|
Endorphin
Endorphins (contracted from endogenous morphine) are chemical signals in the brain that block the perception of pain and increase feelings of wellbeing. They are produced and stored in an area of the brain known as the pituitary gland. History Opioid peptides in the brain were first discovered in 1973 by investigators at the University of Aberdeen, John Hughes (neuroscientist), John Hughes and Hans Kosterlitz. They isolated "enkephalins" (from the Greek language, Greek , ') from pig brain, identified as Met-enkephalin and Leu-enkephalin. This came after the discovery of a receptor that was proposed to produce the pain-relieving analgesic effects of morphine and other opioids, which led Kosterlitz and Hughes to their discovery of the endogenous opioid ligands. Research during this time was focused on the search for a painkiller that did not have the addictive character or overdose risk of morphine. Rabi Simantov and Solomon H. Snyder isolated morphine-like peptides from cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
╬▓-endorphin
''beta''-Endorphin (╬▓-endorphin) is an endogenous opioid neuropeptide and peptide hormone that is produced in certain neurons within the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. It is one of three endorphins that are produced in humans, the others of which include ╬▒-endorphin and ╬│-endorphin. The amino acid sequence is: tyrosine, Tyr-Glycine, Gly-Gly-Phenylalanine, Phe-Methionine, Met-Threonine, Thr-Serine, Ser-glutamic acid, Glu-Lysine, Lys-Ser-Glutamine, Gln-Thr-Proline, Pro-Leucine, Leu-Valine, Val-Thr-Leu-Phe-Lys-Asparagine, Asn-Alanine, Ala-Isoleucine, Ile-Ile-Lys-Asn-Ala-Tyr-Lys-Lys-Gly-Glu (31 amino acids). The first 16 amino acids are identical to ╬▒-endorphin. ╬▓-Endorphin is considered to be a part of the endogenous opioid and endorphin classes of neuropeptides; all of the established endogenous opioid peptides contain the same N-terminal amino acid sequence, Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe, followed by either or . Function of ╬▓-endorphin has been known to be assoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
╬▒-endorphin
╬▒-Endorphin is an endogenous opioid peptide with a length of 16 amino acids, and the amino acid sequence: tyrosine, Tyr-glycine, Gly-Gly-phenylalanine, Phe-methionine, Met-threonine, Thr-serine, Ser-glutamic acid, Glu-lysine, Lys-Ser-glutamine, Gln-Thr-proline, Pro-leucine, Leu-valine, Val-Thr. With the use of mass spectrometry, Nicholas Ling was able to determine the primary sequence of a-endorphin. Relation to beta- and gamma-endorphin Endorphins are generally known as neurotransmitters that are released when the body goes into pain. The three endorphins that play a role in this response are Alpha-endorphins, Beta-Endorphin, Beta-endorphins, and Gamma-Endorphin, Gamma-endorphins which are all derived from the same polypeptide known as Proopiomelanocortin, pro-opiomelanocortin. Although all play roles as neurotransmitters, the specific effects of all three differ. The most studied endorphin of the three is Beta-endorphin. Alpha-endorphins are known to contain one less amino a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
╬│-endorphin
╬│-Endorphin (''gamma''-endorphin) is an opioid peptide that is characterized by the presence of 17 amino acids. The first 16 amino acids are identical to ╬▒-endorphin; leucine added at the end. In addition, ╬│-endorphin is identical to the first 17 amino acids of ╬▓-endorphin. Similar to other endorphins, research focusing upon ╬│-endorphin has been ongoing since its discovery in the 1970s. Yet, most of the information about the substance's exact role within the body is speculation that has yet to be proven. Some studies have indicated, however, that the polypeptide has antipsychotic effects on a certain category of patients with schizophrenia, while others suggest that ╬│-endorphin may act to help regulate blood pressure. Further research is needed, but if ╬│-endorphin does indeed possess such characteristics, the substance could eventually be utilized as a useful means of medical treatment. It has been hypothesized that ╬│-endorphin may play a role in substance abuse, as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opioid Peptide
Opioid peptides are peptides that bind to opioid receptors in the brain; opiates and opioids mimic the effect of these peptides. Such peptides may be produced by the body itself, for example endorphins. The effects of these peptides vary, but they all resemble those of opiates. Brain opioid peptide systems are known to play an important role in motivation, emotion, attachment behaviour, the response to stress and pain, control of food intake, and the rewarding effects of alcohol and nicotine. Opioid-like peptides may also be absorbed from partially digested food ( casomorphins, exorphins, and rubiscolins). The opioid food peptides have lengths of typically 4ÔÇô8 amino acids. The body's own opioids are generally much longer. Opioid peptides are released by post-translational proteolytic cleavage of precursor proteins. The precursors consist of the following components: a signal sequence that precedes a conserved region of about 50 residues; a variable-length region; an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derek George Smyth
Derek Smyth (born 24 April 1927) is a British biochemist who specialises in peptide structure and function. In 2002, he was admitted as a Fellow of the Royal Society of Chemistry. Background Derek Smyth was Head of the Laboratory of Peptide Chemistry at the National Institute for Medical Research (NIMR) in Mill Hill, London from 1972 to 1992. He had worked previously with Professor Joseph Fruton, Head of the Biochemistry Department at Yale University, where he gained experience in protein and peptide chemistry (1-3) and in 1960 transferred to Rockefeller University in New York City where in the laboratory of Stanford Moore and William Howard Stein (Nobel Prize winners) he reinvestigated and established the definitive amino acid sequence of pancreatic ribonuclease (4-8), the first enzyme (some say the first protein) to have its primary structure determined (9). On moving to NIMR in 1963, Smyth prepared two novel derivatives of oxytocin, N-carbamylcystine-1-oxytocin and N-ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-lipotropin
Lipotropin is the name for two hormones produced by the cleavage of pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC). The anterior pituitary gland produces the pro-hormone POMC, which is then cleaved again to form adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) and ╬▓-lipotropin (╬▓-LPH). ╬▓-Lipotropin ╬▓-Lipotropin is a 90- amino acid polypeptide that is the carboxy-terminal fragment of POMC. It was initially reported to stimulate melanocytes to produce melanin. It was also reported to perform lipid-mobilizing functions such as lipolysis and steroidogenesis. However, no subsequent studies have been published that support these early findings and no receptor has been identified for ╬▓-lipotropin. ╬▓-Lipotropin can be cleaved into smaller peptides. In humans, ╬│-lipotropin, ╬▓-MSH, and ╬▓-endorphin, are all possible fragments of ╬▓-lipotropin. ╬▓-endorphin is the predominant opioid of the anterior human and rat pituitary gland. Birdsall and Hulme demonstrated that the C-fragment of lipotropin (╬▓-endorphin) h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enkephalin
An enkephalin is a pentapeptide involved in regulating nociception in the body. The enkephalins are termed endogenous ligands, as they are internally derived and bind to the body's opioid receptors. Discovered in 1975, two forms of enkephalin have been found, one containing leucine ("leu"), and the other containing methionine ("met"). Both are products of the proenkephalin gene. * Met-enkephalin is Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Met. * Leu-enkephalin has Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu. Endogenous opioid peptides There are three well-characterized families of opioid peptides produced by the body: enkephalins, B-endorphin, and dynorphins. The met-enkephalin peptide sequence is coded for by the enkephalin gene; the leu-enkephalin peptide sequence is coded for by both the enkephalin gene and the dynorphin gene. The proopiomelanocortin gene ( POMC) also contains the met-enkephalin sequence on the N-terminus of beta-endorphin, but the endorphin peptide is not processed into enkephalin. Effects on stre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proopiomelanocortin
Pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) is a precursor polypeptide with 241 amino acid residues. POMC is synthesized in corticotrophs of the anterior pituitary from the 267-amino-acid-long polypeptide precursor pre-pro-opiomelanocortin (pre-POMC), by the removal of a 26-amino-acid-long signal peptide sequence during translation. POMC is part of the central melanocortin system. Function POMC is cut (cleaved) to give rise to multiple peptide hormones. Each of these peptides is packaged in large dense-core vesicles that are released from the cells by exocytosis in response to appropriate stimulation: * ╬▒-MSH produced by neurons in the ventromedial nucleus has important roles in the regulation of appetite (POMC neuron stimulation results in satiety.) and sexual behavior, while ╬▒-MSH secreted from the intermediate lobe of the pituitary regulates the movement of melanin produced from melanocytes in skin. * ACTH is a peptide hormone that regulates the secretion of mainly glucocorticoids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
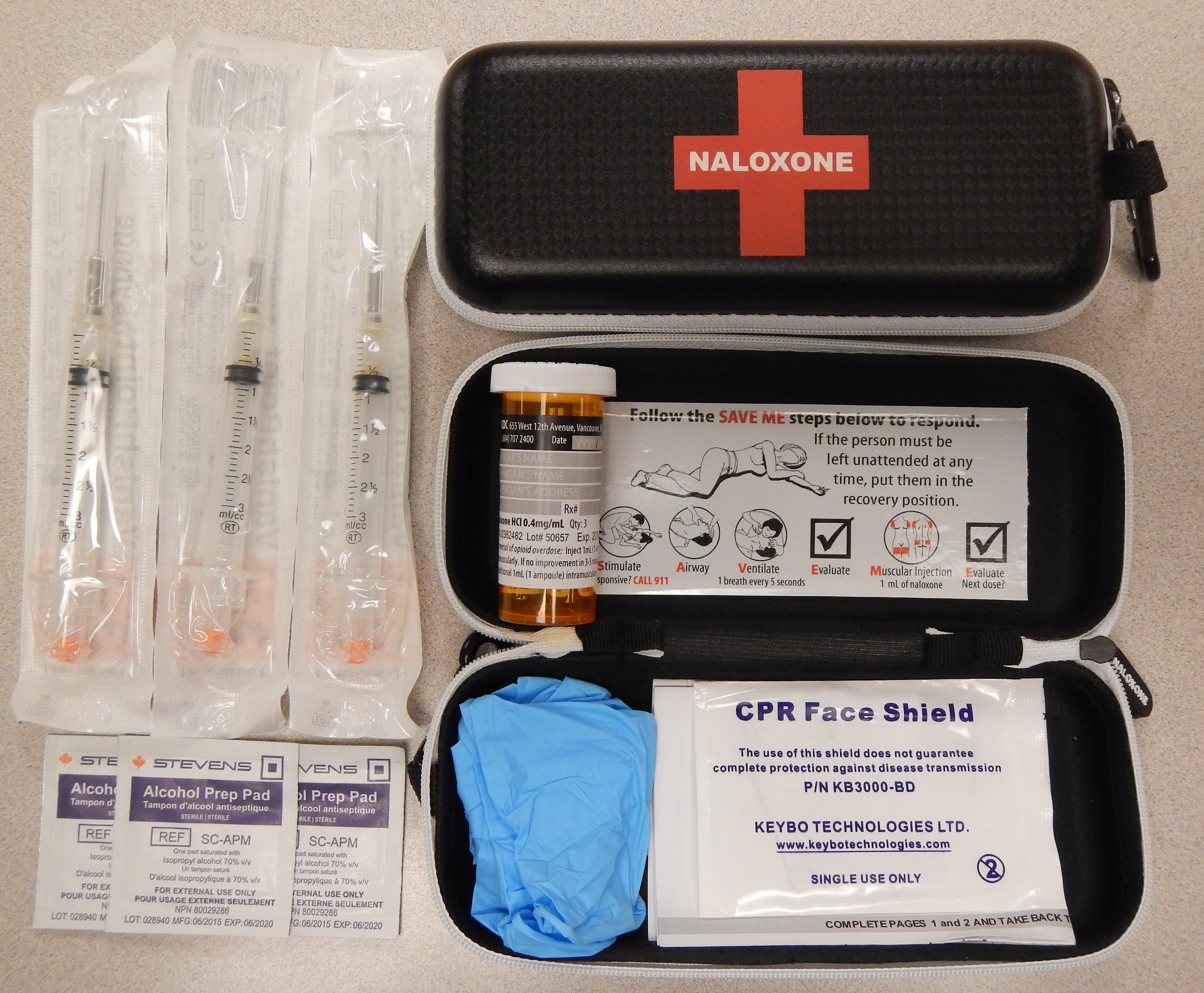
Naloxone
Naloxone, sold under the brand names Narcan (4 mg) and Kloxxado (8 mg) among others, is a medication used to reverse or reduce the effects of opioids. It is commonly used to counter decreased breathing in opioid overdose. Effects begin within two minutes when given intravenously, and within five minutes when injected into a muscle. The medicine can also be administered by spraying it into a person's nose. Naloxone commonly blocks the effects of opioids for 30 to 90 minutes. Multiple doses may be required, as the duration of action of some opioids is greater than that of naloxone. Administration to opioid-dependent individuals may cause symptoms of opioid withdrawal, including restlessness, agitation, nausea, vomiting, a fast heart rate, and sweating. To prevent this, small doses every few minutes can be given until the desired effect is reached. In those with previous heart disease or taking medications that negatively affect the heart, further heart problems have occu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
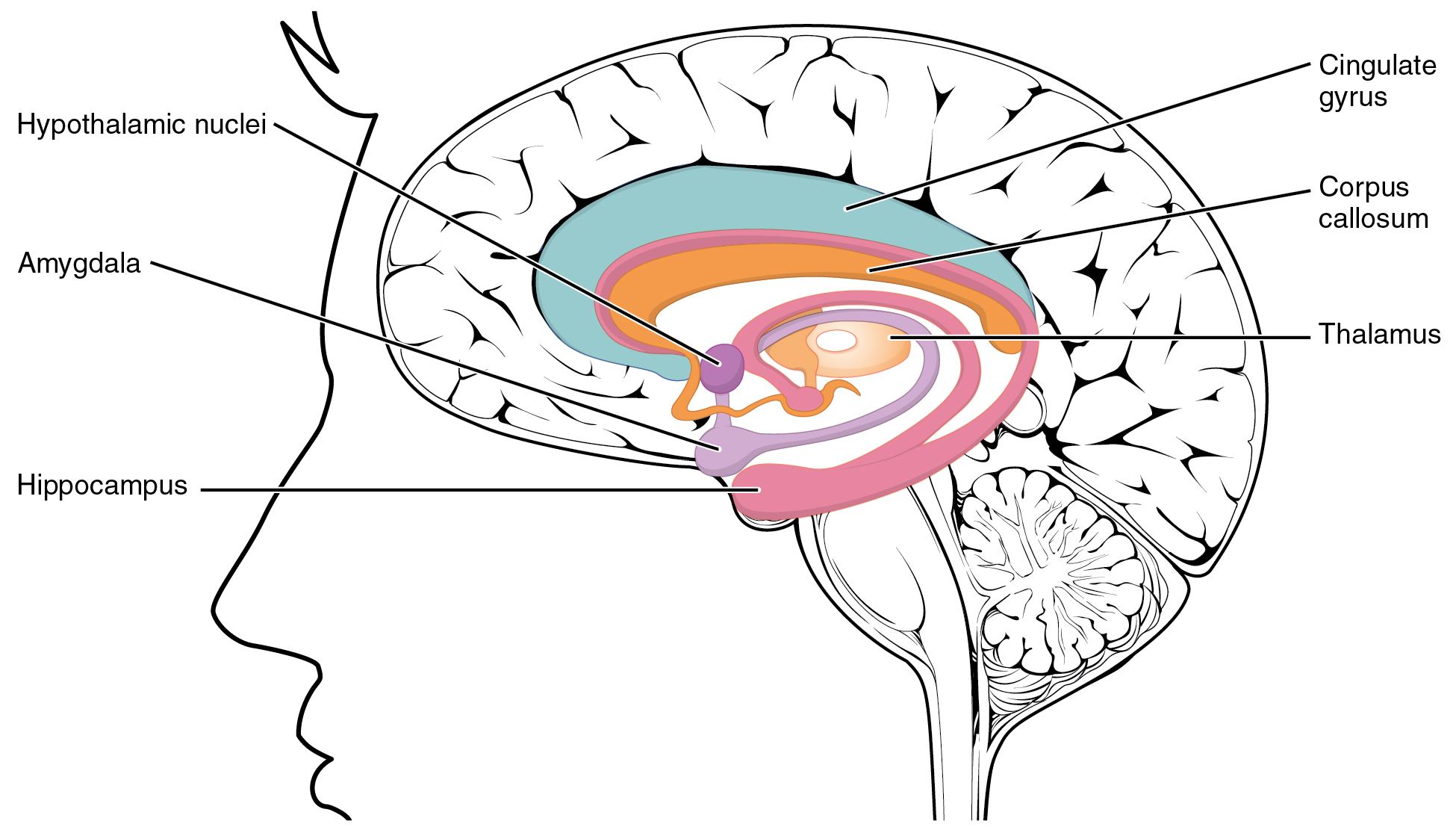
Pituitary Gland
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a chickpea and weighing, on average, in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The hypophysis rests upon the hypophyseal fossa of the sphenoid bone in the center of the middle cranial fossa and is surrounded by a small bony cavity ( sella turcica) covered by a dural fold ( diaphragma sellae). The anterior pituitary (or adenohypophysis) is a lobe of the gland that regulates several physiological processes including stress, growth, reproduction, and lactation. The intermediate lobe synthesizes and secretes melanocyte-stimulating hormone. The posterior pituitary (or neurohypophysis) is a lobe of the gland that is functionally connected to the hypothalamus by the median eminence via a small tube called the pituitary stalk (also called the infundibular stalk or the infundibulum). Hormones secreted from the pituitary glan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Kosterlitz
Hans Walter Kosterlitz FRS (27 April 1903 – 26 October 1996) was a German-born British biochemist. Biography Hans Walter Kosterlitz was born on 27 April 1903 in Berlin. He was the elder son of Bernhard Kosterlitz, a physician, and Selma Helena Lepman. KosterlitzÔÇÖs father had recommended a career in law. He gave it a try for six months at the University of Berlin, but then switched to medicine. He graduated in 1928 and worked in the department of Wilhelm His. From 1930-33 he was an assistant at the Charit├ę hospital, University of Berlin, where he worked in the radiology department. His daytime job in clinical radiology funded his evening researches in the laboratory, where he developed an interest in carbohydrate metabolism. In 1933 Adolf Hitler passed the Law for the Restoration of the Professional Civil Service, which applied to non-Aryans. Later a similar law was passed to cover all lawyers, doctors and other professions. Kosterlitz, who had Jewish ancestry, cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies ('' Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a pain medication, and is also commonly used recreationally, or to make other illicit opioids. There are numerous methods used to administer morphine: oral; sublingual; via inhalation; injection into a muscle; by injection under the skin; intravenously; injection into the space around the spinal cord; transdermal; or via rectal suppository. It acts directly on the central nervous system (CNS) to induce analgesia and alter perception and emotional response to pain. Physical and psychological dependence and tolerance may develop with repeated administration. It can be taken for both acute pain and chronic pain and is frequently used for pain from myocardial infarction, kidney stones, and during labor. Its maximum effect is reached after about 20 minutes when administered intravenously and 60 minutes when administered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |