|
Prometheus Society
The Prometheus Society is a high IQ society, similar to Mensa International, but much more restrictive. The entry criterion, achievable by a number of tests, is designed to be passable by 1 in 30,000 of the population, while Mensa entry is achievable by 1 in 50. The society produces a magazine, ''Gift of Fire'', published ten times per year. History Background An earlier organization, Mensa International, was founded by Roland Berrill and Lancelot Ware, who noted from their first conversation that although they came from different backgrounds, they were able to communicate and had much in common. They hypothesized that what they had in common was intelligence, and decided to see if a society of people selected for intelligence (using the only means then available, IQ tests) would also have much in common. They decided to focus on people whose IQ test scores would place them at or above the 98th percentile. Beyond the 98th percentile In the late 1930s Leta Stetter Hollingwor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High IQ Society
A high-IQ society is an organization that limits its membership to people who have attained a specified score on an IQ test, usually in the top two percent of the population (98th percentile) or above. These may also be referred to as genius societies. The largest and oldest such society is Mensa International, which was founded by Roland Berrill and Lancelot Ware in 1946. Entry requirements High-IQ societies typically accept a variety of IQ tests for membership eligibility; these include WAIS, Stanford-Binet, and Raven's Advanced Progressive Matrices Raven's Progressive Matrices (often referred to simply as Raven's Matrices) or RPM is a non-verbal test typically used to measure general human intelligence and abstract reasoning and is regarded as a non-verbal estimate of fluid intelligence. It ..., amongst many others deemed to sufficiently measure or correlate with intelligence. Tests deemed to insufficiently correlate with intelligence (e.g. post-1994 SAT, in the case of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychometrics
Psychometrics is a field of study within psychology concerned with the theory and technique of measurement. Psychometrics generally refers to specialized fields within psychology and education devoted to testing, measurement, assessment, and related activities. Psychometrics is concerned with the objective measurement of latent constructs that cannot be directly observed. Examples of latent constructs include intelligence, introversion, mental disorders, and educational achievement. The levels of individuals on nonobservable latent variables are inferred through mathematical modeling based on what is observed from individuals' responses to items on tests and scales. Practitioners are described as psychometricians, although not all who engage in psychometric research go by this title. Psychometricians usually possess specific qualifications such as degrees or certifications, and most are psychologists with advanced graduate training in psychometrics and measurement theory. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ronald K
Ronald is a masculine given name derived from the Old Norse ''Rögnvaldr'', Hanks; Hardcastle; Hodges (2006) p. 234; Hanks; Hodges (2003) § Ronald. or possibly from Old English '' Regenweald''. In some cases ''Ronald'' is an Anglicised form of the Gaelic '' Raghnall'', a name likewise derived from ''Rögnvaldr''. The latter name is composed of the Old Norse elements ''regin'' ("advice", "decision") and ''valdr'' ("ruler"). ''Ronald'' was originally used in England and Scotland, where Scandinavian influences were once substantial, although now the name is common throughout the English-speaking world. A short form of ''Ronald'' is ''Ron''. Pet forms of ''Ronald'' include ''Roni'' and ''Ronnie''. ''Ronalda'' and ''Rhonda'' are feminine forms of ''Ronald''. '' Rhona'', a modern name apparently only dating back to the late nineteenth century, may have originated as a feminine form of ''Ronald''. Hanks; Hardcastle; Hodges (2006) pp. 230, 408; Hanks; Hodges (2003) § Rhona. The names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mike Sager
Mike Sager (born August 17, 1956) is an American author, journalist, and educator. A former ''Washington Post'' staff writer, ''Rolling Stone'' contributing editor, and writer at large for '' GQ'', Sager has been a contributing writer for ''Esquire'' for more than three decades. In 2010 he received the American Society of Magazine Editors' National Magazine award for profile writing for his story "The Man Who Never Was," which appeared in ''Esquire''. He is the author of more than a dozen books, and has served as an editor on several journalism text books. Sager has read and lectured at American schools of journalism. In 2012 he founded The Sager Group LLC, a content brand with a variety of functions ranging from publishing to film making, to general marketing. Early life and education Sager was born in Charlottesville, Virginia, to Beverly Rosenberg and Marvin Miles Sager—from, respectively, Culpeper and Fredericksburg, Virginia. The family, along with younger sister Wen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times Crossword Puzzle
''The New York Times'' crossword puzzle is a daily crossword puzzle published in '' The New York Times'', online on the newspaper's website, syndicated to more than 300 other newspapers and journals, and on mobile apps. The puzzle is created by various freelance constructors and has been edited by Will Shortz since 1993. The crosswords are designed to increase in difficulty throughout the week, with the easiest puzzle on Monday and the most difficult on Saturday. The larger Sunday crossword, which appears in '' The New York Times Magazine'', is an icon in American culture; it is typically intended to be as difficult as a Thursday puzzle. The standard daily crossword is 15 by 15 squares, while the Sunday crossword measures 21 by 21 squares. History Although crosswords became popular in the early 1920s, ''The New York Times'' (which initially regarded crosswords as frivolous, calling them "a primitive form of mental exercise") did not begin to run a crossword until 1942, in its S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoffrey Miller (evolutionary Psychologist)
Geoffrey Franklin Miller (born 1965) is an American evolutionary psychologist, author, and associate professor of psychology at the University of New Mexico. He is known for his research on sexual selection in human evolution. Education, career, and personal life Born in Cincinnati, Ohio, Miller graduated from Columbia University in 1987, where he earned a BA in biology and psychology. He received his PhD in cognitive psychology from Stanford University in 1993, under the guidance of Roger Shepard. Miller has held positions as a postdoctoral researcher in the evolutionary and adaptive systems group in the School of Cognitive and Computing Sciences at the University of Sussex (1992–94); lecturer in the department of psychology at the University of Nottingham (1995); research scientist at the Center for Adaptive Behavior and Cognition at the Max Planck Institute for Psychological Research, Munich, Germany (1995–96); and senior research fellow at the Centre for Economic Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castle (TV Series)
''Castle'' is an American crime mystery/comedy-drama television series that aired on ABC for a total of eight seasons from March 9, 2009, to May 16, 2016. The series was produced jointly by Beacon Pictures and ABC Studios. Created by Andrew W. Marlowe, it primarily traces the lives of Richard Castle (Nathan Fillion), a best-selling mystery novelist, and Kate Beckett ( Stana Katic), a homicide detective, as they solve various unusual crimes in New York City. Detective Beckett is initially infuriated at the thought of working with a writer and goes to great lengths to keep him out of her way. However, the two soon start developing feelings for each other. The overarching plot of the series focused on the romance between the two lead characters and their ongoing investigation of the murder of Beckett's mother. On May 12, 2016, it was announced that despite some cast members signing one-year contracts for a potential ninth season, the show was canceled. Premise Richard Castl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Da Capo Press
Da Capo Press is an American publishing company with headquarters in Boston, Massachusetts. It is now an imprint of Hachette Books. History Founded in 1964 as a publisher of music books, as a division of Plenum Publishers, it had additional offices in New York City, Philadelphia, Los Angeles, and Emeryville, California. The year prior, Da Capo Press had net sales of over $2.5 million. Da Capo Press became a general trade publisher in the mid-1970s. It was sold to the Perseus Books Group in 1999 after Plenum was sold to Wolters Kluwer. In the last decade, its production has consisted of mostly nonfiction titles, both hardcover and paperback, focusing on history, music, the performing arts, sports, and popular culture. In 2003, Lifelong Books was founded as a health and wellness imprint. When Marlowe & Company became part of the imprint in 2007, Lifelong's range was expanded to include the New Glucose Revolution series and numerous diabetes titles, as well as books on healthf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cattell Culture Fair III
The Culture Fair Intelligence Test (CFIT) was created by Raymond Cattell in 1949 as an attempt to measure cognitive abilities devoid of sociocultural and environmental influences. Scholars have subsequently concluded that the attempt to construct measures of cognitive abilities devoid of the influences of experiential and cultural conditioning is a challenging one. Cattell proposed that general intelligence (g) comprises both fluid intelligence (Gf) and crystallized intelligence (Gc). Whereas Gf is biologically and constitutionally based, Gc is the actual level of a person's cognitive functioning, based on the augmentation of Gf through sociocultural and experiential learning (including formal schooling). Cattell built into the CFIT a standard deviation of 16 IQ points. Cultural and age differences Crystallized intelligence (Gc) refers to that aspect of cognition in which initial intelligent judgments have become crystallized as habits. Fluid intelligence (Gf) is in several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
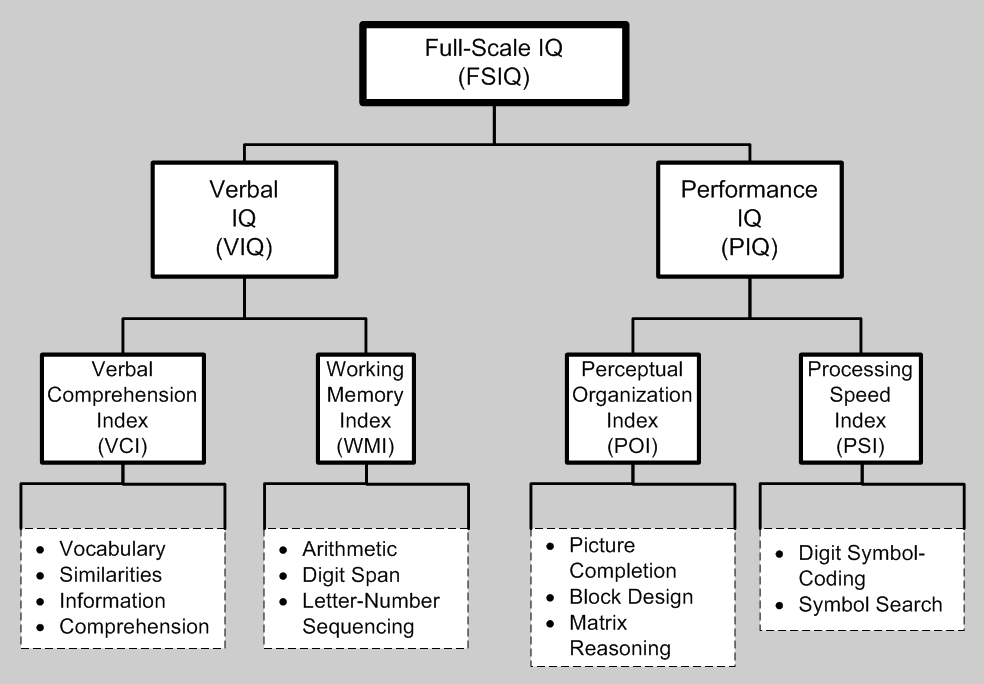
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale
The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) is an IQ test designed to measure intelligence and cognitive ability in adults and older adolescents. The original WAIS (Form I) was published in February 1955 by David Wechsler, as a revision of the Wechsler–Bellevue Intelligence Scale, released in 1939. It is currently in its fourth edition (''WAIS-IV'') released in 2008 by Pearson, and is the most widely used IQ test, for both adults and older adolescents, in the world. History The WAIS is founded on Wechsler's definition of intelligence, which he defined as "... the global capacity of a person to act purposefully, to think rationally, and to deal effectively with his environment." He believed that intelligence was made up of specific elements that could be isolated, defined, and subsequently measured. However, these individual elements were not entirely independent, but were all interrelated. His argument, in other words, is that general intelligence is composed of various spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
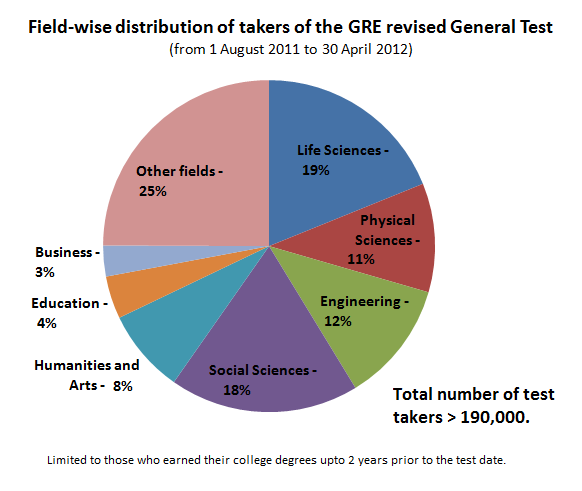
Graduate Record Examination
The Graduate Record Examinations (GRE) is a standardized test that is an admissions requirement for many graduate schools in the United States and Canada and a few other countries. The GRE is owned and administered by Educational Testing Service (ETS). The test was established in 1936 by the Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching. According to ETS, the GRE aims to measure verbal reasoning, quantitative reasoning, analytical writing, and critical thinking skills that have been acquired over a long period of learning. The content of the GRE consists of certain specific algebra, geometry, arithmetic, and vocabulary sections. The GRE General Test is offered as a computer-based exam administered at testing centers and institution owned or authorized by Prometric. In the graduate school admissions process, the level of emphasis that is placed upon GRE scores varies widely between schools and departments within schools. The importance of a GRE score can range from bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Distribution
In statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is : f(x) = \frac e^ The parameter \mu is the mean or expectation of the distribution (and also its median and mode), while the parameter \sigma is its standard deviation. The variance of the distribution is \sigma^2. A random variable with a Gaussian distribution is said to be normally distributed, and is called a normal deviate. Normal distributions are important in statistics and are often used in the natural and social sciences to represent real-valued random variables whose distributions are not known. Their importance is partly due to the central limit theorem. It states that, under some conditions, the average of many samples (observations) of a random variable with finite mean and variance is itself a random variable—whose distribution converges to a normal d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |