|
Fokos
The shepherd's axe is a long thin light axe of Eurasian origin used in past centuries by shepherds in the Carpathian Mountains and in other territories which comprise today Slovakia, Czech Republic, Poland, Ukraine, Romania and Hungary. The features of a shepherd's axe combine a tool with a walking stick, that could be used as a light weapon. It has symbolic historical and cultural connotations and is still used as a prop in many traditional dances, for example the odzemek. Languages Depending on the language, the axe is called as follows: ; , lit. "Romanian"; Polish (depending on the region): ''ciupaga, rąbanica, obuszek, cekanka, wataha, wataszka'', the latter two from Romanian ''vătaf'' ("master shepherd"); ; ; , lit. "Romanian"; ). Appearance A shepherd's axe is a light axe with a long and straight wooden shaft, often with a metal butt. The length of the shaft is usually slightly more than 1 metre. The shafts were usually engraved as their owners had plenty of tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciupaga
The shepherd's axe is a long thin light axe of Eurasian origin used in past centuries by shepherds in the Carpathian Mountains and in other territories which comprise today Slovakia, Czech Republic, Poland, Ukraine, Romania and Hungary. The features of a shepherd's axe combine a tool with a walking stick, that could be used as a light weapon. It has symbolic historical and cultural connotations and is still used as a prop in many traditional dances, for example the odzemek. Languages Depending on the language, the axe is called as follows: ; , lit. "Romanian"; Polish (depending on the region): ''ciupaga, rąbanica, obuszek, cekanka, wataha, wataszka'', the latter two from Romanian ''vătaf'' ("master shepherd"); ; ; , lit. "Romanian"; ). Appearance A shepherd's axe is a light axe with a long and straight wooden shaft, often with a metal butt. The length of the shaft is usually slightly more than 1 metre. The shafts were usually engraved as their owners had plenty of ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
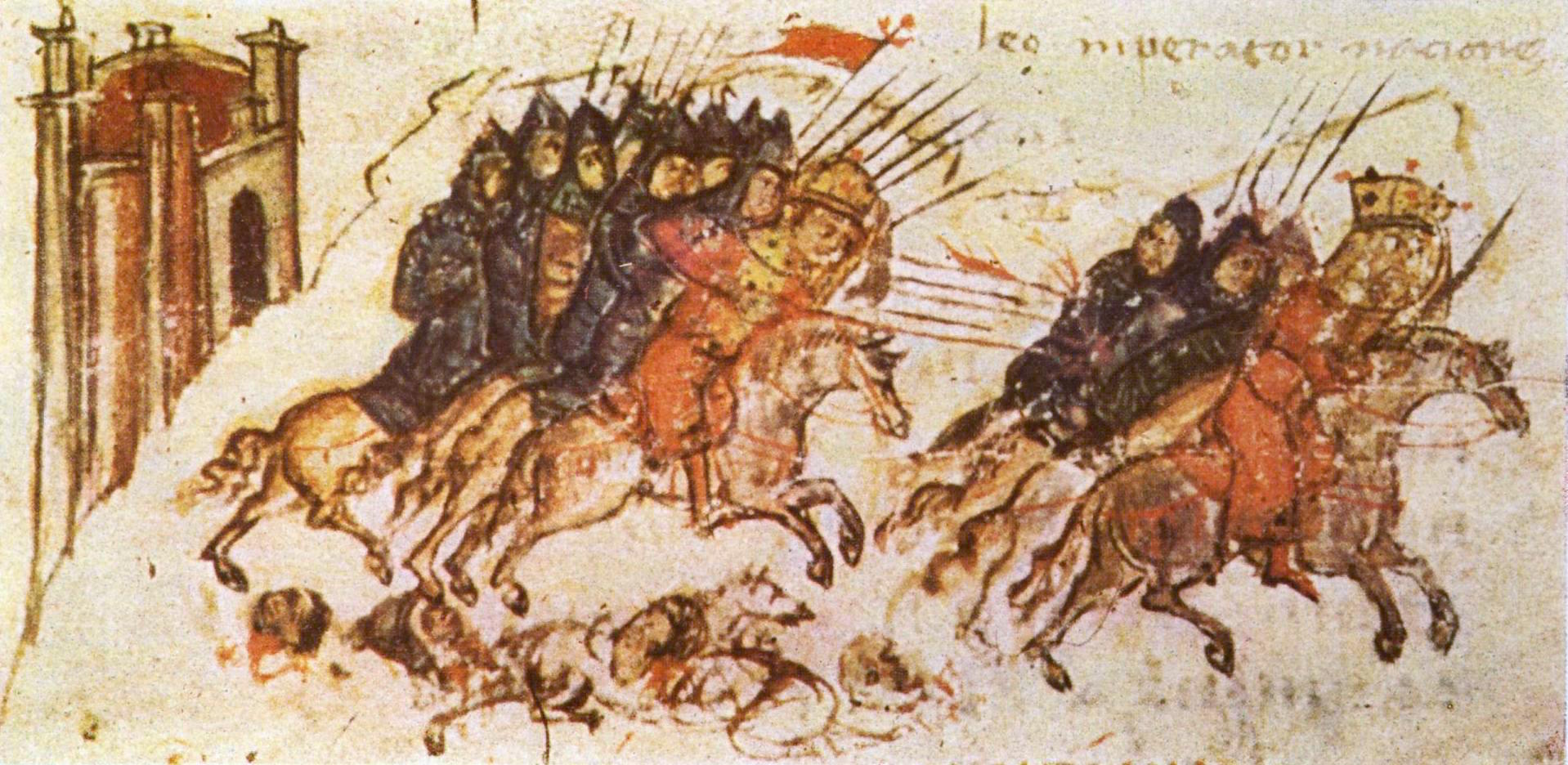
Pannonian Avars
The Pannonian Avars () were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in chronicles of Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai ( el, Βαρχονίτες, Varchonítes), or Pseudo-Avars in Byzantine sources, and the Apar ( otk, 𐰯𐰺) to the Göktürks (). They established the Avar Khaganate, which spanned the Pannonian Basin and considerable areas of Central and Eastern Europe from the late 6th to the early 9th century. The name Pannonian Avars (after the area in which they settled) is used to distinguish them from the Avars of the Caucasus, a separate people with whom the Pannonian Avars might or might not have had links. Although the name ''Avar'' first appeared in the mid-5th century, the Pannonian Avars entered the historical scene in the mid-6th century, on the Pontic–Caspian steppe as a people who wished to escape the rule of the Göktürks. They are probably best known for their invasions and destruction in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juraj Jánošík
Juraj Jánošík (first name also ''Juro'' or ''Jurko'', ; baptised 25 January 1688, died 17 March 1713) was a Slovak highwayman. Jánošík has been the main character of many Slovak novels, poems, and films. According to the legend, he robbed nobles and gave the loot to the poor, a deed often attributed to the famous Robin Hood. The legend is known in neighboring Poland (under the name ''Jerzy Janoszik'' also ''Janosik'', ''Janiczek'' or ''Janicek'') and the Czech Republic. The actual robber had little to do with the modern legend, whose content partly reflects the ubiquitous folk myths of a hero taking from the rich and giving to the poor. However, the legend was also shaped in important ways by the activists and writers in the 19th century when Jánošík became the key highwayman character in stories that spread in the north counties of the Kingdom of Hungary (much in present Slovakia) and among the local Gorals inhabitants of the Podhale region north of the Tatras. The imag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovak Culture
The culture of Slovakia has various folk traditions influenced by its location in Central Europe. It shares similarities with Czech, Austrian, German, Hungarian and Ukrainian culture. Folk tradition Folk tradition has rooted strongly in Slovakia and is reflected in literature, music, dance and architecture. The prime example is a Slovak national anthem, ''"Nad Tatrou sa blýska"'', which is based on a melody from ''" Kopala studienku"'' folk song. Manifestation of Slovak folklore culture is the "''Východná''" Folklore Festival. It is the oldest and largest nationwide festival with international participation, which takes place in Východná annually. Slovakia is usually represented by many groups but mainly by SĽUK (''Slovenský ľudový umelecký kolektív—Slovak folk art collective''). SĽUK is the largest Slovak folk art group, trying to preserve the folklore tradition. An example of wooden folk architecture in Slovakia can be seen in the well preserved village of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinaric Mountains
The Dinaric Alps (), also Dinarides, are a mountain range in Southern and Southcentral Europe, separating the continental Balkan Peninsula from the Adriatic Sea. They stretch from Italy in the northwest through Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia, Montenegro, and Kosovo to Albania in the southeast. The Dinaric Alps extend for approximately along the western Balkan peninsula from the Julian Alps of the northeast Italy, downwards to the Šar and Korab massif, where their direction changes. The Accursed Mountains, is the highest section of the entire Dinaric Alps; this section stretches from Albania to Kosovo and eastern Montenegro. Maja Jezercë is the highest peak and is located in Albania, standing at above the Adriatic. The Dinaric Alps are one of the most rugged and extensive mountainous areas of Europe, alongside the Caucasus Mountains, Alps, Pyrenees, Carpathian Mountains and Scandinavian Mountains. They are formed largely of Mesozoic and Cenozoic se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the area's history. The concept of "Central Europe" appeared in the 19th century. Central Europe comprised most of the territories of the Holy Roman Empire and those of the two neighboring kingdoms of Poland and Hungary. Hungary and parts of Poland were later part of the Habsburg monarchy, which also significantly shaped the history of Central Europe. Unlike their Western European (Portugal, Spain et al.) and Eastern European (Russia) counterparts, the Central European nations never had any notable colonies (either overseas or adjacent) due to their inland location and other factors. It has often been argued that one of the contributing causes of both World War I and World War II was Germany's lack of original overseas colonies. After World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vlachs
"Vlach" ( or ), also "Wallachian" (and many other variants), is a historical term and exonym used from the Middle Ages until the Modern Era to designate mainly Romanians but also Aromanians, Megleno-Romanians, Istro-Romanians and other Eastern Romance-speaking subgroups of Central and Eastern Europe. As a contemporary term, in the English language, the Vlachs are the Balkan Romance-speaking peoples who live south of the Danube in what are now southern Albania, Bulgaria, northern Greece, North Macedonia, and eastern Serbia as native ethnic groups, such as the Aromanians, Megleno-Romanians and the Timok Romanians. The term also became a synonym in the Balkans for the social category of shepherds, and was also used for non-Romance-speaking peoples, in recent times in the western Balkans derogatively. The term is also used to refer to the ethnographic group of Moravian Vlachs who speak a Slavic language but originate from Romanians. "Vlachs" were initially identified and des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, mainly inhabiting Central and Eastern Europe, and the Balkans to the west; and Siberia to the east. A large Slavic minority is also scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, while a substantial Slavic diaspora is found throughout the Americas, as a result of immigration. Present-day Slavs are classified into East Slavs (chiefly Belarusians, Russians, Rusyns, and Ukrainians), West Slavs (chiefly Czechs, Kashubians, Poles, Slovaks and Sorbs) and South Slavs (chiefly Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs and Slovenes). The vast majority of Slavs are traditionally Christians. However, modern Slavic nations and ethnic groups are considerably diverse both genetically and culturally, and relations between them � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
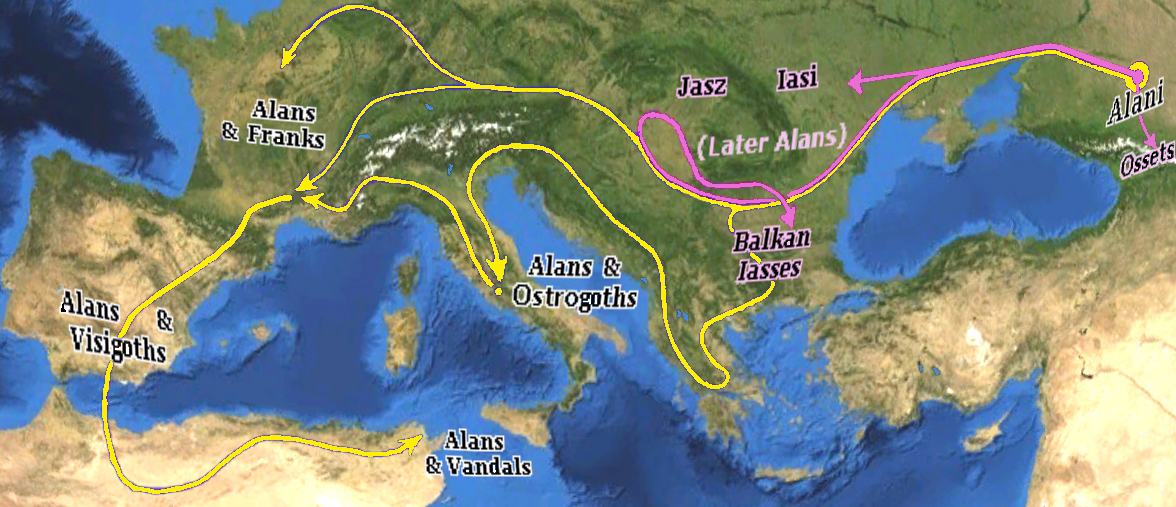
Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the Alans with the Central Asian Yancai of Chinese sources and with the Aorsi of Roman sources. Having migrated westwards and becoming dominant among the Sarmatians on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Alans are mentioned by Roman sources in the . At that time they had settled the region north of the Black Sea and frequently raided the Parthian Empire and the Caucasian provinces of the Roman Empire. From the Goths broke their power on the Pontic Steppe. Upon the Hunnic defeat of the Goths on the Pontic Steppe around , many of the Alans migrated westwards along with various Germanic tribes. They crossed the Rhine in 406CE along with the Vandals and Suebi, settling in Orléans and Valence. Around 409 CE they joined the Vandals and Suebi in cro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region during the 7th century. They became known as nomadic equestrians in the Volga-Ural region, but some researchers say that their ethnic roots can be traced to Central Asia. During their westward migration across the Eurasian steppe, the Bulgar tribes absorbed other tribal groups and cultural influences in a process of ethnogenesis, including Iranian, Finnic and Hunnic tribes. Modern genetic research on Central Asian Turkic people and ethnic groups related to the Bulgars points to an affiliation with Western Eurasian populations. The Bulgars spoke a Turkic language, i.e. Bulgar language of Oghuric branch. They preserved the military titles, organization and customs of Eurasian steppes, as well as pagan shamanism and belief in the sky deity Tangra. The Bulgars became semi-sedentary durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Language
Hungarian () is an Uralic language spoken in Hungary and parts of several neighbouring countries. It is the official language of Hungary and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Outside Hungary, it is also spoken by Hungarian communities in southern Slovakia, western Ukraine ( Subcarpathia), central and western Romania (Transylvania), northern Serbia (Vojvodina), northern Croatia, northeastern Slovenia (Prekmurje), and eastern Austria. It is also spoken by Hungarian diaspora communities worldwide, especially in North America (particularly the United States and Canada) and Israel. With 17 million speakers, it is the Uralic family's largest member by number of speakers. Classification Hungarian is a member of the Uralic language family. Linguistic connections between Hungarian and other Uralic languages were noticed in the 1670s, and the family itself (then called Finno-Ugric) was established in 1717. Hungarian has traditionally been assigned to the Ugric alo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Academy Of Sciences
The Hungarian Academy of Sciences ( hu, Magyar Tudományos Akadémia, MTA) is the most important and prestigious learned society of Hungary. Its seat is at the bank of the Danube in Budapest, between Széchenyi rakpart and Akadémia utca. Its main responsibilities are the cultivation of science, dissemination of scientific findings, supporting research and development, and representing Hungarian science domestically and around the world. History The history of the academy began in 1825 when Count István Széchenyi offered one year's income of his estate for the purposes of a ''Learned Society'' at a district session of the Diet in Pressburg (Pozsony, present Bratislava, seat of the Hungarian Parliament at the time), and his example was followed by other delegates. Its task was specified as the development of the Hungarian language and the study and propagation of the sciences and the arts in Hungarian. It received its current name in 1845. Its central building was inaugurate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |