|
Fibrinolytic Enzyme
Fibrinolysis is a process that prevents blood clots from growing and becoming problematic. Primary fibrinolysis is a normal body process, while secondary fibrinolysis is the breakdown of clots due to a medicine, a medical disorder, or some other cause. In fibrinolysis, a fibrin clot, the product of coagulation, is broken down. Its main enzyme plasmin cuts the fibrin mesh at various places, leading to the production of circulating fragments that are cleared by other proteases or by the kidney and liver. Physiology Plasmin is produced in an inactive form, plasminogen, in the liver. Although plasminogen cannot cleave fibrin, it still has an affinity for it, and is incorporated into the clot when it is formed. Tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) and urokinase are the agents that convert plasminogen to the active plasmin, thus allowing fibrinolysis to occur. t-PA is released into the blood slowly by the damaged endothelium of the blood vessels, such that, after several days (when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombus
A thrombus ( thrombi) is a solid or semisolid aggregate from constituents of the blood (platelets, fibrin, red blood cells, white blood cells) within the circulatory system during life. A blood clot is the final product of the blood coagulation step in hemostasis in or out of the circulatory system. There are two components to a thrombus: aggregated platelets and red blood cells that form a plug, and a mesh of cross-linked fibrin protein. The substance making up a thrombus is sometimes called cruor. A thrombus is a healthy response to injury intended to stop and prevent further bleeding, but can be harmful in thrombosis, when a clot obstructs blood flow through a healthy blood vessel in the circulatory system. In the microcirculation consisting of the very small and smallest blood vessels the capillaries, tiny thrombi known as microclots can obstruct the flow of blood in the capillaries. This can cause a number of problems particularly affecting the pulmonary alveolus, alveoli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissue Plasminogen Activator
Tissue-type plasminogen activator, short name tPA, is a protein that facilitates the breakdown of blood clots. It acts as an enzyme to convert plasminogen into its active form plasmin, the major enzyme responsible for clot breakdown. It is a serine protease () found on endothelial cells lining the blood vessels. Human tPA is encoded by the ''PLAT'' gene, and has a molecular weight of ~70 kDa in the single-chain form. tPA can be manufactured using recombinant biotechnology techniques, producing types of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rtPA) such as alteplase, reteplase, and tenecteplase. These drugs are used in clinical medicine to treat embolic or thrombotic stroke, but they are contraindicated and dangerous in cases of hemorrhagic stroke and head trauma. The antidote for tPA in case of toxicity is aminocaproic acid. Medical uses tPA is used in some cases of diseases that feature blood clots, such as pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, and stroke, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euglobulin Lysis Time
The euglobulin lysis time (ELT) is a test that measures overall fibrinolysis. The test is performed by mixing citrated platelet-poor plasma with acid in a glass test tube. This acidification causes the precipitation of certain clotting factors in a complex called the ''euglobulin fraction''. The euglobulin fraction contains the important fibrinolytic factors fibrinogen, PAI-1, tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), plasminogen, and to a lesser extent α2-antiplasmin. The euglobulin fraction also contains factor VIII. After precipitation, the euglobulin fraction is resuspended in a borate solution. Clotting is then activated by the addition of calcium chloride at 37 °C. Historically, subsequent amount of fibrinolysis was determined by eye, by observing the clot within the test tube at ten-minute intervals until complete lysis had occurred. Newer automated methods have also been developed. These methods use the same principle as the older technique, but use a spectrophotome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aprotinin
The drug aprotinin (Trasylol, previously Bayer and now Nordic Group pharmaceuticals), is a small protein bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (BPTI), or basic trypsin inhibitor of bovine pancreas, which is an antifibrinolytic molecule that inhibits trypsin and related proteolytic enzymes. Under the trade name Trasylol, aprotinin was used as a medication administered by injection to reduce bleeding during complex surgery, such as heart and liver surgery. Its main effect is the slowing down of fibrinolysis, the process that leads to the breakdown of blood clots. The aim in its use was to decrease the need for blood transfusions during surgery, as well as end-organ damage due to hypotension (low blood pressure) as a result of marked blood loss. The drug was temporarily withdrawn worldwide in 2007 after studies suggested that its use increased the risk of complications or death; this was confirmed by follow-up studies. Trasylol sales were suspended in May 2008, except for very restrict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
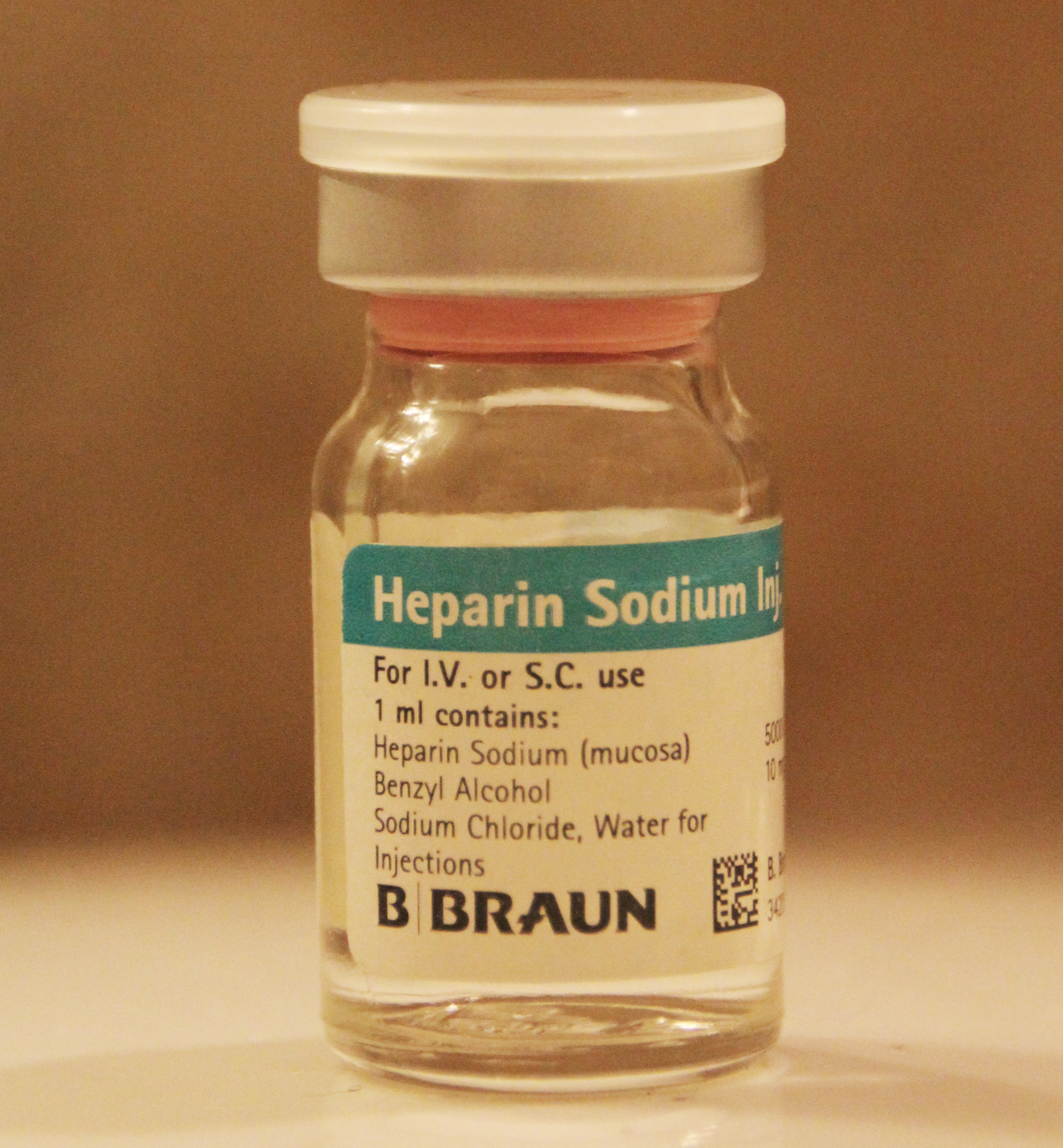
Heparin
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Heparin is a blood anticoagulant that increases the activity of antithrombin. It is used in the treatment of myocardial infarction, heart attacks and unstable angina. It can be given intravenously or by subcutaneous injection, injection under the skin. Its anticoagulant properties make it useful to prevent blood clotting in blood specimen test tubes and kidney dialysis machines. Common side effects include bleeding, pain at the injection site, and thrombocytopenia, low blood platelets. Serious side effects include heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Greater care is needed in those with poor kidney function. Heparin is contraindicated for suspected cases of Post-vaccination embolic and thrombotic events, vaccine-induced pro-thrombotic immune thrombocytopenia (VIPIT) secondary to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, as heparin may further increase the risk of bleeding in an anti-PF4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thromboelastometry
Thromboelastometry (TEM), previously named rotational thromboelastography (ROTEG) or rotational thromboelastometry (ROTEM), is an established viscoelastic method for hemostasis testing in whole blood. It is a modification of traditional thromboelastography (TEG). TEM investigates the interaction of coagulation factors, their inhibitors, anticoagulant drugs, blood cells, specifically platelets, during clotting and subsequent fibrinolysis. The rheological conditions mimic the sluggish flow of blood in veins. While traditional thromboelastography is a global assay for blood clotting disorders and drug effects, TEM is primarily used in combination with appropriate differential assays. They allow testing in the presence of therapeutic heparin concentrations and provide differential diagnostic information to support decisions in therapy. In numerous publications, the validity of the method is shown. Application of TEM at the point of care (POC) or in emergency laboratories is g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocardial Infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is retrosternal Angina, chest pain or discomfort that classically radiates to the left shoulder, arm, or jaw. The pain may occasionally feel like heartburn. This is the dangerous type of acute coronary syndrome. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, presyncope, feeling faint, a diaphoresis, cold sweat, Fatigue, feeling tired, and decreased level of consciousness. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms. Women more often present without chest pain and instead have neck pain, arm pain or feel tired. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an Cardiac arrhythmia, irregular heartbeat, cardiogenic shock or cardiac arrest. Most MIs occur d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition in which blood clots form throughout the body, blocking Microvessel, small blood vessels. Symptoms may include chest pain, shortness of breath, leg pain, problems speaking, or problems moving parts of the body. As clotting factors and platelets are used up, bleeding may occur. This may include hematuria, blood in the urine, GI bleed, blood in the stool, or bleeding into the skin. Complications may include organ failure. Relatively common causes include sepsis, surgery, major trauma, cancer, and complications of pregnancy. Less common causes include snake bites, frostbite, and burns. There are two main types: acute (rapid onset) and chronic (slow onset). Diagnosis is typically based on blood tests. Findings may include thrombocytopenia, low platelets, low fibrinogen, high International normalized ratio, INR, or high D-dimer. Treatment is mainly directed towards the underlying condition. Other measures may include givin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an pulmonary artery, artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include dyspnea, shortness of breath, chest pain particularly upon breathing in, and coughing up blood. Symptoms of a deep vein thrombosis, blood clot in the leg may also be present, such as a erythema, red, warm, swollen, and painful leg. Signs of a PE include low blood oxygen saturation, oxygen levels, tachypnea, rapid breathing, tachycardia, rapid heart rate, and sometimes a mild fever. Severe cases can lead to Syncope (medicine), passing out, shock (circulatory), abnormally low blood pressure, obstructive shock, and cardiac arrest, sudden death. PE usually results from a blood clot in the leg that travels to the lung. The risk of blood clots is increased by advanced age, cancer, prolonged bed rest and immobilization, smoking, stroke, long-haul travel over 4 hours, certain genetics, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep-vein Thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enlarged veins in the affected area, but some DVTs have no symptoms. The most common life-threatening concern with DVT is the potential for a clot to embolize (detach from the veins), travel as an embolus through the right side of the heart, and become lodged in a pulmonary artery that supplies blood to the lungs. This is called a pulmonary embolism (PE). DVT and PE comprise the cardiovascular disease of venous thromboembolism (VTE). About two-thirds of VTE manifests as DVT only, with one-third manifesting as PE with or without DVT. The most frequent long-term DVT Complication (medicine), complication is post-thrombotic syndrome, which can cause pain, swelling, a sensation of heaviness, itching, and in severe cases, ulcers. Recurrent VTE o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D-dimer
D-dimer (or D dimer) is a dimer that is a fibrin degradation product (FDP), a small protein fragment present in the blood after a blood clot is degraded by fibrinolysis. It is so named because it contains two D fragments of the fibrin protein joined by a cross-link, hence forming a protein dimer. D-dimer concentration may be determined by a blood test to help diagnose thrombosis. Since its introduction in the 1990s, it has become an important test performed in people with suspected thrombotic disorders, such as venous thromboembolism. While a negative result practically rules out thrombosis, a positive result can indicate thrombosis but does not exclude other potential causes. Its main use, therefore, is to exclude thromboembolic disease where the probability is low. D-dimer levels are used as a predictive biomarker for the blood disorder disseminated intravascular coagulation and in the coagulation disorders associated with COVID-19 infection. A four-fold increase in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibrin Degradation Product
Fibrin degradation products (FDPs), also known as fibrin split products, are components of the blood produced by clot degeneration. Clotting, also called coagulation, at the wound site produces a mass of fibrin threads called a net that remains in place until the cut is healed. As a cut heals, the clotting slows down. Eventually the clot is broken down and dissolved by plasmin. When the clot and fibrin net dissolve, fragments of protein are released into the body. These fragments are fibrin degradation products or FDPs. If your body is unable to dissolve a clot, you may have abnormal levels of FDPs. The most notable subtype of fibrin degradation products is D-dimer. The levels of these FDPs rise after any thrombotic event. Fibrin and fibrinogen degradation product (FDP) testing is commonly used to diagnose disseminated intravascular coagulation. As tumor marker A tumor marker known as AMDL-ELISA DR-70 (FDP), and now as Onko-Sure, was approved by the US FDA on July 1, 2008 for in v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |