It features octahedral (high spin) Ni centers with Ni-F bond lengths of 2.006 Å. This green solid is a salt of tetrafluoronickelate. It is prepared by melting a mixture of nickel(II) fluoride, potassium fluoride, and potassium bifluoride. The compound adopts a perovskite-like structure consisting of layers of octahedral Ni centers interconnected by doubly bridging fluoride ligands. The layers are interconnected by potassium cations. It is one of the principal Ruddlesden-Popper phases. Early discoveries on cuprate superconductors focused on compounds with structures closely related to K2NiF4, e.g. lanthanum cuprate and derivative lanthanum barium copper oxide Lanthanum barium copper oxide, or LBCO, is an inorganic compound with the formula CuBa0.15La1.85O4. It is a black solid produced by heating an intimate mixture of barium oxide, copper(II) oxide, and lanthanum oxide in the presence of oxyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanthanum Barium Copper Oxide
Lanthanum barium copper oxide, or LBCO, is an inorganic compound with the formula CuBa0.15La1.85O4. It is a black solid produced by heating an intimate mixture of barium oxide, copper(II) oxide, and lanthanum oxide in the presence of oxygen. The material was discovered in 1986 and was the first high temperature superconductor. Johannes Georg Bednorz and K. Alex Müller shared the 1987 Nobel Prize in physics for the discovery that this material exhibits superconductivity at the then unusually high temperature. This finding led to intense and fruitful efforts to generate other cuprate superconductor Cuprate superconductors are a family of high-temperature superconducting materials made of layers of copper oxides (CuO2) alternating with layers of other metal oxides, which act as charge reservoirs. At ambient pressure, cuprate superconductor ...s. Lanthanum barium copper oxide is related to the far simpler compound lanthanum cuprate, which has a similar structure. In lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
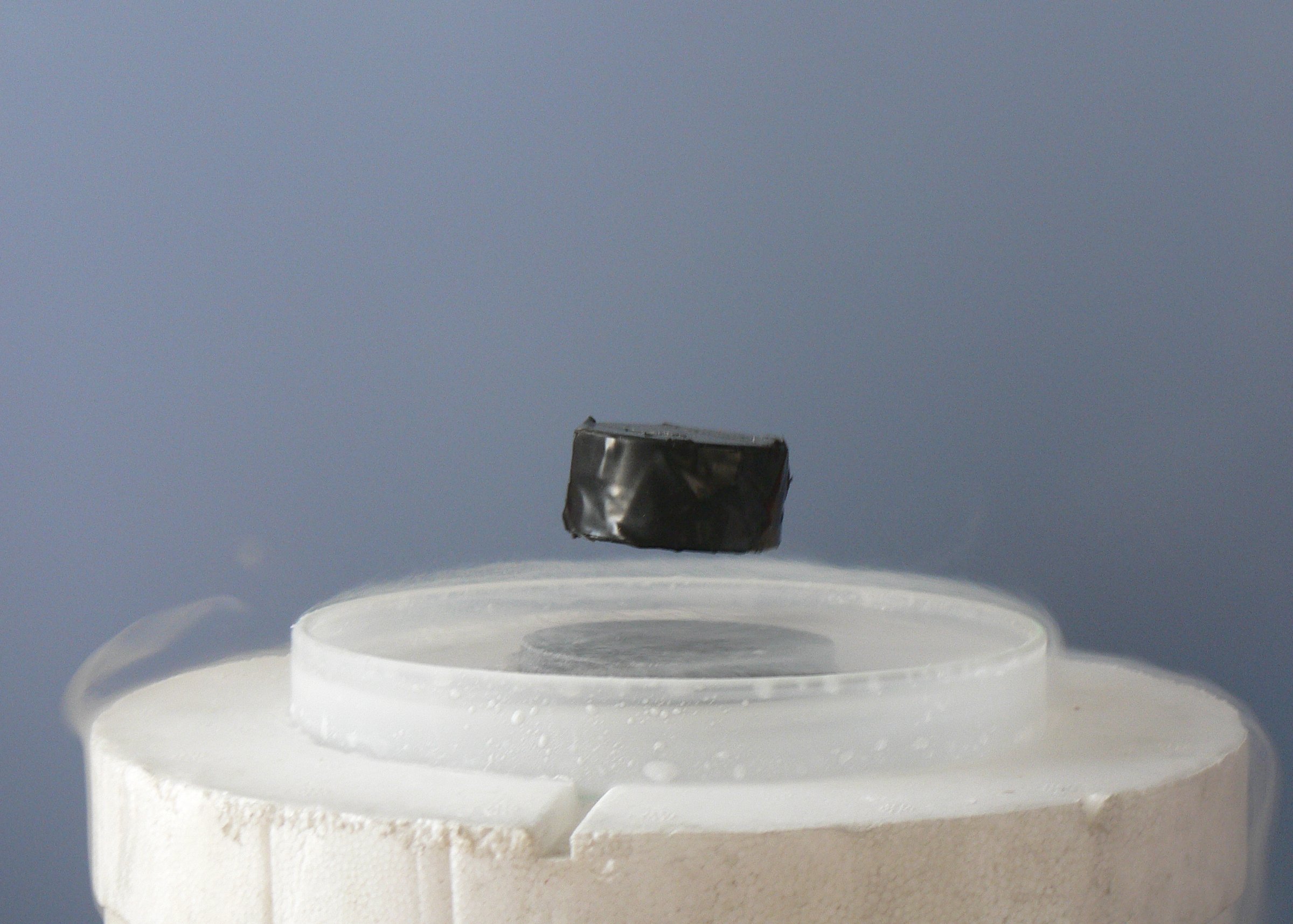
Superconductivity
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in certain materials where electrical resistance vanishes and magnetic flux fields are expelled from the material. Any material exhibiting these properties is a superconductor. Unlike an ordinary metallic conductor, whose resistance decreases gradually as its temperature is lowered even down to near absolute zero, a superconductor has a characteristic critical temperature below which the resistance drops abruptly to zero. An electric current through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source. The superconductivity phenomenon was discovered in 1911 by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a phenomenon which can only be explained by quantum mechanics. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete ejection of magnetic field lines from the interior of the superconductor during its transitions into the sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuprate Superconductor
Cuprate superconductors are a family of high-temperature superconducting materials made of layers of copper oxides (CuO2) alternating with layers of other metal oxides, which act as charge reservoirs. At ambient pressure, cuprate superconductors are the highest temperature superconductors known. However, the mechanism by which superconductivity occurs is still not understood. History The first cuprate superconductor was found in 1986 in the non-stoichiometric cuprate lanthanum barium copper oxide by IBM researchers Georg Bednorz and Karl Alex Müller. The critical temperature for this material was 35K, well above the previous record of 23 K. The discovery led to a sharp increase in research on the cuprates, resulting in thousands of publications between 1986 and 2001. Bednorz and Müller were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1987, only a year after their discovery. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Prize In Physics
) , image = Nobel Prize.png , alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "MDCCCXXXIII" above, followed by (smaller) "OB•" then "MDCCCXCVI" below. , awarded_for = Outstanding contributions for humankind in the field of Physics , presenter = Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences , location = Stockholm, Sweden , date = , reward = 9 million Swedish kronor (2017) , year = 1901 , holder_label = Most recently awarded to , holder = Alain Aspect, John Clauser, and Anton Zeilinger , most_awards = John Bardeen (2) , website nobelprize.org, previous = 2021 , year2=2022, main=2022, next=2023 The Nobel Prize in Physics is a yearly award given by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for those who have made the most outstanding contributions for humankind in the field of physics. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Bednorz
Johannes Georg Bednorz (; born 16 May 1950) is a German physicist who, together with K. Alex Müller, discovered high-temperature superconductivity in ceramics, for which they shared the 1987 Nobel Prize in Physics. Life and work Bednorz was born in Neuenkirchen, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany to elementary-school teacher Anton and piano teacher Elisabeth Bednorz, as the youngest of four children. His parents were both from Silesia in Central Europe, but were forced to move westwards in turbulences of World War II. including the Nobel Lecture, December 8, 1987 ''Perovskite-Type Oxides – The New Approach to High-Tc Superconductivity'' As a child, his parents tried to get him interested in classical music, but he was more practically inclined, preferring to work on motorcycles and cars. (Although as a teenager he did eventually learn to play the violin and trumpet.) In high school he developed an interest in the natural sciences, focusing on chemistry, which he could learn in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Compounds
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep mantle remain active areas of investigation. Some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon (graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, etc.), carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbides, and the following salts of inorganic anions: carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, and thiocyanates. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it does not occur within living things. History Friedrich Wöhler's conversion of ammonium cyanate into urea in 1828 is often cited as the starting point of modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)