|
Pituitary Gland
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a chickpea and weighing, on average, in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The hypophysis rests upon the hypophyseal fossa of the sphenoid bone in the center of the middle cranial fossa and is surrounded by a small bony cavity ( sella turcica) covered by a dural fold ( diaphragma sellae). The anterior pituitary (or adenohypophysis) is a lobe of the gland that regulates several physiological processes including stress, growth, reproduction, and lactation. The intermediate lobe synthesizes and secretes melanocyte-stimulating hormone. The posterior pituitary (or neurohypophysis) is a lobe of the gland that is functionally connected to the hypothalamus by the median eminence via a small tube called the pituitary stalk (also called the infundibular stalk or the infundibulum). Hormones secreted from the pituitary glan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
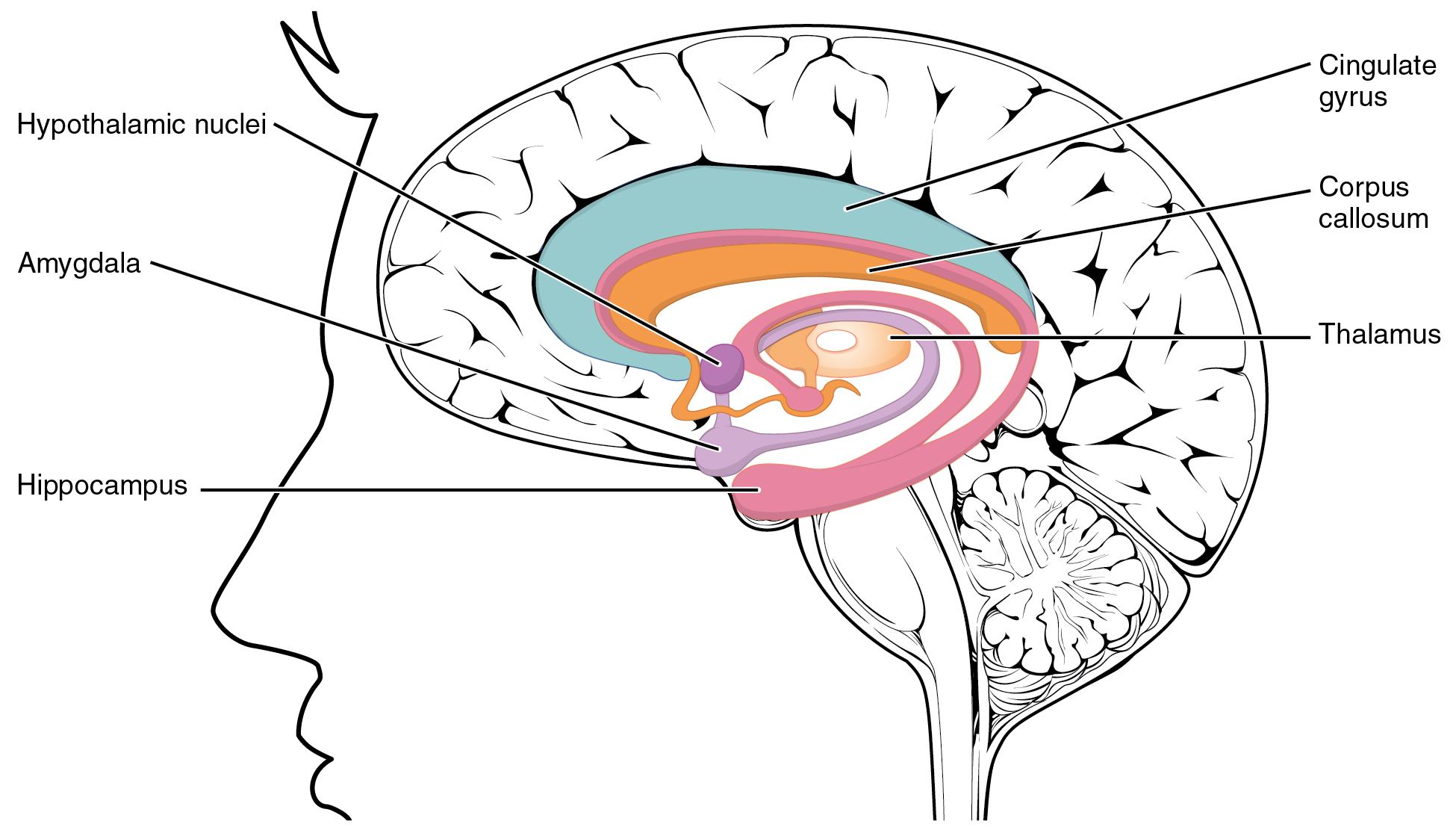
Human Brain
The human brain is the central organ (anatomy), organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the activities of the human body, body, processing, integrating, and coordinating the information it receives from the Sensory nervous system, sense organs, and making decisions as to the instructions sent to the rest of the body. The brain is contained in, and protected by, the neurocranium, skull bones of the human head, head. The cerebrum, the largest part of the human brain, consists of two cerebral hemispheres. Each hemisphere has an inner core composed of white matter, and an outer surface – the cerebral cortex – composed of grey matter. The cortex has an outer layer, the neocortex, and an inner allocortex. The neocortex is made up of six Cerebral cortex#Layers of neocortex, neuronal layers, while the allocortex has three or four. Each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypophyseal Fossa
The sella turcica ( Latin for 'Turkish saddle') is a saddle-shaped depression in the body of the sphenoid bone of the human skull and of the skulls of other hominids including chimpanzees, gorillas and orangutans. It serves as a cephalometric landmark. The pituitary gland or hypophysis is located within the most inferior aspect of the sella turcica, the hypophyseal fossa. Structure The sella turcica is located in the sphenoid bone behind the chiasmatic groove and the tuberculum sellae. It belongs to the middle cranial fossa. The sella turcica's most inferior portion is known as the hypophyseal fossa (the "seat of the saddle"), and contains the pituitary gland (hypophysis). In front of the hypophyseal fossa is the tuberculum sellae. Completing the formation of the saddle posteriorly is the dorsum sellae, which is continuous with the clivus, inferoposteriorly. The dorsum sellae is terminated laterally by the posterior clinoid processes. Development It is widely b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" refers to the pressure in the large arteries. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure (maximum pressure during one heartbeat) over diastolic pressure (minimum pressure between two heartbeats) in the cardiac cycle. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) above the surrounding atmospheric pressure. Blood pressure is one of the vital signs—together with respiratory rate, heart rate, oxygen saturation, and body temperature—that healthcare professionals use in evaluating a patient's health. Normal resting blood pressure, in an adult is approximately systolic over diastolic, denoted as "120/80 mmHg". Globally, the average blood pressure, age standardized, has remained about the sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Development (biology)
Development of the human body is the process of Cell growth, growth to Adulthood, maturity. The process begins with Human fertilization, fertilization, where an egg released from the ovary of a female is penetrated by a spermatozoan, sperm cell from a male. The resulting zygote develops through mitosis and cell differentiation, and the resulting embryo then Implantation (human embryo), implants in the uterus, where the embryo continues development through a fetus, fetal stage until Childbirth, birth. Further growth and development continues after birth, and includes both physical development, physical and psychological development, influenced by Genetics, genetic, hormonal, environmental and other factors. This continues throughout life: through childhood and adolescence into adulthood. Before birth Development before birth, or prenatal development () is the process in which a zygote, and later an embryo and then a fetus develops during gestation. Prenatal development starts wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required for the correct development of animals, plants and fungi. Due to the broad definition of a hormone (as a signaling molecule that exerts its effects far from its site of production), numerous kinds of molecules can be classified as hormones. Among the substances that can be considered hormones, are eicosanoids (e.g. prostaglandins and thromboxanes), steroids (e.g. oestrogen and brassinosteroid), amino acid derivatives (e.g. epinephrine and auxin), protein or peptides (e.g. insulin and CLE peptides), and gases (e.g. ethylene and nitric oxide). Hormones are used to communicate between organs and tissues. In vertebrates, hormones are responsible for regulating a variety of physiological processes and behavioral activities such as diges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median Eminence
The median eminence, part of the inferior boundary of the hypothalamus in the brain, is attached to the infundibulum. The median eminence is a small swelling on the tuber cinereum, posterior to and atop the pituitary stalk; it lies in the area roughly bounded on its posterolateral region by the cerebral peduncles, and on its anterolateral region by the optic chiasm. As one of the seven areas of the brain devoid of a blood–brain barrier, the median eminence is a circumventricular organ having permeable capillaries. Its main function is as a gateway for release of hypothalamic hormones, although it does share contiguous perivascular spaces with the adjacent hypothalamic arcuate nucleus, indicating a potential sensory role. __TOC__ Physiology The median eminence is a part of the hypothalamus from which regulatory hormones are released. It is integral to the hypophyseal portal system, which connects the hypothalamus with the pituitary gland. The pars nervosa (part of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Pituitary
The posterior pituitary (or neurohypophysis) is the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland which is part of the endocrine system. The posterior pituitary is not glandular as is the anterior pituitary. Instead, it is largely a collection of axonal projections from the hypothalamus that terminate behind the anterior pituitary, and serve as a site for the secretion of neurohypophysial hormones ( oxytocin and vasopressin) directly into the blood. The hypothalamic–neurohypophyseal system is composed of the hypothalamus (the paraventricular nucleus and supraoptic nucleus), posterior pituitary, and these axonal projections. Structure The posterior pituitary consists mainly of neuronal projections (axons) of magnocellular neurosecretory cells extending from the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei of the hypothalamus. These axons store and release neurohypophysial hormones oxytocin and vasopressin into the neurohypophyseal capillaries, from there they get into the systemic ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanocyte-stimulating Hormone
The melanocyte-stimulating hormones, known collectively as MSH, also known as melanotropins or intermedins, are a family of peptide hormones and neuropeptides consisting of α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH), β-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (β-MSH), and γ-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (γ-MSH) that are produced by cells in the pars intermedia of the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. Synthetic analogues of α-MSH, such as afamelanotide (melanotan I; Scenesse), melanotan II, and bremelanotide (PT-141), have been developed and researched. Biosynthesis The various forms of MSH are generated from different cleavages of the proopiomelanocortin protein, which also yields other important neuropeptides like adrenocorticotropic hormone. Melanocytes in skin make and secrete MSH in response to ultraviolet light, where it increases synthesis of melanin. Some neurons in arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus make and secrete α-MSH in response to leptin; α-MSH is also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermediate Lobe
Pars intermedia is the boundary between the anterior and posterior lobes of the pituitary. It contains colloid-filled cysts and two types of cells - basophils and chromophobes. The cysts are the remainder of Rathke’s pouch. In human fetal life, this area produces melanocyte stimulating hormone The melanocyte-stimulating hormones, known collectively as MSH, also known as melanotropins or intermedins, are a family of peptide hormones and neuropeptides consisting of α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH), β-melanocyte-stimulating h ... or MSH which causes the release of melanin pigment in skin melanocytes (pigment cells). However, the pars intermedia is normally either very small or entirely absent in adulthood. In lower vertebrates (fish, amphibians) MSH from the pars intermedia is responsible for darkening of the skin, often in response to changes in background color. This color change is due to MSH stimulating the dispersion of melanin pigment in dermal (skin) mel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactation
Lactation describes the secretion of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. The process naturally occurs with all sexually mature female mammals, although it may predate mammals. The process of feeding milk in all animals (including humans) is called ''nursing'', and in humans it is also called '' breastfeeding''. Newborn infants often produce some milk from their own breast tissue, known colloquially as witch's milk. In most species, lactation is a sign that the female has been pregnant at some point in her life, although it can happen without pregnancy. Nearly every species of mammal has nipples; except for monotremes, egg-laying mammals, which instead release milk through ducts in the abdomen. In only one species of mammal, the Dayak fruit bat from Southeast Asia, is milk production a normal male function. ''Galactopoiesis'' is the maintenance of milk production. This stage requires prolactin. Oxytocin is cri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Pituitary
A major organ of the endocrine system, the anterior pituitary (also called the adenohypophysis or pars anterior) is the glandular, anterior lobe that together with the posterior lobe ( posterior pituitary, or the neurohypophysis) makes up the pituitary gland (hypophysis). The anterior pituitary regulates several physiological processes, including stress, growth, reproduction, and lactation. Proper functioning of the anterior pituitary and of the organs it regulates can often be ascertained via blood tests that measure hormone levels. Structure The pituitary gland sits in a protective bony enclosure called the sella turcica (''Turkish chair/saddle''). It is composed of three lobes: the anterior, intermediate, and posterior lobes. In many animals, these lobes are distinct. However, in humans, the intermediate lobe is but a few cell layers thick and indistinct; as a result, it is often considered part of the anterior pituitary. In all animals, the fleshy, glandular anterior pit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |