|
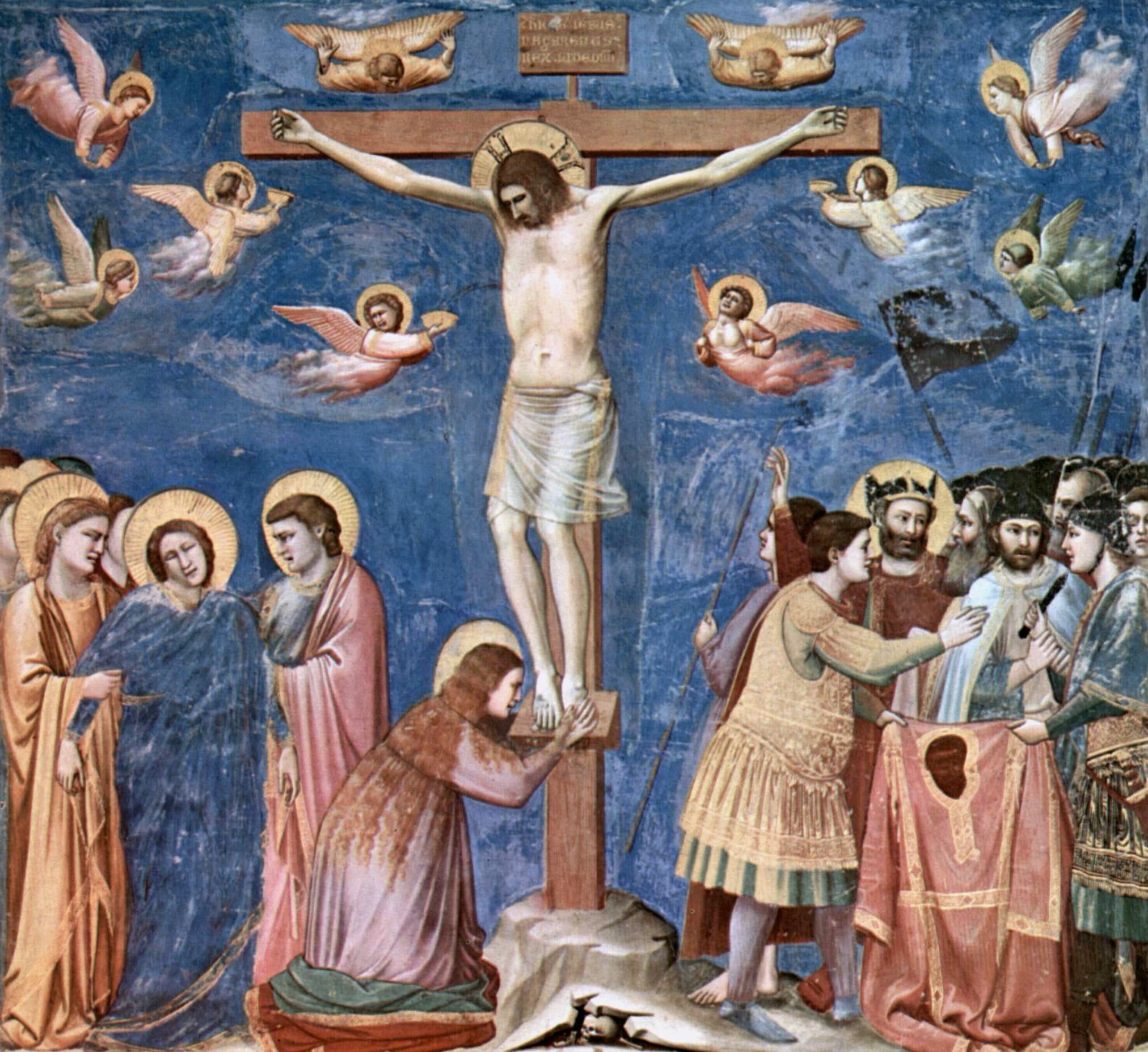
Crucifixion Of Jesus
The crucifixion and death of Jesus occurred in 1st-century Judea, most likely in AD 30 or AD 33. It is described in the four canonical gospels, referred to in the New Testament epistles, attested to by other ancient sources, and considered an established historical event. There is no consensus among historians on the details. Christopher M. Tuckett in ''The Cambridge companion to Jesus'' edited by Markus N. A. Bockmuehl 2001 Cambridge Univ Press pp. 123–124 In the canonical gospels, Jesus is arrested and tried by the Sanhedrin, and then by Pontius Pilate, who sentences him to flagellation and finally crucifixion by the Roman Empire.''The Cradle, the Cross, and the Crown: An Introduction to the New Testament'' by Andreas J. Köstenberger, L. Scott Kellum 2009 pp. 104–108Evans, Craig A. (2001). ''Jesus and His Contemporaries: Comparative Studies'' p. 316 Jesus was stripped of his clothing and offered vinegar mixed with myrrh or gall (likely posca), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazarene (title)
Nazarene is a title used to describe people from the city of Nazareth in the New Testament (there is no mention of either Nazareth or Nazarene in the Old Testament), and is a title applied to Jesus, who, according to the New Testament, grew up in Nazareth,"Jesus was a Galilean from Nazareth, a village near Sepphoris, one of the two major cities of Galilee". ("Jesus Christ." ''Encyclopædia Britannica,'' Chicago, 2009.)"esusspent His boyhood in the Galilean town of Nazareth." (Bromiley, Geoffrey W., "Nazarene," ''The International Standard Bible Encyclopedia: K-P'', pp. 499-500.) a town in Galilee, now in northern Israel. The word is used to translate two related terms that appear in the Greek New Testament: ('Nazarene') and (' Nazorean'). The phrases traditionally rendered as "Jesus of Nazareth" can also be translated as "Jesus the Nazarene" or "Jesus the Nazorean", and the title ''Nazarene'' may have a religious significance instead of denoting a place of origin. Both ''Nazarene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulgate
The Vulgate (; also called (Bible in common tongue), ) is a late-4th-century Latin translation of the Bible. The Vulgate is largely the work of Jerome who, in 382, had been commissioned by Pope Damasus I to revise the Gospels used by the Roman Church. Later, on his own initiative, Jerome extended this work of revision and translation to include most of the books of the Bible. The Vulgate became progressively adopted as the Bible text within the Western Church. Over succeeding centuries, it eventually eclipsed the . By the 13th century it had taken over from the former version the designation (the "version commonly used") or for short. The Vulgate also contains some ''Vetus Latina'' translations which Jerome did not work on. The Vulgate was to become the Catholic Church's officially promulgated Latin version of the Bible as the Sixtine Vulgate (1590), then as the Clementine Vulgate (1592), and then as the '' Nova Vulgata'' (1979). The Vulgate is stil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Sebastian Bach
Johann Sebastian Bach (28 July 1750) was a German composer and musician of the late Baroque period. He is known for his orchestral music such as the '' Brandenburg Concertos''; instrumental compositions such as the Cello Suites; keyboard works such as the '' Goldberg Variations'' and '' The Well-Tempered Clavier''; organ works such as the '' Schubler Chorales'' and the Toccata and Fugue in D minor; and vocal music such as the '' St Matthew Passion'' and the Mass in B minor. Since the 19th-century Bach revival he has been generally regarded as one of the greatest composers in the history of Western music. The Bach family already counted several composers when Johann Sebastian was born as the last child of a city musician in Eisenach. After being orphaned at the age of 10, he lived for five years with his eldest brother Johann Christoph, after which he continued his musical education in Lüneburg. From 1703 he was back in Thuringia, working as a musician for Protest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
True Cross
The True Cross is the cross upon which Jesus was said to have been crucified, particularly as an object of religious veneration. There are no early accounts that the apostles or early Christians preserved the physical cross themselves, although protective use of the sign of the cross was common by at least the 2nd century. Post-Nicene historians such as Socrates of Constantinople relate that Helena, the mother of the Roman emperor ConstantineI, travelled to the Holy Land in the years 326–328, founding churches and establishing relief agencies for the poor. The late 4th-century historians Gelasius of Caesarea and Tyrannius Rufinus claimed that while there she discovered the hiding place of three crosses that were believed to have been used at the crucifixion of Jesus and the two thieves, St. Dismas and Gestas, executed with him. To one cross was affixed the titulus bearing Jesus's name, but according to Rufinus, Helena was not sure until a miracle revealed that this w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Re Militari
''De re militari'' (Latin "Concerning Military Matters"), also ''Epitoma rei militaris'', is a treatise by the Late Latin writer Publius Flavius Vegetius Renatus about Roman warfare and military principles as a presentation of the methods and practices in use during the height of the Roman Empire and responsible for its power. The extant text dates to the 5th century. Vegetius emphasized things such as training of soldiers as a disciplined force, orderly strategy, maintenance of supply lines and logistics, quality leadership and use of tactics and even deceit to ensure advantage over the opposition. He was concerned about selection of good soldiers and recommended hard training of at least four months before the soldier was accepted into the ranks. The leader of the army (''dux'') had to take care of the men under his command and keep himself informed about the movements of the enemy to gain advantage in the battle. ''De re militari'' became a military guide in the Middle A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bibliography
Bibliography (from and ), as a discipline, is traditionally the academic study of books as physical, cultural objects; in this sense, it is also known as bibliology (from ). English author and bibliographer John Carter describes ''bibliography'' as a word having two senses: one, a list of books for further study or of works consulted by an author (or enumerative bibliography); the other one, applicable for collectors, is "the study of books as physical objects" and "the systematic description of books as objects" (or descriptive bibliography). Etymology The word was used by Greek writers in the first three centuries CE to mean the copying of books by hand. In the 12th century, the word started being used for "the intellectual activity of composing books." The 17th century then saw the emergence of the modern meaning, that of description of books. Currently, the field of bibliography has expanded to include studies that consider the book as a material object. Bibliography, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bible (American Standard)/John
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a variety of forms originally written in Hebrew, Aramaic, and Koine Greek. These texts include instructions, stories, poetry, and prophecies, among other genres. The collection of materials that are accepted as part of the Bible by a particular religious tradition or community is called a biblical canon. Believers in the Bible generally consider it to be a product of divine inspiration, but the way they understand what that means and interpret the text can vary. The religious texts were compiled by different religious communities into various official collections. The earliest contained the first five books of the Bible. It is called the Torah in Hebrew and the Pentateuch (meaning ''five books'') in Greek; the second oldest part was a coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious leader; he is the central figure of Christianity, the world's largest religion. Most Christians believe he is the incarnation of God the Son and the awaited Messiah (the Christ) prophesied in the Hebrew Bible. Virtually all modern scholars of antiquity agree that Jesus existed historically. Research into the historical Jesus has yielded some uncertainty on the historical reliability of the Gospels and on how closely the Jesus portrayed in the New Testament reflects the historical Jesus, as the only detailed records of Jesus' life are contained in the Gospels. Jesus was a Galilean Jew who was circumcised, was baptized by John the Baptist, began his own ministry and was often referred to as " rabbi". Jesus debated with fell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
INRI
In the New Testament, Jesus is referred to as the King of the Jews, both at the beginning of his life and at the end. In the Koine Greek of the New Testament, e.g., in John 19:3, this is written as ''Basileus ton Ioudaion'' (). Both uses of the title lead to dramatic results in the New Testament accounts. In the account of the nativity of Jesus in the Gospel of Matthew, the Biblical Magi who come from the east call Jesus the " King of the Jews", causing Herod the Great to order the Massacre of the Innocents. Towards the end of the accounts of all four canonical Gospels, in the narrative of the Passion of Jesus, the title "King of the Jews" leads to charges against Jesus that result in his crucifixion. The initialism INRI ( la, Iēsus Nazarēnus, Rēx Iūdaeōrum) represents the Latin inscription (in John 19:19), which in English translates to "Jesus the Nazarene, King of the Jews", and John 19:20 states that this was written in three languages—Hebrew, Latin, and Greek—d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligence Quotient
An intelligence quotient (IQ) is a total score derived from a set of standardized tests or subtests designed to assess human intelligence. The abbreviation "IQ" was coined by the psychologist William Stern for the German term ''Intelligenzquotient'', his term for a scoring method for intelligence tests at University of Breslau he advocated in a 1912 book. Historically, IQ was a score obtained by dividing a person's mental age score, obtained by administering an intelligence test, by the person's chronological age, both expressed in terms of years and months. The resulting fraction ( quotient) was multiplied by 100 to obtain the IQ score. For modern IQ tests, the raw score is transformed to a normal distribution with mean 100 and standard deviation 15. This results in approximately two-thirds of the population scoring between IQ 85 and IQ 115 and about 2.5 percent each above 130 and below 70. Scores from intelligence tests are estimates of intelligence. Unlike, for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prometheus Society
The Prometheus Society is a high IQ society, similar to Mensa International, but much more restrictive. The entry criterion, achievable by a number of tests, is designed to be passable by 1 in 30,000 of the population, while Mensa entry is achievable by 1 in 50. The society produces a magazine, ''Gift of Fire'', published ten times per year. History Background An earlier organization, Mensa International, was founded by Roland Berrill and Lancelot Ware, who noted from their first conversation that although they came from different backgrounds, they were able to communicate and had much in common. They hypothesized that what they had in common was intelligence, and decided to see if a society of people selected for intelligence (using the only means then available, IQ tests) would also have much in common. They decided to focus on people whose IQ test scores would place them at or above the 98th percentile. Beyond the 98th percentile In the late 1930s Leta Stetter Hollingwor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


.jpg)

